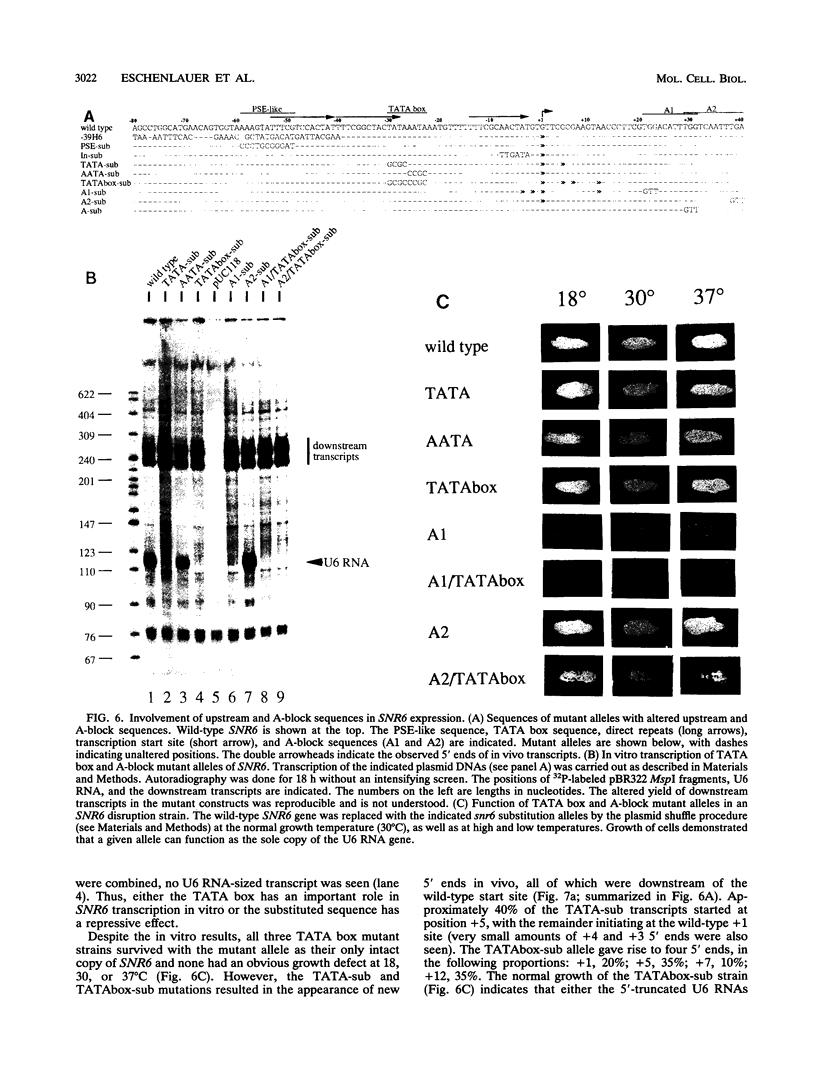
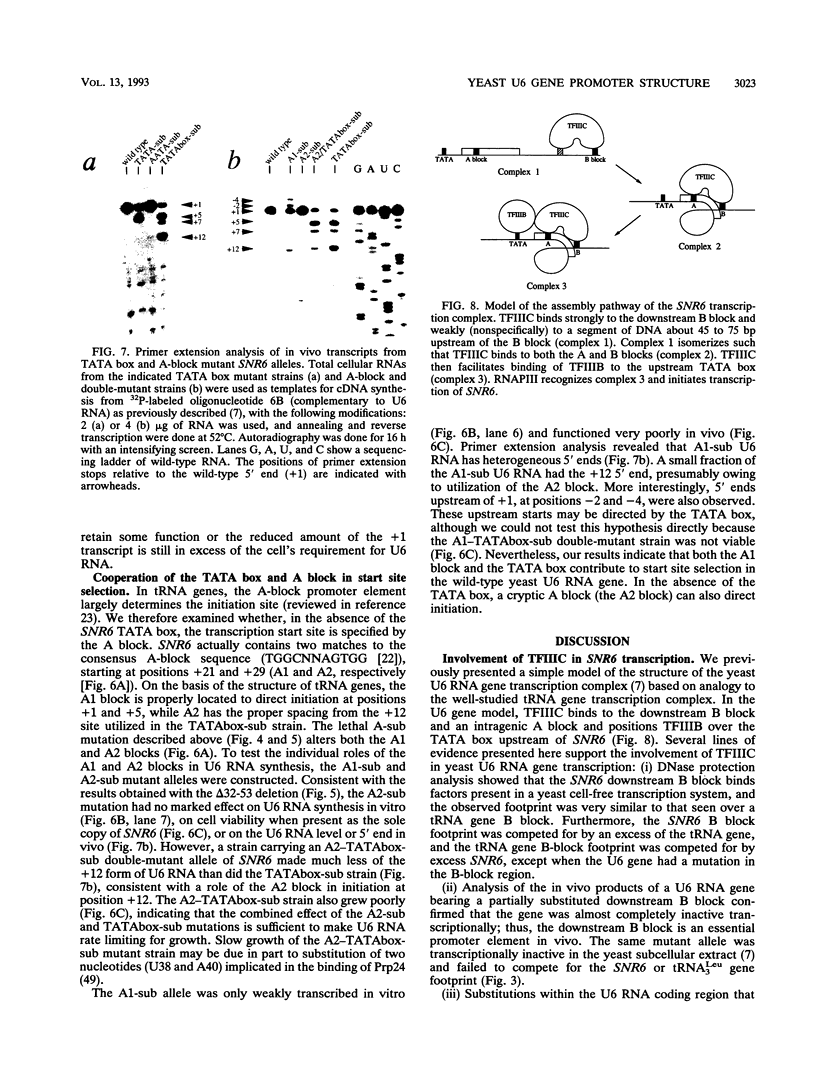
Abstract
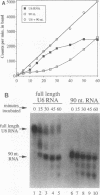
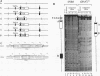
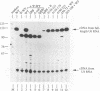
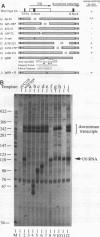
The promoters of vertebrate and yeast U6 small nuclear RNA genes are structurally dissimilar, although both are recognized by RNA polymerase III. Vertebrate U6 RNA genes have exclusively upstream promoters, while the U6 RNA gene from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae (SNR6) has internal and downstream promoter elements that match the tRNA gene intragenic A- and B-block elements, respectively. Substitution of the SNR6 A or B block greatly diminished U6 RNA accumulation in vivo, and a subcellular extract competent for RNA polymerase III transcription generated nearly identical DNase I protection patterns over the SNR6 downstream B block and a tRNA gene intragenic B block. We conclude that the SNR6 promoter is functionally similar to tRNA gene promoters, although the effects of extragenic deletion mutations suggest that the downstream location of the SNR6 B block imposes unique positional constraints on its function. Both vertebrate and yeast U6 RNA genes have an upstream TATA box element not normally found in tRNA genes. Substitution of the SNR6 TATA box altered the site of transcription initiation in vivo, while substitution of sequences further upstream had no effect on SNR6 transcription. We present a model for the SNR6 transcription complex that explains these results in terms of their effects on the binding of transcription initiation factor TFIIIB.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker R. E., Camier S., Sentenac A., Hall B. D. Gene size differentially affects the binding of yeast transcription factor tau to two intragenic regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8768–8772. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker R. E., Gabrielsen O., Hall B. D. Effects of tRNATyr point mutations on the binding of yeast RNA polymerase III transcription factor C. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 25;261(12):5275–5282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordonné R., Guthrie C. Human and human-yeast chimeric U6 snRNA genes identify structural elements required for expression in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Feb 11;20(3):479–485. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.3.479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branch A. D., Benenfeld B. J., Robertson H. D. RNA fingerprinting. Methods Enzymol. 1989;180:130–154. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)80098-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brow D. A., Guthrie C. Spliceosomal RNA U6 is remarkably conserved from yeast to mammals. Nature. 1988 Jul 21;334(6179):213–218. doi: 10.1038/334213a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brow D. A., Guthrie C. Transcription of a yeast U6 snRNA gene requires a polymerase III promoter element in a novel position. Genes Dev. 1990 Aug;4(8):1345–1356. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.8.1345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brow D. A. In vitro transcripts of a yeast variant 5 S rRNA gene exhibit alterations in 3'-end processing and protein binding. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 15;262(29):13959–13965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buratowski S., Zhou H. A suppressor of TBP mutations encodes an RNA polymerase III transcription factor with homology to TFIIB. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):221–230. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90351-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camier S., Gabrielsen O., Baker R., Sentenac A. A split binding site for transcription factor tau on the tRNA3Glu gene. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):491–500. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03655.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon R. E., Wu G. J., Railey J. F. Functions of and interactions between the A and B blocks in adenovirus type 2-specific VARNA1 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1285–1289. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbon P., Murgo S., Ebel J. P., Krol A., Tebb G., Mattaj L. W. A common octamer motif binding protein is involved in the transcription of U6 snRNA by RNA polymerase III and U2 snRNA by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1987 Oct 9;51(1):71–79. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90011-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colbert T., Hahn S. A yeast TFIIB-related factor involved in RNA polymerase III transcription. Genes Dev. 1992 Oct;6(10):1940–1949. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.10.1940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cormack B. P., Struhl K. The TATA-binding protein is required for transcription by all three nuclear RNA polymerases in yeast cells. Cell. 1992 May 15;69(4):685–696. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90232-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlberg J. E., Lund E. How does III x II make U6? Science. 1991 Dec 6;254(5037):1462–1463. doi: 10.1126/science.1962205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das G., Henning D., Wright D., Reddy R. Upstream regulatory elements are necessary and sufficient for transcription of a U6 RNA gene by RNA polymerase III. EMBO J. 1988 Feb;7(2):503–512. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02838.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingermann T., Sharp S., Schaack J., Söll D. Stable transcription complex formation of eukaryotic tRNA genes is dependent on a limited separation of the two intragenic control regions. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10395–10402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin S. C. The formation and function of DNase I hypersensitive sites in the process of gene activation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19259–19262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elledge S. J., Davis R. W. A family of versatile centromeric vectors designed for use in the sectoring-shuffle mutagenesis assay in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1988 Oct 30;70(2):303–312. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90202-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans C. F., Engelke D. R. Yeast extracts for transfer RNA gene transcription and processing. Methods Enzymol. 1990;181:439–450. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)81142-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabrizio P., Coppo A., Fruscoloni P., Benedetti P., Di Segni G., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. Comparative mutational analysis of wild-type and stretched tRNA3(Leu) gene promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8763–8767. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabrielsen O. S., Sentenac A. RNA polymerase III (C) and its transcription factors. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Nov;16(11):412–416. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90166-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli G., Hofstetter H., Birnstiel M. L. Two conserved sequence blocks within eukaryotic tRNA genes are major promoter elements. Nature. 1981 Dec 17;294(5842):626–631. doi: 10.1038/294626a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiduschek E. P., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. Transcription by RNA polymerase III. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:873–914. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.004301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausner T. P., Giglio L. M., Weiner A. M. Evidence for base-pairing between mammalian U2 and U6 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12A):2146–2156. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12a.2146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James P., Hall B. D., Whelen S., Craig E. A. Multiple protein tyrosine phosphatase-encoding genes in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1992 Dec 1;122(1):101–110. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90037-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones E. W. Tackling the protease problem in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:428–453. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94034-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Braun B. R., Nguyen L. H., Geiduschek E. P. S. cerevisiae TFIIIB is the transcription initiation factor proper of RNA polymerase III, while TFIIIA and TFIIIC are assembly factors. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):235–245. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90739-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Joazeiro C. A., Pisano M., Geiduschek E. P., Colbert T., Hahn S., Blanco J. A. The role of the TATA-binding protein in the assembly and function of the multisubunit yeast RNA polymerase III transcription factor, TFIIIB. Cell. 1992 Dec 11;71(6):1055–1064. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90399-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klekamp M. S., Weil P. A. Specific transcription of homologous class III genes in yeast-soluble cell-free extracts. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8432–8441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel G. R., Maser R. L., Calvet J. P., Pederson T. U6 small nuclear RNA is transcribed by RNA polymerase III. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8575–8579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel G. R., Pederson T. Transcription of a human U6 small nuclear RNA gene in vivo withstands deletion of intragenic sequences but not of an upstream TATATA box. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 25;17(18):7371–7379. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.18.7371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel G. R., Pederson T. Upstream elements required for efficient transcription of a human U6 RNA gene resemble those of U1 and U2 genes even though a different polymerase is used. Genes Dev. 1988 Feb;2(2):196–204. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.2.196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel G. R. RNA polymerase III transcription of genes that lack internal control regions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jan 17;1088(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(91)90146-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefebvre O., Carles C., Conesa C., Swanson R. N., Bouet F., Riva M., Sentenac A. TFC3: gene encoding the B-block binding subunit of the yeast transcription factor IIIC. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10512–10516. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobo S. M., Hernandez N. A 7 bp mutation converts a human RNA polymerase II snRNA promoter into an RNA polymerase III promoter. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):55–67. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90402-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobo S. M., Lister J., Sullivan M. L., Hernandez N. The cloned RNA polymerase II transcription factor IID selects RNA polymerase III to transcribe the human U6 gene in vitro. Genes Dev. 1991 Aug;5(8):1477–1489. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.8.1477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobo S. M., Tanaka M., Sullivan M. L., Hernandez N. A TBP complex essential for transcription from TATA-less but not TATA-containing RNA polymerase III promoters is part of the TFIIIB fraction. Cell. 1992 Dec 11;71(6):1029–1040. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90397-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-De-León A., Librizzi M., Puglia K., Willis I. M. PCF4 encodes an RNA polymerase III transcription factor with homology to TFIIB. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):211–220. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90350-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madhani H. D., Bordonné R., Guthrie C. Multiple roles for U6 snRNA in the splicing pathway. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12B):2264–2277. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12b.2264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margottin F., Dujardin G., Gérard M., Egly J. M., Huet J., Sentenac A. Participation of the TATA factor in transcription of the yeast U6 gene by RNA polymerase C. Science. 1991 Jan 25;251(4992):424–426. doi: 10.1126/science.1989075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W., Dathan N. A., Parry H. D., Carbon P., Krol A. Changing the RNA polymerase specificity of U snRNA gene promoters. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):435–442. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90029-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon M. E., Stamenkovich D., Petes T. D. Tandemly arranged variant 5S ribosomal RNA genes in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 12;12(21):8001–8016. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.21.8001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moenne A., Camier S., Anderson G., Margottin F., Beggs J., Sentenac A. The U6 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is transcribed by RNA polymerase C (III) in vivo and in vitro. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):271–277. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08105.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy R., Henning D., Das G., Harless M., Wright D. The capped U6 small nuclear RNA is transcribed by RNA polymerase III. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 5;262(1):75–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz M. C., Reeder R. H., Hahn S. Variants of the TATA-binding protein can distinguish subsets of RNA polymerase I, II, and III promoters. Cell. 1992 May 15;69(4):697–702. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90233-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shannon K. W., Guthrie C. Suppressors of a U4 snRNA mutation define a novel U6 snRNP protein with RNA-binding motifs. Genes Dev. 1991 May;5(5):773–785. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.5.773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Boeke J. D. In vitro mutagenesis and plasmid shuffling: from cloned gene to mutant yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:302–318. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmen K. A., Bernués J., Parry H. D., Stunnenberg H. G., Berkenstam A., Cavallini B., Egly J. M., Mattaj I. W. TFIID is required for in vitro transcription of the human U6 gene by RNA polymerase III. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1853–1862. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07711.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taggart A. K., Fisher T. S., Pugh B. F. The TATA-binding protein and associated factors are components of pol III transcription factor TFIIIB. Cell. 1992 Dec 11;71(6):1015–1028. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90396-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valenzuela P., Bell G. I., Venegas A., Sewell E. T., Masiarz F. R., DeGennaro L. J., Weinberg F., Rutter W. J. Ribosomal RNA genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. II. Physical map and nucleotide sequence of the 5 S ribosomal RNA gene and adjacent intergenic regions. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 25;252(22):8126–8135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. Production of single-stranded plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:3–11. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldschmidt R., Seifart K. H. TFIIA is required for in vitro transcription of mammalian U6 genes by RNA polymerase III. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16359–16364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldschmidt R., Wanandi I., Seifart K. H. Identification of transcription factors required for the expression of mammalian U6 genes in vitro. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2595–2603. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07801.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. J., Jackson S. P. Mechanism of TATA-binding protein recruitment to a TATA-less class III promoter. Cell. 1992 Dec 11;71(6):1041–1053. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90398-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. J., Jackson S. P., Rigby P. W. A role for the TATA-box-binding protein component of the transcription factor IID complex as a general RNA polymerase III transcription factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1949–1953. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise J. A., Tollervey D., Maloney D., Swerdlow H., Dunn E. J., Guthrie C. Yeast contains small nuclear RNAs encoded by single copy genes. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):743–751. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90107-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Dunstan H. M., Witte P. R., Smith T. P., Ottonello S., Sprague K. U. A class III transcription factor composed of RNA. Science. 1991 Apr 26;252(5005):542–546. doi: 10.1126/science.1708526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]