Abstract
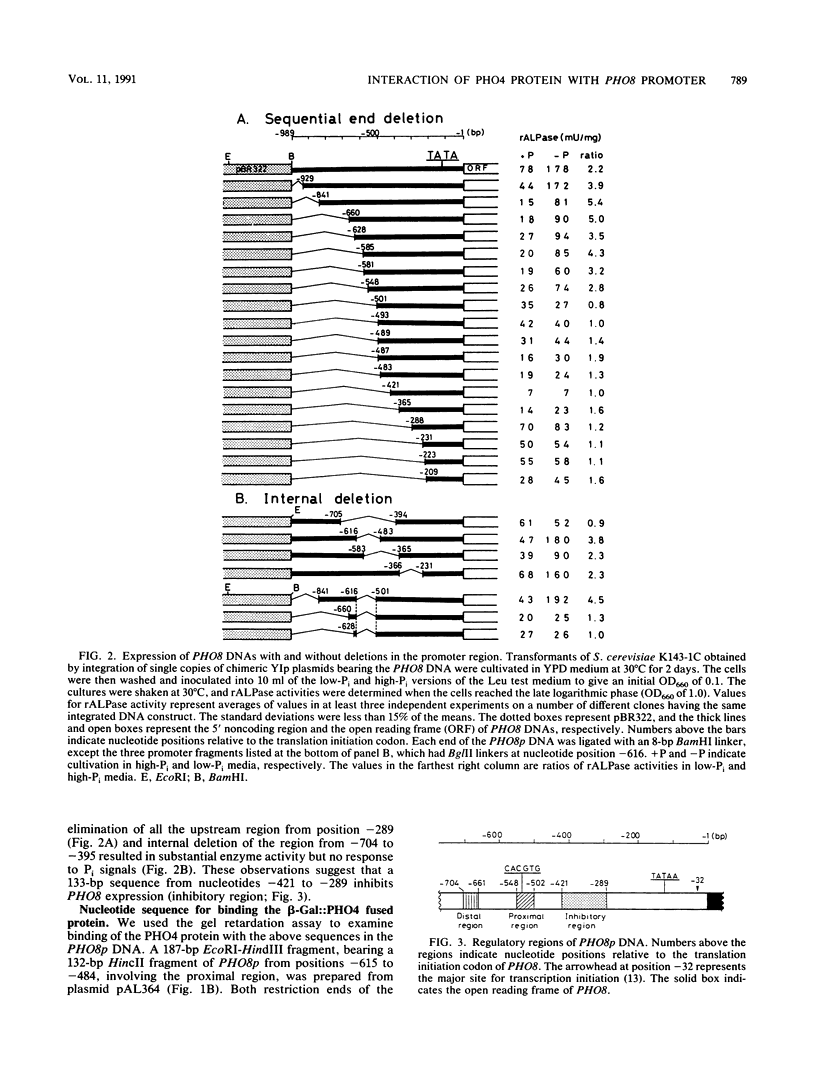
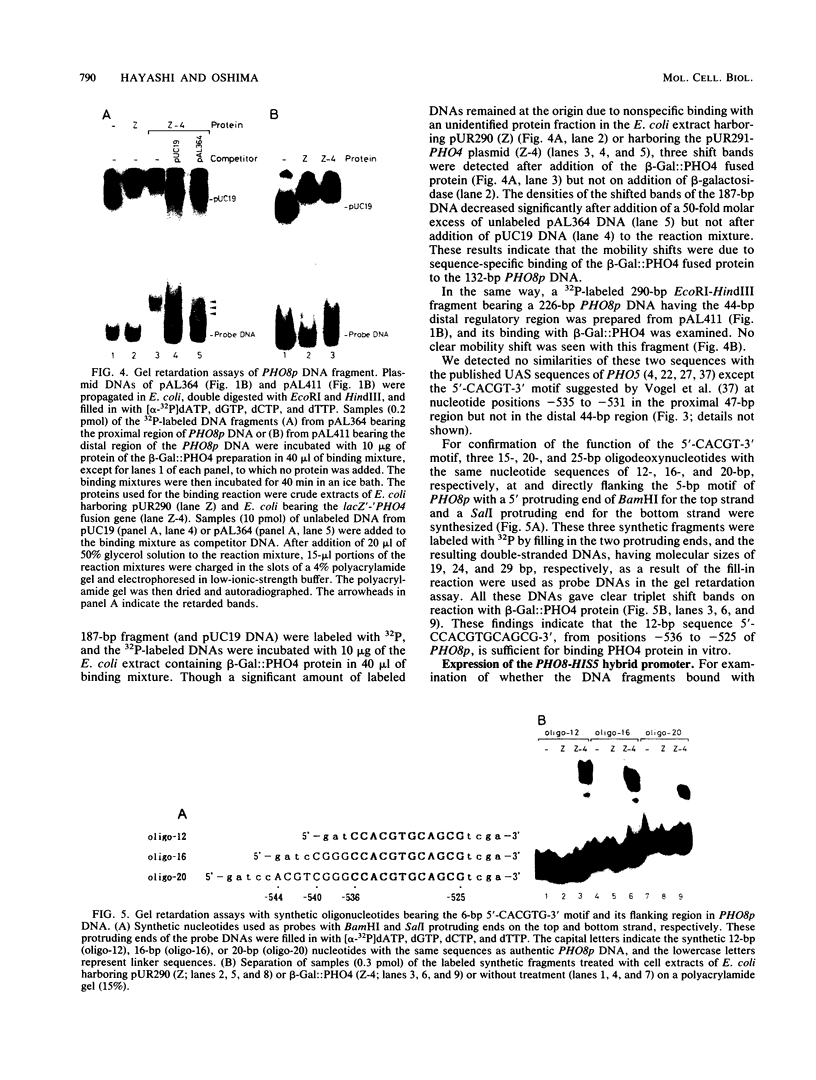
The PHO8 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae encodes repressible alkaline phosphatase (rALPase; EC 3.1.3.1). The rALPase activity of the cells is two to three times higher in medium containing a low concentration of Pi than in high-Pi medium due to transcription of PHO8. The Pi signals are conveyed to PHO8 by binding of PHO4 protein, a positive regulatory factor, to a promoter region of PHO8 (PHO8p) under the influence of the PHO regulatory circuit. Deletion analysis of PHO8p DNA revealed two separate regulatory regions required for derepression of rALPase located at nucleotide positions -704 to -661 (distal region) and -548 to -502 (proximal region) and an inhibitory region located at -421 to -289 relative to the translation initiation codon. Gel retardation experiments showed that a beta-galactosidase-PHO4 fusion protein binds to a 132-bp PHO8p fragment bearing the proximal region but not to a 226-bp PHO8 DNA bearing the distal region. The fusion protein also binds to a synthetic oligonucleotide having the same 12-bp nucleotide sequence as the PHO8p DNA from positions -536 to -525. The 132-bp PHO8p fragment, connected at position -281 of the 5' upstream region of a HIS5'-'lacZ fused gene, could sense Pi signals in vivo, but a 20-bp synthetic oligonucleotide having the same sequence from -544 to -525 of the PHO8p DNA could not. Linker insertions in the PHO8p DNA indicated that the 5-bp sequence 5'-CACGT-3' from positions -535 to -531 is essential for binding the beta-galactosidase-PHO4 fusion protein and for derepression of rALPase.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almer A., Rudolph H., Hinnen A., Hörz W. Removal of positioned nucleosomes from the yeast PHO5 promoter upon PHO5 induction releases additional upstream activating DNA elements. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2689–2696. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04552.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ammerer G., Hunter C. P., Rothman J. H., Saari G. C., Valls L. A., Stevens T. H. PEP4 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae encodes proteinase A, a vacuolar enzyme required for processing of vacuolar precursors. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2490–2499. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arndt K. T., Styles C., Fink G. R. Multiple global regulators control HIS4 transcription in yeast. Science. 1987 Aug 21;237(4817):874–880. doi: 10.1126/science.3303332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergman L. W., McClinton D. C., Madden S. L., Preis L. H. Molecular analysis of the DNA sequences involved in the transcriptional regulation of the phosphate-repressible acid phosphatase gene (PHO5) of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):6070–6074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.6070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai M., Davis R. W. Yeast centromere binding protein CBF1, of the helix-loop-helix protein family, is required for chromosome stability and methionine prototrophy. Cell. 1990 May 4;61(3):437–446. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90525-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carthew R. W., Chodosh L. A., Sharp P. A. An RNA polymerase II transcription factor binds to an upstream element in the adenovirus major late promoter. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):439–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90174-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark D. W., Tkacz J. S., Lampen J. O. Asparagine-linked carbohydrate does not determine the cellular location of yeast vacuolar nonspecific alkaline phosphatase. J Bacteriol. 