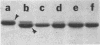Abstract
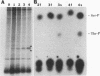
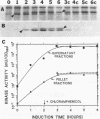
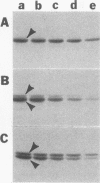
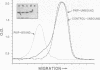
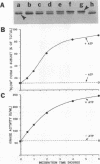
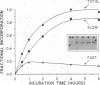
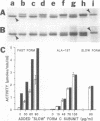
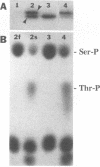
We recently found, using cultured mouse cell systems, that newly synthesized catalytic (C) subunits of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase undergo a posttranslational modification that reduces their electrophoretic mobilities in sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)-polyacrylamide gels and activates them for binding to a Sepharose-conjugated inhibitor peptide. Using an Escherichia coli expression system, we now show that recombinant murine C alpha subunit undergoes a similar modification and that the modification results in a large increase in protein kinase activity. Threonine phosphorylation appears to be responsible for both the enzymatic activation and the electrophoretic mobility shift. The phosphothreonine-deficient form of C subunit had reduced affinities for the ATP analogs p-fluorosulfonyl-[14C]benzoyl 5'-adenosine and adenosine 5'-O-(3-thiotriphosphate) as well as for the Sepharose-conjugated inhibitor peptide; it also had markedly elevated Kms for both ATP and peptide substrates. Autophosphorylation of C-subunit preparations enriched for this phosphothreonine-deficient form reproduced the changes in enzyme activity and SDS-gel mobility that occur in intact cells. A mutant form of the recombinant C subunit with Ala substituted for Thr-197 (the only C-subunit threonine residue known to be phosphorylated in mammalian cells) was similar in SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis mobility and activity to the phosphothreonine-deficient form of wild-type C subunit. In contrast to the wild-type subunit, however, the Ala-197 mutant form could not be shifted or activated by incubation with the phosphothreonine-containing wild-type form. We conclude that posttranslational autophosphorylation of Thr-197 is a critical step in intracellular expression of active C subunit.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booher R., Beach D. Site-specific mutagenesis of cdc2+, a cell cycle control gene of the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3523–3530. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown N. A., Stofko R. E., Uhler M. D. Induction of alkaline phosphatase in mouse L cells by overexpression of the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):13181–13189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs C. S., Knighton D. R., Sowadski J. M., Taylor S. S., Zoller M. J. Systematic mutational analysis of cAMP-dependent protein kinase identifies unregulated catalytic subunits and defines regions important for the recognition of the regulatory subunit. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 5;267(7):4806–4814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huggenvik J. I., Collard M. W., Stofko R. E., Seasholtz A. F., Uhler M. D. Regulation of the human enkephalin promoter by two isoforms of the catalytic subunit of cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Jul;5(7):921–930. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-7-921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp B. E., Graves D. J., Benjamini E., Krebs E. G. Role of multiple basic residues in determining the substrate specificity of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):4888–4894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knighton D. R., Zheng J. H., Ten Eyck L. F., Ashford V. A., Xuong N. H., Taylor S. S., Sowadski J. M. Crystal structure of the catalytic subunit of cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Science. 1991 Jul 26;253(5018):407–414. doi: 10.1126/science.1862342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knighton D. R., Zheng J. H., Ten Eyck L. F., Xuong N. H., Taylor S. S., Sowadski J. M. Structure of a peptide inhibitor bound to the catalytic subunit of cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Science. 1991 Jul 26;253(5018):414–420. doi: 10.1126/science.1862343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kong C. T., Cook P. F. Isotope partitioning in the adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate dependent protein kinase reaction indicates a steady-state random kinetic mechanism. Biochemistry. 1988 Jun 28;27(13):4795–4799. doi: 10.1021/bi00413a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin L. R., Zoller M. J. Association of catalytic and regulatory subunits of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase requires a negatively charged side group at a conserved threonine. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1066–1075. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Sedman S. A., Ebert M. H. Ultrasensitive stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels shows regional variation in cerebrospinal fluid proteins. Science. 1981 Mar 27;211(4489):1437–1438. doi: 10.1126/science.6162199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobashery S., Kaiser E. T. Identification of amino acid residues involved in substrate recognition by the catalytic subunit of bovine cyclic AMP dependent protein kinase: peptide-based affinity labels. Biochemistry. 1988 May 17;27(10):3691–3696. doi: 10.1021/bi00410a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orellana S. A., McKnight G. S. Mutations in the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase result in unregulated biological activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4726–4730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne D. M., Rossomando A. J., Martino P., Erickson A. K., Her J. H., Shabanowitz J., Hunt D. F., Weber M. J., Sturgill T. W. Identification of the regulatory phosphorylation sites in pp42/mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAP kinase). EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):885–892. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08021.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roskoski R., Jr Assays of protein kinase. Methods Enzymol. 1983;99:3–6. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)99034-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoji S., Ericsson L. H., Walsh K. A., Fischer E. H., Titani K. Amino acid sequence of the catalytic subunit of bovine type II adenosine cyclic 3',5'-phosphate dependent protein kinase. Biochemistry. 1983 Jul 19;22(15):3702–3709. doi: 10.1021/bi00284a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoji S., Titani K., Demaille J. G., Fischer E. H. Sequence of two phosphorylated sites in the catalytic subunit of bovine cardiac muscle adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 25;254(14):6211–6214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuntoh H., Steinberg R. A. Analysis of the dominance of mutations in cAMP-binding sites of murine type I cAMP-dependent protein kinase in activation of kinase from heterozygous mutant lymphoma cells. J Cell Physiol. 1991 Jan;146(1):86–93. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041460112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slice L. W., Taylor S. S. Expression of the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 15;264(35):20940–20946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg R. A. A kinase-negative mutant of S49 mouse lymphoma cells is defective in posttranslational maturation of catalytic subunit of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):705–712. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg R. A., Agard D. A. Studies on the phosphorylation and synthesis of type I regulatory subunit of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase in intact S49 mouse lymphoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):11356–11364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. S., Buechler J. A., Yonemoto W. cAMP-dependent protein kinase: framework for a diverse family of regulatory enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:971–1005. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.004543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toner-Webb J., van Patten S. M., Walsh D. A., Taylor S. S. Autophosphorylation of the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 15;267(35):25174–25180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhler M. D., McKnight G. S. Expression of cDNAs for two isoforms of the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 5;262(31):15202–15207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehouse S., Walsh D. A. Mg X ATP2-dependent interaction of the inhibitor protein of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase with the catalytic subunit. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3682–3692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonemoto W. M., McGlone M. L., Slice L. W., Taylor S. S. Prokaryotic expression of catalytic subunit of adenosine cyclic monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Methods Enzymol. 1991;200:581–596. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)00173-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Nelson N. C., Taylor S. S. Affinity labeling of cAMP-dependent protein kinase with p-fluorosulfonylbenzoyl adenosine. Covalent modification of lysine 71. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):10837–10842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Taylor S. S. Affinity labeling of the nucleotide binding site of the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase using p-fluorosulfonyl-[14C]benzoyl 5'-adenosine. Identification of a modified lysine residue. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8363–8368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]