Abstract
Nitrosodiethylamine (NDEA) is a potent carcinogen widely existing in the environment. Our previous study has demonstrated that garlic oil (GO) could prevent NDEA-induced hepatocarcinogenesis in rats, but the underlying mechanisms are not fully understood. It has been well documented that the metabolic activation may play important roles in NDEA-induced hepatocarcinogenesis. Therefore, we designed the current study to explore the potential mechanisms by investigating the changes of hepatic phase Ⅰ enzymes (including cytochrome P450 enzyme (CYP) 2E1, CYP1A2 and CYP1A1) and phase Ⅱ enzymes (including glutathione S transferases (GSTs) and UDP- Glucuronosyltransferases (UGTs)) by using enzymatic methods, real-time PCR, and western blotting analysis. We found that NDEA treatment resulted in significant decreases of the activities of CYP2E1, CYP1A2, GST alpha, GST mu, UGTs and increases of the activities of CYP1A1 and GST pi. Furthermore, the mRNA and protein levels of CYP2E1, CYP1A2, GST alpha, GST mu and UGT1A6 in the liver of NDEA-treated rats were significantly decreased compared with those of the control group rats, while the mRNA and protein levels of CYP1A1 and GST pi were dramatically increased. Interestingly, all these adverse effects induced by NDEA were simultaneously and significantly suppressed by GO co-treatment. These data suggest that the protective effects of GO against NDEA-induced hepatocarcinogenesis might be, at least partially, attributed to the modulation of phase I and phase II enzymes.
Keywords: Garlic oil, Nitrosodiethylamine, Cytochrome P450 enzyme, Glutathione S transferase, UDP-glucuronosyltransferase.
Introduction
N-nitroso compounds are well-known hepatic carcinogens 1-2. These compounds are considered to be critical environmental factors influencing cancer risk in humans, as they widely exist in the environment, in certain occupational settings, in food stuffs such as meat products and milk, as well as an endogenous formation in the human body from dietary components 3. A variety of studies have demonstrated that N-nitroso compounds could cause a wide range of tumors in many animal species 4-6. Nitrosodiethylamine (NDEA) is one of the most potent chemical hepatocarcinogens of this class, which can induce a variety of liver lesions in rodents. NDEA exposure occurs through diet, as it is detectable in edible vegetable oil, alcoholic drinks, steamed and fried fish 7.
It has been well recognized that NDEA undergoes redox reactions catalyzed by cytochrome P450 enzymes (CYPs) to produce reactive alkylating agents, leading to the alkylation of DNA, which may ultimately result in oncogenesis 8-9. NDEA is primarily metabolized to α-hydroxy derivative (ethyl-acet-oxyethyl-nitrosamine) by CYPs, especially CYP2E1. The intermediate could either be conjugated by phase I enzymes to produce an ethyl-diazonium ion, which can react with nucleophilic sites of DNA to generate adducts 10. The formation of DNA adducts is recognized as the initial step in NDEA-induced carcinogenesis. Accordingly, blocking the formation of DNA adducts would be the first line of defense against NDEA-induced carcinogenesis. Furthermore, some phase II enzymes, such as glutathione S transferases (GSTs), UDP-glucuronosyltransferases (UGTs), NAD(P)H: quinone oxidoreductase-1 (NQO1), could inactivate chemical carcinogens to less toxic or inactive metabolites through reduction of DNA adducts formation 11. Therefore, compounds with phase II enzymes inducing effects could theoretically block NDEA-induced hepatocarcinogenesis.
Garlic has been used as a folk medicine as well as a flavor enhancer since ancient time in many countries 12. The anti-cancer effects of garlic have been proposed since ancient times 13-14. In view of the epidemiological studies conducted in the last 30 years, there is convincing evidence that consumption of garlic can reduce the risk of colorectal, stomach, lung and esophageal cancers 15. Garlic oil (GO), usually prepared by steam distillation, is one of the commercial garlic products, and has been demonstrated to prevent many chemicals-induced liver injury 16-18. Chemical analysis reveals that GO contains more than 30 organosulfur compounds (OSCs) 19, which are believed to be the major anti-cancer active constituents of garlic 20-23. In our previous study, we have demonstrated that GO could effectively inhibit NDEA-induced hepatocarcinogenesis in male Wistar rats 24. In that study, we found that GO counteracted NDEA-induced oxidative stress in rat liver evidenced by the decrease of the malondialdehyde (MDA, a wildly used oxidative stress biomarker) level and the increase of the antioxidant glutathione (GSH) level. Furthermore, GO also promoted the apoptosis of tumor cells by decreasing the mRNA and protein levels of Bcl-2, Bcl-xl, and β-arrestin-2 and increasing the mRNA and protein levels of Bax and caspase-3 24.
