Abstract
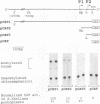
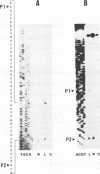
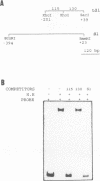
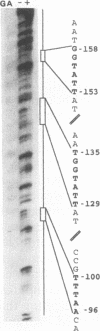
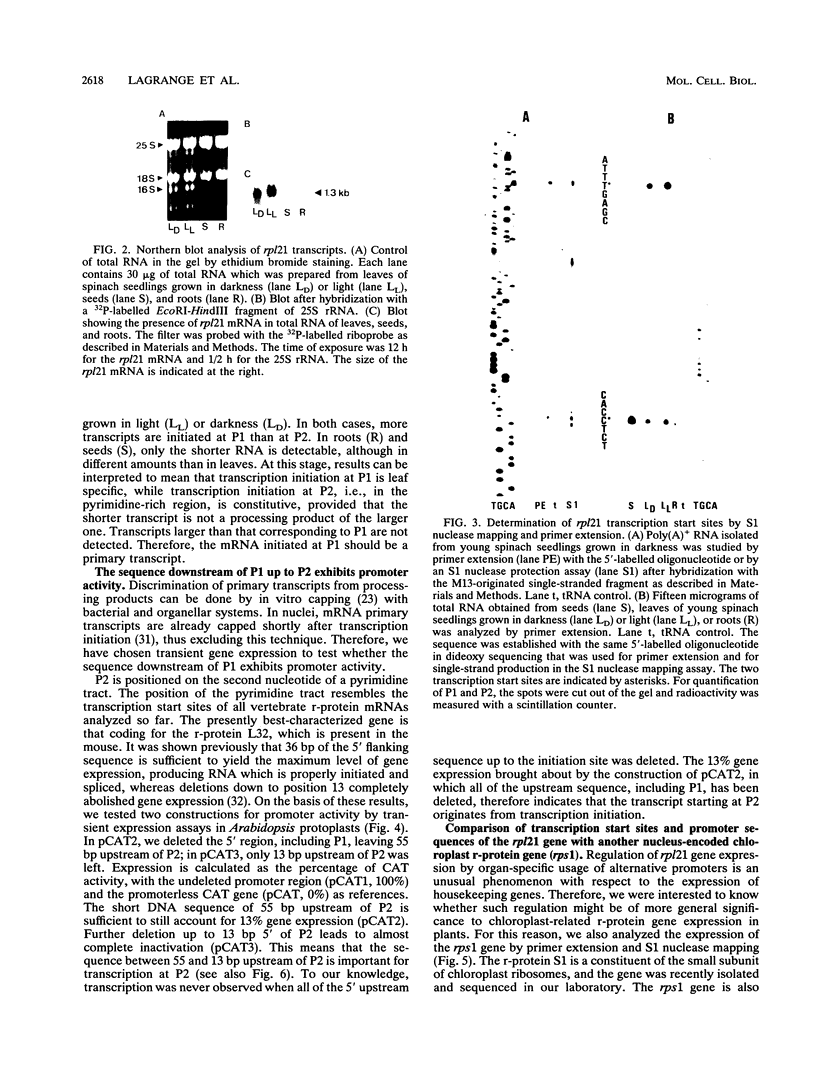
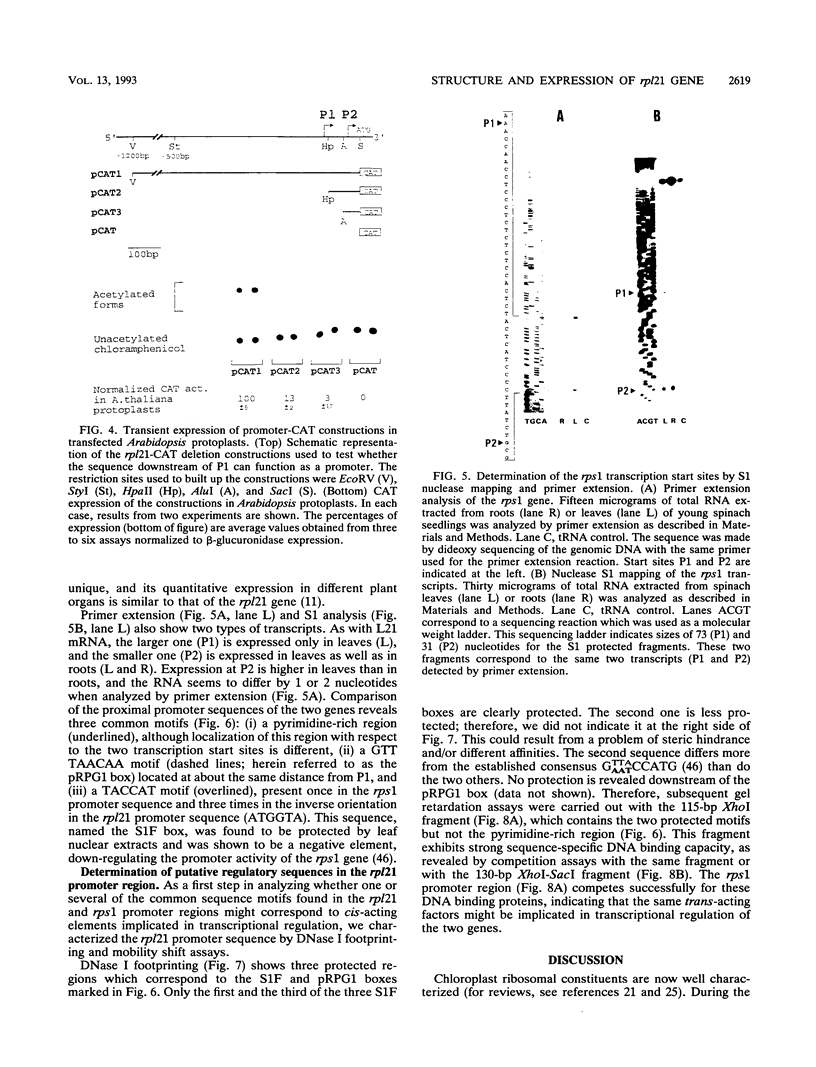
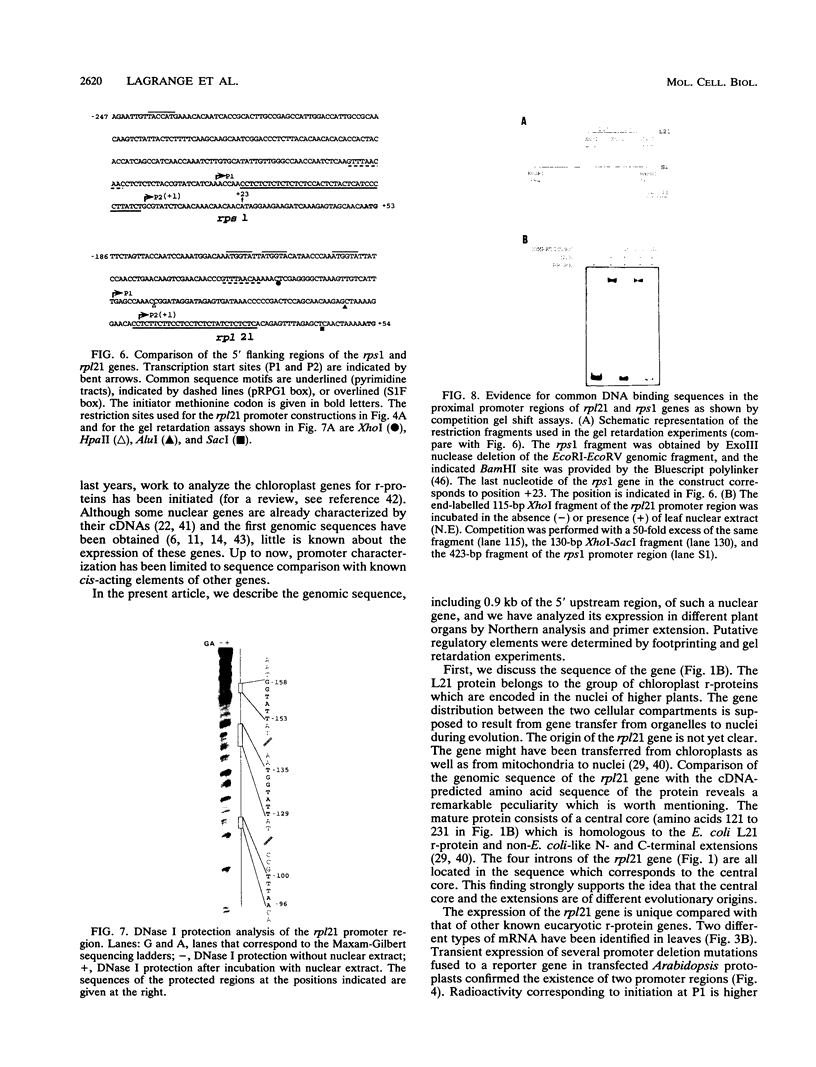
We have cloned and sequenced the nuclear gene of the chloroplast ribosomal protein L21 (rpl21) of Spinacia oleracea. The gene consists of five exons and four introns. All introns are located in the sequence which corresponds to the Escherichia coli-like central core of the protein. L21 mRNA is present in photosynthetic (leaves) and nonphotosynthetic (roots and seeds) plant organs, although large quantitative differences exist. Primer extension and S1 nuclease mapping experiments revealed the existence of two types of transcripts in leaves. The two corresponding start sites were defined as P1 and P2. In roots and seeds, we found only the shorter of the two transcripts (initiated at P2). The nucleotide sequence surrounding P2 resembles promoters for housekeeping and vertebrate r-protein genes. Analysis of several promoter constructions by transient expression confirmed that both transcripts originate from transcription initiation. Results are interpreted to mean that the expression of the rpl21 gene is regulated by alternative promoters. One of the promoters (P2) is constitutive, and the other one (P1) is specifically induced in leaves, i.e., its activation should be related to the transformation of amyloplasts or proplastids to chloroplasts. The gene thus represents the first example of a housekeeping gene which is regulated by the organ-specific usage of alternative promoters. Primer extension analysis and S1 nuclease mapping of another nucleus-encoded chloroplast ribosomal protein gene (rps1) give evidence that the same type of regulation by two-promoter usage might be a more general phenomenon of plant chloroplast-related ribosomal protein genes. Preliminary results indicate that presence of conserved sequences within the rpl21 and rps1 promoter regions which compete for the same DNA binding activities.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agrawal M. G., Bowman L. H. Transcriptional and translational regulation of ribosomal protein formation during mouse myoblast differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4868–4875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amaldi F., Bozzoni I., Beccari E., Pierandrei-Amaldi P. Expression of ribosomal protein genes and regulation of ribosome biosynthesis in Xenopus development. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 May;14(5):175–178. