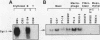Abstract
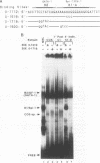
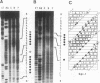
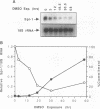
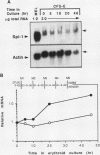
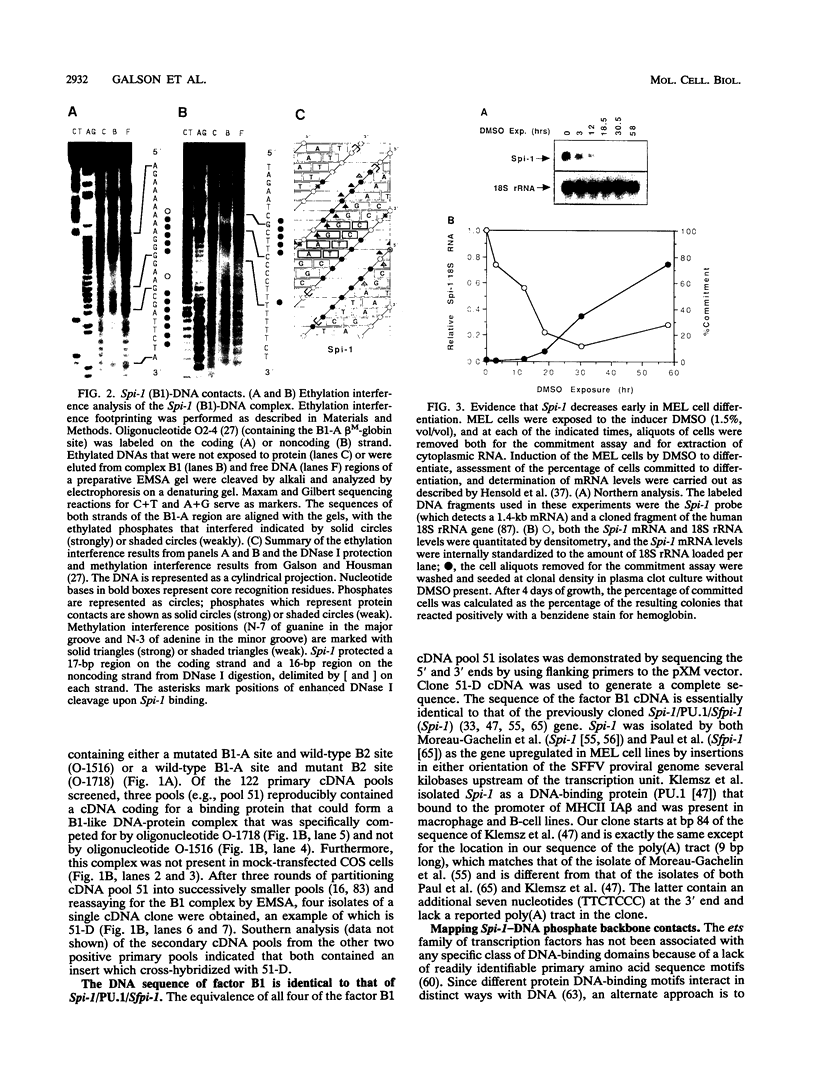
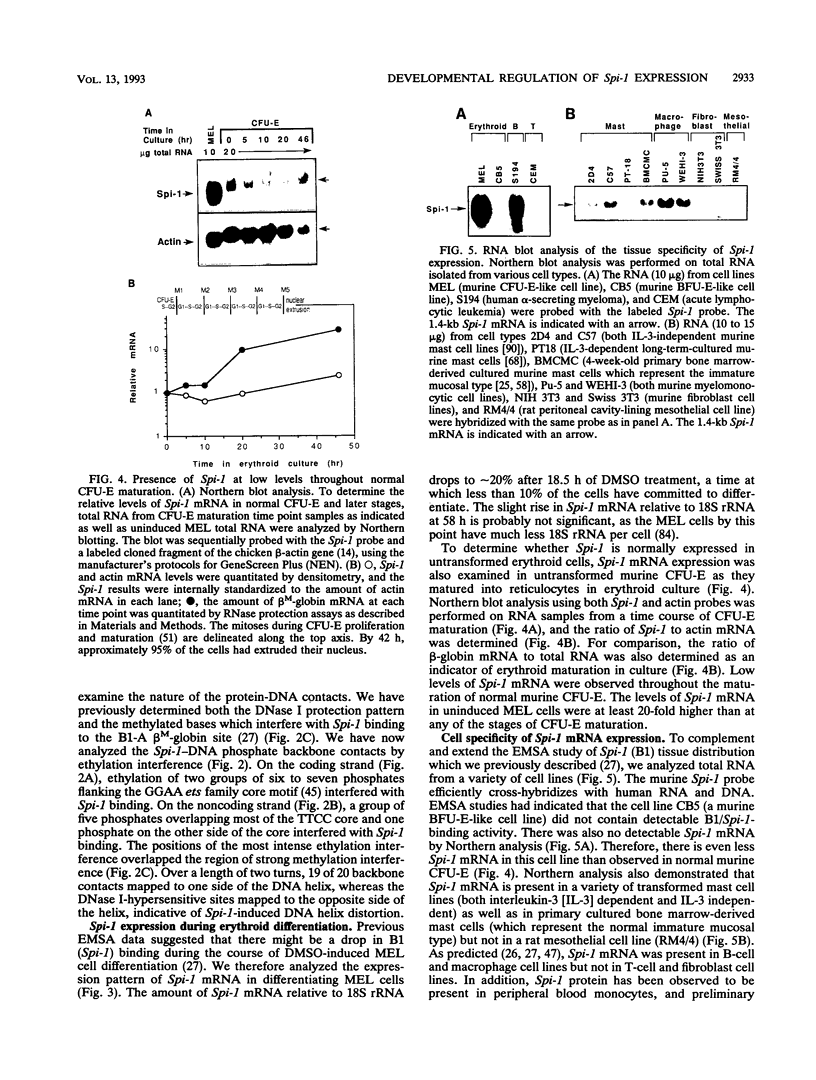
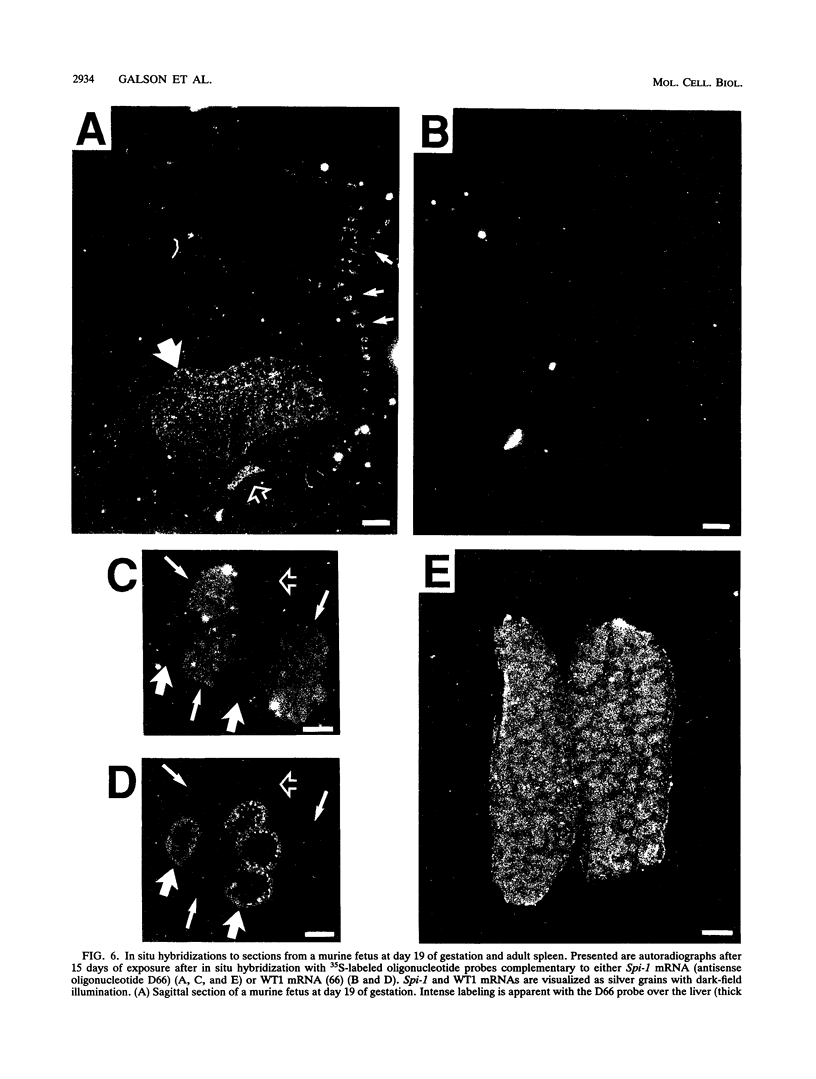
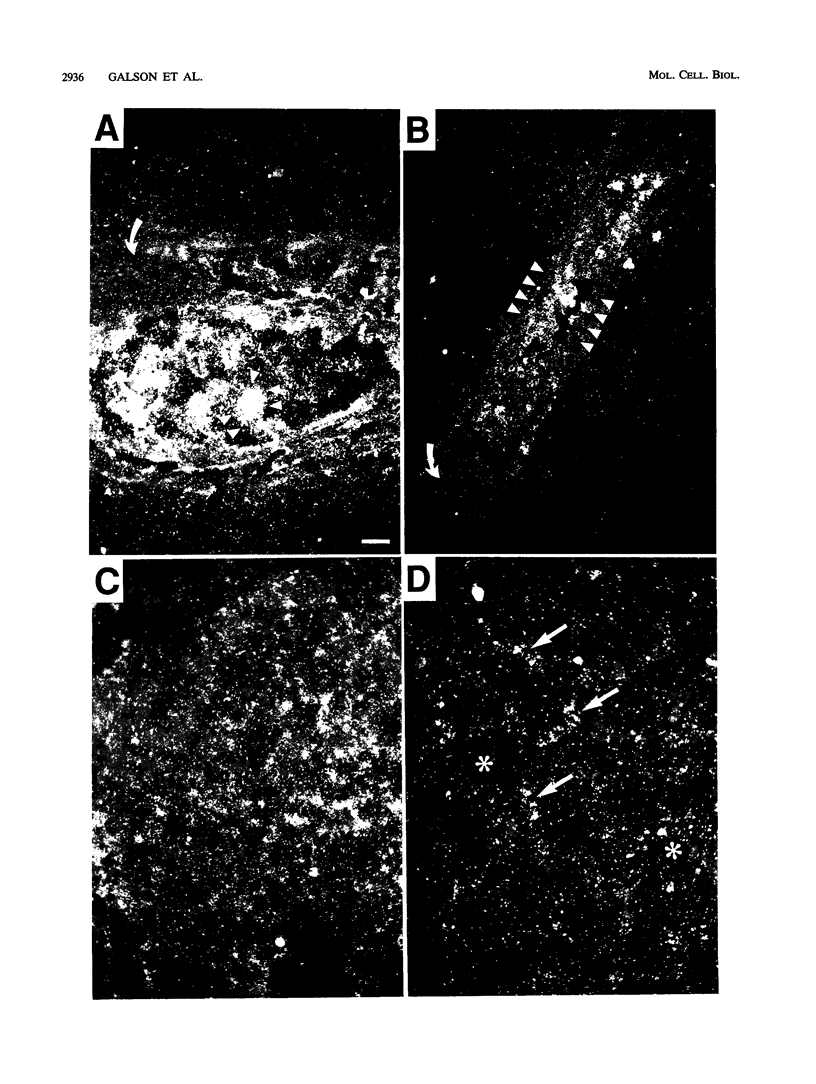
The hematopoietic-specific DNA-binding protein B1 binds to the DNA consensus sequence AAAGRGGAARYG located twice in intervening sequence 2 of both of the mouse beta-globin genes (D. L. Galson and D.E. Housman, Mol. Cell. Biol. 8:381-392, 1988). B1 was cloned by expression of a murine erythroleukemia (MEL) cell cDNA library in transfected COS cells and screening by electrophoretic mobility shift analysis. B1 is identical to the proto-oncogene Spi-1/PU.1 (Spi-1), an ets family member. Protein-DNA contacts are shown to resemble those of the helix-turn-helix homeodomain proteins. By Northern (RNA) analysis, we found that Spi-1 mRNA is present at low levels during murine CFU-E maturation and is at least 20-fold higher in uninduced MEL, a transformed proerythroblast-like cell line which contains an activating/transforming insertion of spleen focus-forming virus at the Spi-1 locus. Dimethyl sulfoxide-induced MEL cell differentiation decreases Spi-1 mRNA to approximately 20% of the uninduced level before commitment occurs. In addition to erythroid cells, Spi-1 mRNA is present in B cells, myelomonocytes, and mast cells but not in T cells and nonhematopoietic cell types. In situ hybridization demonstrated Spi-1 mRNA expression in bone marrow, spleen, interstitial nonhepatocytes of the liver, and interstitial nontubular cells of the testis. The Spi-1 locus was mapped on human chromosome 11 to the same interval as ACP2 (lysosomal acid phosphatase), between the anonymous DNA markers D11S33 and D11S14. This region has not yet been found to be associated with a human malignancy.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Affolter M., Percival-Smith A., Müller M., Leupin W., Gehring W. J. DNA binding properties of the purified Antennapedia homeodomain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4093–4097. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balcarek J. M., McMorris F. A. DNase I hypersensitive sites of globin genes of uninduced Friend erythroleukemia cells and changes during induction with dimethyl sulfoxide. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10622–10628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-David Y., Bernstein A. Friend virus-induced erythroleukemia and the multistage nature of cancer. Cell. 1991 Sep 6;66(5):831–834. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90428-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-David Y., Giddens E. B., Bernstein A. Identification and mapping of a common proviral integration site Fli-1 in erythroleukemia cells induced by Friend murine leukemia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1332–1336. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-David Y., Giddens E. B., Letwin K., Bernstein A. Erythroleukemia induction by Friend murine leukemia virus: insertional activation of a new member of the ets gene family, Fli-1, closely linked to c-ets-1. Genes Dev. 1991 Jun;5(6):908–918. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.6.908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender M. A., Miller A. D., Gelinas R. E. Expression of the human beta-globin gene after retroviral transfer into murine erythroleukemia cells and human BFU-E cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1725–1735. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benezra R., Cantor C. R., Axel R. Nucleosomes are phased along the mouse beta-major globin gene in erythroid and nonerythroid cells. Cell. 1986 Mar 14;44(5):697–704. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90835-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulukos K. E., Pognonec P., Rabault B., Begue A., Ghysdael J. Definition of an Ets1 protein domain required for nuclear localization in cells and DNA-binding activity in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5718–5721. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer S. H., Landschulz K. T., Bishop T. R. Patterns of differential gene expression during maturation of erythroid colony forming units. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1987;251:43–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burd P. R., Rogers H. W., Gordon J. R., Martin C. A., Jayaraman S., Wilson S. D., Dvorak A. M., Galli S. J., Dorf M. E. Interleukin 3-dependent and -independent mast cells stimulated with IgE and antigen express multiple cytokines. J Exp Med. 1989 Jul 1;170(1):245–257. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.1.245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Lopata M. A., MacDonald R. J., Cowan N. J., Rutter W. J., Kirschner M. W. Number and evolutionary conservation of alpha- and beta-tubulin and cytoplasmic beta- and gamma-actin genes using specific cloned cDNA probes. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90238-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Andrea A. D., Lodish H. F., Wong G. G. Expression cloning of the murine erythropoietin receptor. Cell. 1989 Apr 21;57(2):277–285. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90965-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalton S., Treisman R. Characterization of SAP-1, a protein recruited by serum response factor to the c-fos serum response element. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):597–612. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90194-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodd I. B., Egan J. B. Improved detection of helix-turn-helix DNA-binding motifs in protein sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 11;18(17):5019–5026. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.17.5019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erselius J. R., Jostes B., Hatzopoulos A. K., Mosthaf L., Gruss P. Cell-type-specific control elements of the lymphotropic papovavirus enhancer. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1657–1666. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1657-1666.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frampton J., Leutz A., Gibson T., Graf T. DNA-binding domain ancestry. Nature. 1989 Nov 9;342(6246):134–134. doi: 10.1038/342134a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Shibuya H., Ohashi T., Yamanishi K., Taniguchi T. Regulation of human interleukin-2 gene: functional DNA sequences in the 5' flanking region for the gene expression in activated T lymphocytes. Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):401–405. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90660-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabrielsen O. S., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. Specific DNA binding by c-Myb: evidence for a double helix-turn-helix-related motif. Science. 1991 Sep 6;253(5024):1140–1143. doi: 10.1126/science.1887237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli S. J., Dvorak A. M., Marcum J. A., Ishizaka T., Nabel G., Der Simonian H., Pyne K., Goldin J. M., Rosenberg R. D., Cantor H. Mast cell clones: a model for the analysis of cellular maturation. J Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;95(2 Pt 1):435–444. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.2.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galson D. L., Housman D. E. Detection of two tissue-specific DNA-binding proteins with affinity for sites in the mouse beta-globin intervening sequence 2. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):381–392. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser T., Housman D., Lewis W. H., Gerhard D., Jones C. A fine-structure deletion map of human chromosome 11p: analysis of J1 series hybrids. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1989 Nov;15(6):477–501. doi: 10.1007/BF01534910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser T., Lewis W. H., Bruns G. A., Watkins P. C., Rogler C. E., Shows T. B., Powers V. E., Willard H. F., Goguen J. M., Simola K. O. The beta-subunit of follicle-stimulating hormone is deleted in patients with aniridia and Wilms' tumour, allowing a further definition of the WAGR locus. 1986 Jun 26-Jul 2Nature. 321(6073):882–887. doi: 10.1038/321882a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser T., Rose E., Morse H., Housman D., Jones C. A panel of irradiation-reduced hybrids selectively retaining human chromosome 11p13: their structure and use to purify the WAGR gene complex. Genomics. 1990 Jan;6(1):48–64. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90447-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goebl M. K. The PU.1 transcription factor is the product of the putative oncogene Spi-1. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1165–1166. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90676-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross D. S., Garrard W. T. Nuclease hypersensitive sites in chromatin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:159–197. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison S. C., Aggarwal A. K. DNA recognition by proteins with the helix-turn-helix motif. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:933–969. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.004441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hensold J. O., Dubyak G., Housman D. E. Calcium ionophore, A23187, induces commitment to differentiation but inhibits the subsequent expression of erythroid genes in murine erythroleukemia cells. Blood. 1991 Mar 15;77(6):1362–1370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hipskind R. A., Rao V. N., Mueller C. G., Reddy E. S., Nordheim A. Ets-related protein Elk-1 is homologous to the c-fos regulatory factor p62TCF. Nature. 1991 Dec 19;354(6354):531–534. doi: 10.1038/354531a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofer E., Hofer-Warbinek R., Darnell J. E., Jr Globin RNA transcription: a possible termination site and demonstration of transcriptional control correlated with altered chromatin structure. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):887–893. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90450-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Eukaryotic transcriptional regulatory proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:799–839. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.004055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C., Kao F. T. Regional mapping of the gene for human lysosomal acid phosphatase (ACP2) using a hybrid clone panel containing segments of human chromosome 11. Hum Genet. 1978 Nov 24;45(1):1–10. doi: 10.1007/BF00277567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junien C., McBride O. W. Report of the committee on the genetic constitution of chromosome 11. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1989;51(1-4):226–258. doi: 10.1159/000132793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabat D. Molecular biology of Friend viral erythroleukemia. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1989;148:1–42. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74700-7_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao F. T., Jones C., Puck T. T. Genetics of somatic mammalian cells: genetic, immunologic, and biochemical analysis with Chinese hamster cell hybrids containing selected human chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jan;73(1):193–197. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.1.193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karim F. D., Urness L. D., Thummel C. S., Klemsz M. J., McKercher S. R., Celada A., Van Beveren C., Maki R. A., Gunther C. V., Nye J. A. The ETS-domain: a new DNA-binding motif that recognizes a purine-rich core DNA sequence. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1451–1453. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kissinger C. R., Liu B. S., Martin-Blanco E., Kornberg T. B., Pabo C. O. Crystal structure of an engrailed homeodomain-DNA complex at 2.8 A resolution: a framework for understanding homeodomain-DNA interactions. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):579–590. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90453-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemsz M. J., McKercher S. R., Celada A., Van Beveren C., Maki R. A. The macrophage and B cell-specific transcription factor PU.1 is related to the ets oncogene. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):113–124. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90219-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kollias G., Wrighton N., Hurst J., Grosveld F. Regulated expression of human A gamma-, beta-, and hybrid gamma beta-globin genes in transgenic mice: manipulation of the developmental expression patterns. Cell. 1986 Jul 4;46(1):89–94. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90862-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaFlamme S., Acuto S., Markowitz D., Vick L., Landschultz W., Bank A. Expression of chimeric human beta- and delta-globin genes during erythroid differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4819–4826. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaMarco K., Thompson C. C., Byers B. P., Walton E. M., McKnight S. L. Identification of Ets- and notch-related subunits in GA binding protein. Science. 1991 Aug 16;253(5021):789–792. doi: 10.1126/science.1876836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz K. T., Boyer S. H., Noyes A. N., Rogers O. C., Frelin L. P. Onset of erythropoietin response in murine erythroid colony-forming units: assignment to early S-phase in a specific cell generation. Blood. 