Abstract
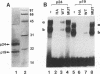
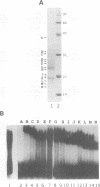
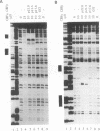
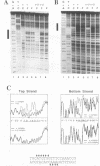
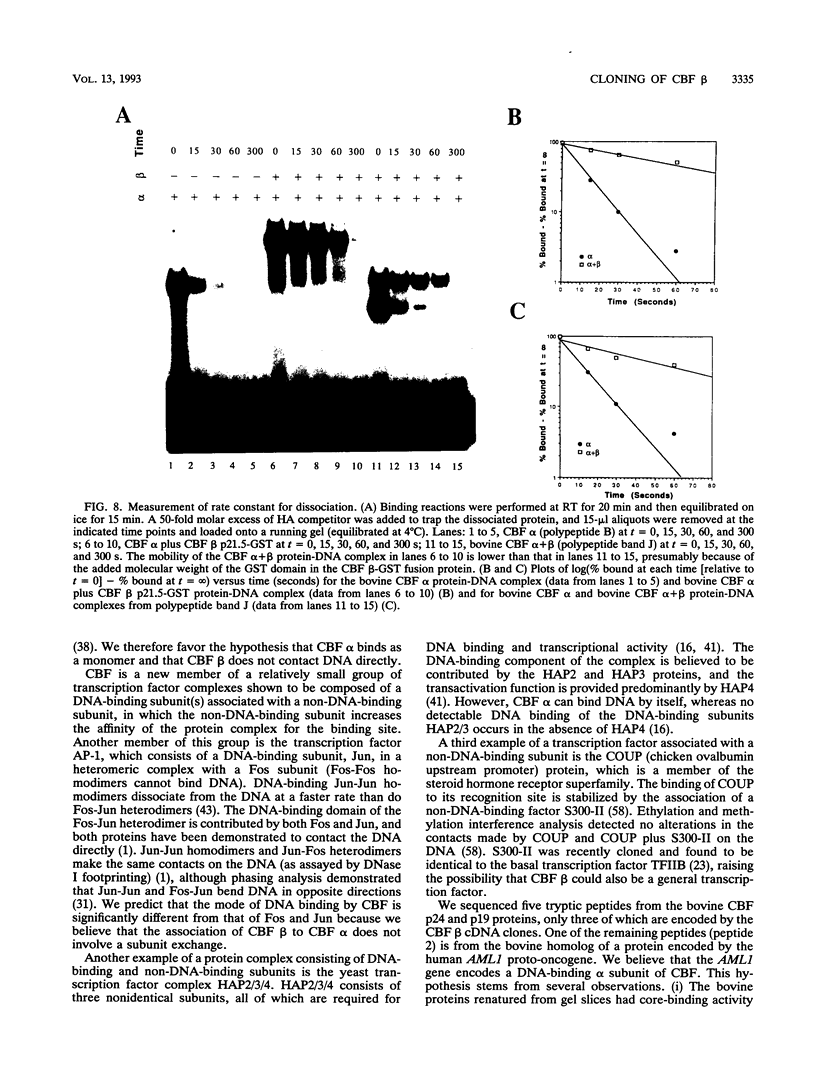
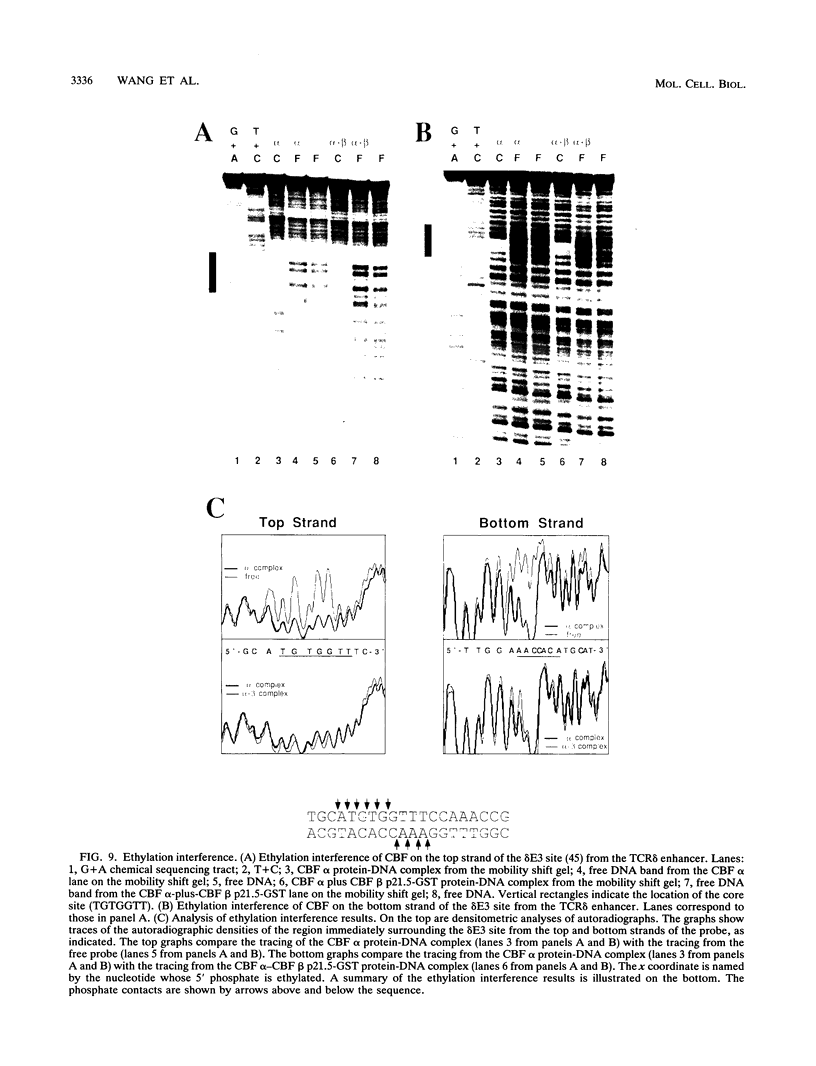
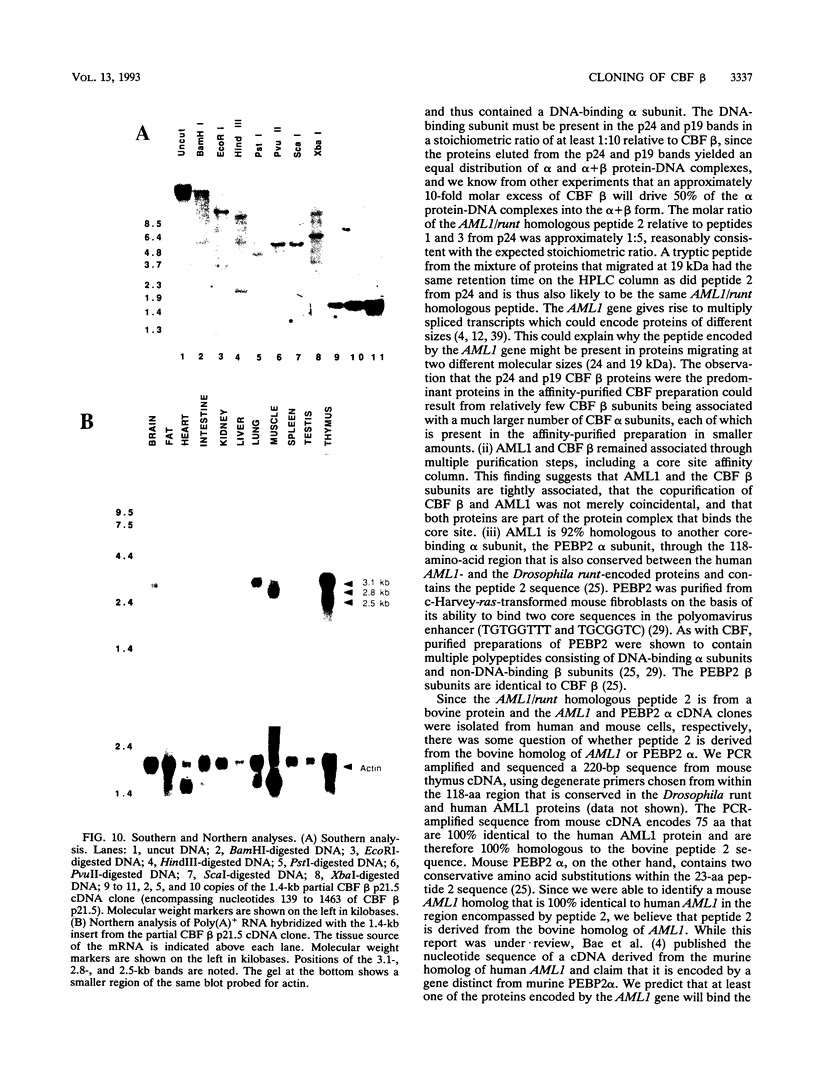
Moloney murine leukemia virus causes thymic leukemias when injected into newborn mice. A major determinant of the thymic disease specificity of Moloney virus genetically maps to the conserved viral core motif in the Moloney virus enhancer. Point mutations introduced into the core site significantly shifted the disease specificity of the Moloney virus from thymic leukemia to erythroid leukemia (N.A. Speck, B. Renjifo, E. Golemis, T.N. Fredrickson, J.W. Hartley, and N. Hopkins, Genes Dev. 4:233-242, 1990). We previously reported the purification of core-binding factors (CBF) from calf thymus nuclei (S. Wang and N.A. Speck, Mol. Cell. Biol. 12:89-102, 1992). CBF binds to core sites in murine leukemia virus and T-cell receptor enhancers. Affinity-purified CBF contains multiple polypeptides. In this study, we sequenced five tryptic peptides from two of the bovine CBF proteins and isolated three cDNA clones from a mouse thymus cDNA library encoding three of the tryptic peptides from the bovine proteins. The cDNA clones, which we call CBF beta p22.0, CBF beta p21.5, and CBF beta p17.6, encode three highly related but distinct proteins with deduced molecular sizes of 22.0, 21.5, and 17.6 kDa that appear to be translated from multiply spliced mRNAs transcribed from the same gene. CBF beta p22.0, CBF beta p21.5, and CBF beta p17.6 do not by themselves bind the core site. However, CBF beta p22.0 and CBF beta p21.5 form a complex with DNA-binding CBF alpha subunits and as a result decrease the rate of dissociation of the CBF protein-DNA complex. Association of the CBF beta subunits does not extend the phosphate contacts in the binding site. We propose that CBF beta is a non-DNA-binding subunit of CBF and does not contact DNA directly.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abate C., Luk D., Gentz R., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Curran T. Expression and purification of the leucine zipper and DNA-binding domains of Fos and Jun: both Fos and Jun contact DNA directly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1032–1036. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aebersold R. H., Leavitt J., Saavedra R. A., Hood L. E., Kent S. B. Internal amino acid sequence analysis of proteins separated by one- or two-dimensional gel electrophoresis after in situ protease digestion on nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):6970–6974. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.6970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bae S. C., Yamaguchi-Iwai Y., Ogawa E., Maruyama M., Inuzuka M., Kagoshima H., Shigesada K., Satake M., Ito Y. Isolation of PEBP2 alpha B cDNA representing the mouse homolog of human acute myeloid leukemia gene, AML1. Oncogene. 1993 Mar;8(3):809–814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell T. K., Weintraub H. Differences and similarities in DNA-binding preferences of MyoD and E2A protein complexes revealed by binding site selection. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1104–1110. doi: 10.1126/science.2174572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boral A. L., Okenquist S. A., Lenz J. Identification of the SL3-3 virus enhancer core as a T-lymphoma cell-specific element. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):76–84. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.76-84.