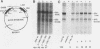Abstract
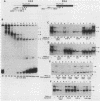
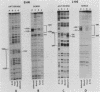
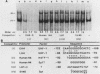
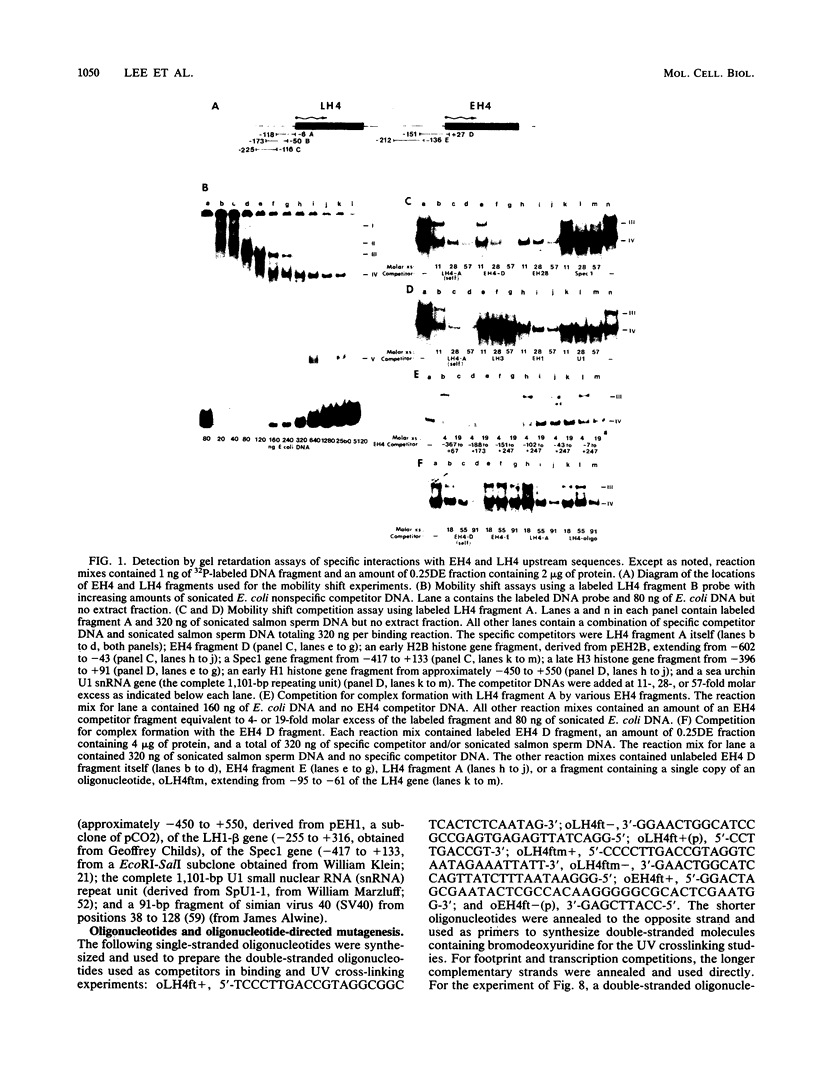
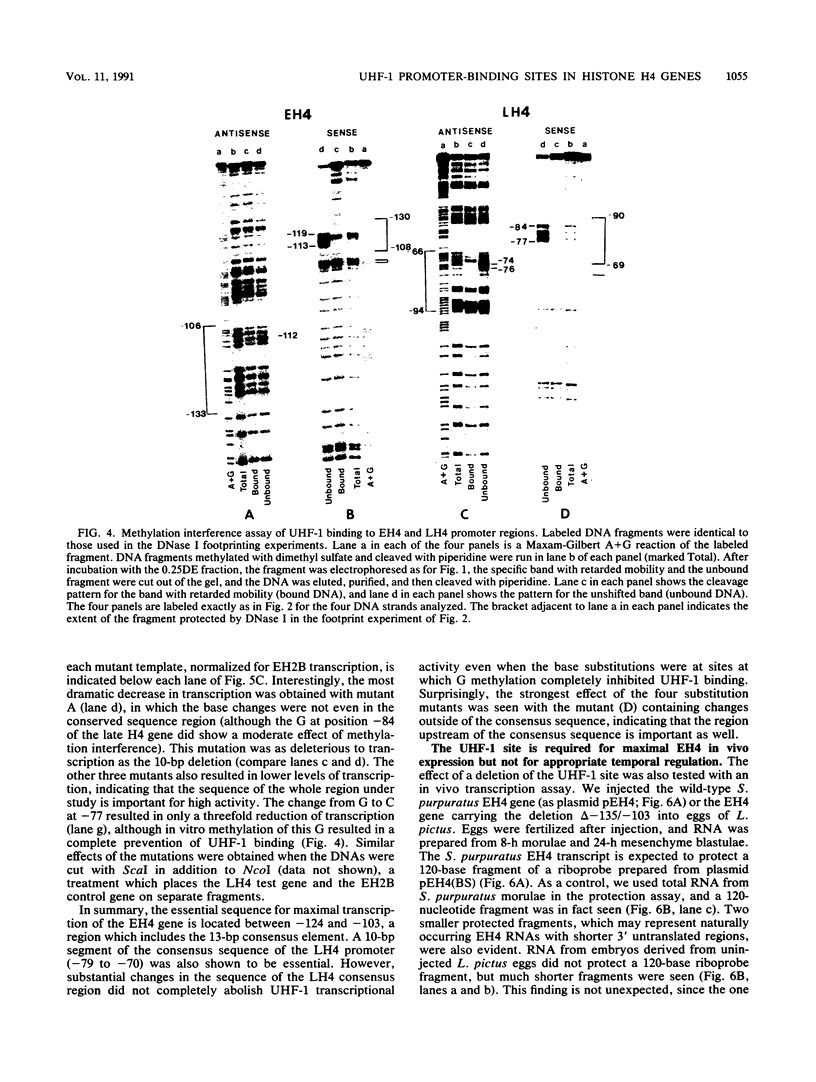
A protein, denoted UHF-1, was found to bind upstream of the transcriptional start site of both the early and late H4 (EH4 and LH4) histone genes of the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. A nuclear extract from hatching blastulae contained proteins that bind to EH4 and LH4 promoter fragments in a band shift assay and produced sharp DNase I footprints upstream of the EH4 gene (from -133 to -106) and the LH4 gene (from -94 to -66). DNase I footprinting performed in the presence of EH4 and LH4 promoter competitor DNAs indicated that UHF-1 binds more strongly to the EH4 site. A sequence match of 11 of 13 nucleotides was found within the two footprinted regions: [sequence: see text]. Methylation interference and footprinting experiments showed that UHF-1 bound to the two sites somewhat differently. DNA-protein UV cross-linking studies indicated that UHF-1 has an electrophoretic mobility on sodium dodecyl sulfate-acrylamide gels of approximately 85 kDa and suggested that additional proteins, specific to each promoter, bind to each site. In vitro and in vivo assays were used to demonstrate that the UHF-1-binding site is essential for maximal transcription of the H4 genes. Deletion of the EH4 footprinted region resulted in a 3-fold decrease in transcription in a nuclear extract and a 2.6-fold decrease in expression in morulae from templates that had been injected into eggs. In the latter case, deletion of the binding site did not grossly disrupt the temporal program of expression from the injected EH4 genes. LH4 templates containing a 10-bp deletion in the consensus region or base substitutions in the footprinted region were transcribed at 14 to 58% of the level of the wild-type LH4 template. UHF-1 is therefore essential for maximal expression of the early and late H4 genes.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barberis A., Superti-Furga G., Vitelli L., Kemler I., Busslinger M. Developmental and tissue-specific regulation of a novel transcription factor of the sea urchin. Genes Dev. 1989 May;3(5):663–675. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.5.663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busslinger M., Barberis A. Synthesis of sperm and late histone cDNAs of the sea urchin with a primer complementary to the conserved 3' terminal palindrome: evidence for tissue-specific and more general histone gene variants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5676–5680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Childs G., Maxson R., Kedes L. H. Histone gene expression during sea urchin embryogenesis: isolation and characterization of early and late messenger RNAs of Strongylocentrotus purpuratus by gene-specific hybridization and template activity. Dev Biol. 1979 Nov;73(1):153–173. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90144-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Childs G., Nocente-McGrath C., Lieber T., Holt C., Knowles J. A. Sea urchin (lytechinus pictus) late-stage histone H3 and H4 genes: characterization and mapping of a clustered but nontandemly linked multigene family. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):383–393. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90132-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chodosh L. A., Carthew R. W., Sharp P. A. A single polypeptide possesses the binding and transcription activities of the adenovirus major late transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4723–4733. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerc R. G., Bucher P., Strub K., Birnstiel M. L. Transcription of a cloned Xenopus laevis H4 histone gene in the homologous frog oocyte system depends on an evolutionary conserved sequence motif in the -50 region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Dec 20;11(24):8641–8657. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.24.8641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colin A. M., Catlin T. L., Kidson S. H., Maxson R. Closely linked early and late histone H2B genes are differentially expressed after microinjection into sea urchin zygotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):507–510. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colin A. M. Rapid repetitive microinjection. Methods Cell Biol. 1986;27:395–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosson J., Kemler I., Tanno S., Busslinger M. Promoter of a somatic histone H2B gene of the sea urchin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 11;16(9):4175–4175. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.9.4175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dailey L., Hanly S. M., Roeder R. G., Heintz N. Distinct transcription factors bind specifically to two regions of the human histone H4 promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7241–7245. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dailey L., Roberts S. B., Heintz N. Purification of the human histone H4 gene-specific transcription factors H4TF-1 and H4TF-2. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12B):1700–1712. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12b.1700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson E. H., Flytzanis C. N., Lee J. J., Robinson J. J., Rose S. J., 3rd, Sucov H. M. Lineage-specific gene expression in the sea urchin embryo. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1985;50:321–328. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1985.050.01.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiLiberto M., Lai Z. C., Fei H., Childs G. Developmental control of promoter-specific factors responsible for the embryonic activation and inactivation of the sea urchin early histone H3 gene. Genes Dev. 1989 Jul;3(7):973–985. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.7.973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher C., Heintz N., Roeder R. G. Purification and characterization of OTF-1, a transcription factor regulating cell cycle expression of a human histone H2b gene. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):773–781. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90100-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flytzanis C. N., McMahon A. P., Hough-Evans B. R., Katula K. S., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Persistence and integration of cloned DNA in postembryonic sea urchins. Dev Biol. 1985 Apr;108(2):431–442. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90046-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M. Hatching in the sea urchin Lytechinus pictus is accompanied by a shift in histone H4 gene activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4135–4139. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halsell S. R., Ito M., Maxson R. Differential expression of early and late embryonic histone genes in adult tissues of the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. Dev Biol. 1987 Jan;119(1):268–274. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90228-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanly S. M., Bleecker G. C., Heintz N. Identification of promoter elements necessary for transcriptional regulation of a human histone H4 gene in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;5(2):380–389. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.2.380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardin S. H., Carpenter C. D., Hardin P. E., Bruskin A. M., Klein W. H. Structure of the Spec1 gene encoding a major calcium-binding protein in the embryonic ectoderm of the sea urchin, Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. J Mol Biol. 1985 Nov 20;186(2):243–255. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90101-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey R. P., Robins A. J., Wells J. R. Independently evolving chicken histone H2B genes: identification of a ubiquitous H2B-specific 5' element. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 11;10(23):7851–7863. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.23.7851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentschel C. C., Birnstiel M. L. The organization and expression of histone gene families. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):301–313. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90048-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hieter P. A., Hendricks M. B., Hemminki K., Weinberg E. S. Histone gene switch in the sea urchin embryo. Identification of late embryonic histone messenger ribonucleic acids and the control of their synthesis. Biochemistry. 1979 Jun 26;18(13):2707–2716. doi: 10.1021/bi00580a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holthuis J., Owen T. A., van Wijnen A. J., Wright K. L., Ramsey-Ewing A., Kennedy M. B., Carter R., Cosenza S. C., Soprano K. J., Lian J. B. Tumor cells exhibit deregulation of the cell cycle histone gene promoter factor HiNF-D. Science. 1990 Mar 23;247(4949 Pt 1):1454–1457. doi: 10.1126/science.247.4949.1454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito M., Bell J., Lyons G., Maxson R. Synthesis and turnover of late H2B histone mRNA in developing embryos of the sea urchin, Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. Dev Biol. 1988 Sep;129(1):147–158. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90169-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Eukaryotic transcriptional regulatory proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:799–839. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.004055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaumeyer J. F., Weinberg E. S. Sequence, organization and expression of late embryonic H3 and H4 histone genes from the sea urchin, Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4557–4576. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemler I., Busslinger M. Characterization of two nonallelic pairs of late histone H2A and H2B genes of the sea urchin: differential regulation in the embryo and tissue-specific expression in the adult. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3746–3754. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles J. A., Childs G. J. Comparison of the late H1 histone genes of the sea urchins Lytechinus pictus and Strongelocentrotus purpuratus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 24;14(20):8121–8133. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.20.8121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles J. A., Childs G. J. Temporal expression of late histone messenger RNA in the sea urchin Lytechinus pictus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2411–2415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles J. A., Lai Z. C., Childs G. J. Isolation, characterization, and expression of the gene encoding the late histone subtype H1-gamma of the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):478–485. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroeger P., Stewart C., Schaap T., van Wijnen A., Hirshman J., Helms S., Stein G., Stein J. Proximal and distal regulatory elements that influence in vivo expression of a cell cycle-dependent human H4 histone gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):3982–3986. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.3982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaBella F., Sive H. L., Roeder R. G., Heintz N. Cell-cycle regulation of a human histone H2b gene is mediated by the H2b subtype-specific consensus element. Genes Dev. 1988 Jan;2(1):32–39. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.1.32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai Z. C., Childs G. Characterization of the structure and transcriptional patterns of the gene encoding the late histone subtype H1-beta of the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1842–1844. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai Z. C., DeAngelo D. J., DiLiberto M., Childs G. An embryonic enhancer determines the temporal activation of a sea urchin late H1 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2315–2321. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai Z. C., Maxson R., Childs G. Both basal and ontogenic promoter elements affect the timing and level of expression of a sea urchin H1 gene during early embryogenesis. Genes Dev. 1988 Feb;2(2):173–183. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.2.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieber T., Weisser K., Childs G. Analysis of histone gene expression in adult tissues of the sea urchins Strongylocentrotus purpuratus and Lytechinus pictus: tissue-specific expression of sperm histone genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2602–2612. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauron A., Kedes L., Hough-Evans B. R., Davidson E. H. Accumulation of individual histone mRNAs during embryogenesis of the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. Dev Biol. 1982 Dec;94(2):425–434. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90359-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxson R. E., Jr, Wilt F. H. Accumulation of the early histone messenger RNAs during the development of Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. Dev Biol. 1982 Dec;94(2):435–440. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90360-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxson R. E., Jr, Wilt F. H. The rate of synthesis of histone mRNA during the development of sea urchin embryos (Strongylocentrotus purpuratus). Dev Biol. 1981 Apr 30;83(2):380–386. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90485-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxson R., Cohn R., Kedes L., Mohun T. Expression and organization of histone genes. Annu Rev Genet. 1983;17:239–277. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.17.120183.001323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxson R., Mohun T., Gormezano G., Childs G., Kedes L. Distinct organizations and patterns of expression of early and late histone gene sets in the sea urchin. Nature. 1983 Jan 13;301(5896):120–125. doi: 10.1038/301120a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxson R., Mohun T., Gormezano G., Kedes L. Evolution of late H2A, H2B, and H4 histone genes of the sea urchin, Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 23;15(24):10569–10582. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.24.10569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon A. P., Flytzanis C. N., Hough-Evans B. R., Katula K. S., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Introduction of cloned DNA into sea urchin egg cytoplasm: replication and persistence during embryogenesis. Dev Biol. 1985 Apr;108(2):420–430. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90045-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris G. F., Marzluff W. F. A factor in sea urchin eggs inhibits transcription in isolated nuclei by sea urchin RNA polymerase III. Biochemistry. 1983 Feb 1;22(3):645–653. doi: 10.1021/bi00272a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris G. F., Price D. H., Marzluff W. F. Synthesis of U1 RNA in a DNA-dependent system from sea urchin embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3674–3678. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash M. A., Sakallah S., Santiago C., Yu J. C., Marzluff W. F. A developmental switch in sea urchin U1 RNA. Dev Biol. 1989 Aug;134(2):289–296. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(89)90101-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overton G. C., Weinberg E. S. Length and sequence heterogeneity of the histone gene repeat unit of the sea urchin, S. purpuratus. Cell. 1978 Jun;14(2):247–257. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90111-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry M., Thomsen G. H., Roeder R. G. Genomic organization and nucleotide sequence of two distinct histone gene clusters from Xenopus laevis. Identification of novel conserved upstream sequence elements. J Mol Biol. 1985 Oct 5;185(3):479–499. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90065-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts S. B., Weisser K. E., Childs G. Sequence comparisons of non-allelic late histone genes and their early stage counterparts. Evidence for gene conversion within the sea urchin late stage gene family. J Mol Biol. 1984 Apr 25;174(4):647–662. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90088-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner W., Kunz G., Daetwyler H., Telford J., Smith H. O., Birnstiel M. L. Genes and spacers of cloned sea urchin histone DNA analyzed by sequencing. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):655–671. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90249-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss F., Varshavsky A. A protein binds to a satellite DNA repeat at three specific sites that would be brought into mutual proximity by DNA folding in the nucleosome. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):889–901. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90424-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sures I., Lowry J., Kedes L. H. The DNA sequence of sea urchin (S. purpuratus) H2A, H2B and H3 histone coding and spacer regions. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):1033–1044. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90287-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tung L., Morris G. F., Yager L. N., Weinberg E. S. Sea urchin early and late H4 histone genes bind a specific transcription factor in a stable preinitiation complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1476–1487. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uzman J. A., Wilt F. H. The role of RNA polymerase initiation and elongation in control of total RNA and histone mRNA synthesis in sea urchin embryos. Dev Biol. 1984 Nov;106(1):174–180. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90073-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. Production of single-stranded plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:3–11. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitelli L., Kemler I., Lauber B., Birnstiel M. L., Busslinger M. Developmental regulation of micro-injected histone genes in sea urchin embryos. Dev Biol. 1988 May;127(1):54–63. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90188-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg E. S., Hendricks M. B., Hemminki K., Kuwabara P. E., Farrelly L. A. Timing and rates of synthesis of early histone mRNA in the embryo of Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. Dev Biol. 1983 Jul;98(1):117–129. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90340-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C., Wilson S., Walker B., Dawid I., Paisley T., Zimarino V., Ueda H. Purification and properties of Drosophila heat shock activator protein. Science. 1987 Nov 27;238(4831):1247–1253. doi: 10.1126/science.3685975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Wijnen A. J., Stein J. L., Stein G. S. A nuclear protein with affinity for the 5' flanking region of a cell cycle dependent human H4 histone gene in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 25;15(4):1679–1698. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.4.1679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Wijnen A. J., Wright K. L., Lian J. B., Stein J. L., Stein G. S. Human H4 histone gene transcription requires the proliferation-specific nuclear factor HiNF-D. Auxiliary roles for HiNF-C (Sp1-like) and HiNF-A (high mobility group-like). J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):15034–15042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]