1992 May 15;79(10):2749–2758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. K., Parker B., Kowalik T. Rapid alkaline blot-transfer of viral dsRNAs. Anal Biochem. 1987 May 15;163(1):210–218. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90115-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks P. A., Rifkind R. A. Erythroleukemic differentiation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:419–448. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.002223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreau-Gachelin F., Ray D., Mattei M. G., Tambourin P., Tavitian A. The putative oncogene Spi-1: murine chromosomal localization and transcriptional activation in murine acute erythroleukemias. Oncogene. 1989 Dec;4(12):1449–1456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreau-Gachelin F., Ray D., de Both N. J., van der Feltz M. J., Tambourin P., Tavitian A. Spi-1 oncogene activation in Rauscher and Friend murine virus-induced acute erythroleukemias. Leukemia. 1990 Jan;4(1):20–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreau-Gachelin F., Tavitian A., Tambourin P. Spi-1 is a putative oncogene in virally induced murine erythroleukaemias. Nature. 1988 Jan 21;331(6153):277–280. doi: 10.1038/331277a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Baltimore D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel G., Galli S. J., Dvorak A. M., Dvorak H. F., Cantor H. Inducer T lymphocytes synthesize a factor that stimulates proliferation of cloned mast cells. Nature. 1981 May 28;291(5813):332–334. doi: 10.1038/291332a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen V. C., Ray D., Gross M. S., de Tand M. F., Frézal J., Moreau-Gachelin F. Localization of the human oncogene SPI1 on chromosome 11, region p11.22. Hum Genet. 1990 May;84(6):542–546. doi: 10.1007/BF00210807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nye J. A., Petersen J. M., Gunther C. V., Jonsen M. D., Graves B. J. Interaction of murine ets-1 with GGA-binding sites establishes the ETS domain as a new DNA-binding motif. Genes Dev. 1992 Jun;6(6):975–990. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.6.975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Aggarwal A. K., Jordan S. R., Beamer L. J., Obeysekare U. R., Harrison S. C. Conserved residues make similar contacts in two repressor-operator complexes. Science. 1990 Mar 9;247(4947):1210–1213. doi: 10.1126/science.2315694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T. Transcription factors: structural families and principles of DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:1053–1095. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.005201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pahl H. L., Scheibe R. J., Zhang D. E., Chen H. M., Galson D. L., Maki R. A., Tenen D. G. The proto-oncogene PU.1 regulates expression of the myeloid-specific CD11b promoter. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 5;268(7):5014–5020. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul R., Schuetze S., Kozak S. L., Kozak C. A., Kabat D. The Sfpi-1 proviral integration site of Friend erythroleukemia encodes the ets-related transcription factor Pu.1. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):464–467. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.464-467.