Abstract
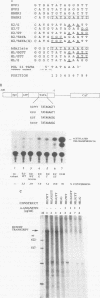
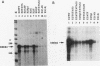
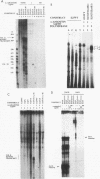
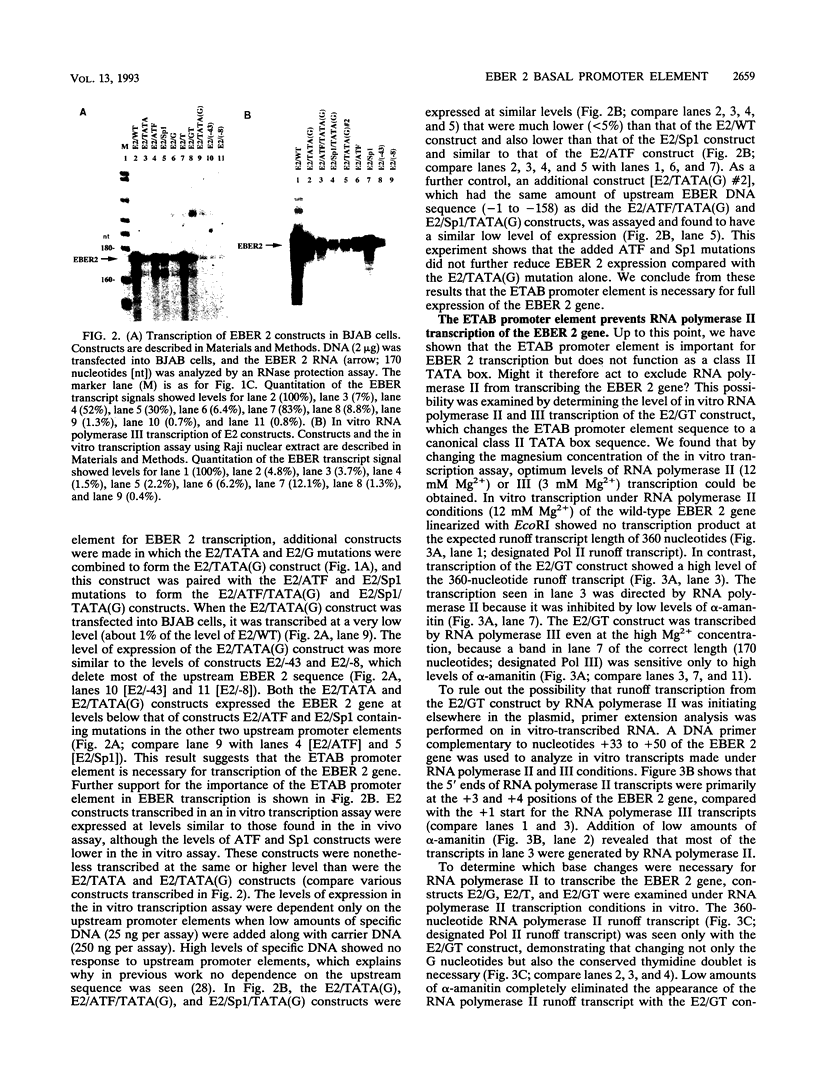
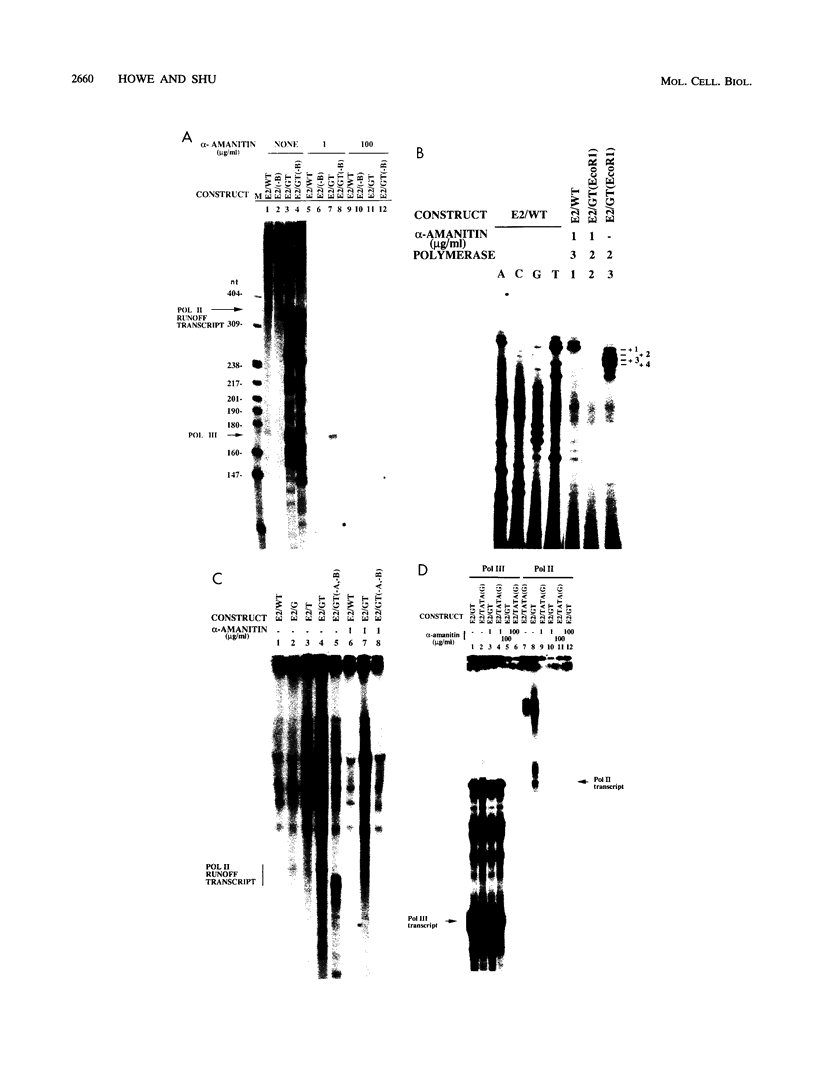
The Epstein-Barr virus-encoded small RNA (EBER) genes are transcribed by RNA polymerase III, but their transcription unit appears to contain both class II and class III promoter elements. One of these promoter element, a TATA-like box which we call the EBER TATA box, or ETAB, is located in a position typical for a class II TATA box but contains G/C residues in the normal T/A motif and a conserved thymidine doublet. Experiments using chloramphenicol acetyltransferase constructs and mutations in the TATA box of the adenovirus major late promoter showed that the ETAB promoter element does not substitute for a class II TATA box. However, when the ETAB promoter element sequence was changed to a class II TATA box consensus sequence, the EBER 2 gene was transcribed in vitro by both RNA polymerases II and III. From these results, we conclude that the ETAB promoter element is important for the exclusive transcription of the EBER 2 gene by RNA polymerase III.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antonarakis S. E., Irkin S. H., Cheng T. C., Scott A. F., Sexton J. P., Trusko S. P., Charache S., Kazazian H. H., Jr beta-Thalassemia in American Blacks: novel mutations in the "TATA" box and an acceptor splice site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1154–1158. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrand J. R., Rymo L. Characterization of the major Epstein-Barr virus-specific RNA in Burkitt lymphoma-derived cells. J Virol. 1982 Feb;41(2):376–389. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.2.376-389.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bark C., Weller P., Zabielski J., Janson L., Pettersson U. A distant enhancer element is required for polymerase III transcription of a U6 RNA gene. Nature. 1987 Jul 23;328(6128):356–359. doi: 10.1038/328356a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartholomew B., Kassavetis G. A., Geiduschek E. P. Two components of Saccharomyces cerevisiae transcription factor IIIB (TFIIIB) are stereospecifically located upstream of a tRNA gene and interact with the second-largest subunit of TFIIIC. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):5181–5189. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.5181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredow S., Kleinert H., Benecke B. J. Sequence and factor requirements for faithful in vitro transcription of human 7SL DNA. Gene. 1990 Feb 14;86(2):217–225. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90282-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredow S., Sürig D., Müller J., Kleinert H., Benecke B. J. Activating-transcription-factor (ATF) regulates human 7S L RNA transcription by RNA polymerase III in vivo and in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):6779–6784. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.6779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brow D. A., Guthrie C. Transcription of a yeast U6 snRNA gene requires a polymerase III promoter element in a novel position. Genes Dev. 1990 Aug;4(8):1345–1356. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.8.1345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucher P., Trifonov E. N. Compilation and analysis of eukaryotic POL II promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Dec 22;14(24):10009–10026. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.24.10009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buratowski S., Hahn S., Guarente L., Sharp P. A. Five intermediate complexes in transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):549–561. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90578-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buratowski S., Hahn S., Sharp P. A., Guarente L. Function of a yeast TATA element-binding protein in a mammalian transcription system. Nature. 