Abstract
Replication-competent avian retroviruses, capable of transducing and expressing up to 2 kb of nonviral sequences, are now available to effect widespread gene transfer in chicken (chick) embryos (S. H. Hughes, J. J. Greenhouse, C. J. Petropoulos, and P. Sutrave, J. Virol. 61:3004-3012, 1987). We have constructed novel avian retroviral vectors that encode human placental alkaline phosphatase as a marker whose expression can be histochemically monitored. These vectors have been tested for expression by introducing them into the embryonic chick nervous system. They have revealed that the expression of retrovirally transduced genes can be spatially and temporally limited without the need for tissue-specific promoters. By varying the site and time of infection, targeted gene transfer can be confined to selected populations of neural cells over the course of several days, a time window that is sufficient for many key developmental processes. The capability of differentially infecting specific target populations may avoid confounding variables such as detrimental effects of a transduced gene on processes unrelated to the cells or tissue of interest. These vectors and methods thus should be useful in studies of the effect of transduced genes on the development of various organs and tissues during avian embryogenesis. In addition, the vectors will facilitate studies aimed at an understanding of viral infection and expression patterns.
Full text
PDF



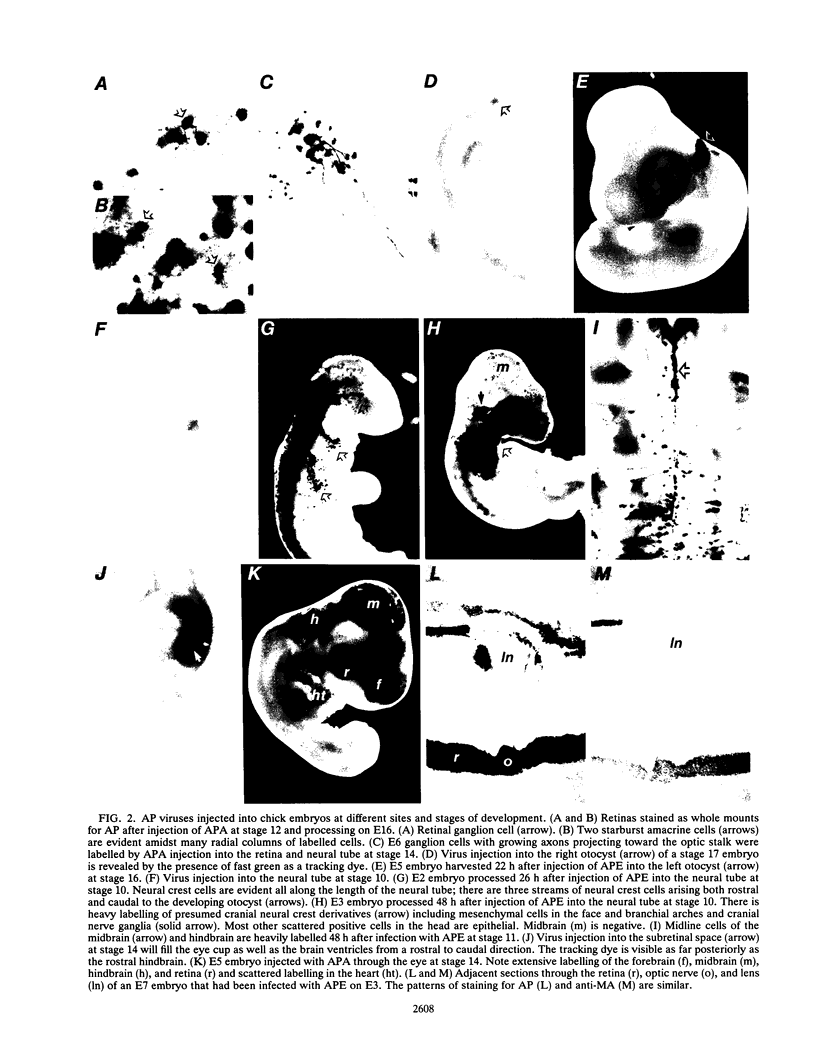

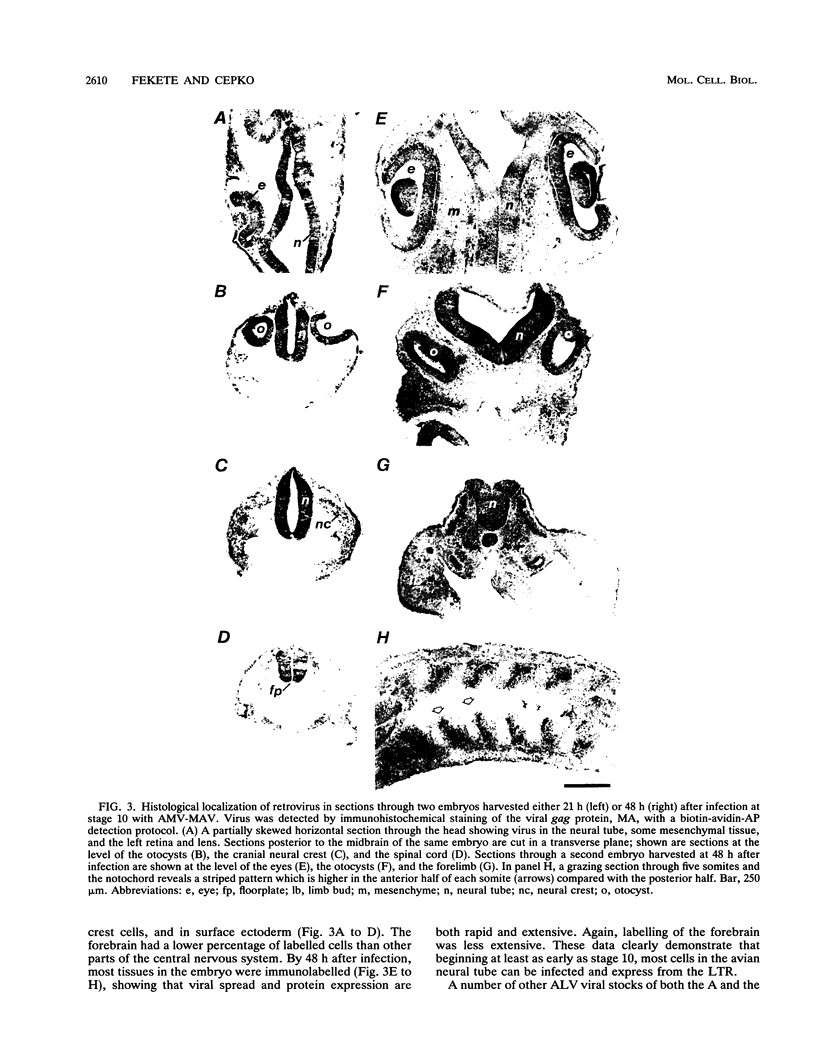



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Astrin S. M., Buss E. G., Haywards W. S. Endogenous viral genes are non-essential in the chicken. Nature. 1979 Nov 15;282(5736):339–341. doi: 10.1038/282339a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger J., Howard A. D., Gerber L., Cullen B. R., Udenfriend S. Expression of active, membrane-bound human placental alkaline phosphatase by transfected simian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4885–4889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briskin M. J., Hsu R. Y., Boggs T., Schultz J. A., Rishell W., Bosselman R. A. Heritable retroviral transgenes are highly expressed in chickens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1736–1740. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. W., Blais B. P., Robinson H. L. Long terminal repeat (LTR) sequences, env, and a region near the 5' LTR influence the pathogenic potential of recombinants between Rous-associated virus types 0 and 1. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3431–3437. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3431-3437.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. W., Robinson H. L. Influence of env and long terminal repeat sequences on the tissue tropism of avian leukosis viruses. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4828–4831. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4828-4831.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cepko C. Retrovirus vectors and their applications in neurobiology. Neuron. 1988 Jul;1(5):345–353. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90184-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dollé P., Izpisúa-Belmonte J. C., Falkenstein H., Renucci A., Duboule D. Coordinate expression of the murine Hox-5 complex homoeobox-containing genes during limb pattern formation. Nature. 1989 Dec 14;342(6251):767–772. doi: 10.1038/342767a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorner A. J., Stoye J. P., Coffin J. M. Molecular basis of host range variation in avian retroviruses. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):32–39. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.32-39.