Abstract
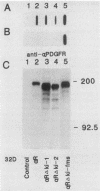
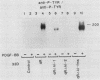
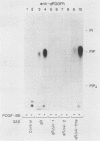
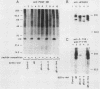
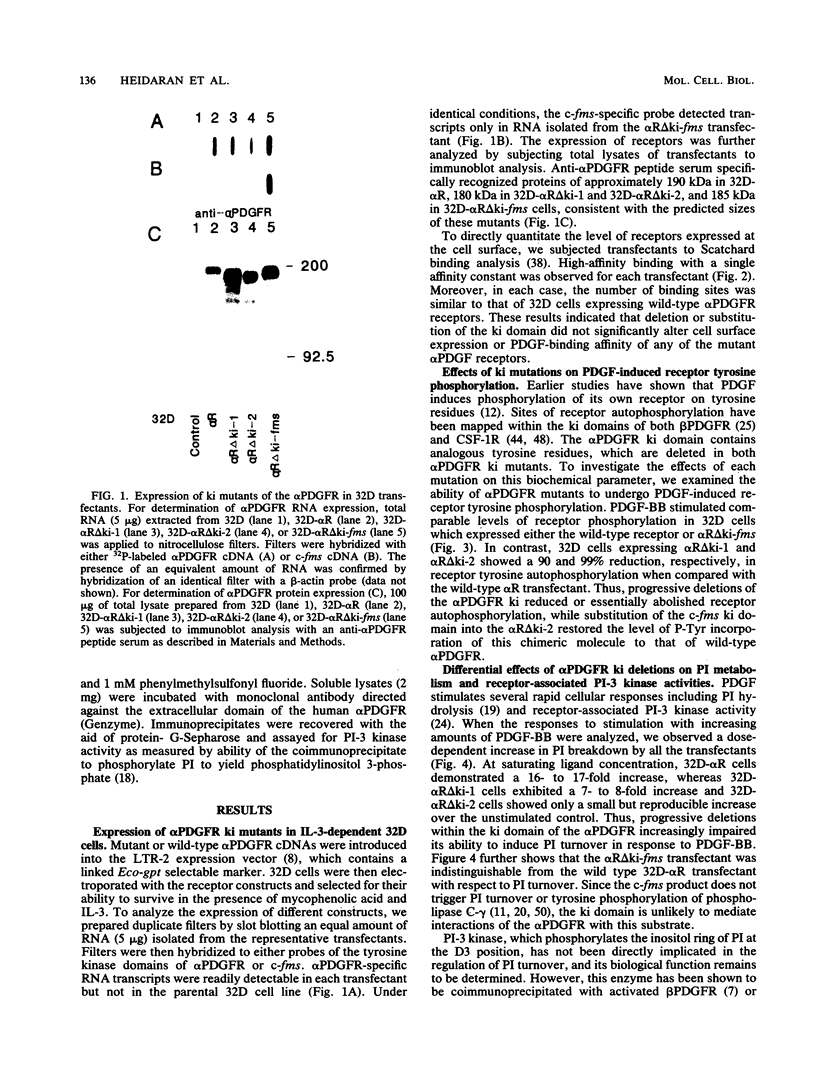
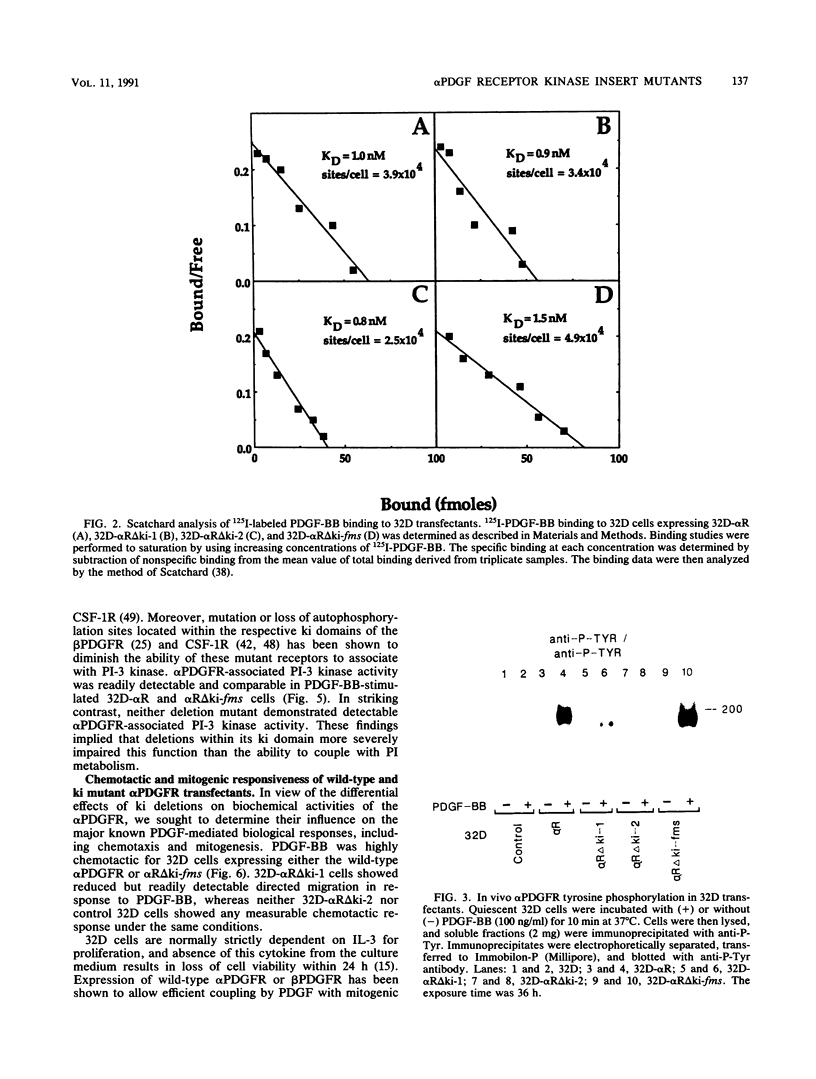
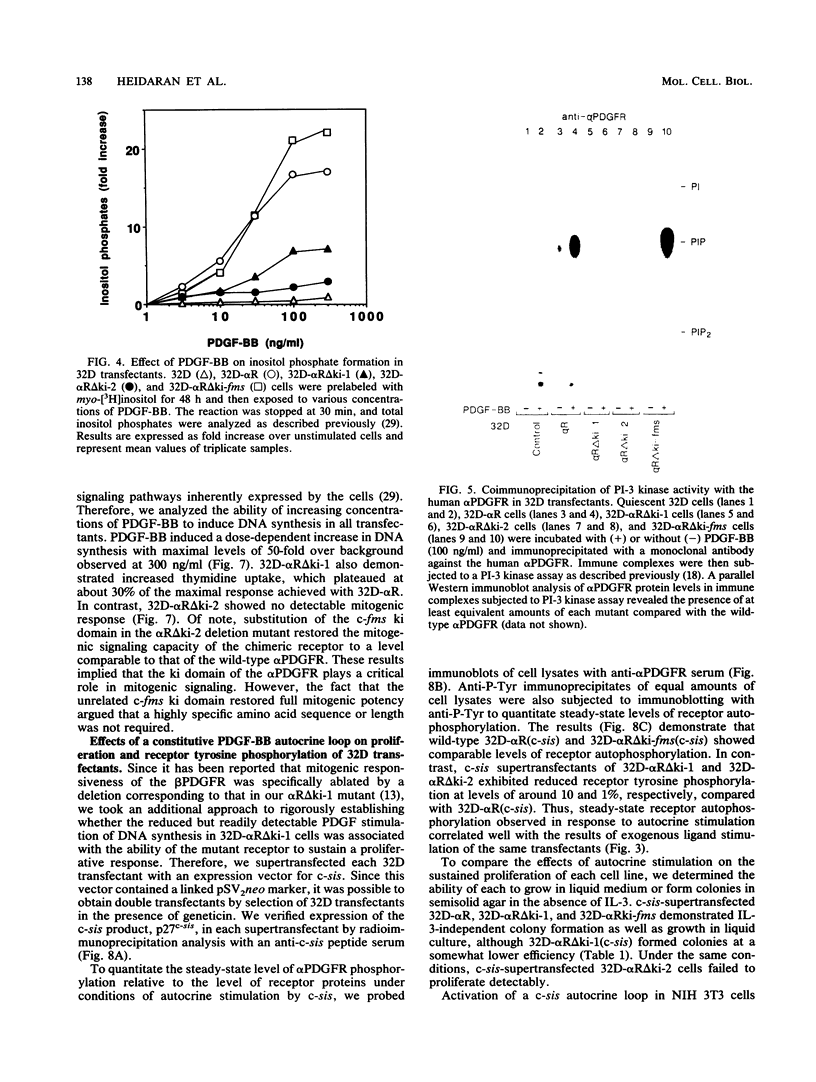
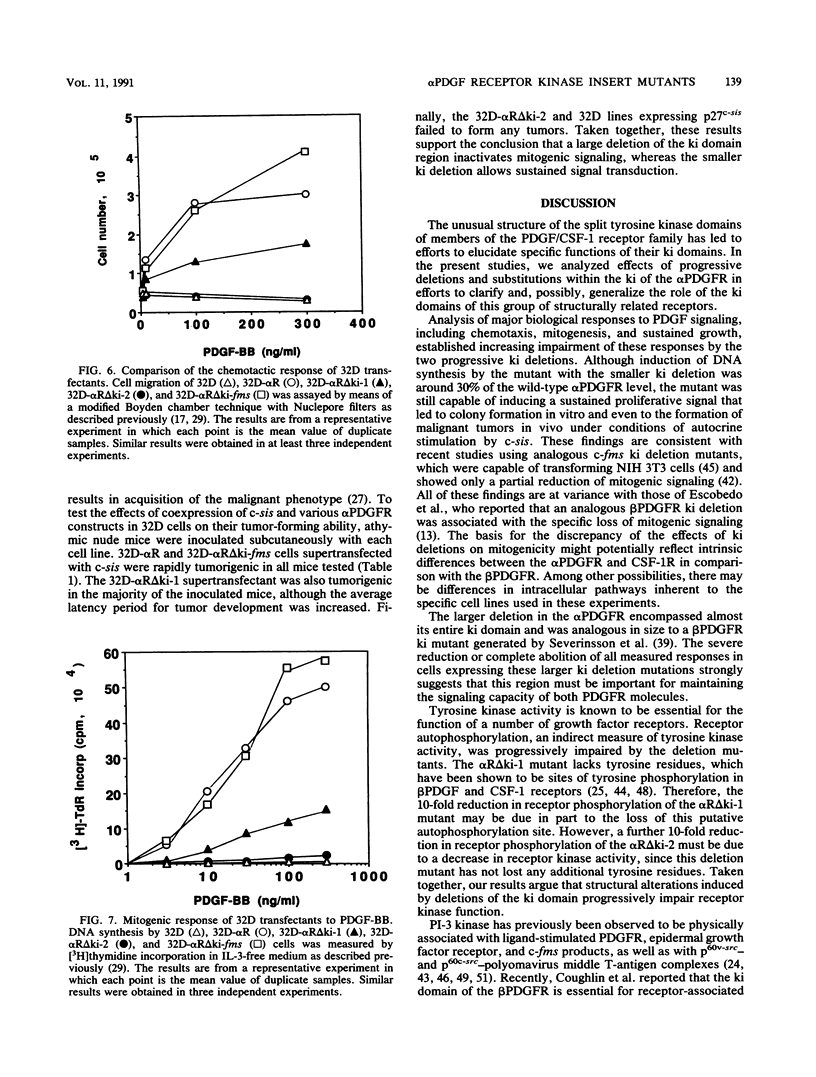
The tyrosine kinase domains of the platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) and colony-stimulating factor-1 (CSF-1)/c-fms receptors are interrupted by kinase inserts (ki) which vary in length and amino acid sequence. To define the role of the ki in the human alpha PDGF receptor (alpha PDGFR), we generated deletion mutants, designated alpha R delta ki-1 and alpha R delta ki-2, which lacked 80 (710 to 789) and 95 (695 to 789) amino acids of the 104-amino-acid ki region, respectively. Their functional characteristics were compared with those of the wild-type alpha PDGFR following introduction into a naive hematopoietic cell line, 32D. Biochemical responses, including PDGF-stimulated PDGFR tyrosine phosphorylation, phosphatidylinositol (PI) turnover, and receptor-associated PI-3 kinase activity, were differentially impaired by the deletions. Despite a lack of any detectable receptor-associated PI-3 kinase activity, 32D cells expressing alpha R delta ki-1 showed only partially impaired chemotactic and mitogenic responses and were capable of sustained proliferation in vitro and in vivo under conditions of autocrine stimulation by the c-sis product. 32D transfectants expressing the larger ki deletion (alpha R delta ki-2) showed markedly decreased or abolished biochemical and biological responses. However, insertion of the highly unrelated smaller c-fms (685 to 750) ki domain into alpha R delta ki-2 restored each of these activities to wild-type alpha PDGFR levels. Since the CSF-1R does not normally induce PI turnover, the ability of the c-fms ki domain to reconstitute PI turnover in the alpha R delta ki-2 transfectant provides evidence that the ki domain of the alpha PDGFR does not directly couple with this pathway. Taken together, all od these bindings imply that their ki domains have evolved to play very similar roles in the known signaling functions PDGF and CSF-1 receptors.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Betsholtz C., Johnsson A., Heldin C. H., Westermark B., Lind P., Urdea M. S., Eddy R., Shows T. B., Philpott K., Mellor A. L. cDNA sequence and chromosomal localization of human platelet-derived growth factor A-chain and its expression in tumour cell lines. Nature. 1986 Apr 24;320(6064):695–699. doi: 10.1038/320695a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton A. E., Hunter W. M. The labelling of proteins to high specific radioactivities by conjugation to a 125I-containing acylating agent. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):529–539. doi: 10.1042/bj1330529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of the secondary structure of proteins from their amino acid sequence. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1978;47:45–148. doi: 10.1002/9780470122921.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claesson-Welsh L., Eriksson A., Morén A., Severinsson L., Ek B., Ostman A., Betsholtz C., Heldin C. H. cDNA cloning and expression of a human platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) receptor specific for B-chain-containing PDGF molecules. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3476–3486. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claesson-Welsh L., Eriksson A., Westermark B., Heldin C. H. cDNA cloning and expression of the human A-type platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) receptor establishes structural similarity to the B-type PDGF receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4917–4921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughlin S. R., Escobedo J. A., Williams L. T. Role of phosphatidylinositol kinase in PDGF receptor signal transduction. Science. 1989 Mar 3;243(4895):1191–1194. doi: 10.1126/science.2466336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Fiore P. P., Pierce J. H., Fleming T. P., Hazan R., Ullrich A., King C. R., Schlessinger J., Aaronson S. A. Overexpression of the human EGF receptor confers an EGF-dependent transformed phenotype to NIH 3T3 cells. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1063–1070. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90592-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Marco E., Pierce J. H., Fleming T. P., Kraus M. H., Molloy C. J., Aaronson S. A., Di Fiore P. P. Autocrine interaction between TGF alpha and the EGF-receptor: quantitative requirements for induction of the malignant phenotype. Oncogene. 1989 Jul;4(7):831–838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E., Devare S. G., Robbins K. C., Aaronson S. A., Antoniades H. N. Simian sarcoma virus onc gene, v-sis, is derived from the gene (or genes) encoding a platelet-derived growth factor. Science. 1983 Jul 15;221(4607):275–277. doi: 10.1126/science.6304883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downing J. R., Margolis B. L., Zilberstein A., Ashmun R. A., Ullrich A., Sherr C. J., Schlessinger J. Phospholipase C-gamma, a substrate for PDGF receptor kinase, is not phosphorylated on tyrosine during the mitogenic response to CSF-1. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3345–3350. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08496.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ek B., Westermark B., Wasteson A., Heldin C. H. Stimulation of tyrosine-specific phosphorylation by platelet-derived growth factor. Nature. 1982 Feb 4;295(5848):419–420. doi: 10.1038/295419a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escobedo J. A., Williams L. T. A PDGF receptor domain essential for mitogenesis but not for many other responses to PDGF. Nature. 