Abstract
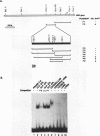
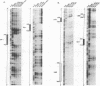
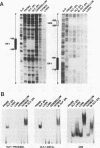
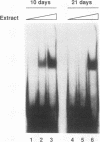
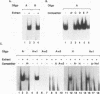
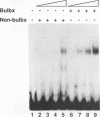
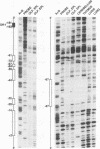
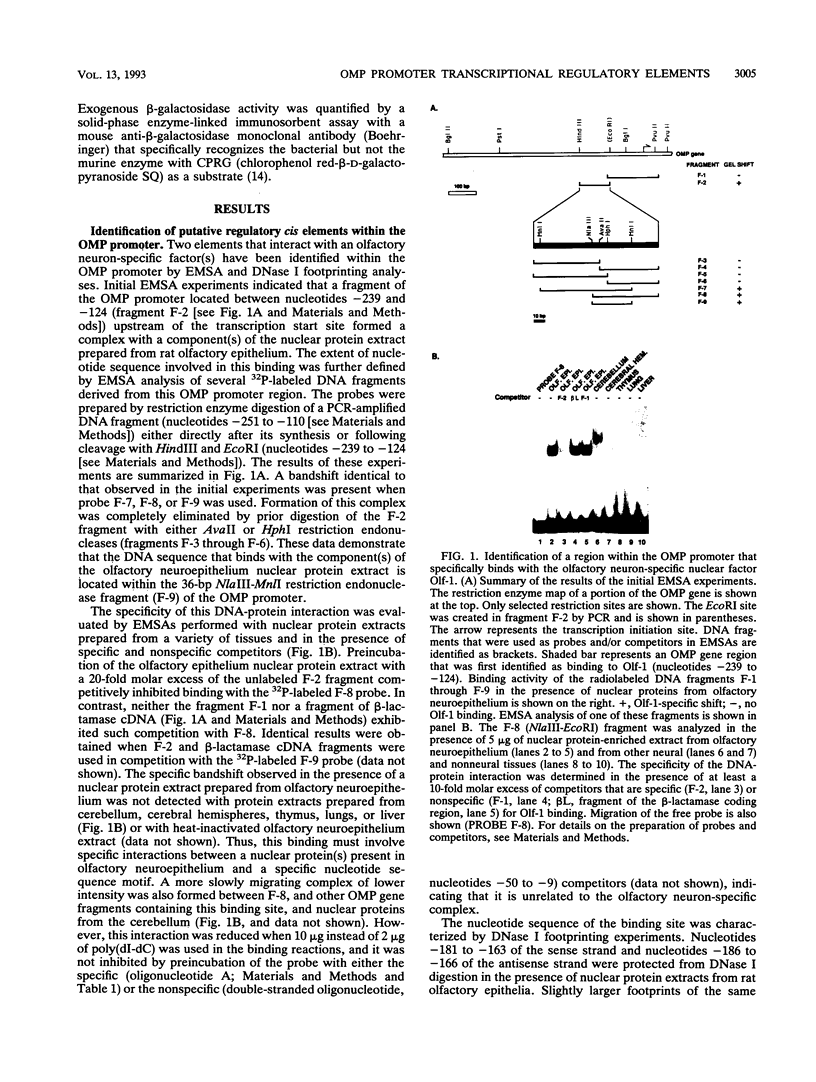
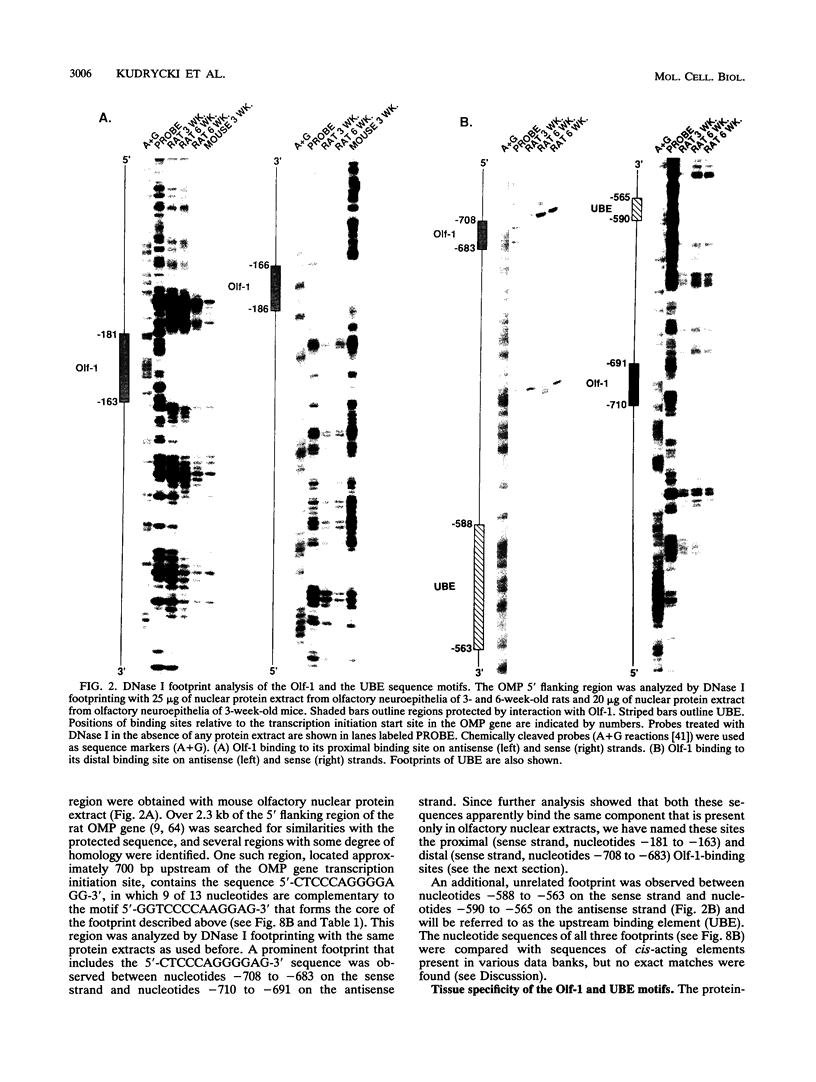
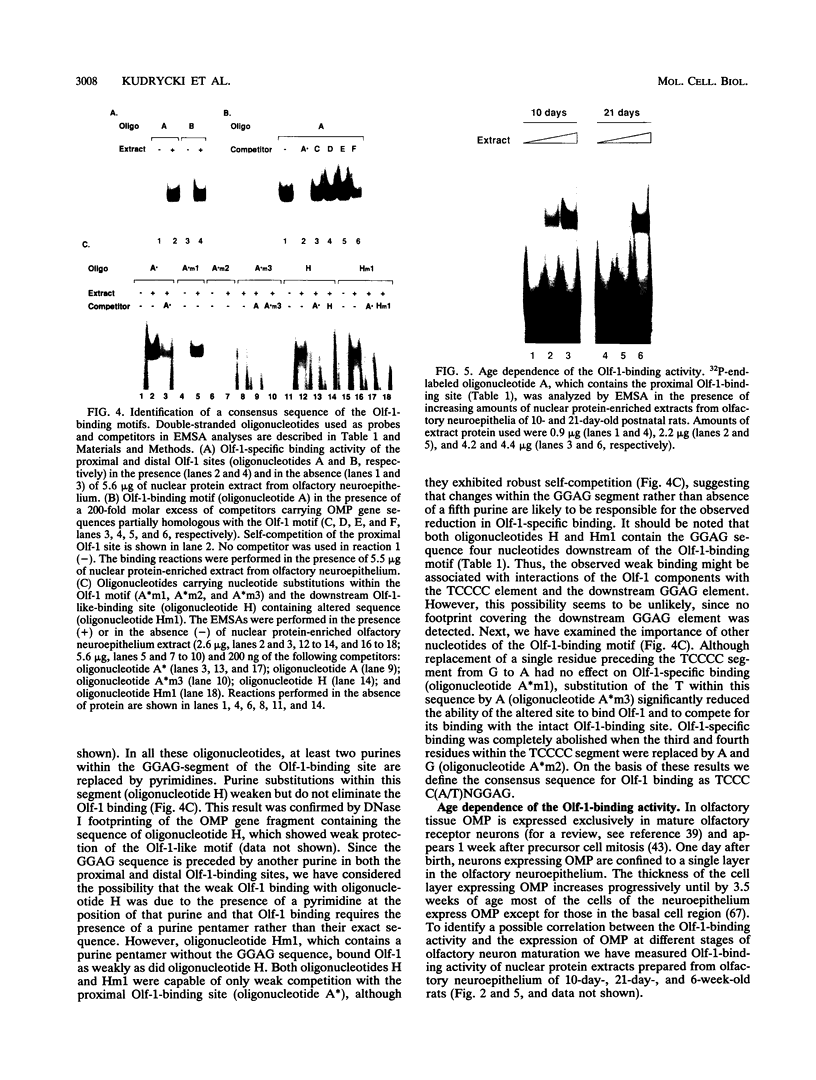
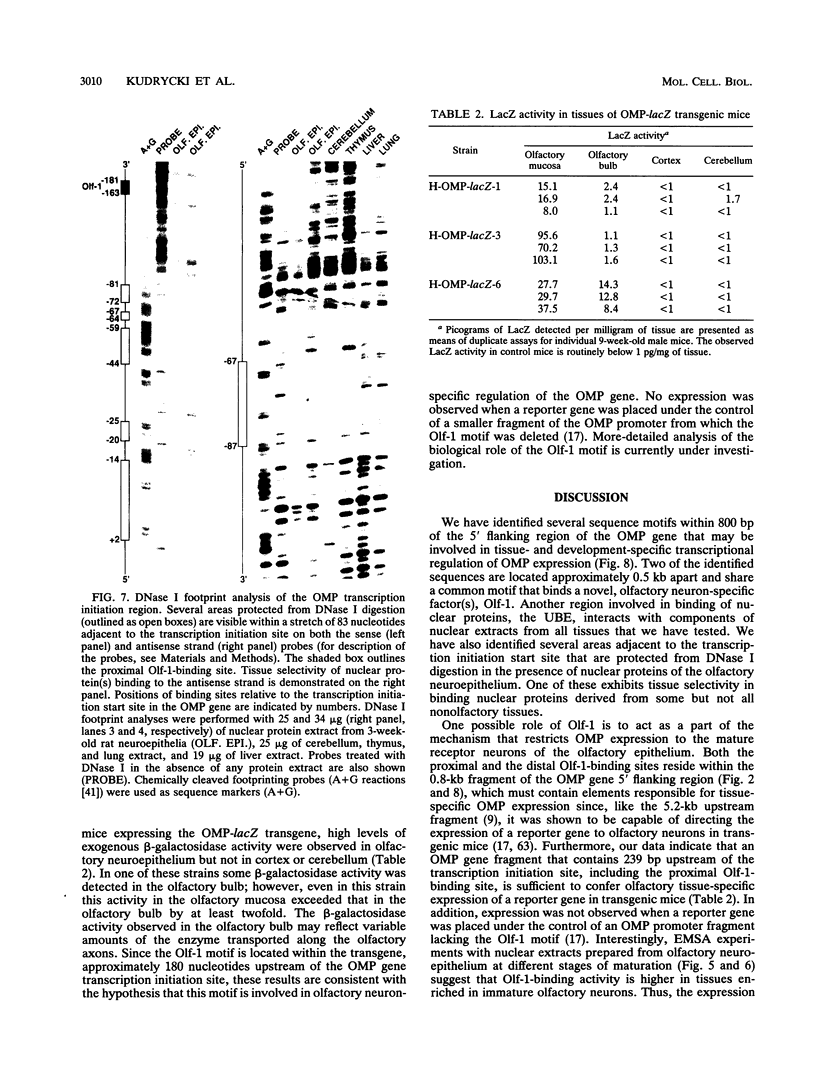
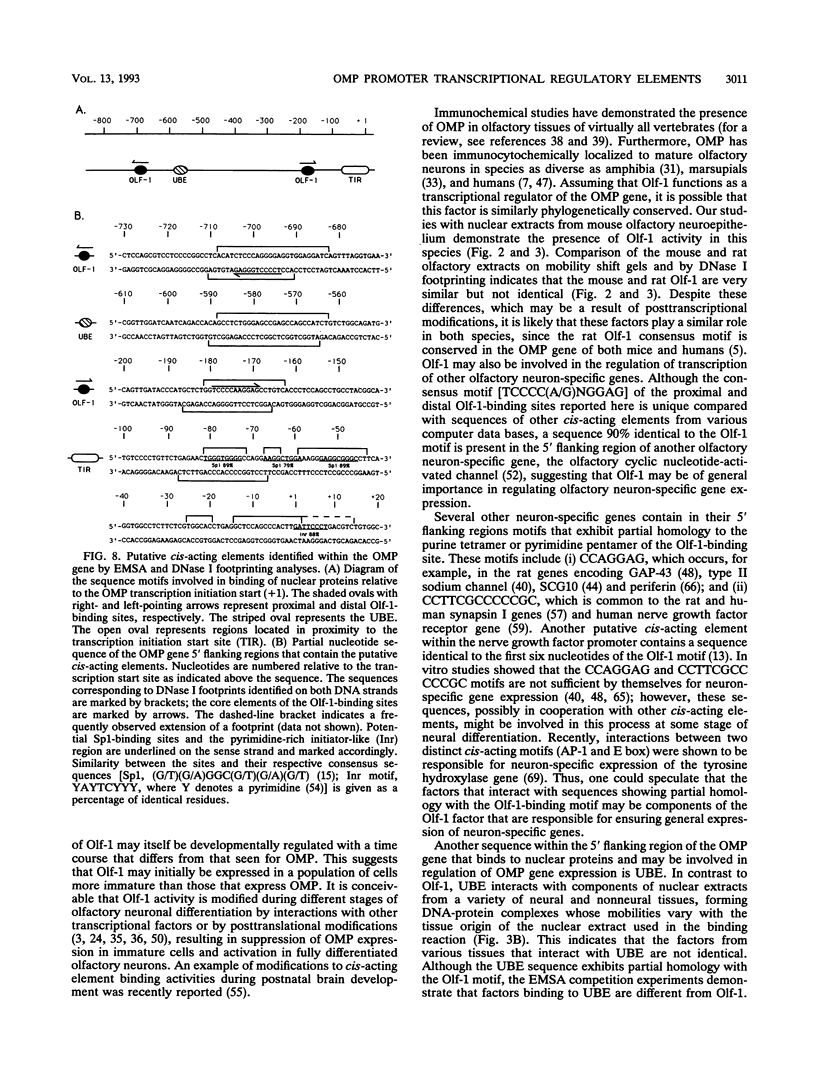
We report characterization of several domains within the 5' flanking region of the olfactory marker protein (OMP) gene that may participate in regulating transcription of this and other olfactory neuron-specific genes. Analysis by electrophoretic mobility shift assay and DNase I footprinting identifies two regions that contain a novel sequence motif. Interactions between this motif and nuclear proteins were detected only with nuclear protein extracts derived from olfactory neuroepithelium, and this activity is more abundant in olfactory epithelium enriched in immature neurons. We have designated a factor(s) involved in this binding as Olf-1. The Olf-1-binding motif consensus sequence was defined as TCCCC(A/T)NGGAG. Studies with transgenic mice indicate that a 0.3-kb fragment of the OMP gene containing one Olf-1 motif is sufficient for olfactory tissue-specific expression of the reporter gene. Some of the other identified sequence motifs also interact specifically with olfactory nuclear protein extracts. We propose that Olf-1 is a novel, olfactory neuron-specific trans-acting factor involved in the cell-specific expression of OMP.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakalyar H. A., Reed R. R. Identification of a specialized adenylyl cyclase that may mediate odorant detection. Science. 1990 Dec 7;250(4986):1403–1406. doi: 10.1126/science.2255909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker H., Grillo M., Margolis F. L. Biochemical and immunocytochemical characterization of olfactory marker protein in the rodent central nervous system. J Comp Neurol. 1989 Jul 8;285(2):246–261. doi: 10.1002/cne.902850207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J. Regulation of eukaryotic transcription factors by post-translational modification. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Nov 2;1009(2):103–109. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(89)90087-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck L., Axel R. A novel multigene family may encode odorant receptors: a molecular basis for odor recognition. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):175–187. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90418-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. Z., Evans G. A. A simple screening method for transgenic mice using the polymerase chain reaction. Biotechniques. 1990 Jan;8(1):32–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuah M. I., Zheng D. R. Olfactory marker protein is present in olfactory receptor cells of human fetuses. Neuroscience. 1987 Oct;23(1):363–370. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)90296-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costanzo R. M., Graziadei P. P. A quantitative analysis of changes in the olfactory epithelium following bulbectomy in hamster. J Comp Neurol. 1983 Apr 20;215(4):370–381. doi: 10.1002/cne.902150403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Mello S. R., Heinrich G. Structural and functional identification of regulatory regions and cis elements surrounding the nerve growth factor gene promoter. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1991 Oct;11(3-4):255–264. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(91)90034-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danciger E., Mettling C., Vidal M., Morris R., Margolis F. Olfactory marker protein gene: its structure and olfactory neuron-specific expression in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8565–8569. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devine-Beach K., Lashgari M. S., Khalili K. Myelin basic protein gene transcription. Identification of proximal and distal cis-acting regulatory elements. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13830–13835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhallan R. S., Yau K. W., Schrader K. A., Reed R. R. Primary structure and functional expression of a cyclic nucleotide-activated channel from olfactory neurons. Nature. 1990 Sep 13;347(6289):184–187. doi: 10.1038/347184a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eustice D. C., Feldman P. A., Colberg-Poley A. M., Buckery R. M., Neubauer R. H. A sensitive method for the detection of beta-galactosidase in transfected mammalian cells. Biotechniques. 1991 Dec;11(6):739-40, 742-3. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faisst S., Meyer S. Compilation of vertebrate-encoded transcription factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 11;20(1):3–26. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.1.3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He X., Rosenfeld M. G. Mechanisms of complex transcriptional regulation: implications for brain development. Neuron. 1991 Aug;7(2):183–196. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90257-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson J., Saffer J., Furneaux H. The transcription factor Sp1 binds to the JC virus promoter and is selectively expressed in glial cells in human brain. Ann Neurol. 1992 Jul;32(1):72–77. doi: 10.1002/ana.410320112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinds J. W., Hinds P. L., McNelly N. A. An autoradiographic study of the mouse olfactory epithelium: evidence for long-lived receptors. Anat Rec. 1984 Oct;210(2):375–383. doi: 10.1002/ar.1092100213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch M. R., Gaugler L., Deagostini-Bazin H., Bally-Cuif L., Goridis C. Identification of positive and negative regulatory elements governing cell-type-specific expression of the neural cell adhesion molecule gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):1959–1968. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howland D. S., Hemmendinger L. M., Carroll P. D., Estes P. S., Melloni R. H., Jr, DeGennaro L. J. Positive- and negative-acting promoter sequences regulate cell type-specific expression of the rat synapsin I gene. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1991 Oct;11(3-4):345–353. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(91)90044-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson S. P., Tjian R. O-glycosylation of eukaryotic transcription factors: implications for mechanisms of transcriptional regulation. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):125–133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90015-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson S. P., Tjian R. Purification and analysis of RNA polymerase II transcription factors by using wheat germ agglutinin affinity chromatography. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):1781–1785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.1781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Eukaryotic transcriptional regulatory proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:799–839. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.004055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. T., Reed R. R. Golf: an olfactory neuron specific-G protein involved in odorant signal transduction. Science. 