Considering the important roles of metabolic activation in the pathogenesis of NDEA-induced hepatocarcinogenesis, it would be interesting to further investigate whether the protective effects of GO were associated with the modulations of phase I and phase II enzymes. Therefore, in the current study, the activities, mRNA and protein levels of phase I enzymes (including CYP2E1, CYP1A2 and CYP1A1) and phase II enzymes (including GSTs and UGTs) were investigated in order to better understand the underlying mechanisms for the protective effects of GO against NDEA-induced hepatocarcinogenesis.
Materials and Methods
Materials
GO (drug grade) was purchased from Xuchang Yuanhua Biotechnology, Inc. (Xuchang, CN). Primary antibodies against CYP2E1, CYP1A2, CYP1A1, GST-alpha, GST-mu, GST-pi, UGT1A6 and β-actin were supplied by Abcam (Cambridge, UK). Western blotting detection reagents (ECL kits) were provided by Millipore Corp. (Bedford, MA, USA). BCATM protein assay kits were purchased from Pierce Biotechnology, Inc. (Rockford, IL, USA). All other chemicals and reagents used were obtained from Sigma (St. Louis, MO, USA) unless indicated otherwise.
Animals and treatments
60 Male Wistar rats, weighing 120-140g, were provided by Laboratory Animal Center of Shandong University. Rats were housed individually with a standard laboratory diet and distilled water ad libitum. The animal room was maintained at 23±1 ℃ and 50% relative humidity with a 12 h (7:00-19:00) light/dark cycle. After 1 week of basal diet for acclimation, the animals were randomly divided into 4 groups, i.e. control group, NDEA group, and two GO co-treatment groups.
The rats in GO co-treatment groups were treated with GO (20 or 40 mg/kg.bw) by gavage for 21 weeks (5 times/week), while other animals received equal volume of corn oil. From the second week, the rats in NDEA and GO co-treatment groups were orally received NDEA (10 mg/kg.bw, 5 times/week), while the animals in control group were administered equal volume of saline. At the end of week 21, all animals were sacrificed by decapitation. The liver tissue was excised and snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen before storing at -80℃. All of the experiments were conducted according to the guidelines of the Ethical Committee of School of Public Health, Shandong University, China.
Preparation of the liver microsomal and cytosolic fractions
The liver microsomal and cytosolic fractions were prepared as we previously described 25. Briefly, the liver tissue was homogenized in 4 volumes of ice-cold TMS buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl, 6.4 mM MgCl2, 0.2 M saccharose, pH 7.5). The homogenates were centrifuged at 12,000g for 15 min, and the supernatants were further centrifuged at 105,000 g for 60 min. The obtained supernatant was considered as the cytosolic fraction. The microsomal pellet was re-suspended in the above buffer. The protein levels were quantified using BCATM protein assay kits. All the procedures were conducted at 4 ℃.
Phase I and phase II enzymes activities assay
The activity of CYP2E1 in liver microsomes was measured with aniline as the substrate 25. The activities of CYP1A2 and CYP1A1 in liver microsomes were determined by measurement of the dealkylation of methoxyresorufin and ethoxyresorufin using Hitachi fluorescence spectrophotometer (Hitachi High-Technologies Corporation, Japan) 26. The activities of cytosolic GST alpha, GST mu and GST pi were determined using the substrates of cumene hydroperoxide (CuOOH), 2, 4-dichloro-1-nitrobenzene (DCNB) and ethacrynic acid, respectively 27. The activities of cytosolic UGTs were determined with p-nitrophenol (PNP) as the substrate 28.
RNA extraction and cDNA synthesis
Total RNA was isolated from the rat liver using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen, USA) according to the manufacturer's instructions. The RNA pellet was dissolved in DEPC water. The concentration and integrity of total RNA was measured using NANO DROP 2000c spectrophotometer (Thermo, USA) and Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer (Agilent, Germany). Complementary DNA was synthesized using the RevertAidTM First Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (Fermentas, UK) according to the manufacture's protocol.
Real-time PCR analysis
The levels of gene expression in rat liver were quantified by real-time PCR. The primers were synthesized by Sangon Biotech Co., Ltd (Shanghai, China) (Table 1). All PCR reactions were performed using Maxima SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix (Fermentas), and were carried out under the following conditions using Mastercycler ep realplex 4 (Eppendorf, Westbury, NY, USA): initial denaturation at 95℃ for 10 min followed by 40 cycles of 15 s at 95℃, 30 s at 60℃ and 30 s at 72℃. Each sample was analyzed in triplicate. Differences in gene expression between groups were calculated using the △△Ct (cycle time, Ct) method 29, which were normalized against glyceraldehydes-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) and expressed as relative mRNA levels compared with controls.
Table 1.
