Abstract
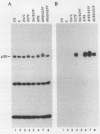
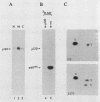
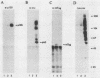
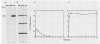
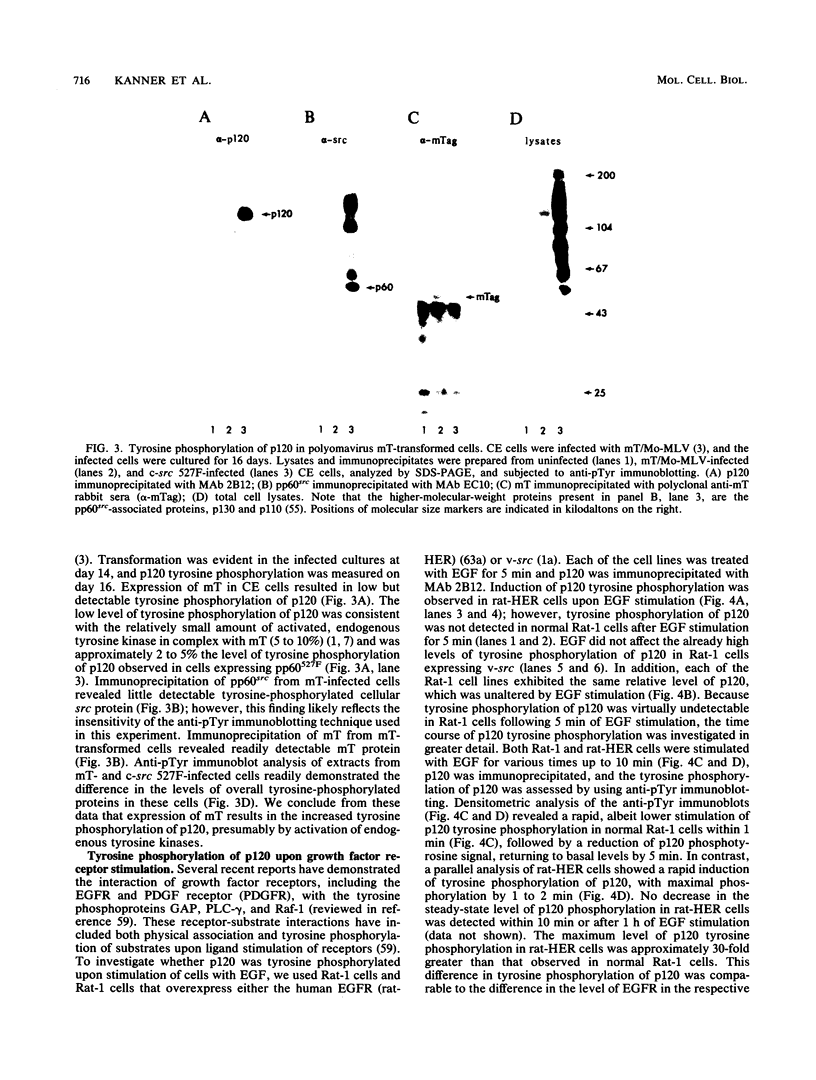
The monoclonal antibody 2B12 is directed toward p120, a 120-kDa cellular protein originally identified as a protein tyrosine kinase substrate in cells expressing membrane-associated oncogenic variants of pp60src. In this report, we show that p120 was tyrosine phosphorylated in avian cells expressing membrane-associated, enzymatically activated variants of c-src, including variants having structural alterations in the src homology regions 2 and 3. In contrast, p120 was not tyrosine phosphorylated in cells expressing enzymatically activated, nonmyristylated pp60src. Furthermore, p120 was tyrosine phosphorylated in avian cells expressing middle T antigen, the transforming protein of polyomavirus, as well as in rodent cells stimulated with either epidermal growth factor (EGF) or platelet-derived growth factor. Analysis of the time course of p120 tyrosine phosphorylation in EGF-stimulated cells revealed a rapid onset of tyrosine phosphorylation. In addition, both the extent and duration of p120 phosphorylation increased when cells overexpressing the EGF receptor were stimulated with EGF. Biochemical analysis showed that p120 (in both normal and src-transformed cells) was membrane associated, was myristylated, and was phosphorylated on serine and threonine residues. Hence, p120 appears to be a substrate of both nonreceptor- and ligand-activated transmembrane receptor tyrosine kinases and of serine/threonine kinases and is perhaps a component of both mitogen-stimulated and tyrosine kinase oncogene-induced signaling pathways.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bolen J. B., DeSeau V., O'Shaughnessy J., Amini S. Analysis of middle tumor antigen and pp60c-src interactions in polyomavirus-transformed rat cells. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3299–3305. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3299-3305.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buss J. E., Sefton B. M. Myristic acid, a rare fatty acid, is the lipid attached to the transforming protein of Rous sarcoma virus and its cellular homolog. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):7–12. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.7-12.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright C. A., Eckhart W., Simon S., Kaplan P. L. Cell transformation by pp60c-src mutated in the carboxy-terminal regulatory domain. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):83–91. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90758-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright C. A., Kaplan P. L., Cooper J. A., Hunter T., Eckhart W. Altered sites of tyrosine phosphorylation in pp60c-src associated with polyomavirus middle tumor antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1562–1570. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng S. H., Harvey R., Espino P. C., Semba K., Yamamoto T., Toyoshima K., Smith A. E. Peptide antibodies to the human c-fyn gene product demonstrate pp59c-fyn is capable of complex formation with the middle-T antigen of polyomavirus. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3845–3855. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03270.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A., Smith A. E. Polyoma virus transforming protein associates with the product of the c-src cellular gene. Nature. 1983 Jun 2;303(5916):435–439. doi: 10.1038/303435a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeClue J. E., Martin G. S. Linker insertion-deletion mutagenesis of the v-src gene: isolation of host- and temperature-dependent mutants. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):542–554. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.542-554.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Fiore P. P., Pierce J. H., Fleming T. P., Hazan R., Ullrich A., King C. R., Schlessinger J., Aaronson S. A. Overexpression of the human EGF receptor confers an EGF-dependent transformed phenotype to NIH 3T3 cells. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1063–1070. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90592-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G., Piwnica-Worms H., Morrison D., Druker B., Roberts T., Beach D. Human cdc2 protein kinase is a major cell-cycle regulated tyrosine kinase substrate. Nature. 1988 Dec 22;336(6201):738–744. doi: 10.1038/336738a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis C., Moran M., McCormick F., Pawson T. Phosphorylation of GAP and GAP-associated proteins by transforming and mitogenic tyrosine kinases. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):377–381. doi: 10.1038/343377a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ely C. M., Oddie K. M., Litz J. S., Rossomando A. J., Kanner S. B., Sturgill T. W., Parsons S. J. A 42-kD tyrosine kinase substrate linked to chromaffin cell secretion exhibits an associated MAP kinase activity and is highly related to a 42-kD mitogen-stimulated protein in fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;110(3):731–742. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.3.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrell J. E., Jr, Martin G. S. Platelet tyrosine-specific protein phosphorylation is regulated by thrombin. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3603–3610. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrell J. E., Jr, Martin G. S. Tyrosine-specific protein phosphorylation is regulated by glycoprotein IIb-IIIa in platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2234–2238. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr Tyrosine phosphorylation of a 22-kDa protein is correlated with transformation by Rous sarcoma virus. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20163–20166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Zokas L., Kamps M. P. Monoclonal antibodies to phosphotyrosine. J Immunol Methods. 1988 May 9;109(2):277–285. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90253-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Zokas L. Novel tyrosine kinase substrates from Rous sarcoma virus-transformed cells are present in the membrane skeleton. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;108(6):2401–2408. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.6.2401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden A., Brugge J. S. Thrombin treatment induces rapid changes in tyrosine phosphorylation in platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):901–905. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamaguchi M., Grandori C., Hanafusa H. Phosphorylation of cellular proteins in Rous sarcoma virus-infected cells: analysis by use of anti-phosphotyrosine antibodies. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3035–3042. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai H., Varmus H. E. Site-directed mutagenesis of the SH2- and SH3-coding domains of c-src produces varied phenotypes, including oncogenic activation of p60c-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1307–1318. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Sefton B. M. Identification of multiple novel polypeptide substrates of the v-src, v-yes, v-fps, v-ros, and v-erb-B oncogenic tyrosine protein kinases utilizing antisera against phosphotyrosine. Oncogene. 1988 Apr;2(4):305–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanner S. B., Gilmer T. M., Reynolds A. B., Parsons J. T. Novel tyrosine phosphorylations accompany the activation of pp60c-src during chemical carcinogenesis. Oncogene. 1989 Mar;4(3):295–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanner S. B., Parsons S. J., Parsons J. T., Gilmer T. M. Activation of pp60c-src tyrosine kinase specific activity in tumor-derived Syrian hamster embryo cells. Oncogene. 1988 Apr;2(4):327–335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanner S. B., Reynolds A. B., Parsons J. T. Immunoaffinity purification of tyrosine-phosphorylated cellular proteins. J Immunol Methods. 1989 Jun 2;120(1):115–124. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90296-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanner S. B., Reynolds A. B., Vines R. R., Parsons J. T. Monoclonal antibodies to individual tyrosine-phosphorylated protein substrates of oncogene-encoded tyrosine kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3328–3332. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. R., Morrison D. K., Wong G., McCormick F., Williams L. T. PDGF beta-receptor stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of GAP and association of GAP with a signaling complex. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):125–133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90220-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato J., Hirota Y., Nakamura N., Nakamura N., Takeya T. Structural features of the carboxy terminus of p60c-src that are required for the regulation of its intrinsic kinase activity. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1987 Dec;78(12):1354–1362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazlauskas A., Cooper J. A. Autophosphorylation of the PDGF receptor in the kinase insert region regulates interactions with cell proteins. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1121–1133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90510-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazlauskas A., Ellis C., Pawson T., Cooper J. A. Binding of GAP to activated PDGF receptors. Science. 1990 Mar 30;247(4950):1578–1581. doi: 10.1126/science.2157284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kmiecik T. E., Shalloway D. Activation and suppression of pp60c-src transforming ability by mutation of its primary sites of tyrosine phosphorylation. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):65–73. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90756-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornbluth S., Sudol M., Hanafusa H. Association of the polyomavirus middle-T antigen with c-yes protein. Nature. 1987 Jan 8;325(7000):171–173. doi: 10.1038/325171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumjian D. A., Wahl M. I., Rhee S. G., Daniel T. O. Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) binding promotes physical association of PDGF receptor with phospholipase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8232–8236. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kypta R. M., Hemming A., Courtneidge S. A. Identification and characterization of p59fyn (a src-like protein tyrosine kinase) in normal and polyoma virus transformed cells. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3837–3844. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03269.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder M. E., Burr J. G. Nonmyristoylated p60v-src fails to phosphorylate proteins of 115-120 kDa in chicken embryo fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2608–2612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luttrell D. K., Luttrell L. M., Parsons S. J. Augmented mitogenic responsiveness to epidermal growth factor in murine fibroblasts that overexpress pp60c-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):497–501. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Bellot F., Honegger A. M., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J., Zilberstein A. Tyrosine kinase activity is essential for the association of phospholipase C-gamma with the epidermal growth factor receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):435–441. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Rhee S. G., Felder S., Mervic M., Lyall R., Levitzki A., Ullrich A., Zilberstein A., Schlessinger J. EGF induces tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-II: a potential mechanism for EGF receptor signaling. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1101–1107. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90047-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer B. J., Hamaguchi M., Hanafusa H. A novel viral oncogene with structural similarity to phospholipase C. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):272–275. doi: 10.1038/332272a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClain D. A., Maegawa H., Levy J., Huecksteadt T., Dull T. J., Lee J., Ullrich A., Olefsky J. M. Properties of a human insulin receptor with a COOH-terminal truncation. I. Insulin binding, autophosphorylation, and endocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):8904–8911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisenhelder J., Suh P. G., Rhee S. G., Hunter T. Phospholipase C-gamma is a substrate for the PDGF and EGF receptor protein-tyrosine kinases in vivo and in vitro. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1109–1122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90048-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molloy C. J., Bottaro D. P., Fleming T. P., Marshall M. S., Gibbs J. B., Aaronson S. A. PDGF induction of tyrosine phosphorylation of GTPase activating protein. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):711–714. doi: 10.1038/342711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morla A. O., Wang J. Y. Protein tyrosine phosphorylation in the cell cycle of BALB/c 3T3 fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8191–8195. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. K., Browning P. J., White M. F., Roberts T. M. Tyrosine phosphorylations in vivo associated with v-fms transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):176–185. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. K., Kaplan D. R., Escobedo J. A., Rapp U. R., Roberts T. M., Williams L. T. Direct activation of the serine/threonine kinase activity of Raf-1 through tyrosine phosphorylation by the PDGF beta-receptor. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):649–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90100-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. K., Kaplan D. R., Rapp U., Roberts T. M. Signal transduction from membrane to cytoplasm: growth factors and membrane-bound oncogene products increase Raf-1 phosphorylation and associated protein kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8855–8859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. K., Kaplan D. R., Rhee S. G., Williams L. T. Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)-dependent association of phospholipase C-gamma with the PDGF receptor signaling complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2359–2366. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishibe S., Wahl M. I., Wedegaertner P. B., Kim J. W., Rhee S. G., Carpenter G., Kim J. J. Selectivity of phospholipase C phosphorylation by the epidermal growth factor receptor, the insulin receptor, and their cytoplasmic domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):424–428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons J. T. Closing the GAP in a signal transduction pathway. Trends Genet. 1990 Jun;6(6):169–171. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90155-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons J. T., Weber M. J. Genetics of src: structure and functional organization of a protein tyrosine kinase. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1989;147:79–127. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74697-0_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons S. J., McCarley D. J., Ely C. M., Benjamin D. C., Parsons J. T. Monoclonal antibodies to Rous sarcoma virus pp60src react with enzymatically active cellular pp60src of avian and mammalian origin. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):272–282. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.272-282.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T. Non-catalytic domains of cytoplasmic protein-tyrosine kinases: regulatory elements in signal transduction. Oncogene. 1988 Nov;3(5):491–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piwnica-Worms H., Saunders K. B., Roberts T. M., Smith A. E., Cheng S. H. Tyrosine phosphorylation regulates the biochemical and biological properties of pp60c-src. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):75–82. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90757-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potts W. M., Reynolds A. B., Lansing T. J., Parsons J. T. Activation of pp60c-src transforming potential by mutations altering the structure of an amino terminal domain containing residues 90-95. Oncogene Res. 1988;3(4):343–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resh M. D., Ling H. P. Identification of a 32K plasma membrane protein that binds to the myristylated amino-terminal sequence of p60v-src. Nature. 