Abstract
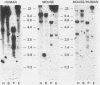
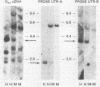
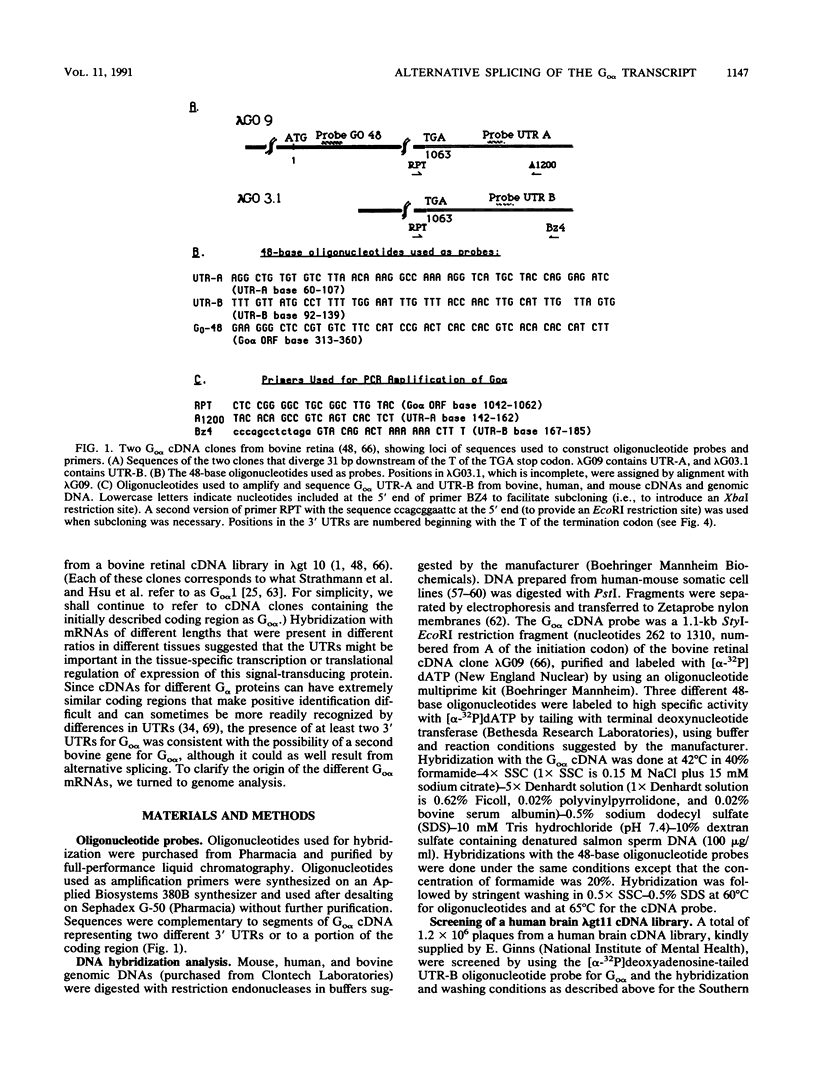
Go alpha, (gene symbol GNA01), a member of the signal-transducing guanine nucleotide-binding (G) protein family, has been implicated in ion channel regulation. Some tissues contain multiple Go alpha mRNAs of different sizes that differ in the 3' untranslated regions (UTRs). Using sequence-specific 48-base oligonucleotides, two complementary to the different 3' UTRs and one complementary to the coding region, we investigated the origin of the multiple Go alpha transcripts, the organization of the Go alpha gene, the interspecies conservation of 3' UTRs, and the chromosomal localization of Go alpha. Oligonucleotides labeled to high specific activity by using terminal deoxynucleotidyltransferase each hybridized with a single band of restriction enzyme-digested mouse and human DNAs. In three of four digests of human DNA, the two probes specific for the different 3' UTRs hybridized with the same restriction fragment. Thus, these nucleotide sequences are in close proximity in the human genome. The order of the UTRs in the bovine, human, and mouse genomes was confirmed directly by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification and sequencing. Hybridization of bovine oligonucleotide sequence with mouse and human genomic DNA indicated a high degree of interspecies sequence conservation: conservation was confirmed by PCR amplification and sequencing. Bands detected by both UTR probes, as well as the predominant bands detected by a bovine Go alpha cDNA, segregated with human chromosome 16 on Southern blot analysis of human-mouse somatic cell hybrids. We conclude that Go alpha mRNAs with different 3' UTRs arise by alternative splicing of transcripts from a single gene. The UTRs, which exhibit a high degree of interspecies conservation, may play a role in regulation of Go alpha expression during differentiation or in specific tissues. The use of oligonucleotide probes of the type described here represents a new strategy, potentially widely applicable for mapping and elucidating structural features of genes.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angus C. W., Van Meurs K. P., Tsai S. C., Adamik R., Miedel M. C., Pan Y. C., Kung H. F., Moss J., Vaughan M. Identification of the probable site of choleragen-catalyzed ADP-ribosylation in a Go alpha-like protein based on cDNA sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5813–5816. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asano T., Morishita R., Sano M., Kato K. The GTP-binding proteins, Go and Gi2, of neural cloned cells and their changes during differentiation. J Neurochem. 1989 Oct;53(4):1195–1198. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb07414.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asano T., Semba R., Kamiya N., Ogasawara N., Kato K. Go, a GTP-binding protein: immunochemical and immunohistochemical localization in the rat. J Neurochem. 1988 Apr;50(4):1164–1169. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb10588.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashley P. L., Ellison J., Sullivan K. A., Bourne H. R., Cox D. R. Chromosomal assignment of the murine Gi alpha and Gs alpha genes. Implications for the obese mouse. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 5;262(31):15299–15301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatt C., Eversole-Cire P., Cohn V. H., Zollman S., Fournier R. E., Mohandas L. T., Nesbitt M., Lugo T., Jones D. T., Reed R. R. Chromosomal localization of genes encoding guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunits in mouse and human. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7642–7646. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brabet P., Dumuis A., Sebben M., Pantaloni C., Bockaert J., Homburger V. Immunocytochemical localization of the guanine nucleotide-binding protein Go in primary cultures of neuronal and glial cells. J Neurosci. 1988 Feb;8(2):701–708. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-02-00701.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brabet P., Pantaloni C., Rodriguez M., Martinez J., Bockaert J., Homburger V. Neuroblastoma differentiation involves the expression of two isoforms of the alpha-subunit of Go. J Neurochem. 1990 Apr;54(4):1310–1320. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb01964.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brann M. R., Collins R. M., Spiegel A. Localization of mRNAs encoding the alpha-subunits of signal-transducing G-proteins within rat brain and among peripheral tissues. FEBS Lett. 1987 Sep 28;222(1):191–198. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80218-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray P., Carter A., Guo V., Puckett C., Kamholz J., Spiegel A., Nirenberg M. Human cDNA clones for an alpha subunit of Gi signal-transduction protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5115–5119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray P., Carter A., Simons C., Guo V., Puckett C., Kamholz J., Spiegel A., Nirenberg M. Human cDNA clones for four species of G alpha s signal transduction protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):8893–8897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.8893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. M., Birnbaumer L. Ionic channels and their regulation by G protein subunits. