Abstract
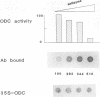
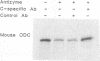
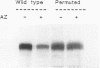
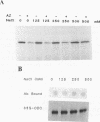
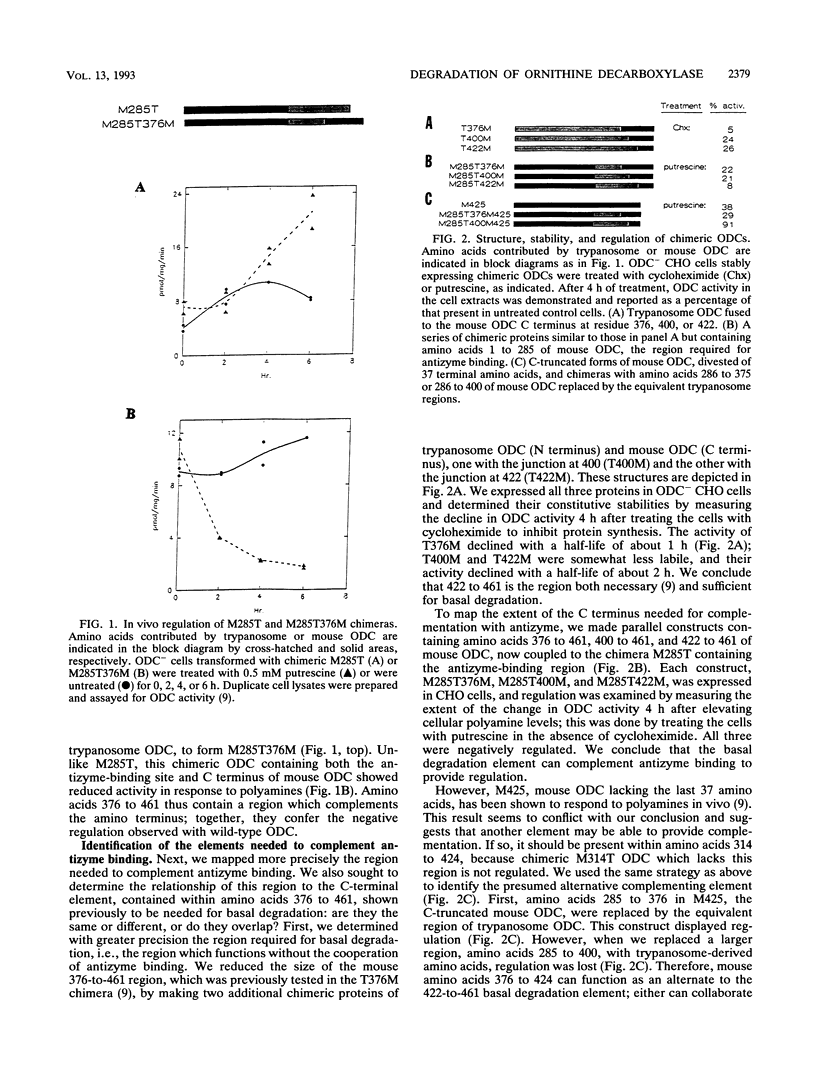
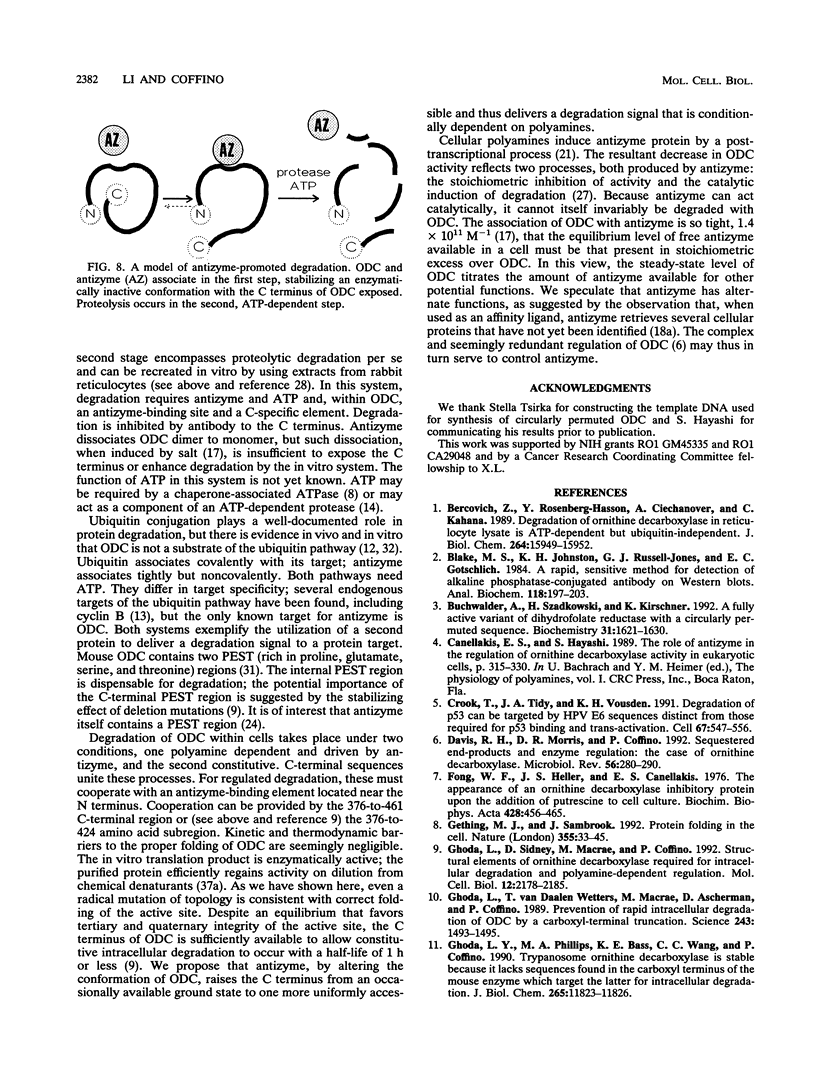
Polyamine-mediated degradation of vertebrate ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) is associated with the production of antizyme, a reversible tightly binding protein inhibitor of ODC activity. The interaction of antizyme with a binding element near the N terminus of ODC is essential but not sufficient for regulation of the enzyme by polyamines (X. Li and P. Coffino, Mol. Cell. Biol. 12:3556-2562, 1992). We now show that a second element present at the C terminus is required for the degradation process. Antizyme caused a conformational change in ODC, which made the C terminus of ODC more accessible. Blocking the C terminus with antibody prevented degradation. Tethering the C terminus by creating a circularly permuted, enzymatically active form of ODC prevented antizyme-mediated degradation. These data elucidate a form of feedback regulation whereby excess polyamines induce destruction of ODC, the enzyme that initiates their biosynthesis.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bercovich Z., Rosenberg-Hasson Y., Ciechanover A., Kahana C. Degradation of ornithine decarboxylase in reticulocyte lysate is ATP-dependent but ubiquitin-independent. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 25;264(27):15949–15952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchwalder A., Szadkowski H., Kirschner K. A fully active variant of dihydrofolate reductase with a circularly permuted sequence. Biochemistry. 1992 Feb 18;31(6):1621–1630. doi: 10.1021/bi00121a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crook T., Tidy J. A., Vousden K. H. Degradation of p53 can be targeted by HPV E6 sequences distinct from those required for p53 binding and trans-activation. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):547–556. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90529-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. H., Morris D. R., Coffino P. Sequestered end products and enzyme regulation: the case of ornithine decarboxylase. Microbiol Rev. 1992 Jun;56(2):280–290. doi: 10.1128/mr.56.2.280-290.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong W. F., Heller J. S., Canellakis E. S. The appearance of an ornithine decarboxylase inhibitory protein upon the addition of putrescine to cell cultures. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 23;428(2):456–465. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90054-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., Sambrook J. Protein folding in the cell. Nature. 1992 Jan 2;355(6355):33–45. doi: 10.1038/355033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghoda L., Phillips M. A., Bass K. E., Wang C. C., Coffino P. Trypanosome ornithine decarboxylase is stable because it lacks sequences found in the carboxyl terminus of the mouse enzyme which target the latter for intracellular degradation. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 15;265(20):11823–11826. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghoda L., Sidney D., Macrae M., Coffino P. Structural elements of ornithine decarboxylase required for intracellular degradation and polyamine-dependent regulation. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 May;12(5):2178–2185. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.5.2178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghoda L., van Daalen Wetters T., Macrae M., Ascherman D., Coffino P. Prevention of rapid intracellular degradation of ODC by a carboxyl-terminal truncation. Science. 