Sequences of primers used for the real-time PCR analysis.
| Gene symbol | Forward primer | Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| CYP2E1 | CCT TTC CCT CTT CCC ATC C | AAC CTC CGC ACA TCC TTC C |
| CYP1A1 | GGG AGG TTA CTG GTT CTG G | ATG AGG CTG TCT GTG ATG TC |
| CYP1A2 | CAT CTT TGG AGC TGG ATT TG | CCA TTC AGT GAG GTG TCC |
| GST-alpha1/2 | CCA CCT GCT GGA ACT TCT CCT CTA T | AGG CTG CTG ATT CTG CTC TTG AAG G |
| GST-mu | GGC GAC GCT CCC GAC TAT GAC AGA A | AAT CCG CTC CTC CTC TGT CTC TCC A |
| GST-pi | TTG AGG CAC CTG GGT CGC TCT TTA G | GGT TCT GGG ACA GCA GGG TCT CAA A |
| UGT1A1 | GCCATGCAGCCTGGATTT | CTCTTGGGCACGTAGGACAAC |
| UGT1A6 | CCGCTATCGCTCCTTTGG | CTGTACTCTCTTAGAGGAGCCATCAG |
| GAPDH | GAT GGT GAA GGT CGG TGT G | ATG AAG GGG TCG TTG ATG G |
Western blotting analysis
The liver tissue was homogenized in RIPA lysis buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl, 150 mM NaCl, 1% Triton X-100, 1% sodium deoxycholate, 0.1% sodium dodecyl sulfate [SDS], 1mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride [PMSF] and 1% cocktail protease inhibitors (Sigma)). The homogenate was centrifuged at 14, 000 g for 15 min to obtain the whole protein extract 30. The protein samples (20-100 μg) were separated on 10% or 12% SDS-polyacrylamide gels. Proteins were transferred to polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membranes (Millipore Corp., Bedford, MA, USA), immunoblotted with primary antibodies overnight at 4℃, followed by the incubation with horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated anti-rabbit or anti-mouse antibodies for 2 h at room temperature. The signals were detected by ECL detection reagents. The relative optical densities of the bands were quantified using Kodak Imaging Program and Image-Pro Plus software.
Statistical analysis
SPSS13.0 was used for the statistical analysis. All data were expressed as mean ± SD, and were analyzed by one-way ANOVA, followed with LSD for the multiple comparisons. P < 0.05 was considered significant.
Results
Effects of GO and NDEA on the activities, mRNA and protein levels of phase I enzymes
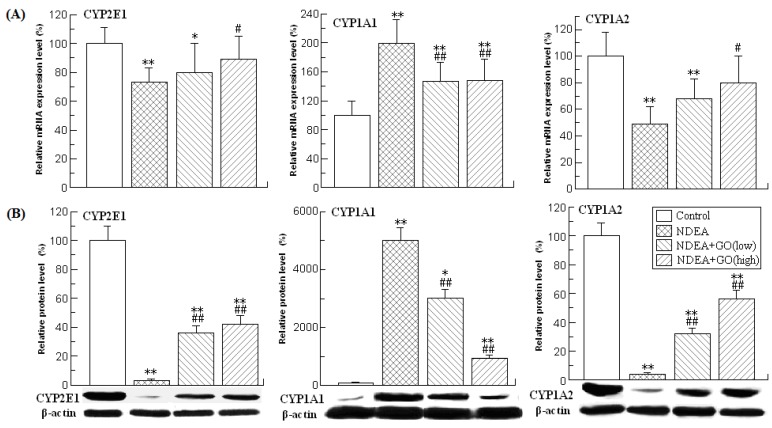
The changes of the activities, mRNA and protein levels of the CYP2E1, CYP1A2 and CYP1A1 were presented in Table 2 and Figure 1.
Table 2.
Effects of GO and NDEA on hepatic CYP2E1, CYP1A1 and CYP1A2 activities.
| Groups | CYP2E1 (nmol/min/mg proteins) |
CYP1A1 (μmol/min/mg proteins) |
CYP1A2 (μmol/min/mg proteins) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 57.79±17.48 | 0.59±0.09 | 2.51±0.68 |
| NDEA | 16.03±5.32** | 0.98±0.19** | 0.27±0.08** |
| NDEA+GO (low) | 32.49±8.77*## | 0.72±0.22*# | 1.10±0.28*## |
| NDEA+GO (high) | 56.19±12.74## | 0.67±0.14## | 1.34±0.26## |
Compared with control group, *P<0.05, **P<0.01; compared with NDEA group, #P<0.05, ##P<0.01.
Figure 1.
Effects of GO and NDEA on the mRNA and protein levels of hepatic CYP2E1, CYP1A1 and CYP1A2. (A) The mRNA levels were quantified by real-time PCR analysis with GAPDH as an internal control, and expressed as % of control. (B) The protein levels were quantified by western blotting method with β-actin as an internal control, and expressed as % of control. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, compared with control group; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01, compared with NDEA group.