1989 May 19;244(4906):790–795. doi: 10.1126/science.2499043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kageyama R., Merlino G. T., Pastan I. Nuclear factor ETF specifically stimulates transcription from promoters without a TATA box. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 15;264(26):15508–15514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korner M., Rattner A., Mauxion F., Sen R., Citri Y. A brain-specific transcription activator. Neuron. 1989 Nov;3(5):563–572. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90266-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraner S. D., Chong J. A., Tsay H. J., Mandel G. Silencing the type II sodium channel gene: a model for neural-specific gene regulation. Neuron. 1992 Jul;9(1):37–44. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90218-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishna N. S., Getchell T. V., Margolis F. L., Getchell M. L. Amphibian olfactory receptor neurons express olfactory marker protein. Brain Res. 1992 Oct 16;593(2):295–298. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)91322-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahiri D. K., Robakis N. K. The promoter activity of the gene encoding Alzheimer beta-amyloid precursor protein (APP) is regulated by two blocks of upstream sequences. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1991 Feb;9(3):253–257. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(91)90009-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin P. J., Phelix C., Krause W. J. An immunohistochemical study of olfactory epithelium in the opossum before and after birth. Z Mikrosk Anat Forsch. 1988;102(2):272–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig J., Margalit T., Eismann E., Lancet D., Kaupp U. B. Primary structure of cAMP-gated channel from bovine olfactory epithelium. FEBS Lett. 1990 Sep 17;270(1-2):24–29. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81226-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maguire H. F., Hoeffler J. P., Siddiqui A. HBV X protein alters the DNA binding specificity of CREB and ATF-2 by protein-protein interactions. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):842–844. doi: 10.1126/science.1827531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Goodbourn S., Fischer J. A. Regulation of inducible and tissue-specific gene expression. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1237–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.3296191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis F. L. A brain protein unique to the olfactory bulb. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 May;69(5):1221–1224. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.5.1221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maue R. A., Kraner S. D., Goodman R. H., Mandel G. Neuron-specific expression of the rat brain type II sodium channel gene is directed by upstream regulatory elements. Neuron. 1990 Feb;4(2):223–231. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90097-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay R. D. The origins of cellular diversity in the mammalian central nervous system. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):815–821. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90934-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miragall F., Monti Graziadei G. A. Experimental studies on the olfactory marker protein. II. Appearance of the olfactory marker protein during differentiation of the olfactory sensory neurons of mouse: an immunohistochemical and autoradiographic study. Brain Res. 1982 May 6;239(1):245–250. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90846-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori N., Schoenherr C., Vandenbergh D. J., Anderson D. J. A common silencer element in the SCG10 and type II Na+ channel genes binds a factor present in nonneuronal cells but not in neuronal cells. Neuron. 1992 Jul;9(1):45–54. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90219-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori N., Stein R., Sigmund O., Anderson D. J. A cell type-preferred silencer element that controls the neural-specific expression of the SCG10 gene. Neuron. 1990 Apr;4(4):583–594. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90116-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadi N. S., Head R., Grillo M., Hempstead J., Grannot-Reisfeld N., Margolis F. L. Chemical deafferentation of the olfactory bulb: plasticity of the levels of tyrosine hydroxylase, dopamine and norepinephrine. Brain Res. 1981 Jun 1;213(2):365–377. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90241-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakashima T., Kimmelman C. P., Snow J. B., Jr Structure of human fetal and adult olfactory neuroepithelium. Arch Otolaryngol. 1984 Oct;110(10):641–646. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1984.00800360013003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nedivi E., Basi G. S., Akey I. V., Skene J. H. A neural-specific GAP-43 core promoter located between unusual DNA elements that interact to regulate its activity. J Neurosci. 1992 Mar;12(3):691–704. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-03-00691.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeuffer E., Mollner S., Lancet D., Pfeuffer T. Olfactory adenylyl cyclase. Identification and purification of a novel enzyme form. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18803–18807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. Gene regulation by proteins acting nearby and at a distance. Nature. 1986 Aug 21;322(6081):697–701. doi: 10.1038/322697a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Transcription from a TATA-less promoter requires a multisubunit TFIID complex. Genes Dev. 1991 Nov;5(11):1935–1945. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.11.1935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers K. E., Dasgupta P., Gubler U., Grillo M., Khew-Goodall Y. S., Margolis F. L. Molecular cloning and sequencing of a cDNA for olfactory marker protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1704–1708. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy A. L., Meisterernst M., Pognonec P., Roeder R. G. Cooperative interaction of an initiator-binding transcription initiation factor and the helix-loop-helix activator USF. Nature. 1991 Nov 21;354(6350):245–248. doi: 10.1038/354245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurai H., Kikuchi K., Tsuchiya T., Kanazawa H., Tsuda M. Developmentally and regionally regulated alterations of octamer- and GC-box-binding activities during the postnatal development of mouse cerebellum. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1991 Aug 19;61(2):161–168. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(91)90127-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samanen D. W., Forbes W. B. Replication and differentiation of olfactory receptor neurons following axotomy in the adult hamster: a morphometric analysis of postnatal neurogenesis. J Comp Neurol. 1984 May 10;225(2):201–211. doi: 10.1002/cne.902250206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauerwald A., Hoesche C., Oschwald R., Kilimann M. W. The 5'-flanking region of the synapsin I gene. A G+C-rich, TATA- and CAAT-less, phylogenetically conserved sequence with cell type-specific promoter function. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 5;265(25):14932–14937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwob J. E., Szumowski K. E., Stasky A. A. Olfactory sensory neurons are trophically dependent on the olfactory bulb for their prolonged survival. J Neurosci. 1992 Oct;12(10):3896–3919. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-10-03896.