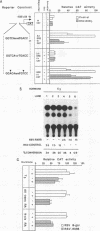
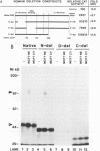
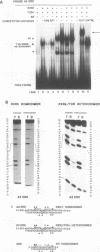
Abstract
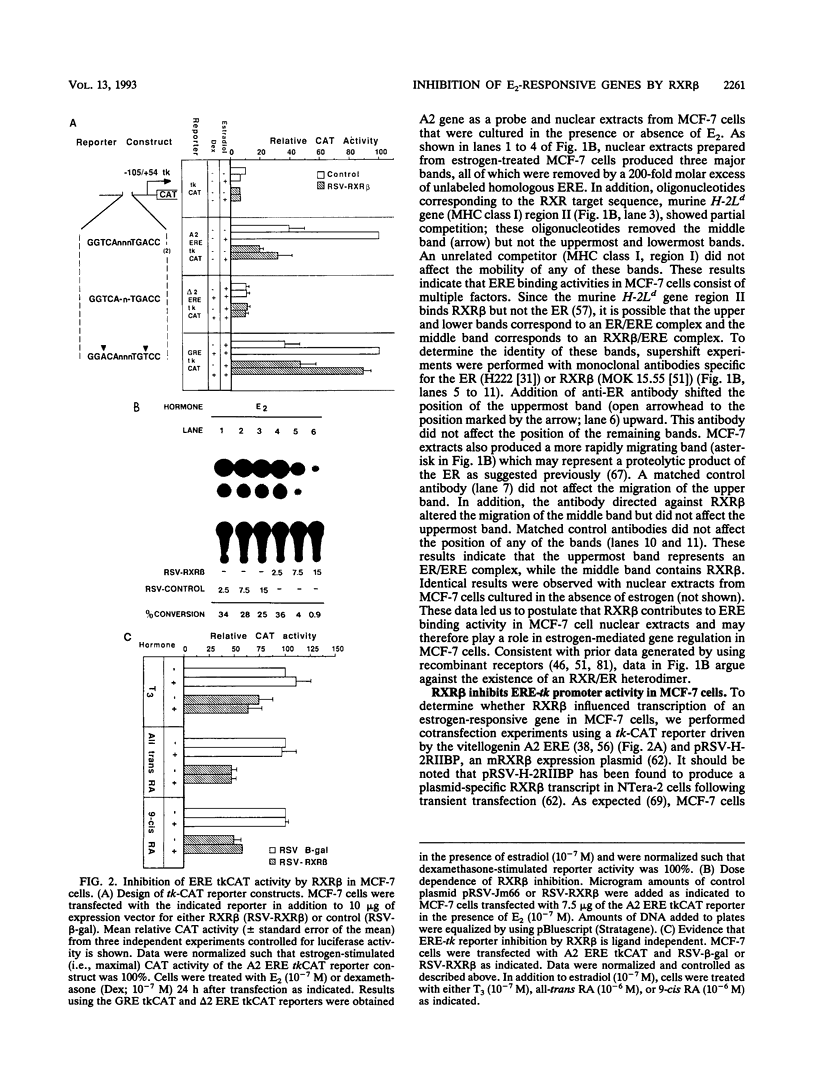
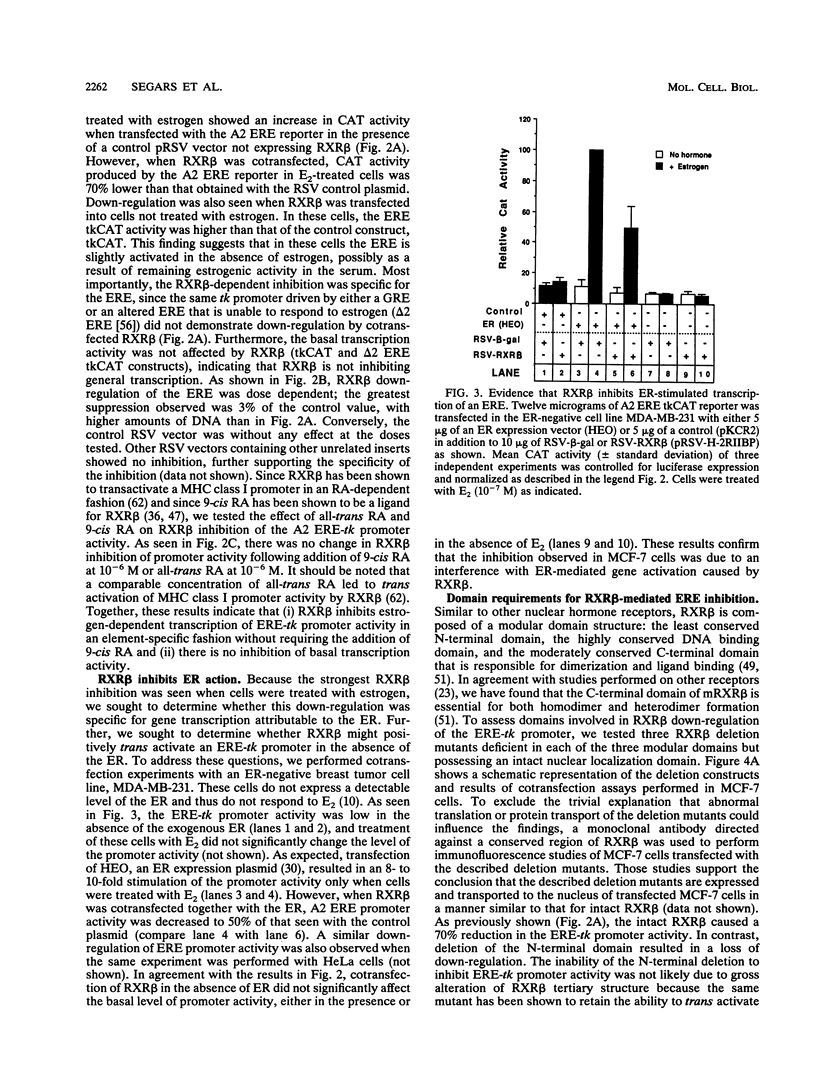
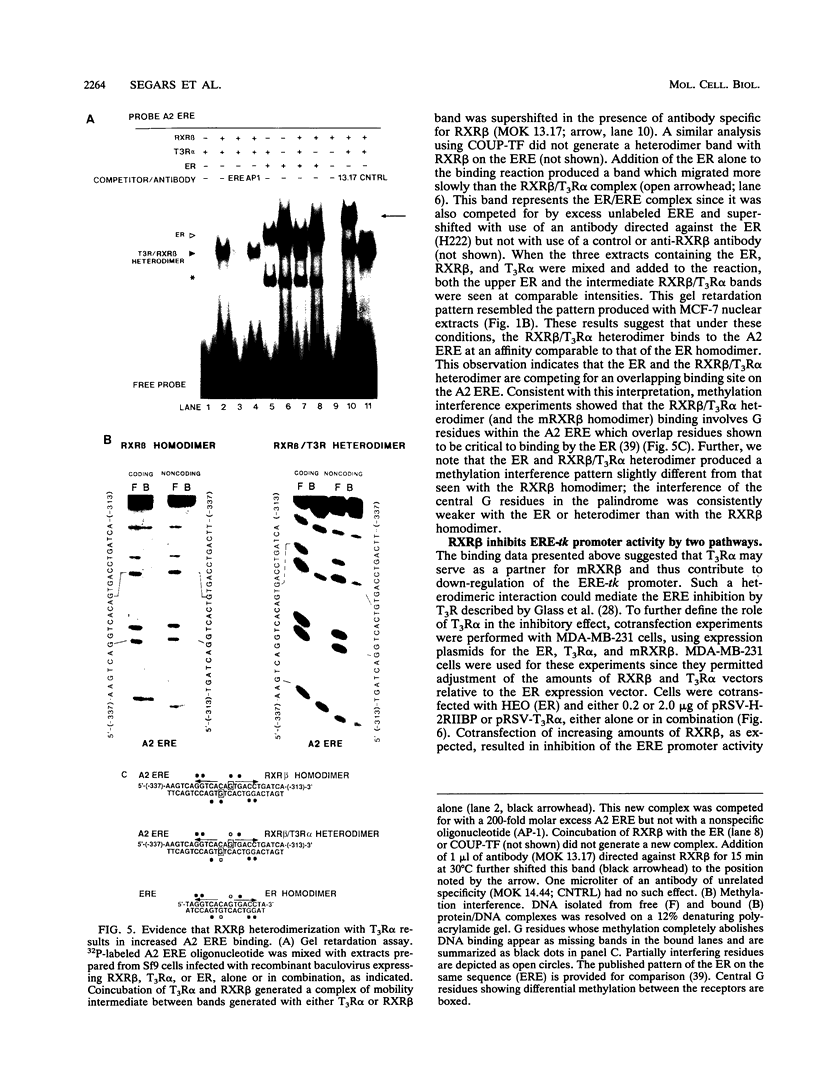
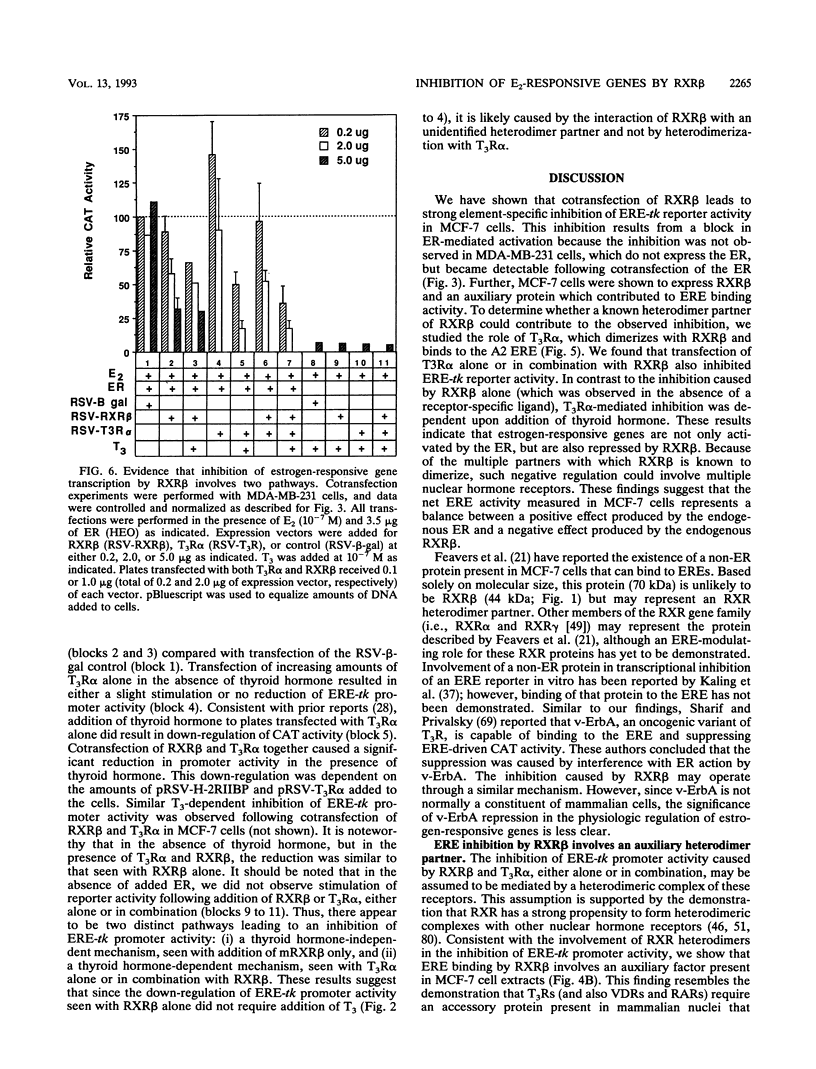
The retinoid X receptor beta (RXR beta; H-2RIIBP) forms heterodimers with various nuclear hormone receptors and binds multiple hormone response elements, including the estrogen response element (ERE). In this report, we show that endogenous RXR beta contributes to ERE binding activity in nuclear extracts of the human breast cancer cell line MCF-7. To define a possible regulatory role of RXR beta regarding estrogen-responsive transcription in breast cancer cells, RXR beta and a reporter gene driven by the vitellogenin A2 ERE were transfected into estrogen-treated MCF-7 cells. RXR beta inhibited ERE-driven reporter activity in a dose-dependent and element-specific fashion. This inhibition occurred in the absence of the RXR ligand 9-cis retinoic acid. The RXR beta-induced inhibition was specific for estrogen receptor (ER)-mediated ERE activation because inhibition was observed in ER-negative MDA-MB-231 cells only following transfection of the estrogen-activated ER. No inhibition of the basal reporter activity was observed. The inhibition was not caused by simple competition of RXR beta with the ER for ERE binding, since deletion mutants retaining DNA binding activity but lacking the N-terminal or C-terminal domain failed to inhibit reporter activity. In addition, cross-linking studies indicated the presence of an auxiliary nuclear factor present in MCF-7 cells that contributed to RXR beta binding of the ERE. Studies using known heterodimerization partners of RXR beta confirmed that RXR beta/triiodothyronine receptor alpha heterodimers avidly bind the ERE but revealed the existence of another triiodothyronine-independent pathway of ERE inhibition. These results indicate that estrogen-responsive genes may be negatively regulated by RXR beta through two distinct pathways.
Full text
PDF

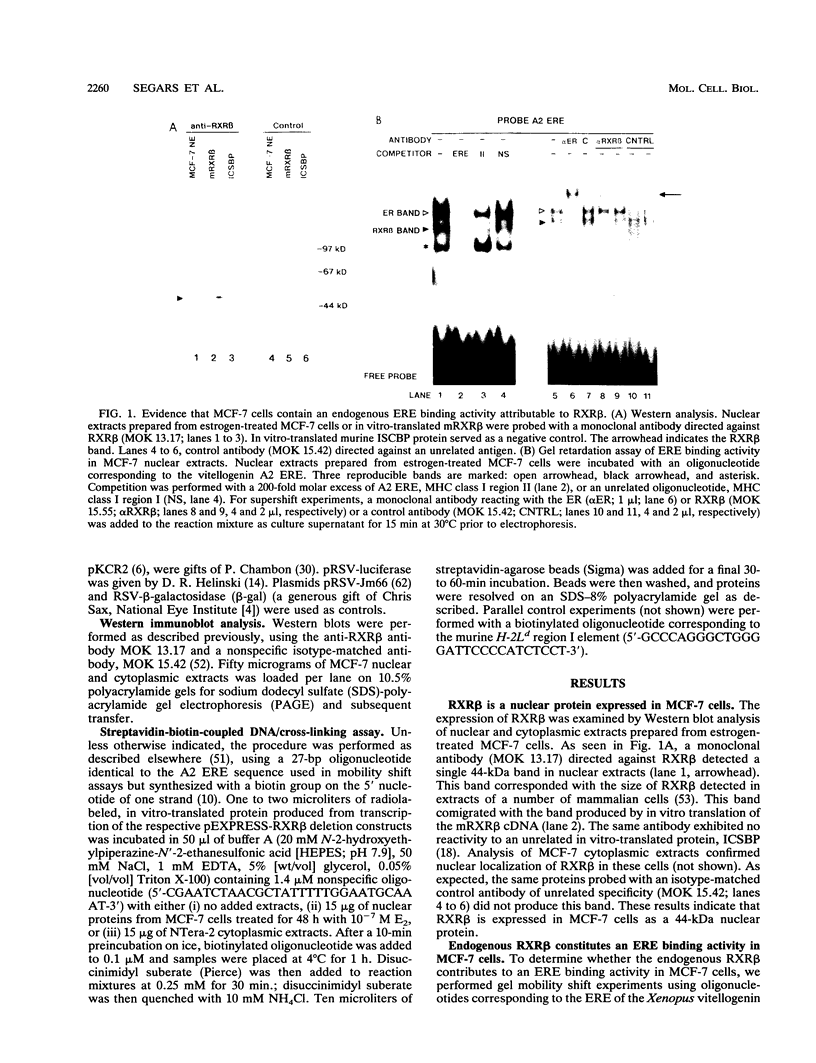




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagchi M. K., Tsai S. Y., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Purification and characterization of chicken ovalbumin gene upstream promoter transcription factor from homologous oviduct cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4151–4158. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbi G. P., Marroni P., Bruzzi P., Nicolò G., Paganuzzi M., Ferrara G. B. Correlation between steroid hormone receptors and prognostic factors in human breast cancer. Oncology. 1987;44(5):265–269. doi: 10.1159/000226492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollag W., Peck R., Frey J. R. Inhibition of proliferation by retinoids, cytokines and their combination in four human transformed epithelial cell lines. Cancer Lett. 1992 Feb 29;62(2):167–172. doi: 10.1016/0304-3835(92)90188-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borrás T., Peterson C. A., Piatigorsky J. Evidence for positive and negative regulation in the promoter of the chicken delta 1-crystallin gene. Dev Biol. 1988 May;127(1):209–219. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90202-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Harris B. A. Plasmids for the cloning and expression of full-length double-stranded cDNAs under control of the SV40 early or late gene promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Oct 25;11(20):7119–7136. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.20.7119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M., Sharp P. A. Human estrogen receptor forms multiple protein-DNA complexes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):11238–11243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bugge T. H., Pohl J., Lonnoy O., Stunnenberg H. G. RXR alpha, a promiscuous partner of retinoic acid and thyroid hormone receptors. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1409–1418. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05186.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cailleau R., Young R., Olivé M., Reeves W. J., Jr Breast tumor cell lines from pleural effusions. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 Sep;53(3):661–674. doi: 10.1093/jnci/53.3.661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corthésy B., Cardinaux J. R., Claret F. X., Wahli W. A nuclear factor I-like activity and a liver-specific repressor govern estrogen-regulated in vitro transcription from the Xenopus laevis vitellogenin B1 promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5548–5562. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danel L., Souweine G., Monier J. C., Saez S. Specific estrogen binding sites in human lymphoid cells and thymic cells. J Steroid Biochem. 1983 May;18(5):559–563. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(83)90131-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darbre P., Yates J., Curtis S., King R. J. Effect of estradiol on human breast cancer cells in culture. Cancer Res. 1983 Jan;43(1):349–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson R. B., McManaway M. E., Lippman M. E. Estrogen-induced factors of breast cancer cells partially replace estrogen to promote tumor growth. Science. 1986 Jun 20;232(4757):1540–1543. doi: 10.1126/science.3715461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doucas V., Spyrou G., Yaniv M. Unregulated expression of c-Jun or c-Fos proteins but not Jun D inhibits oestrogen receptor activity in human breast cancer derived cells. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2237–2245. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07760.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driggers P. H., Elenbaas B. A., An J. B., Lee I. J., Ozato K. Two upstream elements activate transcription of a major histocompatibility complex class I gene in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 May 25;20(10):2533–2540. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.10.2533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):889–895. doi: 10.1126/science.3283939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fawell S. E., Lees J. A., White R., Parker M. G. Characterization and colocalization of steroid binding and dimerization activities in the mouse estrogen receptor. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):953–962. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90343-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feavers I. M., Jiricny J., Moncharmont B., Saluz H. P., Jost J. P. Interaction of two nonhistone proteins with the estradiol response element of the avian vitellogenin gene modulates the binding of estradiol-receptor complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7453–7457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontana J. A., Mezu A. B., Cooper B. N., Miranda D. Retinoid modulation of estradiol-stimulated growth and of protein synthesis and secretion in human breast carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 1990 Apr 1;50(7):1997–2002. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forman B. M., Samuels H. H. Interactions among a subfamily of nuclear hormone receptors: the regulatory zipper model. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Sep;4(9):1293–1301. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-9-1293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forman B. M., Samuels H. H. pEXPRESS: a family of expression vectors containing a single transcription unit active in prokaryotes, eukaryotes and in vitro. Gene. 1991 Aug 30;105(1):9–15. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90507-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox H. S., Bond B. L., Parslow T. G. Estrogen regulates the IFN-gamma promoter. J Immunol. 1991 Jun 15;146(12):4362–4367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaub M. P., Bellard M., Scheuer I., Chambon P., Sassone-Corsi P. Activation of the ovalbumin gene by the estrogen receptor involves the fos-jun complex. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1267–1276. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90422-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass C. K., Devary O. V., Rosenfeld M. G. Multiple cell type-specific proteins differentially regulate target sequence recognition by the alpha retinoic acid receptor. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):729–738. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90139-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass C. K., Holloway J. M., Devary O. V., Rosenfeld M. G. The thyroid hormone receptor binds with opposite transcriptional effects to a common sequence motif in thyroid hormone and estrogen response elements. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):313–323. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90194-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S., Walter P., Kumar V., Krust A., Bornert J. M., Argos P., Chambon P. Human oestrogen receptor cDNA: sequence, expression and homology to v-erb-A. Nature. 1986 Mar 13;320(6058):134–139. doi: 10.1038/320134a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene G. L., Sobel N. B., King W. J., Jensen E. V. Immunochemical studies of estrogen receptors. J Steroid Biochem. 