Abstract
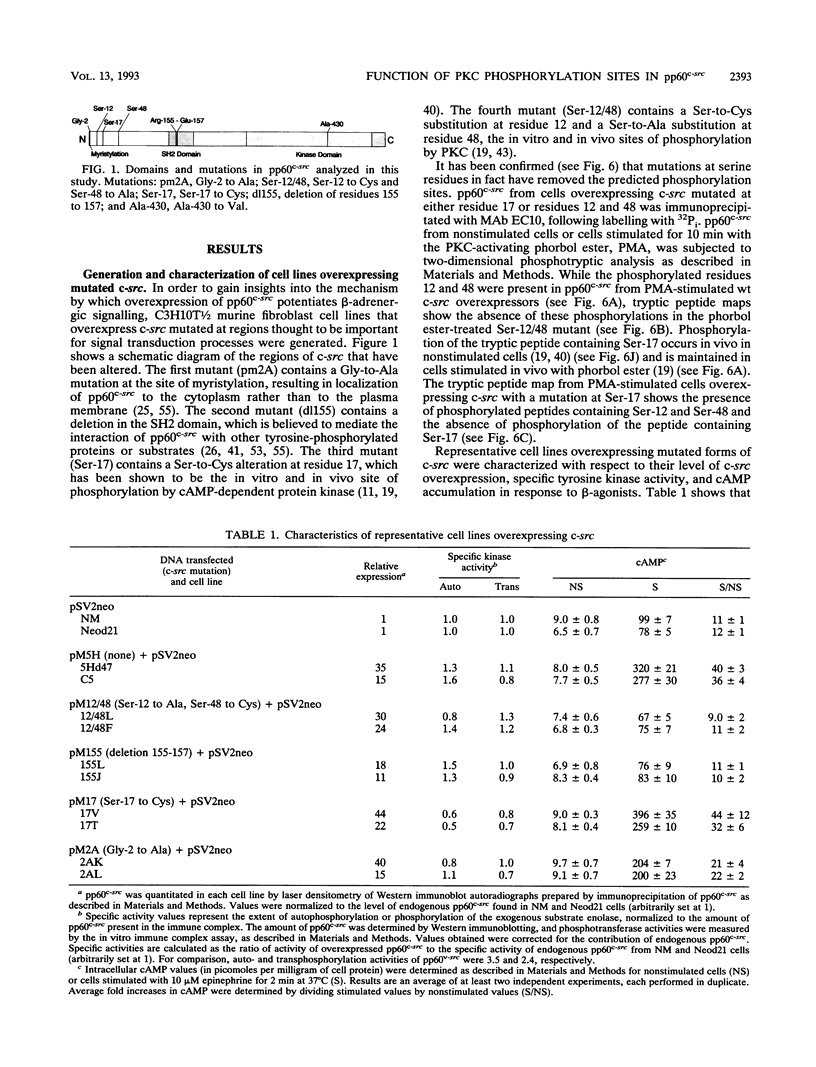
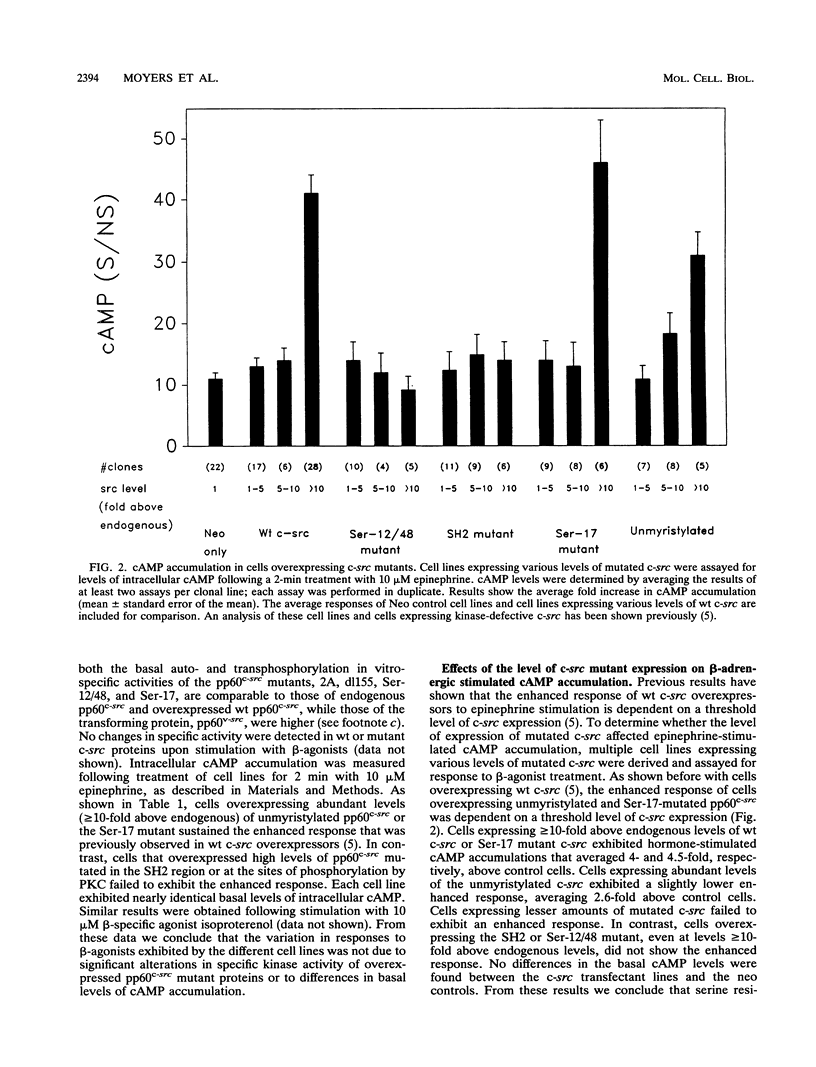
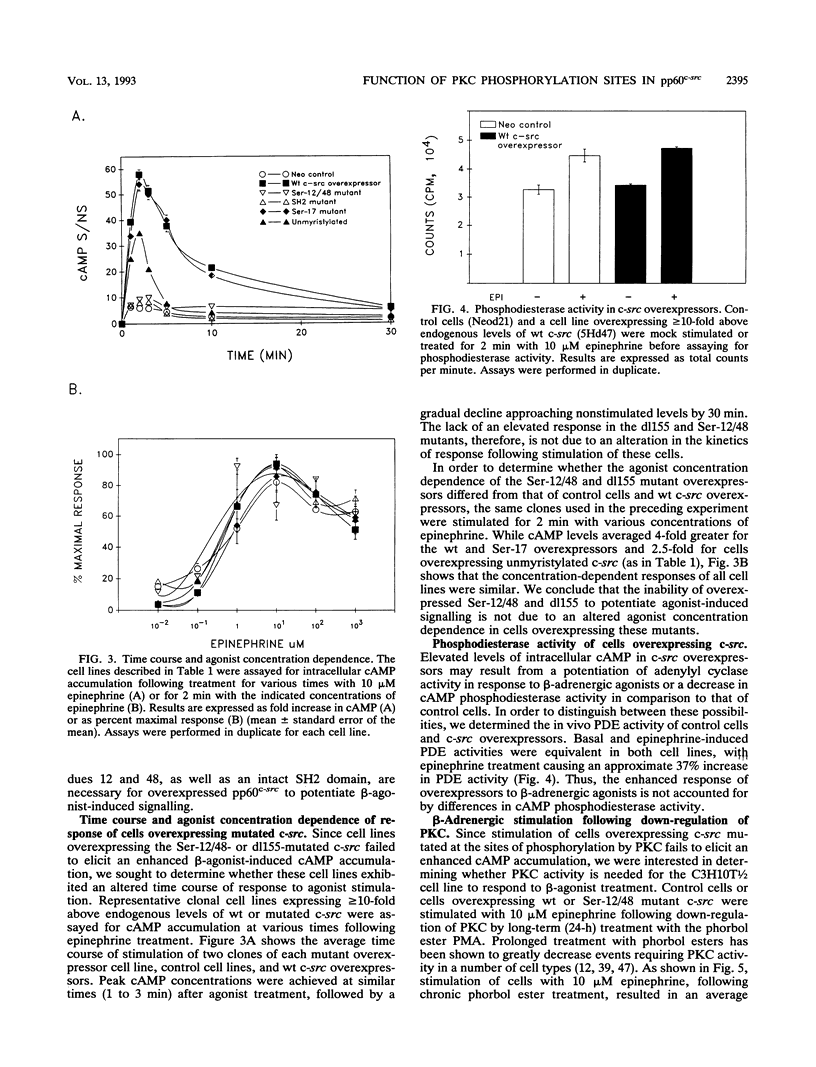
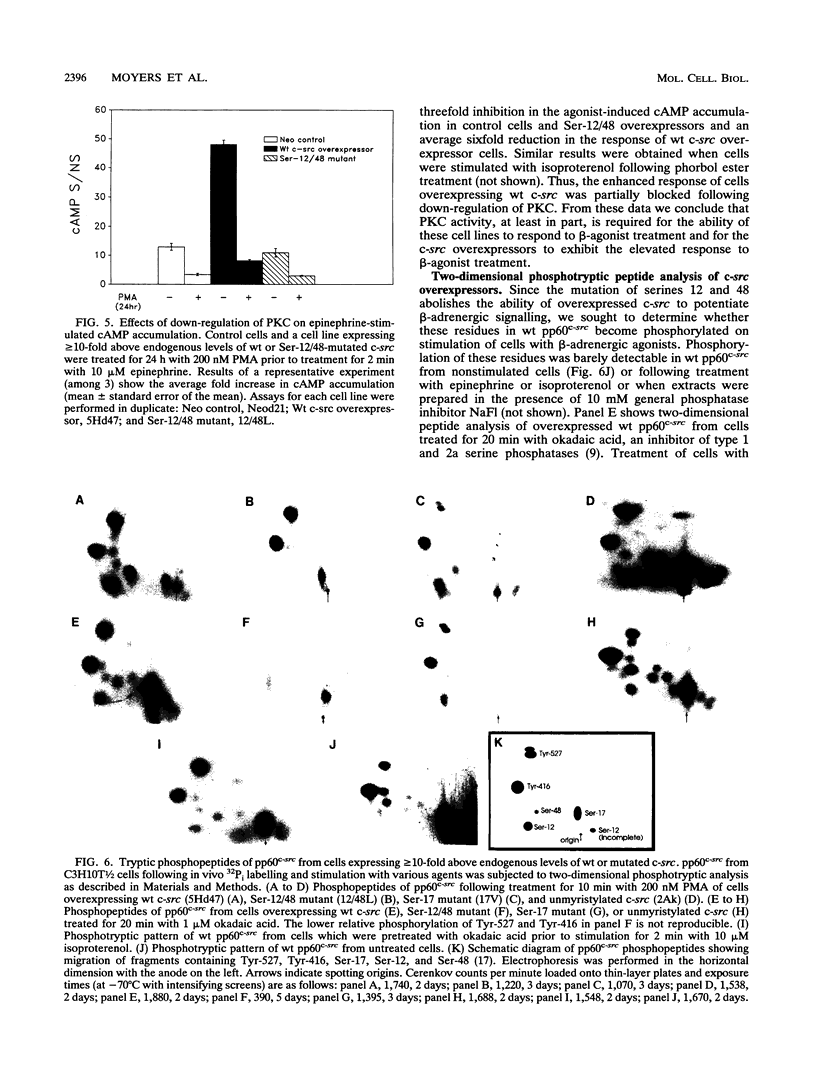
Previously we demonstrated that C3H10T1/2 murine fibroblasts overexpressing avian c-src exhibit elevated levels of cyclic AMP (cAMP) in response to beta-adrenergic agonists compared with that in control cells and that this enhanced response requires c-src kinase activity (W. A. Bushman, L. K. Wilson, D. K. Luttrell, J. S. Moyers, and S. J. Parsons, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87:7462-7466, 1990). However, it is not yet known which components of the beta-adrenergic receptor pathway, if any, interact with pp60c-src. It has recently been shown that immune complexes of pp60c-src phosphorylate recombinant G alpha proteins in vitro to stoichiometric levels, resulting in alterations of GTP binding and GTPase activity (W. P. Hausdorff, J. A. Pitcher, D. K. Luttrell, M. E. Linder, H. Kurose, S. J. Parsons, M. G. Caron, and R. J. Lefkowitz, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89:5720-5724, 1992), raising the possibility that the Gs alpha protein may be an in vivo target for the interaction with pp60c-src. To further characterize the involvement of pp60c-src in the beta-adrenergic signalling pathway, we have overexpressed, in 10T1/2 cells, pp60c-src containing mutations in several domains which are believed to be important for signalling processes. In this study we show that the sites of phosphorylation by protein kinase C (PKC) (Ser-12 and Ser-48) as well as the SH2 region of pp60c-src are required for the enhanced response of c-src overexpressors to beta-agonist stimulation. Mutation at the site of myristylation (Gly-2) results in a decrease in the enhanced response, while mutation at the site of phosphorylation by cAMP-dependent protein kinase (Ser-17) has no effect. Two-dimensional phosphotryptic analyses indicate that phosphorylation on Ser-12 and Ser-48 in unstimulated cells is associated with the ability of overexpressed pp60c-src to potentiate beta-adrenergic signalling. Cells overexpressing wild-type c-src also exhibit enhanced cAMP accumulation upon treatment with cholera toxin, an effect that is abated in cells overexpressing pp60c-src defective in the kinase or SH2 domains or altered at the sites of phosphorylation by PKC. These studies provide the first evidence for the physiological significance of the pp60c-src sites of PKC phosphorylation. In addition, they show that the SH2, Ser-12/48, and myristylation regions may be important for efficient interaction of pp60c-src with components of the beta-adrenergic pathway. Our data also support the possibility that the Gs alpha protein may be an in vivo target for alteration by pp60c-src.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexandropoulos K., Joseph C. K., Spangler R., Foster D. A. Evidence that a G-protein transduces signals initiated by the protein-tyrosine kinase v-Fps. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15583–15586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beavo J. A., Hansen R. S., Harrison S. A., Hurwitz R. L., Martins T. J., Mumby M. C. Identification and properties of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1982 Nov-Dec;28(3):387–410. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(82)90135-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvier M., Leeb-Lundberg L. M., Benovic J. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Regulation of adrenergic receptor function by phosphorylation. II. Effects of agonist occupancy on phosphorylation of alpha 1- and beta 2-adrenergic receptors by protein kinase C and the cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3106–3113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle W. J., van der Geer P., Hunter T. Phosphopeptide mapping and phosphoamino acid analysis by two-dimensional separation on thin-layer cellulose plates. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:110–149. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01013-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushman W. A., Wilson L. K., Luttrell D. K., Moyers J. S., Parsons S. J. Overexpression of c-src enhances beta-adrenergic-induced cAMP accumulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7462–7466. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buss J. E., Sefton B. M. Myristic acid, a rare fatty acid, is the lipid attached to the transforming protein of Rous sarcoma virus and its cellular homolog. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):7–12. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.7-12.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calothy G., Laugier D., Cross F. R., Jove R., Hanafusa T., Hanafusa H. The membrane-binding domain and myristylation of p60v-src are not essential for stimulation of cell proliferation. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1678–1681. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1678-1681.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Holmes C. F., Tsukitani Y. Okadaic acid: a new probe for the study of cellular regulation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Mar;15(3):98–102. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90192-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Brugge J. S., Erikson R. L. Characterization of a normal avian cell protein related to the avian sarcoma virus transforming gene product. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1363–1369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90061-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Erikson E., Purchio A. F., Brugge J. S., Erikson R. L. A normal cell protein similar in structure and function to the avian sarcoma virus transforming gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3159–3163. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M. K., Rozengurt E. Homologous and heterologous mitogenic desensitization of Swiss 3T3 cells to phorbol esters and vasopressin: role of receptor and postreceptor steps. J Cell Physiol. 1984 Feb;118(2):133–142. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041180205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross F. R., Hanafusa H. Local mutagenesis of Rous sarcoma virus: the major sites of tyrosine and serine phosphorylation of pp60src are dispensable for transformation. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):597–607. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90392-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felgner P. L., Gadek T. R., Holm M., Roman R., Chan H. W., Wenz M., Northrop J. P., Ringold G. M., Danielsen M. Lipofection: a highly efficient, lipid-mediated DNA-transfection procedure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7413–7417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gawler D., Houslay M. D. Insulin stimulates a novel GTPase activity in human platelets. FEBS Lett. 1987 May 25;216(1):94–98. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80763-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden A., Nemeth S. P., Brugge J. S. Blood platelets express high levels of the pp60c-src-specific tyrosine kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):852–856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Hunter T. Platelet-derived growth factor induces multisite phosphorylation of pp60c-src and increases its protein-tyrosine kinase activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3345–3356. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Woodgett J. R., Cooper J. A., Buss J. E., Shalloway D., Hunter T. Protein kinase C phosphorylates pp60src at a novel site. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90281-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. F., Brooker G. Femtomole sensitive radioimmunoassay for cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP after 2'0 acetylation by acetic anhydride in aqueous solution. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1975;1(4):207–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart M. J., Polakis P. G., Evans T., Cerione R. A. The identification and characterization of an epidermal growth factor-stimulated phosphorylation of a specific low molecular weight GTP-binding protein in a reconstituted phospholipid vesicle system. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 15;265(11):5990–6001. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausdorff W. P., Pitcher J. A., Luttrell D. K., Linder M. E., Kurose H., Parsons S. J., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Tyrosine phosphorylation of G protein alpha subunits by pp60c-src. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):5720–5724. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.5720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirota Y., Kato J., Takeya T. Substitution of Ser-17 of pp60c-src: biological and biochemical characterization in chicken embryo fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1826–1830. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imamura K., Kufe D. Colony-stimulating factor 1-induced Na+ influx into human monocytes involves activation of a pertussis toxin-sensitive GTP-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14093–14098. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Buss J. E., Sefton B. M. Mutation of NH2-terminal glycine of p60src prevents both myristoylation and morphological transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4625–4628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C. A., Anderson D., Moran M. F., Ellis C., Pawson T. SH2 and SH3 domains: elements that control interactions of cytoplasmic signaling proteins. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):668–674. doi: 10.1126/science.1708916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupinski J., Rajaram R., Lakonishok M., Benovic J. L., Cerione R. A. Insulin-dependent phosphorylation of GTP-binding proteins in phospholipid vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12333–12341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kypta R. M., Goldberg Y., Ulug E. T., Courtneidge S. A. Association between the PDGF receptor and members of the src family of tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):481–492. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsich L. A., Lewis A. J., Brugge J. S. Isolation of monoclonal antibodies that recognize the transforming proteins of avian sarcoma viruses. J Virol. 1983 Nov;48(2):352–360. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.2.352-360.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeffler J. P., Barthel F., Feltz P., Behr J. P., Sassone-Corsi P., Feltz A. Lipopolyamine-mediated transfection allows gene expression studies in primary neuronal cells. J Neurochem. 1990 May;54(5):1812–1815. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb01240.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo K., Hurley T. R., Sefton B. M. Transfer of proteins to membranes facilitates both cyanogen bromide cleavage and two-dimensional proteolytic mapping. Oncogene. 1990 Jun;5(6):921–923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luttrell D. K., Hausdorff W. P., Moyers J. E., Gilmer T. M., Parsons S. J., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Overexpression of pp60c-src is associated with altered regulation of adenylyl cyclase. Cell Signal. 1992 Sep;4(5):531–541. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(92)90022-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luttrell D. K., Luttrell L. M., Parsons S. J. Augmented mitogenic responsiveness to epidermal growth factor in murine fibroblasts that overexpress pp60c-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):497–501. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maa M. C., Wilson L. K., Moyers J. S., Vines R. R., Parsons J. T., Parsons S. J. Identification and characterization of a cytoskeleton-associated, epidermal growth factor sensitive pp60c-src substrate. Oncogene. 1992 Dec;7(12):2429–2438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattingly R. R., Wasilenko W. J., Woodring P. J., Garrison J. C. Selective amplification of endothelin-stimulated inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and calcium signaling by v-src transformation of rat-1 fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 15;267(11):7470–7477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons J. T., Weber M. J. Genetics of src: structure and functional organization of a protein tyrosine kinase. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1989;147:79–127. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74697-0_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons S. J., Creutz C. E. p60c-src activity detected in the chromaffin granule membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jan 29;134(2):736–742. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80482-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasti G., Lacal J. C., Warren B. S., Aaronson S. A., Blumberg P. M. Loss of mouse fibroblast cell response to phorbol esters restored by microinjected protein kinase C. 1986 Nov 27-Dec 3Nature. 324(6095):375–377. doi: 10.1038/324375a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patschinsky T., Hunter T., Sefton B. M. Phosphorylation of the transforming protein of Rous sarcoma virus: direct demonstration of phosphorylation of serine 17 and identification of an additional site of tyrosine phosphorylation in p60v-src of Prague Rous sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1986 Jul;59(1):73–81. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.1.73-81.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T. Non-catalytic domains of cytoplasmic protein-tyrosine kinases: regulatory elements in signal transduction. Oncogene. 1988 Nov;3(5):491–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pendergast A. M., Muller A. J., Havlik M. H., Maru Y., Witte O. N. BCR sequences essential for transformation by the BCR-ABL oncogene bind to the ABL SH2 regulatory domain in a non-phosphotyrosine-dependent manner. Cell. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):161–171. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90148-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purchio A. F., Shoyab M., Gentry L. E. Site-specific increased phosphorylation of pp60v-src after treatment of RSV-transformed cells with a tumor promoter. Science. 1985 Sep 27;229(4720):1393–1395. doi: 10.1126/science.2994221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyne N. J., Freissmuth M., Palmer S. Phosphorylation of the spliced variant forms of the recombinant stimulatory guanine-nucleotide-binding regulatory protein (Gs alpha) by protein kinase C. Biochem J. 1992 Jul 1;285(Pt 1):333–338. doi: 10.1042/bj2850333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralston R., Bishop J. M. The product of the protooncogene c-src is modified during the cellular response to platelet-derived growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7845–7849. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resh M. D. Reconstitution of the Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein pp60v-src into phospholipid vesicles. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):1896–1905. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.1896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Pena A., Rozengurt E. Disappearance of Ca2+-sensitive, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase activity in phorbol ester-treated 3T3 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 May 16;120(3):1053–1059. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80213-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross C. A., Wright G. E., Resh M. D., Pearson R. C., Snyder S. H. Brain-specific src oncogene mRNA mapped in rat brain by in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9831–9835. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadler S. E., Maller J. L. In vivo regulation of cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase in Xenopus oocytes. Stimulation by insulin and insulin-like growth factor 1. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10644–10650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Telfer J. C., Rudd C. E. A 32-kD GTP-binding protein associated with the CD4-p56lck and CD8-p56lck T cell receptor complexes. Science. 1991 Oct 18;254(5030):439–441. doi: 10.1126/science.1925604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waksman G., Kominos D., Robertson S. C., Pant N., Baltimore D., Birge R. B., Cowburn D., Hanafusa H., Mayer B. J., Overduin M. Crystal structure of the phosphotyrosine recognition domain SH2 of v-src complexed with tyrosine-phosphorylated peptides. Nature. 1992 Aug 20;358(6388):646–653. doi: 10.1038/358646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H. C., Parsons J. T. Deletions and insertions within an amino-terminal domain of pp60v-src inactivate transformation and modulate membrane stability. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):291–302. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.291-302.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiestler O. D., Walter G. Developmental expression of two forms of pp60c-src in mouse brain. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):502–504. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson L. K., Luttrell D. K., Parsons J. T., Parsons S. J. pp60c-src tyrosine kinase, myristylation, and modulatory domains are required for enhanced mitogenic responsiveness to epidermal growth factor seen in cells overexpressing c-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1536–1544. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson L. K., Parsons S. J. Enhanced EGF mitogenic response is associated with enhanced tyrosine phosphorylation of specific cellular proteins in fibroblasts overexpressing c-src. Oncogene. 1990 Oct;5(10):1471–1480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaciuk P., Choi J. K., Shalloway D. Mutation of amino acids in pp60c-src that are phosphorylated by protein kinases C and A. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2453–2463. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimasa T., Sibley D. R., Bouvier M., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G. Cross-talk between cellular signalling pathways suggested by phorbol-ester-induced adenylate cyclase phosphorylation. Nature. 1987 May 7;327(6117):67–70. doi: 10.1038/327067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zick Y., Sagi-Eisenberg R., Pines M., Gierschik P., Spiegel A. M. Multisite phosphorylation of the alpha subunit of transducin by the insulin receptor kinase and protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9294–9297. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