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehgal A., Patil N., Chao M. A constitutive promoter directs expression of the nerve growth factor receptor gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3160–3167. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto E., Shi Y., Shenk T. YY1 is an initiator sequence-binding protein that directs and activates transcription in vitro. Nature. 1991 Nov 21;354(6350):241–245. doi: 10.1038/354241a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Baltimore D. The "initiator" as a transcription control element. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90176-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiel G., Greengard P., Südhof T. C. Characterization of tissue-specific transcription by the human synapsin I gene promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3431–3435. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson M. A., Ziff E. B. Structure of the gene encoding peripherin, an NGF-regulated neuronal-specific type III intermediate filament protein. Neuron. 1989 Jan;2(1):1043–1053. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90228-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhaagen J., Oestreicher A. B., Gispen W. H., Margolis F. L. The expression of the growth associated protein B50/GAP43 in the olfactory system of neonatal and adult rats. J Neurosci. 1989 Feb;9(2):683–691. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-02-00683.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhaagen J., Oestreicher A. B., Grillo M., Khew-Goodall Y. S., Gispen W. H., Margolis F. L. Neuroplasticity in the olfactory system: differential effects of central and peripheral lesions of the primary olfactory pathway on the expression of B-50/GAP43 and the olfactory marker protein. J Neurosci Res. 1990 May;26(1):31–44. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490260105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoon S. O., Chikaraishi D. M. Tissue-specific transcription of the rat tyrosine hydroxylase gene requires synergy between an AP-1 motif and an overlapping E box-containing dyad. Neuron. 1992 Jul;9(1):55–67. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90220-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenzie-Gregory B., O'Shea-Greenfield A., Smale S. T. Similar mechanisms for transcription initiation mediated through a TATA box or an initiator element. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 5;267(4):2823–2830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]