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90269-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atchison M. L., Meyuhas O., Perry R. P. Localization of transcriptional regulatory elements and nuclear factor binding sites in mouse ribosomal protein gene rpL32. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2067–2074. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelos M., Bardet C., Liboz T., Le Van Thai A., Curie C., Lescure B. The gene family encoding the Arabidopsis thaliana translation elongation factor EF-1 alpha: molecular cloning, characterization and expression. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Oct;219(1-2):106–112. doi: 10.1007/BF00261164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benfey P. N., Chua N. H. The Cauliflower Mosaic Virus 35S Promoter: Combinatorial Regulation of Transcription in Plants. Science. 1990 Nov 16;250(4983):959–966. doi: 10.1126/science.250.4983.959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisanz-Seyer C., Mache R. Organization and expression of the nuclear gene coding for the plastid-specific S22 ribosomal protein from spinach. Plant Mol Biol. 1992 Jan;18(2):337–341. doi: 10.1007/BF00034960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung S., Perry R. P. Importance of introns for expression of mouse ribosomal protein gene rpL32. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2075–2082. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzetti B., Zhou D. X., Mache R. Structure and expression of the nuclear gene coding for the plastid CS1 ribosomal protein from spinach. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Aug 25;20(16):4153–4157. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.16.4153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm M., Taylor L. P., Walbot V. Expression of genes transferred into monocot and dicot plant cells by electroporation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5824–5828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gantt J. S., Baldauf S. L., Calie P. J., Weeden N. F., Palmer J. D. Transfer of rpl22 to the nucleus greatly preceded its loss from the chloroplast and involved the gain of an intron. EMBO J. 1991 Oct;10(10):3073–3078. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07859.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giese K., Subramanian A. R. Chloroplast ribosomal protein L12 is encoded in the nucleus: construction and identification of its cDNA clones and nucleotide sequence including the transit peptide. Biochemistry. 1989 Apr 18;28(8):3525–3529. doi: 10.1021/bi00434a056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green P. J., Kay S. A., Chua N. H. Sequence-specific interactions of a pea nuclear factor with light-responsive elements upstream of the rbcS-3A gene. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2543–2549. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02542.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanley B. A., Schuler M. A. Plant intron sequences: evidence for distinct groups of introns. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 25;16(14B):7159–7176. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.14.7159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hariharan N., Perry R. P. A characterization of the elements comprising the promoter of the mouse ribosomal protein gene RPS16. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 11;17(13):5323–5337. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.13.5323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hariharan N., Perry R. P. Functional dissection of a mouse ribosomal protein promoter: significance of the polypyrimidine initiator and an element in the TATA-box region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1526–1530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson R. A., Kavanagh T. A., Bevan M. W. GUS fusions: beta-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):3901–3907. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02730.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levens D., Ticho B., Ackerman E., Rabinowitz M. Transcriptional initiation and 5' termini of yeast mitochondrial RNA. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):5226–5232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy S., Avni D., Hariharan N., Perry R. P., Meyuhas O. Oligopyrimidine tract at the 5' end of mammalian ribosomal protein mRNAs is required for their translational control. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3319–3323. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mager W. H. Control of ribosomal protein gene expression. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jan 25;949(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(88)90048-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mager W. H., Planta R. J. Coordinate expression of ribosomal protein genes in yeast as a function of cellular growth rate. 1991 May 29-Jun 12Mol Cell Biochem. 104(1-2):181–187. doi: 10.1007/BF00229818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mariottini P., Amaldi F. The 5' untranslated region of mRNA for ribosomal protein S19 is involved in its translational regulation during Xenopus development. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):816–822. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W., Lagrange T., Li Y. F., Bisanz-Seyer C., Mache R. Hypothesis for the evolutionary origin of the chloroplast ribosomal protein L21 of spinach. Curr Genet. 