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll S. B., Scott M. P. Zygotically active genes that affect the spatial expression of the fushi tarazu segmentation gene during early Drosophila embryogenesis. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):113–126. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90543-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll S. B., Vavra S. H. The zygotic control of Drosophila pair-rule gene expression. II. Spatial repression by gap and pair-rule gene products. Development. 1989 Nov;107(3):673–683. doi: 10.1242/dev.107.3.673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daga A., Tighe J. E., Calabi F. Leukaemia/Drosophila homology. Nature. 1992 Apr 9;356(6369):484–484. doi: 10.1038/356484b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsburg S. L., Guarente L. Identification and characterization of HAP4: a third component of the CCAAT-bound HAP2/HAP3 heteromer. Genes Dev. 1989 Aug;3(8):1166–1178. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.8.1166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch M., Levine M. Complementary patterns of even-skipped and fushi tarazu expression involve their differential regulation by a common set of segmentation genes in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1987 Nov;1(9):981–995. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.9.981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hager D. A., Burgess R. R. Elution of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels, removal of sodium dodecyl sulfate, and renaturation of enzymatic activity: results with sigma subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase, wheat germ DNA topoisomerase, and other enzymes. Anal Biochem. 1980 Nov 15;109(1):76–86. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallberg B., Schmidt J., Luz A., Pedersen F. S., Grundström T. SL3-3 enhancer factor 1 transcriptional activators are required for tumor formation by SL3-3 murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4177–4181. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4177-4181.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper K. L., Parkhurst S. M., Ish-Horowicz D. Spatial control of hairy protein expression during embryogenesis. Development. 1989 Nov;107(3):489–504. doi: 10.1242/dev.107.3.489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ing N. H., Beekman J. M., Tsai S. Y., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Members of the steroid hormone receptor superfamily interact with TFIIB (S300-II). J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 5;267(25):17617–17623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Eukaryotic transcriptional regulatory proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:799–839. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.004055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Tjian R. Affinity purification of sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5889–5893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon D., Richardson W. D., Markham A. F., Smith A. E. Sequence requirements for nuclear location of simian virus 40 large-T antigen. Nature. 1984 Sep 6;311(5981):33–38. doi: 10.1038/311033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamachi Y., Ogawa E., Asano M., Ishida S., Murakami Y., Satake M., Ito Y., Shigesada K. Purification of a mouse nuclear factor that binds to both the A and B cores of the polyomavirus enhancer. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):4808–4819. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.4808-4819.