1984 Jan;20(1):51–56. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(84)90188-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronemeyer H. Transcription activation by estrogen and progesterone receptors. Annu Rev Genet. 1991;25:89–123. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.25.120191.000513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman C. J. Interactions between the gonadal steroids and the immune system. Science. 1985 Jan 18;227(4684):257–261. doi: 10.1126/science.3871252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallenbeck P. L., Marks M. S., Lippoldt R. E., Ozato K., Nikodem V. M. Heterodimerization of thyroid hormone (TH) receptor with H-2RIIBP (RXR beta) enhances DNA binding and TH-dependent transcriptional activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5572–5576. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada K., Gleason S. L., Levi B. Z., Hirschfeld S., Appella E., Ozato K. H-2RIIBP, a member of the nuclear hormone receptor superfamily that binds to both the regulatory element of major histocompatibility class I genes and the estrogen response element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8289–8293. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyman R. A., Mangelsdorf D. J., Dyck J. A., Stein R. B., Eichele G., Evans R. M., Thaller C. 9-cis retinoic acid is a high affinity ligand for the retinoid X receptor. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):397–406. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90479-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaling M., Weimar-Ehl T., Kleinhans M., Ryffel G. U. Transcription factors different from the estrogen receptor stimulate in vitro transcription from promoters containing estrogen response elements. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1990 Mar 5;69(2-3):167–178. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(90)90010-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein-Hitpass L., Schorpp M., Wagner U., Ryffel G. U. An estrogen-responsive element derived from the 5' flanking region of the Xenopus vitellogenin A2 gene functions in transfected human cells. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1053–1061. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90705-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein-Hitpass L., Tsai S. Y., Greene G. L., Clark J. H., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Specific binding of estrogen receptor to the estrogen response element. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):43–49. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliewer S. A., Umesono K., Mangelsdorf D. J., Evans R. M. Retinoid X receptor interacts with nuclear receptors in retinoic acid, thyroid hormone and vitamin D3 signalling. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):446–449. doi: 10.1038/355446a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krust A., Green S., Argos P., Kumar V., Walter P., Bornert J. M., Chambon P. The chicken oestrogen receptor sequence: homology with v-erbA and the human oestrogen and glucocorticoid receptors. EMBO J. 1986 May;5(5):891–897. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04300.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar V., Chambon P. The estrogen receptor binds tightly to its responsive element as a ligand-induced homodimer. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):145–156. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90017-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar V., Green S., Stack G., Berry M., Jin J. R., Chambon P. Functional domains of the human estrogen receptor. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):941–951. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90581-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazar M. A., Berrodin T. J., Harding H. P. Differential DNA binding by monomeric, homodimeric, and potentially heteromeric forms of the thyroid hormone receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):5005–5015. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.5005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leid M., Kastner P., Lyons R., Nakshatri H., Saunders M., Zacharewski T., Chen J. Y., Staub A., Garnier J. M., Mader S. Purification, cloning, and RXR identity of the HeLa cell factor with which RAR or TR heterodimerizes to bind target sequences efficiently. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):377–395. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90478-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin A. A., Sturzenbecker L. J., Kazmer S., Bosakowski T., Huselton C., Allenby G., Speck J., Kratzeisen C., Rosenberger M., Lovey A. 9-cis retinoic acid stereoisomer binds and activates the nuclear receptor RXR alpha. Nature. 1992 Jan 23;355(6358):359–361. doi: 10.1038/355359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipkin S. M., Nelson C. A., Glass C. K., Rosenfeld M. G. A negative retinoic acid response element in the rat oxytocin promoter restricts transcriptional stimulation by heterologous transactivation domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 15;89(4):1209–1213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.4.1209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangelsdorf D. J., Borgmeyer U., Heyman R. A., Zhou J. Y., Ong E. S., Oro A. E., Kakizuka A., Evans R. M. Characterization of three RXR genes that mediate the action of 9-cis retinoic acid. Genes Dev. 1992 Mar;6(3):329–344. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.3.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangelsdorf D. J., Ong E. S., Dyck J. A., Evans R. M. Nuclear receptor that identifies a novel retinoic acid response pathway. Nature. 1990 May 17;345(6272):224–229. doi: 10.1038/345224a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks M. S., Hallenbeck P. L., Nagata T., Segars J. H., Appella E., Nikodem V. M., Ozato K. H-2RIIBP (RXR beta) heterodimerization provides a mechanism for combinatorial diversity in the regulation of retinoic acid and thyroid hormone responsive genes. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1419–1435. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05187.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks M. S., Levi B. Z., Segars J. H., Driggers P. H., Hirschfeld S., Nagata T., Appella E., Ozato K. H-2RIIBP expressed from a baculovirus vector binds to multiple hormone response elements. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Feb;6(2):219–230. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.2.1569965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez E., Dusserre Y., Wahli W., Mermod N. Synergistic transcriptional activation by CTF/NF-I and the estrogen receptor involves stabilized interactions with a limiting target factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):2937–2945. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.2937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez E., Givel F., Wahli W. The estrogen-responsive element as an inducible enhancer: DNA sequence requirements and conversion to a glucocorticoid-responsive element. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3719–3727. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02706.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez E., Wahli W. Cooperative binding of estrogen receptor to imperfect estrogen-responsive DNA elements correlates with their synergistic hormone-dependent enhancer activity. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3781–3791. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08555.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer R. A., Notides A. C. Identification of an estrogen-responsive element from the 5'-flanking region of the rat prolactin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4247–4254. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger D., White J. H., Chambon P. The human oestrogen receptor functions in yeast. Nature. 1988 Jul 7;334(6177):31–36. doi: 10.1038/334031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer M. E., Pornon A., Ji J. W., Bocquel M. T., Chambon P., Gronemeyer H. Agonistic and antagonistic activities of RU486 on the functions of the human progesterone receptor. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):3923–3932. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07613.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata T., Segars J. H., Levi B. Z., Ozato K. Retinoic acid-dependent transactivation of major histocompatibility complex class I promoters by the nuclear hormone receptor H-2RIIBP in undifferentiated embryonal carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 1;89(3):937–941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.3.937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunez A. M., Berry M., Imler J. L., Chambon P. The 5' flanking region of the pS2 gene contains a complex enhancer region responsive to oestrogens, epidermal growth factor, a tumour promoter (TPA), the c-Ha-ras oncoprotein and the c-jun protein. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):823–829. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03443.