As shown in Table 2, NDEA treatment resulted in the dramatic reduction of the CYP2E1 and CYP1A2 activities, and the significant increase of the CYP1A1 activity. Compared with those of the control group, the activities of CYP2E1 and CYP1A2 in rats of NDEA group were decreased by 72% and 89%, respectively, while the activity of CYP1A1 was increased by 66% (P<0.01) (Table 2). The changes of mRNA and protein levels of the above three phase I enzymes were paralleled with those of the activities (Figure 1). Interestingly, all these adverse effects induced by NDEA were significantly suppressed by GO co-treatment. The protein level of CYP1A1 in rats of NDEA group was about 50 fold of the control value, which was only about 30 and 9.5 fold of the control value in rats treated with 20 and 40 mg/kg.bw GO, respectively. GO co-treatment also significantly inhibited NDEA-induced decreases of CYP2E1 and CYP1A2 protein levels. Similarly, GO co-treatment also significantly inhibited the increases of the activities and mRNA levels of CYP1A1, as well as the decreases of the activities and mRNA levels of CYP2E1 and CYP1A2.
Effects of GO and NDEA on the activities, mRNA and protein levels of different GSTs in rat liver
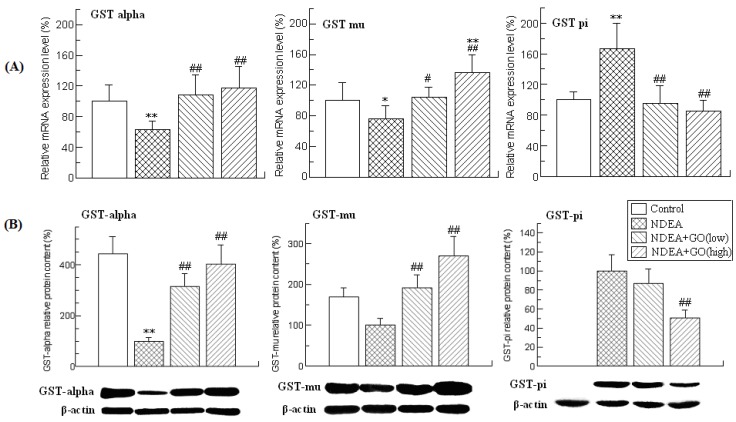
GSTs constitute a superfamily of ubiquitous, multifunctional enzymes which play a key role in cellular detoxification, protecting macromolecules from attack by reactive electrophiles, including environmental carcinogens, reactive oxygen species and chemotherapeutic agents. The important anticarcinogenic roles of GSTs have been well documented 11, 31. Among the seven identified classes of GSTs, GST alpha, GST mu and GST-pi are the three mostly investigated isoforms. Therefore, the activities, mRNA and protein levels of these three GST isoforms were investigated.
The activities of different isoforms of GSTs in different groups were presented in Table 3. As shown in Table 3, the activities of GST alpha and GST mu in the rat liver of NDEA group were slightly but significantly decreased compared with those of the control group rats, while the activity of GST pi was obviously increased (about 3.08 fold) (P<0.01). However, GO co-treatment significantly inhibited the increase of GST pi activity, and the decreases of GST alpha and GST mu activities (P<0.01).
Table 3.
Effects of GO and NDEA on hepatic GSTs activities.
| Groups | GST alpha (nmol NADPH/min/mg protein) |
GST mu (pmol/min/mg protein) |
GST pi (nmol/min/mg protein) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 21.11±2.18 | 21.43±4.49 | 3.44±0.68 |
| NDEA | 13.36±2.23** | 15.84±1.34* | 10.61±2.47** |
| NDEA+GO (low) | 19.78±3.28## | 27.86±5.98## | 6.12±1.13*## |
| NDEA+GO (high) | 21.09±4.29## | 25.75±2.83## | 5.31±1.44## |
Compared with control group, *P<0.05, **P<0.01; compared with NDEA group, #P<0.05, ##P<0.01.
The changes of the mRNA and protein levels of GSTs were similar to those of the activities (Figure 2). Compared with those of control group rats, the mRNA levels of GST alpha and GST mu in the liver of NDEA group rats were decreased by 37% and 24%, respectively, while the mRNA level of GST pi was increased by 170% (P<0.01). NDEA treatment also reduced the protein levels of GST alpha and GST mu in the liver of rats. The GST pi protein could not be detected in control group rat liver, but was abundantly expressed in the liver of NDEA group rats. However, all these adverse effects induced by NDEA were simultaneously attenuated and even abrogated in GO co-treated rats liver.
Figure 2.
Effects of GO and NDEA on the mRNA and protein levels of GST alpha, GST mu and GST pi. (A) The mRNA levels were quantified by real-time PCR analysis with GAPDH as an internal control, and expressed as % of control. (B) The protein levels were quantified by western blotting method with β-actin as an internal control, and expressed as % of control. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, compared with control group; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01, compared with NDEA group.