1989 Mar 17;243(4897):1493–1495. doi: 10.1126/science.2928784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass J. R., Gerner E. W. Spermidine mediates degradation of ornithine decarboxylase by a non-lysosomal, ubiquitin-independent mechanism. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Jan;130(1):133–141. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041300119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glotzer M., Murray A. W., Kirschner M. W. Cyclin is degraded by the ubiquitin pathway. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):132–138. doi: 10.1038/349132a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. L. The mechanism and functions of ATP-dependent proteases in bacterial and animal cells. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Jan 15;203(1-2):9–23. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb19822.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller J. S., Fong W. F., Canellakis E. S. Induction of a protein inhibitor to ornithine decarboxylase by the end products of its reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1858–1862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton R. M., Hunt H. D., Ho S. N., Pullen J. K., Pease L. R. Engineering hybrid genes without the use of restriction enzymes: gene splicing by overlap extension. Gene. 1989 Apr 15;77(1):61–68. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90359-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitani T., Fujisawa H. Influence of salts on the activity and the subunit structure of ornithine decarboxylase from rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jan 31;784(2-3):164–167. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(84)90123-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X., Coffino P. Regulated degradation of ornithine decarboxylase requires interaction with the polyamine-inducible protein antizyme. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;12(8):3556–3562. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.8.3556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luger K., Hommel U., Herold M., Hofsteenge J., Kirschner K. Correct folding of circularly permuted variants of a beta alpha barrel enzyme in vivo. Science. 1989 Jan 13;243(4888):206–210. doi: 10.1126/science.2643160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrae M., Coffino P. Complementation of a polyamine-deficient Escherichia coli mutant by expression of mouse ornithine decarboxylase. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):564–567. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsufuji S., Miyazaki Y., Kanamoto R., Kameji T., Murakami Y., Baby T. G., Fujita K., Ohno T., Hayashi S. Analyses of ornithine decarboxylase antizyme mRNA with a cDNA cloned from rat liver. J Biochem. 1990 Sep;108(3):365–371. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConlogue L., Dana S. L., Coffino P. Multiple mechanisms are responsible for altered expression of ornithine decarboxylase in overproducing variant cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2865–2871. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell J. L., Rynning M. D., Chen H. J., Hicks M. F. Interrelation between the charge isoforms of mammalian ornithine decarboxylase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Feb 1;260(2):585–594. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90485-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki Y., Matsufuji S., Hayashi S. Cloning and characterization of a rat gene encoding ornithine decarboxylase antizyme. Gene. 1992 Apr 15;113(2):191–197. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90395-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami Y., Fujita K., Kameji T., Hayashi S. Accumulation of ornithine decarboxylase-antizyme complex in HMOA cells. Biochem J. 1985 Feb 1;225(3):689–697. doi: 10.1042/bj2250689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami Y., Hayashi S. Role of antizyme in degradation of ornithine decarboxylase in HTC cells. Biochem J. 1985 Mar 15;226(3):893–896. doi: 10.1042/bj2260893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami Y., Matsufuji S., Miyazaki Y., Hayashi S. Destabilization of ornithine decarboxylase by transfected antizyme gene expression in hepatoma tissue culture cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13138–13141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami Y., Tanaka K., Matsufuji S., Miyazaki Y., Hayashi S. Antizyme, a protein induced by polyamines, accelerates the degradation of ornithine decarboxylase in Chinese-hamster ovary-cell extracts. Biochem J. 1992 May 1;283(Pt 3):661–664. doi: 10.1042/bj2830661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips M. A., Coffino P., Wang C. C. Cloning and sequencing of the ornithine decarboxylase gene from Trypanosoma brucei. Implications for enzyme turnover and selective difluoromethylornithine inhibition. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8721–8727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechsteiner M. Regulation of enzyme levels by proteolysis: the role of pest regions. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1988;27:135–151. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(88)90014-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers S., Wells R., Rechsteiner M. Amino acid sequences common to rapidly degraded proteins: the PEST hypothesis. Science. 1986 Oct 17;234(4774):364–368. doi: 10.1126/science.2876518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg-Hasson Y., Bercovich Z., Ciechanover A., Kahana C. Degradation of ornithine decarboxylase in mammalian cells is ATP dependent but ubiquitin independent. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Nov 6;185(2):469–474. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15138.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffner M., Werness B. A., Huibregtse J. M., Levine A. J., Howley P. M. The E6 oncoprotein encoded by human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 promotes the degradation of p53. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1129–1136. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90409-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. E., Fisher P. A. Identification, developmental regulation, and response to heat shock of two antigenically related forms of a major nuclear envelope protein in Drosophila embryos: application of an improved method for affinity purification of antibodies using polypeptides immobilized on nitrocellulose blots. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;99(1 Pt 1):20–28. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.1.20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steglich C., Scheffler I. E. An ornithine decarboxylase-deficient mutant of Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4603–4609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. R., Capecchi M. R. Site-directed mutagenesis by gene targeting in mouse embryo-derived stem cells. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):503–512. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90646-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werness B. A., Levine A. J., Howley P. M. Association of human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 E6 proteins with p53. Science. 1990 Apr 6;248(4951):76–79. doi: 10.1126/science.2157286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Daalen Wetters T., Macrae M., Brabant M., Sittler A., Coffino P. Polyamine-mediated regulation of mouse ornithine decarboxylase is posttranslational. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5484–5490. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]