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:197–213. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.52.030190.001213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. J., Pugh W., Blanchard S. G., McDermed J., Tam J. P. Antibody specific to the alpha subunit of the guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory protein Go: developmental appearance and immunocytochemical localization in brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4929–4933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Codina J., Olate J., Abramowitz J., Mattera R., Cook R. G., Birnbaumer L. Alpha i-3 cDNA encodes the alpha subunit of Gk, the stimulatory G protein of receptor-regulated K+ channels. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6746–6750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M. L., Hunsaker W. R. Improved hybridization assays employing tailed oligonucleotide probes: a direct comparison with 5'-end-labeled oligonucleotide probes and nick-translated plasmid probes. Anal Biochem. 1985 Dec;151(2):211–224. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90168-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eschenfeldt W. H., Puskas R. S., Berger S. L. Homopolymeric tailing. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:337–342. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52040-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong H. K., Yoshimoto K. K., Eversole-Cire P., Simon M. I. Identification of a GTP-binding protein alpha subunit that lacks an apparent ADP-ribosylation site for pertussis toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3066–3070. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freissmuth M., Casey P. J., Gilman A. G. G proteins control diverse pathways of transmembrane signaling. FASEB J. 1989 Aug;3(10):2125–2131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabrion J., Brabet P., Nguyen Than Dao B., Homburger V., Dumuis A., Sebben M., Rouot B., Bockaert J. Ultrastructural localization of the GTP-binding protein Go in neurons. Cell Signal. 1989;1(1):107–123. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(89)90025-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gierschik P., Milligan G., Pines M., Goldsmith P., Codina J., Klee W., Spiegel A. Use of specific antibodies to quantitate the guanine nucleotide-binding protein Go in brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2258–2262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith P., Backlund P. S., Jr, Rossiter K., Carter A., Milligan G., Unson C. G., Spiegel A. Purification of heterotrimeric GTP-binding proteins from brain: identification of a novel form of Go. Biochemistry. 1988 Sep 6;27(18):7085–7090. doi: 10.1021/bi00418a062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granneman J. G., Kapatos G. Developmental expression of Go in neuronal cultures from rat mesencephalon and hypothalamus. J Neurochem. 1990 Jun;54(6):1995–2001. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb04903.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyllensten U. B., Erlich H. A. Generation of single-stranded DNA by the polymerase chain reaction and its application to direct sequencing of the HLA-DQA locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7652–7656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. G., Sharp P. M. Fast and sensitive multiple sequence alignments on a microcomputer. Comput Appl Biosci. 1989 Apr;5(2):151–153. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/5.2.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn G. T., Richards B., Klinger K. W. Amplification of a highly polymorphic VNTR segment by the polymerase chain reaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 11;17(5):2140–2140. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.5.2140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu W. H., Rudolph U., Sanford J., Bertrand P., Olate J., Nelson C., Moss L. G., Boyd A. E., Codina J., Birnbaumer L. Molecular cloning of a novel splice variant of the alpha subunit of the mammalian Go protein. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):11220–11226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh H., Kozasa T., Nagata S., Nakamura S., Katada T., Ui M., Iwai S., Ohtsuka E., Kawasaki H., Suzuki K. Molecular cloning and sequence determination of cDNAs for alpha subunits of the guanine nucleotide-binding proteins Gs, Gi, and Go from rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3776–3780. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh H., Toyama R., Kozasa T., Tsukamoto T., Matsuoka M., Kaziro Y. Presence of three distinct molecular species of Gi protein alpha subunit. Structure of rat cDNAs and human genomic DNAs. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6656–6664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. T., Reed R. R. Molecular cloning of five GTP-binding protein cDNA species from rat olfactory neuroepithelium. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 15;262(29):14241–14249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi I., Shibasaki H., Takahashi K., Kikkawa S., Ui M., Katada T. Purification of GTP-binding proteins from bovine brain membranes. Identification of heterogeneity of the alpha-subunit of Go proteins. FEBS Lett. 1989 Oct 23;257(1):177–180. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81815-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozasa T., Itoh H., Tsukamoto T., Kaziro Y. Isolation and characterization of the human Gs alpha gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2081–2085. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Largent B. L., Jones D. T., Reed R. R., Pearson R. C., Snyder S. H. G protein mRNA mapped in rat brain by in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2864–2868. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavu S., Clark J., Swarup R., Matsushima K., Paturu K., Moss J., Kung H. F. Molecular cloning and DNA sequence analysis of the human guanine nucleotide-binding protein Go alpha. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jan 29;150(2):811–815. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90463-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lochrie M. A., Simon M. I. G protein multiplicity in eukaryotic signal transduction systems. Biochemistry. 1988 Jul 12;27(14):4957–4965. doi: 10.1021/bi00414a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters S. B., Stroud R. M., Bourne H. R. Family of G protein alpha chains: amphipathic analysis and predicted structure of functional domains. Protein Eng. 1986 Oct-Nov;1(1):47–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G., Tanfin Z., Goureau O., Unson C., Harbon S. Identification of both Gi2 and a novel, immunologically distinct, form of Go in rat myometrial membranes. FEBS Lett. 1989 Feb 27;244(2):411–416. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80574-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J., Vaughan M. ADP-ribosylation of guanyl nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins by bacterial toxins. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1988;61:303–379. doi: 10.1002/9780470123072.ch6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullaney I., Magee A. I., Unson C. G., Milligan G. Differential regulation of amounts of the guanine-nucleotide-binding proteins Gi and Go in neuroblastoma x glioma hybrid cells in response to dibutyryl cyclic AMP. Biochem J. 1988 Dec 1;256(2):649–656. doi: 10.1042/bj2560649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura Y., Leppert M., O'Connell P., Wolff R., Holm T., Culver M., Martin C., Fujimoto E., Hoff M., Kumlin E. Variable number of tandem repeat (VNTR) markers for human gene mapping. Science. 1987 Mar 27;235(4796):1616–1622. doi: 10.1126/science.3029872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman S. B., Wunsch C. D. A general method applicable to the search for similarities in the amino acid sequence of two proteins. J Mol Biol. 1970 Mar;48(3):443–453. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90057-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neer E. J., Michel T., Eddy R., Shows T., Seidman J. G. Genes for two homologous G-protein alpha subunits map to different human chromosomes. Hum Genet. 1987 Nov;77(3):259–262. doi: 10.1007/BF00284481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestler E. J., Erdos J. J., Terwilliger R., Duman R. S., Tallman J. F. Regulation of G proteins by chronic morphine in the rat locus coeruleus. Brain Res. 1989 Jan 9;476(2):230–239. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)91243-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestler E. J., Terwilliger R. Z., Walker J. R., Sevarino K. A., Duman R. S. Chronic cocaine treatment decreases levels of the G protein subunits Gi alpha and Go alpha in discrete regions of rat brain. J Neurochem. 1990 Sep;55(3):1079–1082. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb04602.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada F., Crow T. J., Roberts G. W. G-proteins (Gi, Go) in the basal ganglia of control and schizophrenic brain. J Neural Transm Gen Sect. 1990;79(3):227–234. doi: 10.1007/BF01245133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Grabowski P. J., Konarska M. M., Seiler S., Sharp P. A. Splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1119–1150. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price S. R., Murtagh J. J., Jr, Tsuchiya M., Serventi I. M., Van Meurs K. P., Angus C. W., Moss J., Vaughan M. Multiple forms of Go alpha mRNA: analysis of the 3'-untranslated regions. Biochemistry. 1990 May 29;29(21):5069–5076. doi: 10.1021/bi00473a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price S. R., Tsai S. C., Adamik R., Angus C. W., Serventi I. M., Tsuchiya M., Moss J., Vaughan M. Expression of Go alpha mRNA and protein in bovine tissues. Biochemistry. 