1982 Nov;152(2):865–873. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.2.865-873.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke L., Carbon J. Functional expression of cloned yeast DNA in Escherichia coli: specific complementation of argininosuccinate lyase (argH) mutations. J Mol Biol. 1978 Apr 25;120(4):517–532. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90351-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones E. W., Zubenko G. S., Parker R. R. PEP4 gene function is required for expression of several vacuolar hydrolases in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1982 Dec;102(4):665–677. doi: 10.1093/genetics/102.4.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko Y., Hayashi N., Toh-e A., Banno I., Oshima Y. Structural characteristics of the PHO8 gene encoding repressible alkaline phosphatase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1987;58(1):137–148. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90036-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko Y., Tamai Y., Toh-e A., Oshima Y. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional control of PHO8 expression by PHO regulatory genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):248–252. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko Y., Toh-e A., Banno I., Oshima Y. Molecular characterization of a specific p-nitrophenylphosphatase gene, PHO13, and its mapping by chromosome fragmentation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Dec;220(1):133–139. doi: 10.1007/BF00260867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko Y., Toh-e A., Oshima Y. Identification of the genetic locus for the structural gene and a new regulatory gene for the synthesis of repressible alkaline phosphatase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;2(2):127–137. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.2.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemire J. M., Willcocks T., Halvorson H. O., Bostian K. A. Regulation of repressible acid phosphatase gene transcription in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):2131–2141. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.2131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. A. Transformation in Escherichia coli: cryogenic preservation of competent cells. J Bacteriol. 1977 Oct;132(1):349–351. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.1.349-351.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao J., Miyanohara A., Toh-e A., Matsubara K. Saccharomyces cerevisiae PHO5 promoter region: location and function of the upstream activation site. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2613–2623. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishiwaki K., Hayashi N., Irie S., Chung D. H., Harashima S., Oshima Y. Structure of the yeast HIS5 gene responsive to general control of amino acid biosynthesis. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Jun;208(1-2):159–167. doi: 10.1007/BF00330437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa N., Oshima Y. Functional domains of a positive regulatory protein, PHO4, for transcriptional control of the phosphatase regulon in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2224–2236. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parent S. A., Fenimore C. M., Bostian K. A. Vector systems for the expression, analysis and cloning of DNA sequences in S. cerevisiae. Yeast. 1985 Dec;1(2):83–138. doi: 10.1002/yea.320010202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudolph H., Hinnen A. The yeast PHO5 promoter: phosphate-control elements and sequences mediating mRNA start-site selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1340–1344. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüther U., Müller-Hill B. Easy identification of cDNA clones. EMBO J. 1983;2(10):1791–1794. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01659.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sengstag C., Hinnen A. A 28-bp segment of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae PHO5 upstream activator sequence confers phosphate control to the CYC1-lacZ gene fusion. Gene. 1988 Jul 30;67(2):223–228. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90399-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli plasmid pBR322. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):77–90. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamai Y., Toh-e A., Oshima Y. Regulation of inorganic phosphate transport systems in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):964–968. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.964-968.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thill G. P., Kramer R. A., Turner K. J., Bostian K. A. Comparative analysis of the 5'-end regions of two repressible acid phosphatase genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Apr;3(4):570–579. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.4.570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toh-E A., Nakamura H., Oshima Y. A gene controlling the synthesis of non specific alkaline phosphatase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Mar 25;428(1):182–192. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90119-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toh-e A., Inouye S., Oshima Y. Structure and function of the PHO82-pho4 locus controlling the synthesis of repressible acid phosphatase of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):221–232. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.221-232.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toh-e A., Shimauchi T. Cloning and sequencing of the PHO80 gene and CEN15 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast. 1986 Jun;2(2):129–139. doi: 10.1002/yea.320020209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toh-e A., Tanaka K., Uesono Y., Wickner R. B. PHO85, a negative regulator of the PHO system, is a homolog of the protein kinase gene, CDC28, of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Sep;214(1):162–164. doi: 10.1007/BF00340196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel K., Hörz W., Hinnen A. The two positively acting regulatory proteins PHO2 and PHO4 physically interact with PHO5 upstream activation regions. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2050–2057. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolford C. A., Daniels L. B., Park F. J., Jones E. W., Van Arsdell J. N., Innis M. A. The PEP4 gene encodes an aspartyl protease implicated in the posttranslational regulation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae vacuolar hydrolases. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2500–2510. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida K., Kuromitsu Z., Ogawa N., Oshima Y. Mode of expression of the positive regulatory genes PHO2 and PHO4 of the phosphatase regulon in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 May;217(1):31–39. doi: 10.1007/BF00330939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida K., Ogawa N., Oshima Y. Function of the PHO regulatory genes for repressible acid phosphatase synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 May;217(1):40–46. doi: 10.1007/BF00330940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubenko G. S., Park F. J., Jones E. W. Mutations in PEP4 locus of Saccharomyces cerevisiae block final step in maturation of two vacuolar hydrolases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):510–514. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]