1990 Jul 5;346(6279):84–86. doi: 10.1038/346084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds A. B., Kanner S. B., Wang H. C., Parsons J. T. Stable association of activated pp60src with two tyrosine-phosphorylated cellular proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):3951–3958. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.3951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds A. B., Roesel D. J., Kanner S. B., Parsons J. T. Transformation-specific tyrosine phosphorylation of a novel cellular protein in chicken cells expressing oncogenic variants of the avian cellular src gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):629–638. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds A. B., Vila J., Lansing T. J., Potts W. M., Weber M. J., Parsons J. T. Activation of the oncogenic potential of the avian cellular src protein by specific structural alteration of the carboxy terminus. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2359–2364. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02512.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
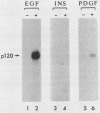
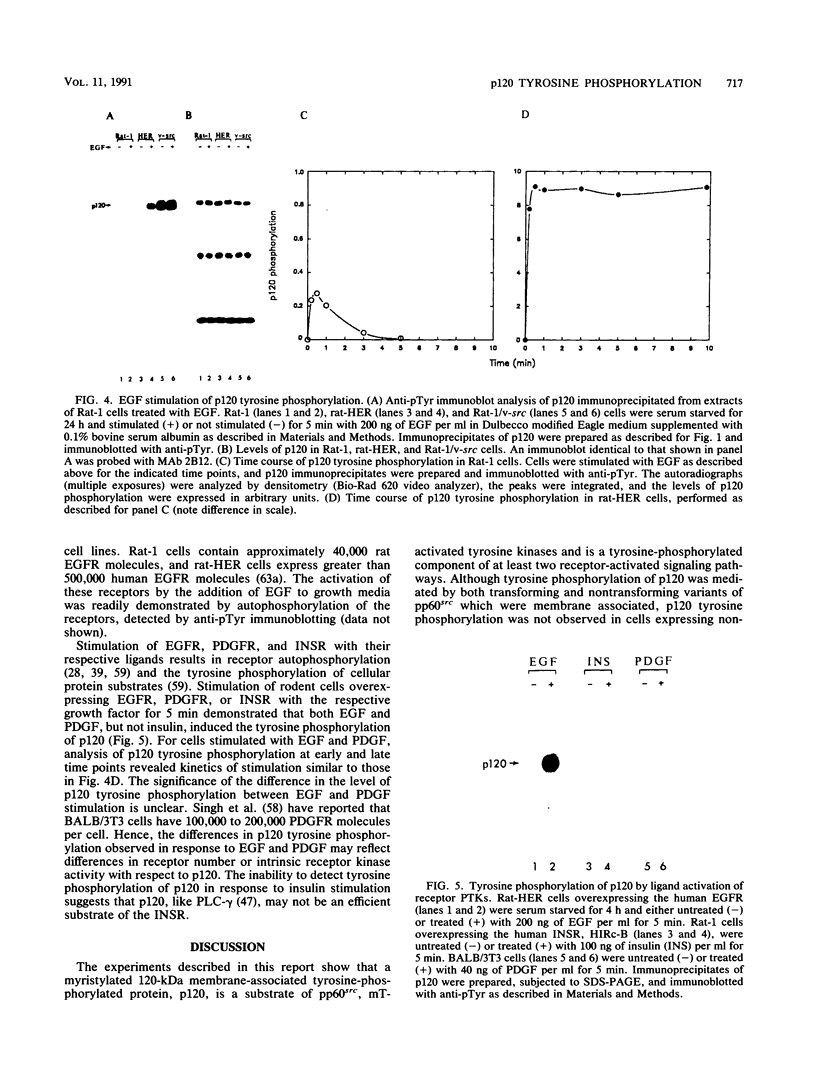
- Singh J. P., Chaikin M. A., Stiles C. D. Phylogenetic analysis of platelet-derived growth factor by radio-receptor assay. J Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;95(2 Pt 1):667–671. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.2.667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl M. L., Ferenz C. R., Kelleher K. L., Kriz R. W., Knopf J. L. Sequence similarity of phospholipase C with the non-catalytic region of src. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):269–272. doi: 10.1038/332269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90801-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velu T. J., Beguinot L., Vass W. C., Willingham M. C., Merlino G. T., Pastan I., Lowy D. R. Epidermal-growth-factor-dependent transformation by a human EGF receptor proto-oncogene. Science. 1987 Dec 4;238(4832):1408–1410. doi: 10.1126/science.3500513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl M. I., Nishibe S., Suh P. G., Rhee S. G., Carpenter G. Epidermal growth factor stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-II independently of receptor internalization and extracellular calcium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1568–1572. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl M. I., Olashaw N. E., Nishibe S., Rhee S. G., Pledger W. J., Carpenter G. Platelet-derived growth factor induces rapid and sustained tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-gamma in quiescent BALB/c 3T3 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):2934–2943. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.2934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H. C., Parsons J. T. Deletions and insertions within an amino-terminal domain of pp60v-src inactivate transformation and modulate membrane stability. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):291–302. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.291-302.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasilenko W. J., Payne D. M., Fitzgerald D. L., Weber M. J. Phosphorylation and activation of epidermal growth factor receptors in cells transformed by the src oncogene. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):309–321. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells A., Welsh J. B., Lazar C. S., Wiley H. S., Gill G. N., Rosenfeld M. G. Ligand-induced transformation by a noninternalizing epidermal growth factor receptor. Science. 1990 Feb 23;247(4945):962–964. doi: 10.1126/science.2305263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. F., Livingston J. N., Backer J. M., Lauris V., Dull T. J., Ullrich A., Kahn C. R. Mutation of the insulin receptor at tyrosine 960 inhibits signal transmission but does not affect its tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):641–649. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]