1989 May 2;28(9):3803–3807. doi: 10.1021/bi00435a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapiejko P. J., Watkins D. C., Ros M., Malbon C. C. G-protein subunit mRNA levels in rat heart, liver, and adipose tissues: analysis by DNA-excess solution hybridization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 May 2;1052(2):348–350. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(90)90233-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen K., Beitner-Johnson D. B., Krystal J. H., Aghajanian G. K., Nestler E. J. Opiate withdrawal and the rat locus coeruleus: behavioral, electrophysiological, and biochemical correlates. J Neurosci. 1990 Jul;10(7):2308–2317. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-07-02308.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. C., Mann D. A. Rapid transfer of DNA from agarose gels to nylon membranes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7207–7221. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robishaw J. D., Smigel M. D., Gilman A. G. Molecular basis for two forms of the G protein that stimulates adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9587–9590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ros M., Northup J. K., Malbon C. C. Steady-state levels of G-proteins and beta-adrenergic receptors in rat fat cells. Permissive effects of thyroid hormones. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 25;263(9):4362–4368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouot B., Carrette J., Lafontan M., Lan Tran P., Fehrentz J. A., Bockaert J., Toutant M. The adipocyte Go alpha-immunoreactive polypeptide is different from the alpha subunit of the brain Go protein. Biochem J. 1989 May 15;260(1):307–310. doi: 10.1042/bj2600307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shows T. B., Brown J. A., Haley L. L., Byers M. G., Eddy R. L., Cooper E. S., Goggin A. P. Assignment of the beta-glucuronidase structural gene to the pter leads to q22 region of chromosome 7 in man. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1978;21(1-2):99–104. doi: 10.1159/000130882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shows T. B. Human genome organization of enzyme loci and metabolic diseases. Isozymes Curr Top Biol Med Res. 1983;10:323–339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shows T. B., Sakaguchi A. Y., Naylor S. L. Mapping the human genome, cloned genes, DNA polymorphisms, and inherited disease. Adv Hum Genet. 1982;12:341–452. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-8315-8_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shows T., Eddy R., Haley L., Byers M., Henry M., Fujita T., Matsui H., Taniguchi T. Interleukin 2 (IL2) is assigned to human chromosome 4. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1984 May;10(3):315–318. doi: 10.1007/BF01535253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. F., Waterman M. S. Identification of common molecular subsequences. J Mol Biol. 1981 Mar 25;147(1):195–197. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90087-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathmann M., Wilkie T. M., Simon M. I. Alternative splicing produces transcripts encoding two forms of the alpha subunit of GTP-binding protein Go. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6477–6481. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L., Bourne H. R. G proteins: a family of signal transducers. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:391–419. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terashima T., Katada T., Okada E., Ui M., Inoue Y. Light microscopy of GTP-binding protein (Go) immunoreactivity within the retina of different vertebrates. Brain Res. 1987 Dec 15;436(2):384–389. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)91685-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Meurs K. P., Angus C. W., Lavu S., Kung H. F., Czarnecki S. K., Moss J., Vaughan M. Deduced amino acid sequence of bovine retinal Go alpha: similarities to other guanine nucleotide-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3107–3111. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins D. C., Northup J. K., Malbon C. C. Regulation of G-proteins in differentiation. Altered ratio of alpha- to beta-subunits in 3T3-L1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10651–10657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worley P. F., Baraban J. M., Van Dop C., Neer E. J., Snyder S. H. Go, a guanine nucleotide-binding protein: immunohistochemical localization in rat brain resembles distribution of second messenger systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4561–4565. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaffe D., Nudel U., Mayer Y., Neuman S. Highly conserved sequences in the 3' untranslated region of mRNAs coding for homologous proteins in distantly related species. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 May 24;13(10):3723–3737. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.10.3723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]