Abstract
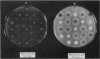
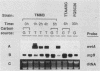
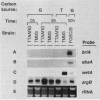
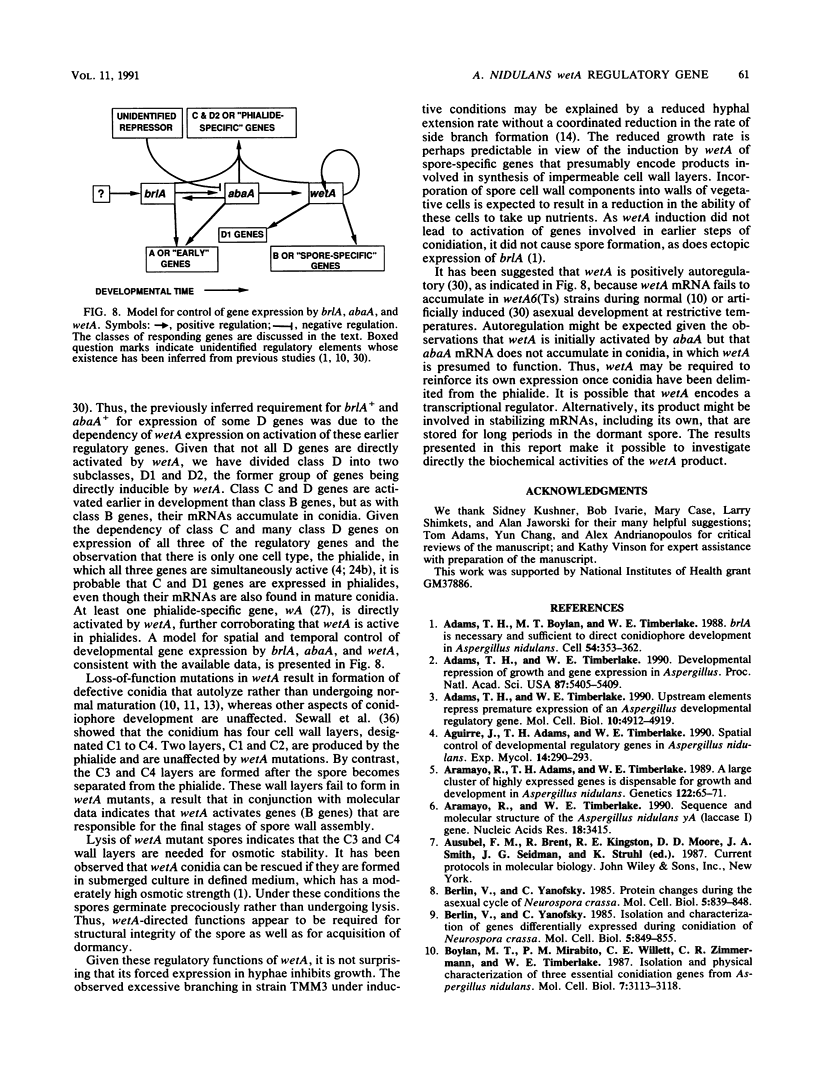
The Aspergillus nidulans wetA gene is required for synthesis of cell wall layers that make asexual spores (conidia) impermeable. In wetA mutant strains, conidia take up water and autolyze rather than undergoing the final stages of maturation. wetA is activated during conidiogenesis by sequential expression of the brlA and abaA regulatory genes. To determine whether wetA regulates expression of other sporulation-specific genes, its coding region was fused to a nutritionally regulated promoter that permits gene activation in vegetative cells (hyphae) under conditions that suppress conidiation. Expression of wetA in hyphae inhibited growth and caused excessive branching. It did not lead to activation of brlA or abaA but did cause accumulation of transcripts from genes that are normally expressed specifically during the late stages of conidiation and whose mRNAs are stored in mature spores. Thus, wetA directly or indirectly regulates expression of some spore-specific genes. At least one gene (wA), whose mRNA does not occur in spores but rather accumulates in the sporogenous phialide cells, was activated by wetA, suggesting that wetA may have a regulatory function in these cells as well as in spores. We propose that wetA is responsible for activating a set of genes whose products make up the final two conidial wall layers or direct their assembly and through this activity is responsible for acquisition of spore dormancy.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams T. H., Boylan M. T., Timberlake W. E. brlA is necessary and sufficient to direct conidiophore development in Aspergillus nidulans. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):353–362. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90198-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams T. H., Timberlake W. E. Developmental repression of growth and gene expression in Aspergillus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5405–5409. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams T. H., Timberlake W. E. Upstream elements repress premature expression of an Aspergillus developmental regulatory gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4912–4919. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aramayo R., Adams T. H., Timberlake W. E. A large cluster of highly expressed genes is dispensable for growth and development in Aspergillus nidulans. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):65–71. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aramayo R., Timberlake W. E. Sequence and molecular structure of the Aspergillus nidulans yA (laccase I) gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 11;18(11):3415–3415. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.11.3415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berlin V., Yanofsky C. Isolation and characterization of genes differentially expressed during conidiation of Neurospora crassa. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):849–855. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berlin V., Yanofsky C. Protein changes during the asexual cycle of Neurospora crassa. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):839–848. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boylan M. T., Mirabito P. M., Willett C. E., Zimmerman C. R., Timberlake W. E. Isolation and physical characterization of three essential conidiation genes from Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3113–3118. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clutterbuck A. J. A mutational analysis of conidial development in Aspergillus nidulans. Genetics. 1969 Oct;63(2):317–327. doi: 10.1093/genetics/63.2.317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo L. H., Wu R. Exonuclease III: use for DNA sequence analysis and in specific deletions of nucleotides. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:60–96. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00046-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gwynne D. I., Buxton F. P., Sibley S., Davies R. W., Lockington R. A., Scazzocchio C., Sealy-Lewis H. M. Comparison of the cis-acting control regions of two coordinately controlled genes involved in ethanol utilization in Aspergillus nidulans. Gene. 1987;51(2-3):205–216. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90309-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gwynne D. I., Miller B. L., Miller K. Y., Timberlake W. E. Structure and regulated expression of the SpoC1 gene cluster from Aspergillus nidulans. J Mol Biol. 1984 Nov 25;180(1):91–109. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90432-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamer J. E., Timberlake W. E. Functional organization of the Aspergillus nidulans trpC promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2352–2359. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III in DNA sequence analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:156–165. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käfer E. Meiotic and mitotic recombination in Aspergillus and its chromosomal aberrations. Adv Genet. 