1988 Sep 1;335(6185):85–87. doi: 10.1038/335085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giese N. A., Robbins K. C., Aaronson S. A. The role of individual cysteine residues in the structure and function of the v-sis gene product. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1315–1318. doi: 10.1126/science.3035718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberger J. S., Sakakeeny M. A., Humphries R. K., Eaves C. J., Eckner R. J. Demonstration of permanent factor-dependent multipotential (erythroid/neutrophil/basophil) hematopoietic progenitor cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):2931–2935. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.2931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronwald R. G., Grant F. J., Haldeman B. A., Hart C. E., O'Hara P. J., Hagen F. S., Ross R., Bowen-Pope D. F., Murray M. J. Cloning and expression of a cDNA coding for the human platelet-derived growth factor receptor: evidence for more than one receptor class. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3435–3439. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grotendorst G. R., Seppä H. E., Kleinman H. K., Martin G. R. Attachment of smooth muscle cells to collagen and their migration toward platelet-derived growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3669–3672. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutkind J. S., Lacal P. M., Robbins K. C. Thrombin-dependent association of phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase with p60c-src and p59fyn in human platelets. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3806–3809. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habenicht A. J., Glomset J. A., King W. C., Nist C., Mitchell C. D., Ross R. Early changes in phosphatidylinositol and arachidonic acid metabolism in quiescent swiss 3T3 cells stimulated to divide by platelet-derived growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):12329–12335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann T., Seuwen K., Roussel M. F., Sherr C. J., Pouysségur J. Functional expression of the human receptor for colony-stimulating factor 1 (CSF-1) in hamster fibroblasts: CSF-1 stimulates Na+/H+ exchange and DNA-synthesis in the absence of phosphoinositide breakdown. Growth Factors. 1990;2(4):289–300. doi: 10.3109/08977199009167024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Protein-tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnsson A., Heldin C. H., Westermark B., Wasteson A. Platelet-derived growth factor: identification of constituent polypeptide chains. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jan 15;104(1):66–74. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91941-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. R., Morrison D. K., Wong G., McCormick F., Williams L. T. PDGF beta-receptor stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of GAP and association of GAP with a signaling complex. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):125–133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90220-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. R., Whitman M., Schaffhausen B., Pallas D. C., White M., Cantley L., Roberts T. M. Common elements in growth factor stimulation and oncogenic transformation: 85 kd phosphoprotein and phosphatidylinositol kinase activity. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1021–1029. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90168-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazlauskas A., Cooper J. A. Autophosphorylation of the PDGF receptor in the kinase insert region regulates interactions with cell proteins. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1121–1133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90510-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G., Silió J., Ruggiero M. Thrombin induces serotonin secretion and aggregation independently of inositol phospholipids hydrolysis and protein phosphorylation in human platelets permeabilized with saponin. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):7078–7083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leal F., Williams L. T., Robbins K. C., Aaronson S. A. Evidence that the v-sis gene product transforms by interaction with the receptor for platelet-derived growth factor. Science. 1985 Oct 18;230(4723):327–330. doi: 10.1126/science.2996133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui T., Heidaran M., Miki T., Popescu N., La Rochelle W., Kraus M., Pierce J., Aaronson S. Isolation of a novel receptor cDNA establishes the existence of two PDGF receptor genes. Science. 1989 Feb 10;243(4892):800–804. doi: 10.1126/science.2536956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molloy C. J., Bottaro D. P., Fleming T. P., Marshall M. S., Gibbs J. B., Aaronson S. A. PDGF induction of tyrosine phosphorylation of GTPase activating protein. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):711–714. doi: 10.1038/342711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. K., Kaplan D. R., Escobedo J. A., Rapp U. R., Roberts T. M., Williams L. T. Direct activation of the serine/threonine kinase activity of Raf-1 through tyrosine phosphorylation by the PDGF beta-receptor. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):649–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90100-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. K., Kaplan D. R., Rhee S. G., Williams L. T. Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)-dependent association of phospholipase C-gamma with the PDGF receptor signaling complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2359–2366. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan R. C., Berg P. Selection for animal cells that express the Escherichia coli gene coding for xanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2072–2076. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce J. H., Ruggiero M., Fleming T. P., Di Fiore P. P., Greenberger J. S., Varticovski L., Schlessinger J., Rovera G., Aaronson S. A. Signal transduction through the EGF receptor transfected in IL-3-dependent hematopoietic cells. Science. 1988 Feb 5;239(4840):628–631. doi: 10.1126/science.3257584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qiu F. H., Ray P., Brown K., Barker P. E., Jhanwar S., Ruddle F. H., Besmer P. Primary structure of c-kit: relationship with the CSF-1/PDGF receptor kinase family--oncogenic activation of v-kit involves deletion of extracellular domain and C terminus. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):1003–1011. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02907.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roussel M. F., Dull T. J., Rettenmier C. W., Ralph P., Ullrich A., Sherr C. J. Transforming potential of the c-fms proto-oncogene (CSF-1 receptor). Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):549–552. doi: 10.1038/325549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Severinsson L., Ek B., Mellström K., Claesson-Welsh L., Heldin C. H. Deletion of the kinase insert sequence of the platelet-derived growth factor beta-receptor affects receptor kinase activity and signal transduction. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):801–809. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr C. J., Rettenmier C. W., Sacca R., Roussel M. F., Look A. T., Stanley E. R. The c-fms proto-oncogene product is related to the receptor for the mononuclear phagocyte growth factor, CSF-1. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):665–676. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80047-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibuya M., Yamaguchi S., Yamane A., Ikeda T., Tojo A., Matsushime H., Sato M. Nucleotide sequence and expression of a novel human receptor-type tyrosine kinase gene (flt) closely related to the fms family. Oncogene. 1990 Apr;5(4):519–524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shurtleff S. A., Downing J. R., Rock C. O., Hawkins S. A., Roussel M. F., Sherr C. J. Structural features of the colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor that affect its association with phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2415–2421. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07417.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto Y., Erikson R. L. Phosphatidylinositol kinase activities in normal and Rous sarcoma virus-transformed cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):3194–3198. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.3194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapley P., Kazlauskas A., Cooper J. A., Rohrschneider L. R. Macrophage colony-stimulating factor-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of c-fms proteins expressed in FDC-P1 and BALB/c 3T3 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2528–2538. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor G. R., Reedijk M., Rothwell V., Rohrschneider L., Pawson T. The unique insert of cellular and viral fms protein tyrosine kinase domains is dispensable for enzymatic and transforming activities. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):2029–2037. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03611.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson D. M., Cochet C., Chambaz E. M., Gill G. N. Separation and characterization of a phosphatidylinositol kinase activity that co-purifies with the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 25;260(15):8824–8830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90801-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varticovski L., Druker B., Morrison D., Cantley L., Roberts T. The colony stimulating factor-1 receptor associates with and activates phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):699–702. doi: 10.1038/342699a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whetton A. D., Monk P. N., Consalvey S. D., Downes C. P. The haemopoietic growth factors interleukin 3 and colony stimulating factor-1 stimulate proliferation but do not induce inositol lipid breakdown in murine bone-marrow-derived macrophages. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3281–3286. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04640.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitman M., Kaplan D. R., Schaffhausen B., Cantley L., Roberts T. M. Association of phosphatidylinositol kinase activity with polyoma middle-T competent for transformation. Nature. 1985 May 16;315(6016):239–242. doi: 10.1038/315239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Escobedo J. A., Kuang W. J., Yang-Feng T. L., Daniel T. O., Tremble P. M., Chen E. Y., Ando M. E., Harkins R. N., Francke U. Structure of the receptor for platelet-derived growth factor helps define a family of closely related growth factor receptors. Nature. 1986 Sep 18;323(6085):226–232. doi: 10.1038/323226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Kuang W. J., Yang-Feng T., Coussens L., Munemitsu S., Dull T. J., Chen E., Schlessinger J., Francke U., Ullrich A. Human proto-oncogene c-kit: a new cell surface receptor tyrosine kinase for an unidentified ligand. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3341–3351. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02655.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Geer P., Hunter T. Identification of tyrosine 706 in the kinase insert as the major colony-stimulating factor 1 (CSF-1)-stimulated autophosphorylation site in the CSF-1 receptor in a murine macrophage cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2991–3002. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]