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- När A. M., Boutin J. M., Lipkin S. M., Yu V. C., Holloway J. M., Glass C. K., Rosenfeld M. G. The orientation and spacing of core DNA-binding motifs dictate selective transcriptional responses to three nuclear receptors. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1267–1279. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90021-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petty K. J., Desvergne B., Mitsuhashi T., Nikodem V. M. Identification of a thyroid hormone response element in the malic enzyme gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 5;265(13):7395–7400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponglikitmongkol M., White J. H., Chambon P. Synergistic activation of transcription by the human estrogen receptor bound to tandem responsive elements. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2221–2231. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07392.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratko T. A., Detrisac C. J., Dinger N. M., Thomas C. F., Kelloff G. J., Moon R. C. Chemopreventive efficacy of combined retinoid and tamoxifen treatment following surgical excision of a primary mammary cancer in female rats. Cancer Res. 1989 Aug 15;49(16):4472–4476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabbah M., Gouilleux F., Sola B., Redeuilh G., Baulieu E. E. Structural differences between the hormone and antihormone estrogen receptor complexes bound to the hormone response element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):390–394. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiler-Tuyns A., Walker P., Martinez E., Mérillat A. M., Givel F., Wahli W. Identification of estrogen-responsive DNA sequences by transient expression experiments in a human breast cancer cell line. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 25;14(22):8755–8770. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.22.8755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharif M., Privalsky M. L. v-erbA oncogene function in neoplasia correlates with its ability to repress retinoic acid receptor action. Cell. 1991 Sep 6;66(5):885–893. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90435-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shupnik M. A., Weinmann C. M., Notides A. C., Chin W. W. An upstream region of the rat luteinizing hormone beta gene binds estrogen receptor and confers estrogen responsiveness. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):80–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shyamala G., Schneider W., Schott D. Developmental regulation of murine mammary progesterone receptor gene expression. Endocrinology. 1990 Jun;126(6):2882–2889. doi: 10.1210/endo-126-6-2882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somasekhar M. B., Gorski J. An estrogen-responsive element from the 5'-flanking region of the rat prolactin gene functions in MCF-7 but not in HeLa cells. Gene. 1988 Sep 15;69(1):23–28. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90374-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparano J. A., O'Boyle K. The potential role for biological therapy in the treatment of breast cancer. Semin Oncol. 