1977;19:33–131. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2660(08)60245-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law D. J., Timberlake W. E. Developmental regulation of laccase levels in Aspergillus nidulans. J Bacteriol. 1980 Nov;144(2):509–517. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.2.509-517.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewin B. Driving the cell cycle: M phase kinase, its partners, and substrates. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):743–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90181-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockington R. A., Sealy-Lewis H. M., Scazzocchio C., Davies R. W. Cloning and characterization of the ethanol utilization regulon in Aspergillus nidulans. Gene. 1985;33(2):137–149. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90088-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinelli S. D., Clutterbuck A. J. A quantitative survey of conidiation mutants in Aspergillus nidulans. J Gen Microbiol. 1971 Dec;69(2):261–268. doi: 10.1099/00221287-69-2-261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinelli S. D. Phenotypes of double conidiation mutants of Aspergillus nidulans. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Oct;114(2):277–287. doi: 10.1099/00221287-114-2-277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayorga M. E., Timberlake W. E. Isolation and molecular characterization of the Aspergillus nidulans wA gene. Genetics. 1990 Sep;126(1):73–79. doi: 10.1093/genetics/126.1.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller B. L., Miller K. Y., Roberti K. A., Timberlake W. E. Position-dependent and -independent mechanisms regulate cell-specific expression of the SpoC1 gene cluster of Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):427–434. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirabito P. M., Adams T. H., Timberlake W. E. Interactions of three sequentially expressed genes control temporal and spatial specificity in Aspergillus development. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):859–868. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90800-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hara E. B., Timberlake W. E. Molecular characterization of the Aspergillus nidulans yA locus. Genetics. 1989 Feb;121(2):249–254. doi: 10.1093/genetics/121.2.249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver P. T. Conidiophore and spore development in Aspergillus nidulans. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Nov;73(1):45–54. doi: 10.1099/00221287-73-1-45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr W. C., Timberlake W. E. Clustering of spore-specific genes in Aspergillus nidulans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5976–5980. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PONTECORVO G., ROPER J. A., HEMMONS L. M., MACDONALD K. D., BUFTON A. W. J. The genetics of Aspergillus nidulans. Adv Genet. 1953;5:141–238. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2660(08)60408-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P., Nurse P. Negative regulation of mitosis by wee1+, a gene encoding a protein kinase homolog. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):559–567. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90458-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sewall T. C., Mims C. W., Timberlake W. E. Conidium differentiation in Aspergillus nidulans wild-type and wet-white (wetA) mutant strains. Dev Biol. 1990 Apr;138(2):499–508. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(90)90215-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer M. L., Yanofsky C. A morphological and genetic analysis of conidiophore development in Neurospora crassa. Genes Dev. 1989 Apr;3(4):559–571. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timberlake W. E., Barnard E. C. Organization of a gene cluster expressed specifically in the asexual spores of A. nidulans. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(1 Pt 1):29–37. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90030-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timberlake W. E. Developmental gene regulation in Aspergillus nidulans. Dev Biol. 1980 Aug;78(2):497–510. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90349-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timberlake W. E., Marshall M. A. Genetic engineering of filamentous fungi. Science. 1989 Jun 16;244(4910):1313–1317. doi: 10.1126/science.2525275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timberlake W. E., Marshall M. A. Genetic regulation of development in Aspergillus nidulans. Trends Genet. 1988 Jun;4(6):162–169. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90022-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann C. R., Orr W. C., Leclerc R. F., Barnard E. C., Timberlake W. E. Molecular cloning and selection of genes regulated in Aspergillus development. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):709–715. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90434-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]