1988 Jul 7;334(6177):37–42. doi: 10.1038/334037a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavallini B., Faus I., Matthes H., Chipoulet J. M., Winsor B., Egly J. M., Chambon P. Cloning of the gene encoding the yeast protein BTF1Y, which can substitute for the human TATA box-binding factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9803–9807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavallini B., Huet J., Plassat J. L., Sentenac A., Egly J. M., Chambon P. A yeast activity can substitute for the HeLa cell TATA box factor. Nature. 1988 Jul 7;334(6177):77–80. doi: 10.1038/334077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comai L., Tanese N., Tjian R. The TATA-binding protein and associated factors are integral components of the RNA polymerase I transcription factor, SL1. Cell. 1992 Mar 6;68(5):965–976. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90039-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Concino M. F., Lee R. F., Merryweather J. P., Weinmann R. The adenovirus major late promoter TATA box and initiation site are both necessary for transcription in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Oct 11;12(19):7423–7433. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.19.7423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison B. L., Egly J. M., Mulvihill E. R., Chambon P. Formation of stable preinitiation complexes between eukaryotic class B transcription factors and promoter sequences. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):680–686. doi: 10.1038/301680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenmann D. M., Dollard C., Winston F. SPT15, the gene encoding the yeast TATA binding factor TFIID, is required for normal transcription initiation in vivo. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1183–1191. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90516-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fire A., Samuels M., Sharp P. A. Interactions between RNA polymerase II, factors, and template leading to accurate transcription. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2509–2516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiduschek E. P., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. Transcription by RNA polymerase III. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:873–914. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.004301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn S., Buratowski S., Sharp P. A., Guarente L. Isolation of the gene encoding the yeast TATA binding protein TFIID: a gene identical to the SPT15 suppressor of Ty element insertions. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1173–1181. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeffler W. K., Kovelman R., Roeder R. G. Activation of transcription factor IIIC by the adenovirus E1A protein. Cell. 1988 Jun 17;53(6):907–920. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)90409-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman A., Sinn E., Yamamoto T., Wang J., Roy A., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. Highly conserved core domain and unique N terminus with presumptive regulatory motifs in a human TATA factor (TFIID). Nature. 1990 Jul 26;346(6282):387–390. doi: 10.1038/346387a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horikoshi M., Wang C. K., Fujii H., Cromlish J. A., Weil P. A., Roeder R. G. Cloning and structure of a yeast gene encoding a general transcription initiation factor TFIID that binds to the TATA box. Nature. 1989 Sep 28;341(6240):299–303. doi: 10.1038/341299a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe J. G., Shu M. D. Epstein-Barr virus small RNA (EBER) genes: unique transcription units that combine RNA polymerase II and III promoter elements. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):825–834. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90797-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe J. G., Shu M. D. Isolation and characterization of the genes for two small RNAs of herpesvirus papio and their comparison with Epstein-Barr virus-encoded EBER RNAs. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2790–2798. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2790-2798.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jat P., Arrand J. R. In vitro transcription of two Epstein-Barr virus specified small RNA molecules. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jun 11;10(11):3407–3425. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.11.3407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao C. C., Lieberman P. M., Schmidt M. C., Zhou Q., Pei R., Berk A. J. Cloning of a transcriptionally active human TATA binding factor. Science. 1990 Jun 29;248(4963):1646–1650. doi: 10.1126/science.2194289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Braun B. R., Nguyen L. H., Geiduschek E. P. S. cerevisiae TFIIIB is the transcription initiation factor proper of RNA polymerase III, while TFIIIA and TFIIIC are assembly factors. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):235–245. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90739-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Riggs D. L., Negri R., Nguyen L. H., Geiduschek E. P. Transcription factor IIIB generates extended DNA interactions in RNA polymerase III transcription complexes on tRNA genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2551–2566. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel G. R., Maser R. L., Calvet J. P., Pederson T. U6 small nuclear RNA is transcribed by RNA polymerase III. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8575–8579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel G. R. RNA polymerase III transcription of genes that lack internal control regions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jan 17;1088(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(91)90146-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson D., Bradford-Wilcox J., Young L. S., Sprague K. U. A short 5' flanking region containing conserved sequences is required for silkworm alanine tRNA gene activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3416–3420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Andrews N. C., Miller G., Steitz J. A. Two small RNAs encoded by Epstein-Barr virus and complexed with protein are precipitated by antibodies from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):805–809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobo S. M., Hernandez N. A 7 bp mutation converts a human RNA polymerase II snRNA promoter into an RNA polymerase III promoter. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):55–67. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90402-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobo S. M., Lister J., Sullivan M. L., Hernandez N. The cloned RNA polymerase II transcription factor IID selects RNA polymerase III to transcribe the human U6 gene in vitro. Genes Dev. 1991 Aug;5(8):1477–1489. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.8.1477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margottin F., Dujardin G., Gérard M., Egly J. M., Huet J., Sentenac A. Participation of the TATA factor in transcription of the yeast U6 gene by RNA polymerase C. Science. 1991 Jan 25;251(4992):424–426. doi: 10.1126/science.1989075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W., Dathan N. A., Parry H. D., Carbon P., Krol A. Changing the RNA polymerase specificity of U snRNA gene promoters. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):435–442. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90029-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton D. G., Sprague K. U. In vitro transcription of a silkworm 5S RNA gene requires an upstream signal. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5519–5522. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy S., Di Liegro C., Melli M. The in vitro transcription of the 7SK RNA gene by RNA polymerase III is dependent only on the presence of an upstream promoter. Cell. 1987 Oct 9;51(1):81–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90012-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy S., Moorefield B., Pieler T. Common mechanisms of promoter recognition by RNA polymerases II and III. Trends Genet. 1989 Apr;5(4):122–126. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90043-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Tilly K., Maniatis T. Fine structure genetic analysis of a beta-globin promoter. Science. 1986 May 2;232(4750):613–618. doi: 10.1126/science.3457470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima N., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II: purification, genetic specificity, and TATA box-promoter interactions of TFIID. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4028–4040. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. S., Topol J. A Drosophila RNA polymerase II transcription factor contains a promoter-region-specific DNA-binding activity. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):357–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90229-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parry H. D., Mattaj I. W. Positive and negative functional interactions between promoter elements from different classes of RNA polymerase III-transcribed genes. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1097–1104. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08215.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson M. G., Tanese N., Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Functional domains and upstream activation properties of cloned human TATA binding protein. Science. 1990 Jun 29;248(4963):1625–1630. doi: 10.1126/science.2363050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Transcription from a TATA-less promoter requires a multisubunit TFIID complex. Genes Dev. 1991 Nov;5(11):1935–1945. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.11.1935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy R., Henning D., Das G., Harless M., Wright D. The capped U6 small nuclear RNA is transcribed by RNA polymerase III. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 5;262(1):75–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinberg D., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription in mammalian RNA polymerase II. Functional analysis of initiation factors IIA and IID and identification of a new factor operating at sequences downstream of the initiation site. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3322–3330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney C., Howe J. G., Speck S. H., Miller G. Influence of Burkitt's lymphoma and primary B cells on latent gene expression by the nonimmortalizing P3J-HR-1 strain of Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1531–1539. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1531-1539.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa M. D., Gottlieb E., Lerner M. R., Steitz J. A. Striking similarities are exhibited by two small Epstein-Barr virus-encoded ribonucleic acids and the adenovirus-associated ribonucleic acids VAI and VAII. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Sep;1(9):785–796. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.9.785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. C., Kao C. C., Pei R., Berk A. J. Yeast TATA-box transcription factor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7785–7789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segall J., Matsui T., Roeder R. G. Multiple factors are required for the accurate transcription of purified genes by RNA polymerase III. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11986–11991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmen K. A., Bernués J., Parry H. D., Stunnenberg H. G., Berkenstam A., Cavallini B., Egly J. M., Mattaj I. W. TFIID is required for in vitro transcription of the human U6 gene by RNA polymerase III. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1853–1862. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07711.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullu E., Weiner A. M. Upstream sequences modulate the internal promoter of the human 7SL RNA gene. 1985 Nov 28-Dec 4Nature. 318(6044):371–374. doi: 10.1038/318371a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. J., Jackson S. P., Rigby P. W. A role for the TATA-box-binding protein component of the transcription factor IID complex as a general RNA polymerase III transcription factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1949–1953. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wobbe C. R., Struhl K. Yeast and human TATA-binding proteins have nearly identical DNA sequence requirements for transcription in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):3859–3867. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.3859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]