Abstract
A system to detect a minimal function of Saccharomyces cerevisiae centromeres in vivo has been developed. Centromere DNA mutants have been examined and found to be active in a plasmid copy number control assay in the absence of segregation. The experiments allow the identification of a minimal centromere unit, CDE III, independently of its ability to mediate chromosome segregation. Centromere-mediated plasmid copy number control correlates with the ability of CDE III to assemble a DNA-protein complex. Cells forced to maintain excess copies of CDE III exhibit increased loss of a nonessential artificial chromosome. Thus, segregationally impaired centromeres can have negative effects in trans on chromosome segregation. The use of a plasmid copy number control assay has allowed assembly steps preceding chromosome segregation to be defined.
Full text
PDF

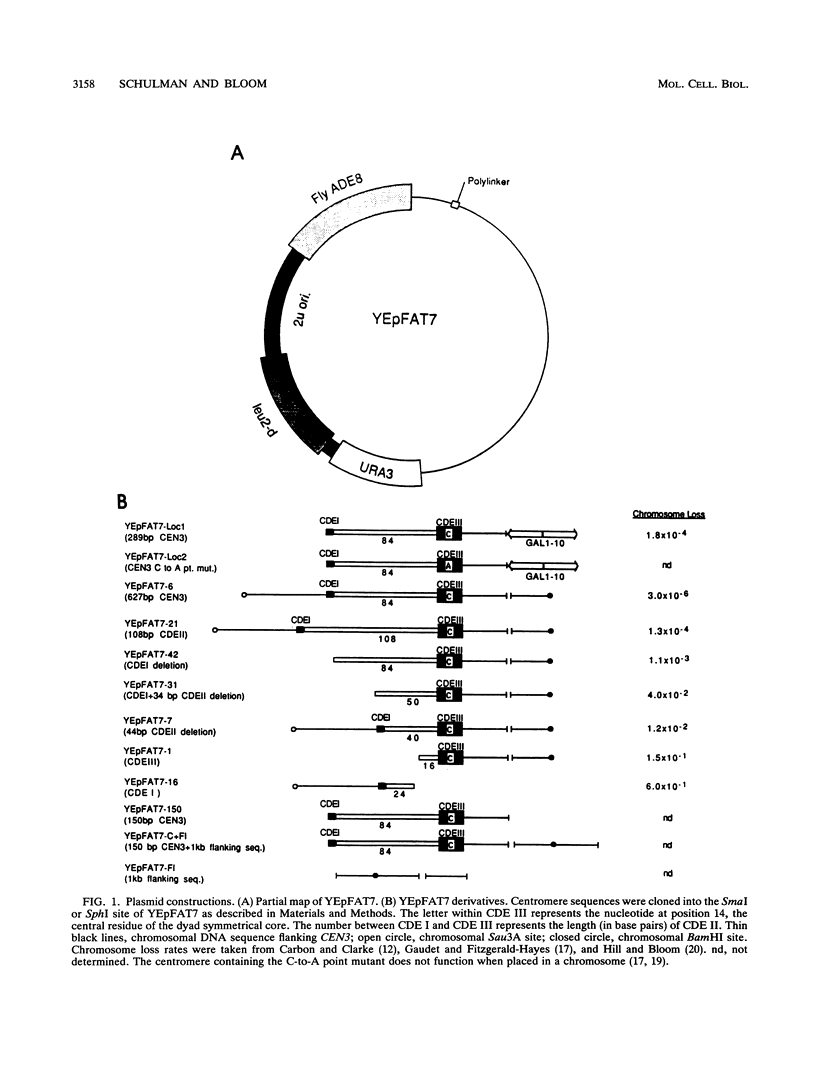








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apostol B., Greer C. L. Copy number and stability of yeast 2 mu-based plasmids carrying a transcription-conditional centromere. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):59–68. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90008-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker R. E., Fitzgerald-Hayes M., O'Brien T. C. Purification of the yeast centromere binding protein CP1 and a mutational analysis of its binding site. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10843–10850. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernat R. L., Borisy G. G., Rothfield N. F., Earnshaw W. C. Injection of anticentromere antibodies in interphase disrupts events required for chromosome movement at mitosis. J Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;111(4):1519–1533. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.4.1519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernat R. L., Delannoy M. R., Rothfield N. F., Earnshaw W. C. Disruption of centromere assembly during interphase inhibits kinetochore morphogenesis and function in mitosis. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1229–1238. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90045-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bitoun R., Zamir A. Spontaneous amplification of yeast CEN ARS plasmids. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Jul;204(1):98–102. doi: 10.1007/BF00330194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom K. S., Carbon J. Yeast centromere DNA is in a unique and highly ordered structure in chromosomes and small circular minichromosomes. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):305–317. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90147-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bram R. J., Kornberg R. D. Isolation of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae centromere DNA-binding protein, its human homolog, and its possible role as a transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):403–409. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai M. J., Davis R. W. Purification of a yeast centromere-binding protein that is able to distinguish single base-pair mutations in its recognition site. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2544–2550. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai M., Davis R. W. Yeast centromere binding protein CBF1, of the helix-loop-helix protein family, is required for chromosome stability and methionine prototrophy. Cell. 1990 May 4;61(3):437–446. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90525-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbon J., Clarke L. Structural and functional analysis of a yeast centromere (CEN3). J Cell Sci Suppl. 1984;1:43–58. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1984.supplement_1.4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chlebowicz-Sledziewska E., Sledziewski A. Z. Construction of multicopy yeast plasmids with regulated centromere function. Gene. 1985;39(1):25–31. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90103-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke L., Baum M. P. Functional analysis of a centromere from fission yeast: a role for centromere-specific repeated DNA sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):1863–1872. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.1863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke L., Carbon J. The structure and function of yeast centromeres. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:29–55. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.000333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erhart E., Hollenberg C. P. The presence of a defective LEU2 gene on 2 mu DNA recombinant plasmids of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is responsible for curing and high copy number. J Bacteriol. 1983 Nov;156(2):625–635. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.2.625-635.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Futcher B., Carbon J. Toxic effects of excess cloned centromeres. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2213–2222. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H., Weinert T. A. Checkpoints: controls that ensure the order of cell cycle events. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):629–634. doi: 10.1126/science.2683079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegemann J. H., Shero J. H., Cottarel G., Philippsen P., Hieter P. Mutational analysis of centromere DNA from chromosome VI of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2523–2535. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill A., Bloom K. Acquisition and processing of a conditional dicentric chromosome in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):1368–1370. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.1368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill A., Bloom K. Genetic manipulation of centromere function. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2397–2405. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jehn B., Niedenthal R., Hegemann J. H. In vivo analysis of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae centromere CDEIII sequence: requirements for mitotic chromosome segregation. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):5212–5221. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.5212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsbury J., Koshland D. Centromere-dependent binding of yeast minichromosomes to microtubules in vitro. Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):483–495. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshland D., Hieter P. Visual assay for chromosome ploidy. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:351–372. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55024-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechner J., Carbon J. A 240 kd multisubunit protein complex, CBF3, is a major component of the budding yeast centromere. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):717–725. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90501-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellor J., Jiang W., Funk M., Rathjen J., Barnes C. A., Hinz T., Hegemann J. H., Philippsen P. CPF1, a yeast protein which functions in centromeres and promoters. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):4017–4026. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07623.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moens P. B. Kinetochore microtubule numbers of different sized chromosomes. J Cell Biol. 1979 Dec;83(3):556–561. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.3.556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy M. R., Fowlkes D. M., Fitzgerald-Hayes M. Analysis of centromere function in Saccharomyces cerevisiae using synthetic centromere mutants. Chromosoma. 1991 Dec;101(3):189–197. doi: 10.1007/BF00355368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng R., Carbon J. Mutational and in vitro protein-binding studies on centromere DNA from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4522–4534. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Runge K. W., Wellinger R. J., Zakian V. A. Effects of excess centromeres and excess telomeres on chromosome loss rates. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):2919–2928. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.2919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Runge K. W., Zakian V. A. Introduction of extra telomeric DNA sequences into Saccharomyces cerevisiae results in telomere elongation. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1488–1497. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders M., Fitzgerald-Hayes M., Bloom K. Chromatin structure of altered yeast centromeres. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(1):175–179. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman I., Bloom K. S. Centromeres: an integrated protein/DNA complex required for chromosome movement. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:311–336. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.001523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shero J. H., Koval M., Spencer F., Palmer R. E., Hieter P., Koshland D. Analysis of chromosome segregation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:749–773. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94057-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simerly C., Balczon R., Brinkley B. R., Schatten G. Microinjected centromere [corrected] kinetochore antibodies interfere with chromosome movement in meiotic and mitotic mouse oocytes. J Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;111(4):1491–1504. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.4.1491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. R., Smyth A. P., Moir D. T. Amplification of large artificial chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8242–8246. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer F., Hieter P. Centromere DNA mutations induce a mitotic delay in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):8908–8912. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.8908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschumper G., Carbon J. Copy number control by a yeast centromere. Gene. 1983 Aug;23(2):221–232. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90054-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