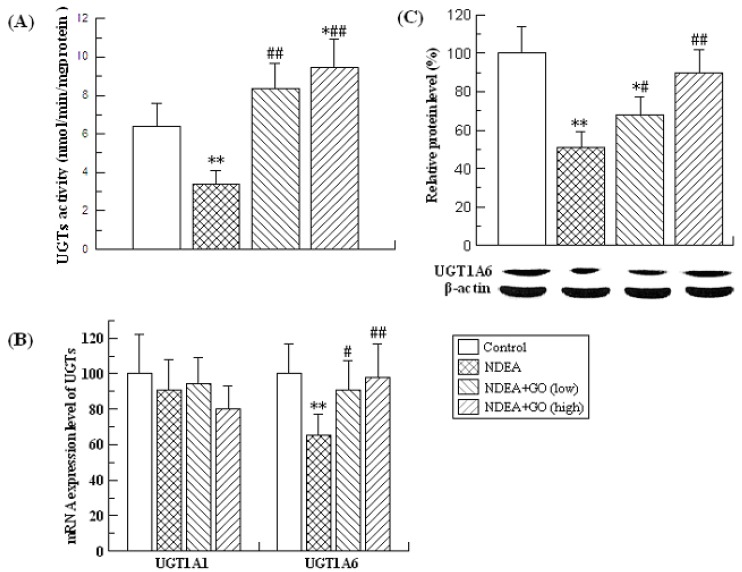
Effects of GO and NDEA on the activities, mRNA and protein levels of UGTs in rat liver
UGTs are the other major detoxifying enzymes for many carcinogens. The effects of GO and NDEA on the activity, mRNA and protein levels of UGTs are shown in Figure 3. NDEA treatment resulted in significant decrease of the UGTs activity, which was significantly inhibited by GO co-treatment. As UGT1A1 and UGT1A6 are the major members of the rat UGTs, the mRNA levels of UGT1A1 and UGT1A6 were detected by real-time PCR. Compared with the control group, the mRNA level of UGT1A6 was decreased by 35% (P<0.01), while no significant alteration of the mRNA level of UGT1A1 was observed. Therefore, we only examined the protein level of UGT1A6, and found that GO also suppressed NDEA-induced the decrease of the protein level of UGT1A6.
Figure 3.
Effects of GO and NDEA on the activity, the mRNA and protein level of UGTs in liver. (A) The activity of hepatic UGTs. (B) The mRNA level was quantified by real-time PCR analysis with GAPDH as an internal control, and expressed as % of control. (C) The protein levels were quantified by western blotting method with β-actin as an internal control, and expressed as % of control. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, compared with control group; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01, compared with NDEA group.
Discussion
NDEA is a potent carcinogenic compound widely existing in the environment. Our previous study has demonstrated that GO could effectively prevent NDEA-induced hepatocarcinogenesis via modulation of the antioxidant capacity and promotion of the apoptosis 24. In the current study, we examined the changes of the activities, mRNA and protein levels of phase I enzymes (including CYP2E1, CYP 1A2, and CYP 1A1) and phase II enzymes (including GSTs and UGTs) for a better understanding of the protective effects of GO against NDEA-induced hepatocarcinogeneis. We found that GO significantly suppressed NDEA-induced the decreases of the protein levels of CYP2E1, CYP1A2, GST alpha, GST mu, UGT1A6, as well as the increases of the protein levels of CYP1A1 and GST pi. The changes of the activities and mRNA levels of the above enzymes were paralleled well with those of the protein levels. These data suggested that the modulation of hepatic phase I and II enzymes by GO might also contribute to its protection against NDEA-induced hepatocarcinogenesis.
It has been well documented that NDEA-induced hepatocarcinogenesis requires metabolic activation by some forms of CYP450s, especially CYP2E1. The critical role of CYP2E1 in the pathogenesis of NDEA-induced hepatocarcinogenesis has been demonstrated by using Cyp2e1-null mice 32. In addition to CYP2E1, CYP1A2 was also reported to be participated in the metabolic activation of NDEA 33. Thus, it is plausible that agents with CYP2E1 and CYP1A2 inhibitory characteristics might possess ability to suppress NDEA-induced hepatocarcinogenesis by reducing its bioactivation. Our previous study showed that GO could inhibit the activities and protein levels of CYP2E1 and CYP1A2 in normal mice liver 25, therefore, it could be speculated that GO may also modulate the metabolic activation of NDEA 34-35. In the current study, NDEA treatment was found to dramatically reduce the activities, mRNA and protein levels of CYP2E1 and CYP1A2. In a recently published in vitro study, the CYP2E1 mRNA levels were decreased when rat hepatocytes were treated with non-cytotoxic concentrations of NDEA (0.21-21 μg/ml), while decreased mRNA levels of CYP2E1 was observed when hepatocytes were treated with higher dose of NDEA (100 μg/ml) 36. Therefore, it may be speculated that low dose of NDEA might induce the expression of CYP2E1, while high dose of NDEA could inhibit expression of CYP2E1. Interestingly, GO co-treatment significantly suppressed the decreases of the activities, mRNA and protein levels of CYP2E1 and CYP1A2 induced by NDEA treatment. CYP1A1 is a key participant in the bioactivation of numerous procarcinogenic substances such as carcinogenic polycyclic hydrocarbons and aromatic amines. Although CYP1A1 is primarily expressed in the liver, the hepatic level of CYP1A1 is very low in normal liver 37. However, the hepatic expression of CYP1A1 could be induced by NDEA treatment 35, 38. Inconsistent with these previous studies, the hepatic CYP1A1 activity, mRNA and protein levels in NDEA-treated rats were sharply increased compared with the control group. However, GO co-treatment significantly suppressed the NDEA-induced the activation of CYP1A1. These data indicated that GO could modulate phase I enzymes involved in NDEA metabolic activation.