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fekete D. M., Cepko C. L. Retroviral infection coupled with tissue transplantation limits gene transfer in the chicken embryo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2350–2354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields-Berry S. C., Halliday A. L., Cepko C. L. A recombinant retrovirus encoding alkaline phosphatase confirms clonal boundary assignment in lineage analysis of murine retina. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 15;89(2):693–697. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.2.693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flamant F., Le Guellec D., Verdier G., Nigon V. M. Tissue specificity of retrovirus expression in inoculated avian embryos revealed by in situ hybridization to whole-body section. Virology. 1987 Sep;160(1):301–304. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90079-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser S., Keynes R., Lumsden A. Segmentation in the chick embryo hindbrain is defined by cell lineage restrictions. Nature. 1990 Mar 29;344(6265):431–435. doi: 10.1038/344431a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliday A. L., Cepko C. L. Generation and migration of cells in the developing striatum. Neuron. 1992 Jul;9(1):15–26. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90216-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hippenmeyer P. J., Krivi G. G., Highkin M. K. Transfer and expression of the bacterial NPT-II gene in chick embryos using a Schmidt-Ruppin retrovirus vector. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7619–7632. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howlett A. R., Cullen B., Hertle M., Bissell M. J. Tissue tropism and temporal expression of Rous sarcoma virus in embryonic avian limb in ovo. Oncogene Res. 1987 Aug;1(3):255–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S. H., Greenhouse J. J., Petropoulos C. J., Sutrave P. Adaptor plasmids simplify the insertion of foreign DNA into helper-independent retroviral vectors. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3004–3012. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3004-3012.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S., Kosik E. Mutagenesis of the region between env and src of the SR-A strain of Rous sarcoma virus for the purpose of constructing helper-independent vectors. Virology. 1984 Jul 15;136(1):89–99. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90250-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter E. Biological techniques for avian sarcoma viruses. Methods Enzymol. 1979;58:379–393. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(79)58153-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jähner D., Stuhlmann H., Stewart C. L., Harbers K., Löhler J., Simon I., Jaenisch R. De novo methylation and expression of retroviral genomes during mouse embryogenesis. Nature. 1982 Aug 12;298(5875):623–628. doi: 10.1038/298623a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leis J., Baltimore D., Bishop J. M., Coffin J., Fleissner E., Goff S. P., Oroszlan S., Robinson H., Skalka A. M., Temin H. M. Standardized and simplified nomenclature for proteins common to all retroviruses. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1808–1809. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1808-1809.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumsden A., Sprawson N., Graham A. Segmental origin and migration of neural crest cells in the hindbrain region of the chick embryo. Development. 1991 Dec;113(4):1281–1291. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.4.1281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitrani E., Coffin J., Boedtker H., Doty P. Rous sarcoma virus is integrated but not expressed in chicken early embryonic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2781–2784. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan B. A., Izpisúa-Belmonte J. C., Duboule D., Tabin C. J. Targeted misexpression of Hox-4.6 in the avian limb bud causes apparent homeotic transformations. Nature. 1992 Jul 16;358(6383):236–239. doi: 10.1038/358236a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscovici C., Moscovici M. G., Jimenez H., Lai M. M., Hayman M. J., Vogt P. K. Continuous tissue culture cell lines derived from chemically induced tumors of Japanese quail. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):95–103. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petropoulos C. J., Hughes S. H. Replication-competent retrovirus vectors for the transfer and expression of gene cassettes in avian cells. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3728–3737. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3728-3737.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petropoulos C. J., Payne W., Salter D. W., Hughes S. H. Appropriate in vivo expression of a muscle-specific promoter by using avian retroviral vectors for gene transfer [corrected]. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3391–3397. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3391-3397.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potts W. M., Olsen M., Boettiger D., Vogt V. M. Epitope mapping of monoclonal antibodies to gag protein p19 of avian sarcoma and leukaemia viruses. J Gen Virol. 1987 Dec;68(Pt 12):3177–3182. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-12-3177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODRIGUEZ J., DEINHARDT F. Preparation of a semipermanent mounting medium for fluorescent antibody studies. Virology. 1960 Oct;12:316–317. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(60)90205-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy S. T., Stoker A. W., Bissell M. J. Expression of Rous sarcoma virus-derived retroviral vectors in the avian blastoderm: potential as stable genetic markers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10505–10509. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rentrop M., Knapp B., Winter H., Schweizer J. Aminoalkylsilane-treated glass slides as support for in situ hybridization of keratin cDNAs to frozen tissue sections under varying fixation and pretreatment conditions. Histochem J. 1986 May;18(5):271–276. doi: 10.1007/BF01676237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson H. L., Jensen L., Coffin J. M. Sequences outside of the long terminal repeat determine the lymphomogenic potential of Rous-associated virus type 1. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):752–759. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.752-759.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoker A. W., Bissell M. J. Quantitative immunocytochemical assay for infectious avian retroviruses. J Gen Virol. 1987 Sep;68(Pt 9):2481–2485. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-9-2481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoker A. W., Hatier C., Bissell M. J. The embryonic environment strongly attenuates v-src oncogenesis in mesenchymal and epithelial tissues, but not in endothelia. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;111(1):217–228. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.1.217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoshima K., Vogt P. K. Enhancement and inhibition of avian sarcoma viruses by polycations and polyanions. Virology. 1969 Jul;38(3):414–426. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90154-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]