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J., Schalling M., Buckler A. J., Rogers A., Haber D. A., Housman D. Expression of the Wilms' tumor gene WT1 in the murine urogenital system. Genes Dev. 1991 Aug;5(8):1345–1356. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.8.1345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petterson M., Schaffner W. A purine-rich DNA sequence motif present in SV40 and lymphotropic papovavirus binds a lymphoid-specific factor and contributes to enhancer activity in lymphoid cells. Genes Dev. 1987 Nov;1(9):962–972. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.9.962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pongubala J. M., Nagulapalli S., Klemsz M. J., McKercher S. R., Maki R. A., Atchison M. L. PU.1 recruits a second nuclear factor to a site important for immunoglobulin kappa 3' enhancer activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):368–378. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray D., Culine S., Tavitain A., Moreau-Gachelin F. The human homologue of the putative proto-oncogene Spi-1: characterization and expression in tumors. Oncogene. 1990 May;5(5):663–668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. C., Mann D. A. Rapid transfer of DNA from agarose gels to nylon membranes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7207–7221. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose E. A., Glaser T., Jones C., Smith C. L., Lewis W. H., Call K. M., Minden M., Champagne E., Bonetta L., Yeger H. Complete physical map of the WAGR region of 11p13 localizes a candidate Wilms' tumor gene. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):495–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90600-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saikumar P., Murali R., Reddy E. P. Role of tryptophan repeats and flanking amino acids in Myb-DNA interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8452–8456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalling M., Friberg K., Seroogy K., Riederer P., Bird E., Schiffmann S. N., Mailleux P., Vanderhaeghen J. J., Kuga S., Goldstein M. Analysis of expression of cholecystokinin in dopamine cells in the ventral mesencephalon of several species and in humans with schizophrenia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8427–8431. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuetze S., Paul R., Gliniak B. C., Kabat D. Role of the PU.1 transcription factor in controlling differentiation of Friend erythroleukemia cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;12(7):2967–2975. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.7.2967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. P., Tamkun J. W., Hartzell G. W., 3rd The structure and function of the homeodomain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jul 28;989(1):25–48. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(89)90033-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheffery M., Rifkind R. A., Marks P. A. Murine erythroleukemia cell differentiation: DNase I hypersensitivity and DNA methylation near the globin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1180–1184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibuya T., Mak T. W. Isolation and induction of erythroleukemic cell lines with properties of erythroid progenitor burst-forming cell (BFU-E) and erythroid precursor cell (CFU-E). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3721–3725. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Gilbert W. Contacts between Escherichia coli RNA polymerase and an early promoter of phage T7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):122–126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. B., Wang C. Y., Ho I. C., Bohjanen P. R., Petryniak B., June C. H., Miesfeldt S., Zhang L., Nabel G. J., Karpinski B. cis-acting sequences required for inducible interleukin-2 enhancer function bind a novel Ets-related protein, Elf-1. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1043–1053. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.1043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. C., Brown T. A., McKnight S. L. Convergence of Ets- and notch-related structural motifs in a heteromeric DNA binding complex. Science. 1991 Aug 16;253(5021):762–768. doi: 10.1126/science.1876833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. F., Martin D. I., Zon L. I., D'Andrea A. D., Wong G. G., Orkin S. H. Cloning of cDNA for the major DNA-binding protein of the erythroid lineage through expression in mammalian cells. Nature. 1989 Jun 8;339(6224):446–451. doi: 10.1038/339446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsiftsoglou A. S., Wong W., Volloch V., Gusella J., Housman D. Commitment of murine erythroleukemia (MEL) cells to terminal differentiation is associated with coordinated expression of globin and ribosomal genes. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1982;102 Pt A:69–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volloch V., Housman D. Terminal differentiation of murine erythroleukemia cells: physical stabilization of end-stage cells. J Cell Biol. 1982 May;93(2):390–394. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.2.390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. Y., Petryniak B., Ho I. C., Thompson C. B., Leiden J. M. Evolutionarily conserved Ets family members display distinct DNA binding specificities. J Exp Med. 1992 May 1;175(5):1391–1399. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.5.1391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson G. N., Hollar B. A., Waterson J. R., Schmickel R. D. Molecular analysis of cloned human 18S ribosomal DNA segments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5367–5371. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolberger C., Vershon A. K., Liu B., Johnson A. D., Pabo C. O. Crystal structure of a MAT alpha 2 homeodomain-operator complex suggests a general model for homeodomain-DNA interactions. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):517–528. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90526-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y. C., Ciarletta A. B., Temple P. A., Chung M. P., Kovacic S., Witek-Giannotti J. S., Leary A. C., Kriz R., Donahue R. E., Wong G. G. Human IL-3 (multi-CSF): identification by expression cloning of a novel hematopoietic growth factor related to murine IL-3. Cell. 1986 Oct 10;47(1):3–10. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90360-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Liu C. C., Butler G., Cohn Z. A., Galli S. J. Identification, purification, and characterization of a mast cell-associated cytolytic factor related to tumor necrosis factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9175–9179. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]