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kania M. A., Bonner A. S., Duffy J. B., Gergen J. P. The Drosophila segmentation gene runt encodes a novel nuclear regulatory protein that is also expressed in the developing nervous system. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1701–1713. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerppola T. K., Curran T. Fos-Jun heterodimers and Jun homodimers bend DNA in opposite orientations: implications for transcription factor cooperativity. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):317–326. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90621-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. At least six nucleotides preceding the AUG initiator codon enhance translation in mammalian cells. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 20;196(4):947–950. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters D. B., Griggs C. T., Berde C. B. High sensitivity quantification of RNA from gels and autoradiograms with affordable optical scanning. Biotechniques. 1992 Jun;12(6):902-6, 908-11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melnikova I. N., Crute B. E., Wang S., Speck N. A. Sequence specificity of the core-binding factor. J Virol. 1993 Apr;67(4):2408–2411. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.4.2408-2411.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyoshi H., Shimizu K., Kozu T., Maseki N., Kaneko Y., Ohki M. t(8;21) breakpoints on chromosome 21 in acute myeloid leukemia are clustered within a limited region of a single gene, AML1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10431–10434. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi Y., Nogawa H., Hashimoto Y., Kishi J., Hayakawa T. Accumulation of collagen III at the cleft points of developing mouse submandibular epithelium. Development. 1988 Sep;104(1):51–59. doi: 10.1242/dev.104.1.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olesen J. T., Guarente L. The HAP2 subunit of yeast CCAAT transcriptional activator contains adjacent domains for subunit association and DNA recognition: model for the HAP2/3/4 complex. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1714–1729. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prosser H. M., Wotton D., Gegonne A., Ghysdael J., Wang S., Speck N. A., Owen M. J. A phorbol ester response element within the human T-cell receptor beta-chain enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9934–9938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Voulalas P. J., Franza B. R., Jr, Curran T. Fos and Jun bind cooperatively to the AP-1 site: reconstitution in vitro. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12B):1687–1699. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12b.1687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redondo J. M., Pfohl J. L., Hernandez-Munain C., Wang S., Speck N. A., Krangel M. S. Indistinguishable nuclear factor binding to functional core sites of the T-cell receptor delta and murine leukemia virus enhancers. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;12(11):4817–4823. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.11.4817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redondo J. M., Pfohl J. L., Krangel M. S. Identification of an essential site for transcriptional activation within the human T-cell receptor delta enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;11(11):5671–5680. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.11.5671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J., Dilworth S. M., Laskey R. A., Dingwall C. Two interdependent basic domains in nucleoplasmin nuclear targeting sequence: identification of a class of bipartite nuclear targeting sequence. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):615–623. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90245-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salinovich O., Montelaro R. C. Reversible staining and peptide mapping of proteins transferred to nitrocellulose after separation by sodium dodecylsulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1986 Aug 1;156(2):341–347. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90263-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satake M., Inuzuka M., Shigesada K., Oikawa T., Ito Y. Differential expression of subspecies of polyomavirus and murine leukemia virus enhancer core binding protein, PEBP2, in various hematopoietic cells. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1992 Jul;83(7):714–722. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1992.tb01971.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Gilbert W. Contacts between Escherichia coli RNA polymerase and an early promoter of phage T7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):122–126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speck N. A., Renjifo B., Golemis E., Fredrickson T. N., Hartley J. W., Hopkins N. Mutation of the core or adjacent LVb elements of the Moloney murine leukemia virus enhancer alters disease specificity. Genes Dev. 1990 Feb;4(2):233–242. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.2.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speck N. A., Renjifo B., Hopkins N. Point mutations in the Moloney murine leukemia virus enhancer identify a lymphoid-specific viral core motif and 1,3-phorbol myristate acetate-inducible element. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):543–550. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.543-550.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer D. M., Hsiang Y. H., Goldman J. P., Raulet D. H. Identification of a T-cell-specific transcriptional enhancer located 3' of C gamma 1 in the murine T-cell receptor gamma locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):800–804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornell A., Hallberg B., Grundström T. Binding of SL3-3 enhancer factor 1 transcriptional activators to viral and chromosomal enhancer sequences. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):42–50. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.42-50.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornell A., Hallberg B., Grundström T. Differential protein binding in lymphocytes to a sequence in the enhancer of the mouse retrovirus SL3-3. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1625–1637. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. Y., Sagami I., Wang H., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Interactions between a DNA-binding transcription factor (COUP) and a non-DNA binding factor (S300-II). Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):701–709. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90328-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. W., Speck N. A. Purification of core-binding factor, a protein that binds the conserved core site in murine leukemia virus enhancers. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):89–102. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winoto A., Baltimore D. A novel, inducible and T cell-specific enhancer located at the 3' end of the T cell receptor alpha locus. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):729–733. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03432.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]