In addition to phase I enzymes, phase II enzymes could conjugate the toxic metabolites to nontoxic endogenous molecules, and thus also play important roles in cancer-protection by reducing the DNA adducts formation11, 39. Among these phase II enzymes, the important anticancer roles of the GSTs and UGTs superfamily have been well documented 40-41. GSTs can catalyze the conjugation of toxic and carcinogenic electrophilic molecules with glutathione and thereby protect cellular macromolecules from damage. In recent years, it is generally considered that an important mechanism of cancer prevention is the induction of GSTs by dietary naturally-occurring anticarcinogens 42-43. At present, seven distinct classes of cytosolic GSTs have been identified (alpha, mu, pi, sigma, theta, delta, and zeta) 44. Among these GSTs, GST alpha, GST mu and GST-pi are the three mostly investigated isoforms. In the current study, we found that NDEA treatment significantly reduced the mRNA and protein levels of GST alpha and GST mu, which were significantly blocked by GO co-treatment. In contrast, the mRNA and protein levels of GST pi were dramatically increased in NDEA-treated rats, which have also been observed in other studies 31. However, GO co-treatment also significantly inhibited the increase of GST pi protein levels. These data suggested that the induction of GST alpha and GST mu and the inhibition of GST pi by GO might be also involved in the protective effects of GO against NDEA-induced hepatocarcinogenesis.
The UGTs belong to a superfamily of membrane bound proteins, localized to the endoplasmic reticulum, which are responsible for glucuronidation of many endobiotics and xenobiotics. Glucuronidation reaction could render the hydrophobic substrates into more polar 'glucuronides', leading them easier for elimination via biliary or renal route 40. Because UGTs facilitate the excretion of potentially carcinogenic compounds, activation of UGTs may reduce cancer risk 45. UGTs consist of two multigene superfamilies, designated UGT1 and UGT2. As UGT1A1 and UGT1A6 are the major members of the rat UGTs, we firstly examined the activity of UGTs, and then the mRNA levels of UGT1A1 and UGT1A6. The results showed that the activity of UGTs and the mRNA level of UGT1A6 in rats of NDEA group were significantly decreased compared with those of control group. GO co-treatment significantly suppressed NDEA-induced decreases of UGTs activity and UGT1A6 mRNA and protein levels in rat liver. However, the mRNA level of UGT1A1 did not differ significantly among the four groups (P>0.05). These data suggested that the protection of GO against NDEA might be also related to the induction of UGT1A6.
Under normal circumstances, the protein level was related to the protein synthesis and degradation. The present study showed that the mRNA level of CYP2E1 in rats of NDEA group was reduced by 29% compared with those of the control group, while the protein level of CYP2E1 was decreased by 97%. Similar phenomenon was also observed for the CYP1A2. These data indicated that the declines of CYP2E1 and CYP1A2 protein levels can not be completely attributed to the declines of the mRNA levels, and the post-translational degradation may play an important role in the decreases of CYP2E1 and CYP1A2 protein levels in NDEA-induced hepatocarcinogenesis. Previous studies have demonstrated that CYP1A2 and CYP2E1 could be degraded by the ubiquitin-dependent proteasomal degradation system (UPS) 46-47. Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4), a typical hepatic toxicant, could induce the decrease of the protein level of CYP2E1 48, which might be related to the induction of the post-translational degradation 49. We speculated that NDEA treatment might also result in the activation of UPS, and accelerate the post-translational degradation of CYP2E1 and CYP1A2. GO co-treatment might suppress the activation of UPS, and thus inhibit the degradation of CYP2E1 and CYP1A2. The exact molecular mechanisms need to be further studied.
In summary, this study demonstrated that GO modulated phase I enzymes (including CYP2E1, CYP1A2 and CYP1A1) and phase II enzymes (including GSTs and UGTs) involved in NDEA metabolism, which might partially contribute to the protective effects of GO against NDEA-induced hepatocarcinogenesis in rats.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Scientific and technological cooperation project of Shandong Province [2008GG2NS02012], Independent innovation fund of Shandong University [2012TS090] and Innovation fund for young scholar of Public Health School.
