Abstract
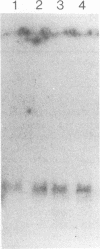
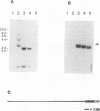
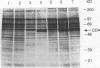
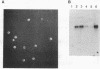
The gene for the human CD4 glycoprotein, which serves as the receptor for human immunodeficiency virus type 1, along with approximately 23 kb of sequence upstream of the translational start site, was cloned. The ability of 5' flanking sequences to direct tissue-specific expression was tested in cell culture and in transgenic mice. A 5' flanking region of 6 kb was able to direct transcription of the CD4 gene in NIH 3T3 cells but did not result in detectable expression in the murine T-cell line EL4 or in four lines of transgenic mice. A larger 5' flanking region of approximately 23 kb directed high-level CD4 transcription in the murine T-cell line EL4 and in three independent lines of transgenic mice. Human CD4 expression in all tissues analyzed was tightly correlated with murine CD4 expression; the highest levels of human CD4 RNA expression were found in the thymus and spleen, with relatively low levels detected in other tissues. Expression of human CD4 protein in peripheral blood mononuclear cells was examined by flow cytometry in these transgenic animals and found to be restricted to the murine CD4+ subset of lymphocytes. Human CD4 protein, detected with an anti-human CD4 monoclonal antibody, was present on the surface of 45 to 50% of the peripheral blood mononuclear cells from all transgenic lines.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agy M. B., Frumkin L. R., Corey L., Coombs R. W., Wolinsky S. M., Koehler J., Morton W. R., Katze M. G. Infection of Macaca nemestrina by human immunodeficiency virus type-1. Science. 1992 Jul 3;257(5066):103–106. doi: 10.1126/science.1621083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barré-Sinoussi F., Chermann J. C., Rey F., Nugeyre M. T., Chamaret S., Gruest J., Dauguet C., Axler-Blin C., Vézinet-Brun F., Rouzioux C. Isolation of a T-lymphotropic retrovirus from a patient at risk for acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Science. 1983 May 20;220(4599):868–871. doi: 10.1126/science.6189183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filice G., Cereda P. M., Varnier O. E. Infection of rabbits with human immunodeficiency virus. Nature. 1988 Sep 22;335(6188):366–369. doi: 10.1038/335366a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fultz P. N., McClure H. M., Swenson R. B., McGrath C. R., Brodie A., Getchell J. P., Jensen F. C., Anderson D. C., Broderson J. R., Francis D. P. Persistent infection of chimpanzees with human T-lymphotropic virus type III/lymphadenopathy-associated virus: a potential model for acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. J Virol. 1986 Apr;58(1):116–124. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.1.116-124.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo R. C., Salahuddin S. Z., Popovic M., Shearer G. M., Kaplan M., Haynes B. F., Palker T. J., Redfield R., Oleske J., Safai B. Frequent detection and isolation of cytopathic retroviruses (HTLV-III) from patients with AIDS and at risk for AIDS. Science. 1984 May 4;224(4648):500–503. doi: 10.1126/science.6200936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene W. C. The molecular biology of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. N Engl J Med. 1991 Jan 31;324(5):308–317. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199101313240506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hague B. F., Sawasdikosol S., Brown T. J., Lee K., Recker D. P., Kindt T. J. CD4 and its role in infection of rabbit cell lines by human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):7963–7967. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.7963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulaga H., Folks T. M., Rutledge R., Kindt T. J. Infection of rabbit T-cell and macrophage lines with human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4455–4459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulaga H., Folks T., Rutledge R., Truckenmiller M. E., Gugel E., Kindt T. J. Infection of rabbits with human immunodeficiency virus 1. A small animal model for acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. J Exp Med. 1989 Jan 1;169(1):321–326. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.1.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard J. M., Abramczuk J. W., Pezen D. S., Rutledge R., Belcher J. H., Hakim F., Shearer G., Lamperth L., Travis W., Fredrickson T. Development of disease and virus recovery in transgenic mice containing HIV proviral DNA. Science. 1988 Dec 23;242(4886):1665–1670. doi: 10.1126/science.3201255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. A., Cheng-Mayer C., Dina D., Luciw P. A. AIDS retrovirus (ARV-2) clone replicates in transfected human and animal fibroblasts. Science. 1986 May 23;232(4753):998–1001. doi: 10.1126/science.3010461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locardi C., Puddu P., Ferrantini M., Parlanti E., Sestili P., Varano F., Belardelli F. Persistent infection of normal mice with human immunodeficiency virus. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1649–1654. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1649-1654.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusso P., Markham P. D., Ranki A., Earl P., Moss B., Dorner F., Gallo R. C., Krohn K. J. Cell-mediated immune response toward viral envelope and core antigens in gibbon apes (Hylobates lar) chronically infected with human immunodeficiency virus-1. J Immunol. 1988 Oct 1;141(7):2467–2473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddon P. J., Dalgleish A. G., McDougal J. S., Clapham P. R., Weiss R. A., Axel R. The T4 gene encodes the AIDS virus receptor and is expressed in the immune system and the brain. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):333–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90590-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddon P. J., Molineaux S. M., Maddon D. E., Zimmerman K. A., Godfrey M., Alt F. W., Chess L., Axel R. Structure and expression of the human and mouse T4 genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9155–9159. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawada S., Littman D. R. Identification and characterization of a T-cell-specific enhancer adjacent to the murine CD4 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;11(11):5506–5515. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.11.5506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tourvieille B., Gorman S. D., Field E. H., Hunkapiller T., Parnes J. R. Isolation and sequence of L3T4 complementary DNA clones: expression in T cells and brain. Science. 1986 Oct 31;234(4776):610–614. doi: 10.1126/science.3094146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildin R. S., Garvin A. M., Pawar S., Lewis D. B., Abraham K. M., Forbush K. A., Ziegler S. F., Allen J. M., Perlmutter R. M. Developmental regulation of lck gene expression in T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1991 Feb 1;173(2):383–393. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.2.383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamura Y., Kotani M., Chowdhury M. I., Yamamoto N., Yamaguchi K., Karasuyama H., Katsura Y., Miyasaka M. Infection of human CD4+ rabbit cells with HIV-1: the possibility of the rabbit as a model for HIV-1 infection. Int Immunol. 1991 Nov;3(11):1183–1187. doi: 10.1093/intimm/3.11.1183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Eb A. J., Graham F. L. Assay of transforming activity of tumor virus DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):826–839. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65077-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]