1992 Jun;19(3):333–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tasset D., Tora L., Fromental C., Scheer E., Chambon P. Distinct classes of transcriptional activating domains function by different mechanisms. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1177–1187. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90394-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tora L., White J., Brou C., Tasset D., Webster N., Scheer E., Chambon P. The human estrogen receptor has two independent nonacidic transcriptional activation functions. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):477–487. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90031-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umesono K., Murakami K. K., Thompson C. C., Evans R. M. Direct repeats as selective response elements for the thyroid hormone, retinoic acid, and vitamin D3 receptors. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1255–1266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90020-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker P., Germond J. E., Brown-Luedi M., Givel F., Wahli W. Sequence homologies in the region preceding the transcription initiation site of the liver estrogen-responsive vitellogenin and apo-VLDLII genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 26;12(22):8611–8626. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.22.8611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H., Tsai S. Y., Cook R. G., Beattie W. G., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. COUP transcription factor is a member of the steroid receptor superfamily. Nature. 1989 Jul 13;340(6229):163–166. doi: 10.1038/340163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster N. J., Green S., Jin J. R., Chambon P. The hormone-binding domains of the estrogen and glucocorticoid receptors contain an inducible transcription activation function. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):199–207. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90552-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu V. C., Delsert C., Andersen B., Holloway J. M., Devary O. V., När A. M., Kim S. Y., Boutin J. M., Glass C. K., Rosenfeld M. G. RXR beta: a coregulator that enhances binding of retinoic acid, thyroid hormone, and vitamin D receptors to their cognate response elements. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1251–1266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90301-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. K., Hoffmann B., Tran P. B., Graupner G., Pfahl M. Retinoid X receptor is an auxiliary protein for thyroid hormone and retinoic acid receptors. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):441–446. doi: 10.1038/355441a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet J. R., Wood K. V., DeLuca M., Helinski D. R., Subramani S. Firefly luciferase gene: structure and expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):725–737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]