References
- 1.Tricker AR, Pfundstein B, Theobald E. et al. Mean daily intake of volatile N-nitrosamines from foods and beverages in West Germany in 1989-1990. Food Chem Toxicol. 1991;29(11):729–32. doi: 10.1016/0278-6915(91)90180-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ferguson LR. Natural and man-made mutagens and carcinogens in the human diet. Mutat Res. 1999;443(1-2):1–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bartsch H, Montesano R. Relevance of nitrosamines to human cancer. Carcinogenesis. 1984;5(11):1381–93. doi: 10.1093/carcin/5.11.1381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Krajka-Kuzniak V, Szaefer H, Ignatowicz E. et al. Effect of Chokeberry (Aronia melanocarpa) juice on the metabolic activation and detoxication of carcinogenic N-nitrosodiethylamine in rat liver. J Agric Food Chem. 2009;57(11):5071–7. doi: 10.1021/jf803973y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Rajkapoor B, Jayakar B, Murugesh N. et al. Chemoprevention and cytotoxic effect of Bauhinia variegata against N-nitrosodiethylamine induced liver tumors and human cancer cell lines. J Ethnopharmacol. 2006;104(3):407–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2005.08.074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Pinto LF, Moraes E, Albano RM. et al. Rat oesophageal cytochrome P450 (CYP) monooxygenase system: comparison to the liver and relevance in N-nitrosodiethylamine carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 2001;22(11):1877–83. doi: 10.1093/carcin/22.11.1877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Fine DH, Ross R, Rounbehler DP. et al. Formation in vivo of volatile N-nitrosamines in man after ingestion of cooked bacon and spinach. Nature. 1977;265(5596):753–5. doi: 10.1038/265753a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Archer MC. Mechanisms of action of N-nitroso compounds. Cancer Surv. 1989;8(2):241–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Nakae D, Kobayashi Y, Akai H. et al. Involvement of 8-hydroxyguanine formation in the initiation of rat liver carcinogenesis by low dose levels of N-nitrosodiethylamine. Cancer Res. 1997;57(7):1281–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Dragan YP, Hully JR, Nakamura J. et al. Biochemical events during initiation of rat hepatocarcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 1994;15(7):1451–8. doi: 10.1093/carcin/15.7.1451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Jana S, Mandlekar S. Role of phase II drug metabolizing enzymes in cancer chemoprevention. Curr Drug Metab. 2009;10(6):595–616. doi: 10.2174/138920009789375379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Zeng T, Xie KQ. The Differential Modulation on Cytochrome P450 Enzymes by Garlic Components. Food Reviews International. 2010;26(4):353–363. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Block E. The chemistry of garlic and onions. Sci Am. 1985;252(3):114–9. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0385-114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hartwell JL. Plants used against cancer. A survey. Lloydia. 1971;34(4):386–425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Thomson M, Ali M. Garlic [Allium sativum]: a review of its potential use as an anti-cancer agent. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2003;3(1):67–81. doi: 10.2174/1568009033333736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Zeng T, Zhang CL, Song FY. et al. Garlic oil alleviated ethanol-induced fat accumulation via modulation of SREBP-1, PPAR-alpha, and CYP2E1. Food Chem Toxicol. 2012;50(3-4):485–91. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2011.11.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Hassan HA, El-Agmy SM, Gaur RL. et al. In vivo evidence of hepato- and reno-protective effect of garlic oil against sodium nitrite-induced oxidative stress. Int J Biol Sci. 2009;5(3):249–55. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.5.249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Liu HG, Xu LH. Garlic oil prevents tributyltin-induced oxidative damage in vivo and in vitro. J Food Prot. 2007;70(3):716–21. doi: 10.4315/0362-028x-70.3.716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Wu CC, Sheen LY, Chen HW. et al. Effects of organosulfur compounds from garlic oil on the antioxidation system in rat liver and red blood cells. Food Chem Toxicol. 2001;39(6):563–9. doi: 10.1016/s0278-6915(00)00171-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Amagase H. Clarifying the real bioactive constituents of garlic. J Nutr. 2006;136(3 Suppl):716S–725S. doi: 10.1093/jn/136.3.716S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Nagini S. Cancer chemoprevention by garlic and its organosulfur compounds-panacea or promise? Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2008;8(3):313–21. doi: 10.2174/187152008783961879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Iciek M, Kwiecien I, Wlodek L. Biological properties of garlic and garlic-derived organosulfur compounds. Environ Mol Mutagen. 2009;50(3):247–65. doi: 10.1002/em.20474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Jones MG, Hughes J, Tregova A. et al. Biosynthesis of the flavour precursors of onion and garlic. J Exp Bot. 2004;55(404):1903–18. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erh138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Zhang CL, Zeng T, Zhao XL. et al. Protective effects of garlic oil on hepatocarcinoma induced by N-nitrosodiethylamine in rats. Int J Biol Sci. 2012;8(3):363–74. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.3796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Zeng T, Zhang CL, Song FY. et al. The modulatory effects of garlic oil on hepatic cytochrome P450s in mice. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2009;28(12):777–83. doi: 10.1177/0960327109353057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Wardlaw SA, Nikula KJ, Kracko DA. et al. Effect of cigarette smoke on CYP1A1, CYP1A2 and CYP2B1/2 of nasal mucosae in F344 rats. Carcinogenesis. 