Abstract
The homeobox gene Hox-2.4 is transcriptionally activated in cells of the mouse myeloid leukemia WEHI-3B. The constitutive Hox-2.4 expression in WEHI-3B cells is due to insertion of a transposable element belonging to the family of intracisternal A particles. In this study, we demonstrated the oncogenic potential of this activated homeobox gene. NIH 3T3 fibroblast clones bearing the activated Hox-2.4 gene produced fibrosarcomas in nude mice.
Full text
PDF


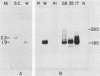
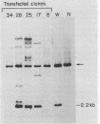
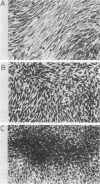
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azumi J. I., Sachs L. Chromosome mapping of the genes that control differentiation and malignancy in myeloid leukemic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):253–257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M. Cellular oncogenes and retroviruses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:301–354. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.001505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatt C., Aberdam D., Schwartz R., Sachs L. DNA rearrangement of a homeobox gene in myeloid leukaemic cells. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4283–4290. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03326.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatt C., Sachs L. Deletion of a homeobox gene in myeloid leukemias with a deletion in chromosome 2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Nov 15;156(3):1265–1270. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80769-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desplan C., Theis J., O'Farrell P. H. The sequence specificity of homeodomain-DNA interaction. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):1081–1090. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90123-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasano O., Birnbaum D., Edlund L., Fogh J., Wigler M. New human transforming genes detected by a tumorigenicity assay. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1695–1705. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han K., Levine M. S., Manley J. L. Synergistic activation and repression of transcription by Drosophila homeobox proteins. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):573–583. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90580-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W., Sturm R. A., Clerc R. G., Corcoran L. M., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A., Ingraham H. A., Rosenfeld M. G., Finney M., Ruvkun G. The POU domain: a large conserved region in the mammalian pit-1, oct-1, oct-2, and Caenorhabditis elegans unc-86 gene products. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1513–1516. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Murre C., Sun X. H., Baltimore D. A new homeobox gene contributes the DNA binding domain of the t(1;19) translocation protein in pre-B ALL. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):547–555. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90658-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappen C., Schughart K., Ruddle F. H. Two steps in the evolution of Antennapedia-class vertebrate homeobox genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5459–5463. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kongsuwan K., Allen J., Adams J. M. Expression of Hox-2.4 homeobox gene directed by proviral insertion in a myeloid leukemia. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 11;17(5):1881–1892. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.5.1881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuziora M. A., McGinnis W. A homeodomain substitution changes the regulatory specificity of the deformed protein in Drosophila embryos. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):563–571. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90039-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land H., Parada L. F., Weinberg R. A. Cellular oncogenes and multistep carcinogenesis. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):771–778. doi: 10.1126/science.6356358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M., Rubin G. M., Tjian R. Human DNA sequences homologous to a protein coding region conserved between homeotic genes of Drosophila. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):667–673. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90261-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis E. B. A gene complex controlling segmentation in Drosophila. Nature. 1978 Dec 7;276(5688):565–570. doi: 10.1038/276565a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis W., Garber R. L., Wirz J., Kuroiwa A., Gehring W. J. A homologous protein-coding sequence in Drosophila homeotic genes and its conservation in other metazoans. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):403–408. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90370-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis W., Hart C. P., Gehring W. J., Ruddle F. H. Molecular cloning and chromosome mapping of a mouse DNA sequence homologous to homeotic genes of Drosophila. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):675–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90262-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nourse J., Mellentin J. D., Galili N., Wilkinson J., Stanbridge E., Smith S. D., Cleary M. L. Chromosomal translocation t(1;19) results in synthesis of a homeobox fusion mRNA that codes for a potential chimeric transcription factor. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):535–545. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90657-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nüsslein-Volhard C., Wieschaus E. Mutations affecting segment number and polarity in Drosophila. Nature. 1980 Oct 30;287(5785):795–801. doi: 10.1038/287795a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pluznik D. H., Sachs L. The cloning of normal "mast" cells in tissue culture. J Cell Physiol. 1965 Dec;66(3):319–324. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030660309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. P., Carroll S. B. The segmentation and homeotic gene network in early Drosophila development. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):689–698. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90092-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih C., Weinberg R. A. Isolation of a transforming sequence from a human bladder carcinoma cell line. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):161–169. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90100-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]