1990 Dec;18(6):553–556. doi: 10.1007/BF00327027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizumoto K., Kaziro Y. Messenger RNA capping enzymes from eukaryotic cells. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1987;34:1–28. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60491-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moura-Neto R., Dudov K. P., Perry R. P. An element downstream of the cap site is required for transcription of the gene encoding mouse ribosomal protein L32. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):3997–4001. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.3997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy F., Kay S. A., Chua N. H. Gene regulation by phytochrome. Trends Genet. 1988 Feb;4(2):37–42. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90064-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phua S. H., Srinivasa B. R., Subramanian A. R. Chloroplast ribosomal protein L13 is encoded in the nucleus and is considerably larger than its bacterial homologue. Construction, immunoisolation, and nucleotide sequence (including transit peptide) its cDNA clone from an angiosperm. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 5;264(4):1968–1971. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quattrocchio F., Tolk M. A., Coraggio I., Mol J. N., Viotti A., Koes R. E. The maize zein gene zE19 contains two distinct promoters which are independently activated in endosperm and anthers of transgenic Petunia plants. Plant Mol Biol. 1990 Jul;15(1):81–93. doi: 10.1007/BF00017726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schibler U., Sierra F. Alternative promoters in developmental gene expression. Annu Rev Genet. 1987;21:237–257. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.21.120187.001321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smooker P. M., Kruft V., Subramanian A. R. A ribosomal protein is encoded in the chloroplast DNA in a lower plant but in the nucleus in angiosperms. Isolation of the spinach L21 protein and cDNA clone with transit and an unusual repeat sequence. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 25;265(27):16699–16703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson M. D., Jacks C. M., Lenvik T. R., Gantt J. S. Characterization of rps17, rp19 and rpl15: three nucleus-encoded plastid ribosomal protein genes. Plant Mol Biol. 1992 Mar;18(5):931–944. doi: 10.1007/BF00019207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou D. X., Li Y. F., Rocipon M., Mache R. Sequence-specific interaction between S1F, a spinach nuclear factor, and a negative cis-element conserved in plastid-related genes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 25;267(33):23515–23519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]