1998;19(4):655–62. doi: 10.1093/carcin/19.4.655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Habig WH, Pabst MJ, Jakoby WB. Glutathione S-transferases. The first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J Biol Chem. 1974;249(22):7130–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Frei J. Multiplicity and specificity of UDP-glucuronyltransferase. I. Effect of divalent cations and EDTA on the activity of UDP-glucuronyltransferase assayed with bilirubin, 4-methylumbelliferone and p-nitrophenol. Enzymol Biol Clin (Basel) 1970;11(5):385–401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 2001;25(4):402–8. doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Zeng T, Zhang CL, Song FY. et al. PI3K/Akt pathway activation was involved in acute ethanol-induced fatty liver in mice. Toxicology. 2012;296(1-3):56–66. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2012.03.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Sheweita SA, Tilmisany AK. Cancer and phase II drug-metabolizing enzymes. Curr Drug Metab. 2003;4(1):45–58. doi: 10.2174/1389200033336919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Kang JS, Wanibuchi H, Morimura K. et al. Role of CYP2E1 in diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatocarcinogenesis in vivo. Cancer Res. 2007;67(23):11141–6. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-1369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Yamazaki H, Oda Y, Funae Y. et al. Participation of rat liver cytochrome P450 2E1 in the activation of N-nitrosodimethylamine and N-nitrosodiethylamine to products genotoxic in an acetyltransferase-overexpressing Salmonella typhimurium strain (NM2009) Carcinogenesis. 1992;13(6):979–85. doi: 10.1093/carcin/13.6.979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Liu YF, Zha BS, Zhang HL. et al. Characteristic gene expression profiles in the progression from liver cirrhosis to carcinoma induced by diethylnitrosamine in a rat model. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2009;28:107. doi: 10.1186/1756-9966-28-107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Degawa M, Miura S, Yoshinari K. et al. Altered expression of hepatic CYP1A enzymes in rat hepatocarcinogenesis. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1995;86(6):535–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1995.tb02431.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Aiub CA, Gadermaier G, Silva IO. et al. N-nitrosodiethylamine genotoxicity evaluation: a cytochrome P450 induction study in rat hepatocytes. Genet Mol Res. 2011;10(4):2340–8. doi: 10.4238/2011.October.5.4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Ioannides C, Lewis DF. Cytochromes P450 in the bioactivation of chemicals. Curr Top Med Chem. 2004;4(16):1767–88. doi: 10.2174/1568026043387188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Liu LL, Gong LK, Qi XM. et al. Altered expression of cytochrome P450 and possible correlation with preneoplastic changes in early stage of rat hepatocarcinogenesis. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2005;26(6):737–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-7254.2005.00737.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Jahan MS, Vani G, Shyamaladevi CS. Effect of Solanum trilobatum on hepatic drug metabolising enzymes during diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatocarcinogenesis promoted by Phenobarbital in rat. Hepatol Res. 2007;37(1):35–49. doi: 10.1111/j.1872-034X.2007.00006.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Desai AA, Innocenti F, Ratain MJ. UGT pharmacogenomics: implications for cancer risk and cancer therapeutics. Pharmacogenetics. 2003;13(8):517–23. doi: 10.1097/01.fpc.0000054116.14659.e5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Hariharan R, Babu JM. et al. Mutational analysis of Smad7 in human cervical cancer. Oncol Rep. 2009;21(4):1001–4. doi: 10.3892/or_00000315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Wattenberg LW. Inhibition of carcinogenesis by minor dietary constituents. Cancer Res. 1992;52(7 Suppl):2085s–2091s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Nijhoff W, Groen G, Peters W. Induction of rat hepatic and intestinal glutathione s-transferases and glutathione by dietary naturally-occurring anticarcinogens. Int J Oncol. 1993;3(6):1131–9. doi: 10.3892/ijo.3.6.1131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Board PG, Baker RT. Chelvanayagam G, et al. Zeta, a novel class of glutathione transferases in a range of species from plants to humans. Biochem J. 1997;328( Pt 3):929–35. doi: 10.1042/bj3280929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Saracino MR, Lampe JW. Phytochemical regulation of UDP-glucuronosyltransferases: implications for cancer prevention. Nutr Cancer. 2007;59(2):121–41. doi: 10.1080/01635580701458178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Roberts BJ. Evidence of proteasome-mediated cytochrome P-450 degradation. J Biol Chem. 1997;272(15):9771–8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.15.9771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Banerjee A, Kocarek TA, Novak RF. Identification of a ubiquitination-Target/Substrate-interaction domain of cytochrome P-450 (CYP) 2E1. Drug Metab Dispos. 2000;28(2):118–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Weerachayaphorn J, Chuncharunee A, Jariyawat S. et al. Protection of centrilobular necrosis by Curcuma comosa Roxb. in carbon tetrachloride-induced mice liver injury. J Ethnopharmacol. 2010;129(2):254–60. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2010.03.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Pan X, Hussain FN, Iqbal J. et al. Inhibiting proteasomal degradation of microsomal triglyceride transfer protein prevents CCl4-induced steatosis. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(23):17078–89. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M701742200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]