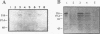Abstract
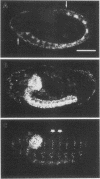
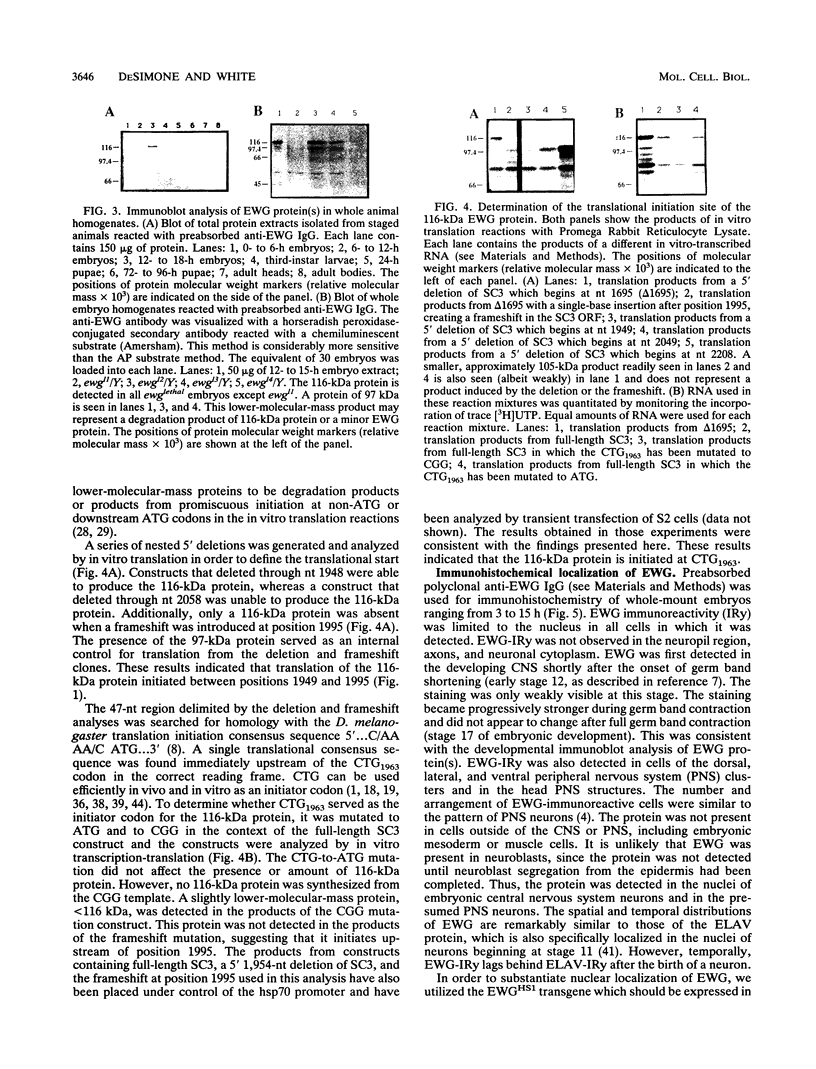
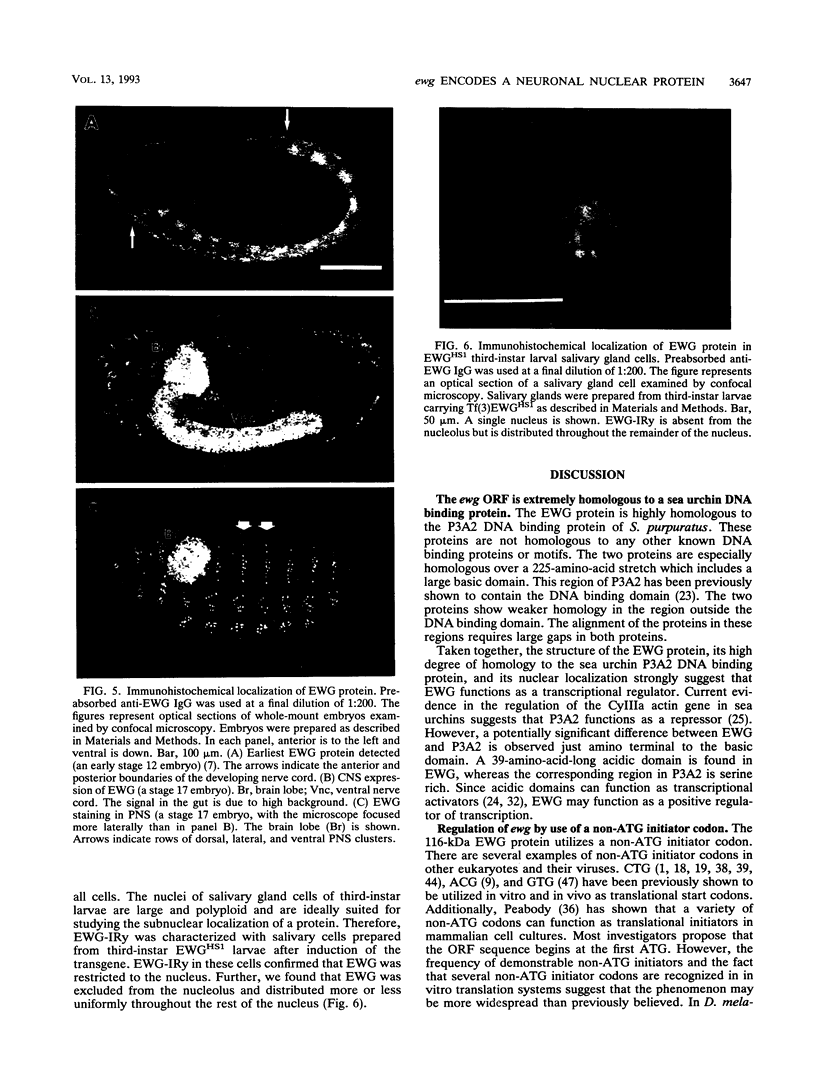
The erect wing (ewg) locus of Drosophila melanogaster encodes a vital function important for the development of the nervous system and the indirect flight muscles. In order to understand the ewg function at a molecular level, cDNA clones were isolated. Sequence analysis of cDNAs revealed a single open reading frame (ORF) encoding a protein of 733 residues. The translational start for this ORF is a CTG codon. A 225-amino-acid region of this protein is 71% identical to the DNA binding region of the Strongylocentrotus purpuratus P3A2 DNA binding protein. Additionally, the ORF contains large acidic and basic domains characteristic of those in proteins involved in nuclear regulatory functions. Immunoblot analysis using polyclonal anti-EWG antisera generated against a bacterial fusion protein reveals a single, 116-kDa protein present throughout development, beginning at approximately stage 12 of embryogenesis, which is enriched in adult heads and absent from embryos carrying certain ewg alleles. Additionally, we show that EWG is localized specifically to the nuclei of virtually all embryonic neurons. Finally, a minigene consisting of an ewg cDNA under control of the hsp70 promoter can provide the ewg function in transgenic ewg mutant flies.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acland P., Dixon M., Peters G., Dickson C. Subcellular fate of the int-2 oncoprotein is determined by choice of initiation codon. Nature. 1990 Feb 15;343(6259):662–665. doi: 10.1038/343662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altschul S. F., Lipman D. J. Protein database searches for multiple alignments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5509–5513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodmer R., Carretto R., Jan Y. N. Neurogenesis of the peripheral nervous system in Drosophila embryos: DNA replication patterns and cell lineages. Neuron. 1989 Jul;3(1):21–32. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90112-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brendel V., Karlin S. Association of charge clusters with functional domains of cellular transcription factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5698–5702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calzone F. J., Hög C., Teplow D. B., Cutting A. E., Zeller R. W., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Gene regulatory factors of the sea urchin embryo. I. Purification by affinity chromatography and cloning of P3A2, a novel DNA-binding protein. Development. 1991 May;112(1):335–350. doi: 10.1242/dev.112.1.335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavener D. R. Comparison of the consensus sequence flanking translational start sites in Drosophila and vertebrates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 25;15(4):1353–1361. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.4.1353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran J., Kolakofsky D. Ribosomal initiation from an ACG codon in the Sendai virus P/C mRNA. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):245–251. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02806.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deak I. I. Mutations of Drosophila melanogaster that affect muscles. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1977 Aug;40:35–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodd I. B., Egan J. B. Improved detection of helix-turn-helix DNA-binding motifs in protein sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 11;18(17):5019–5026. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.17.5019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming R. J., DeSimone S. M., White K. Molecular isolation and analysis of the erect wing locus in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):719–725. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florkiewicz R. Z., Sommer A. Human basic fibroblast growth factor gene encodes four polypeptides: three initiate translation from non-AUG codons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):3978–3981. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.3978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann S. R., King M. W., Bentley D. L., Anderson C. W., Eisenman R. N. A non-AUG translational initiation in c-myc exon 1 generates an N-terminally distinct protein whose synthesis is disrupted in Burkitt's lymphomas. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):185–195. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90507-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope I. A., Mahadevan S., Struhl K. Structural and functional characterization of the short acidic transcriptional activation region of yeast GCN4 protein. Nature. 1988 Jun 16;333(6174):635–640. doi: 10.1038/333635a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hough-Evans B. R., Franks R. R., Zeller R. W., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Negative spatial regulation of the lineage specific CyIIIa actin gene in the sea urchin embryo. Development. 1990 Sep;110(1):41–50. doi: 10.1242/dev.110.1.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hög C., Calzone F. J., Cutting A. E., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Gene regulatory factors of the sea urchin embryo. II. Two dissimilar proteins, P3A1 and P3A2, bind to the same target sites that are required for early territorial gene expression. Development. 1991 May;112(1):351–364. doi: 10.1242/dev.112.1.351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Eukaryotic transcriptional regulatory proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:799–839. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.004055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Context effects and inefficient initiation at non-AUG codons in eucaryotic cell-free translation systems. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5073–5080. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Evaluation of the fidelity of initiation of translation in reticulocyte lysates from commercial sources. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 11;18(9):2828–2828. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.9.2828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo L. Q., Martin-Morris L. E., White K. Identification, secretion, and neural expression of APPL, a Drosophila protein similar to human amyloid protein precursor. J Neurosci. 1990 Dec;10(12):3849–3861. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-12-03849.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J., Ptashne M. A new class of yeast transcriptional activators. Cell. 1987 Oct 9;51(1):113–119. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90015-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Morris L. E., White K. The Drosophila transcript encoded by the beta-amyloid protein precursor-like gene is restricted to the nervous system. Development. 1990 Sep;110(1):185–195. doi: 10.1242/dev.110.1.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noselli S., Vincent A. A Drosophila nuclear localisation signal included in an 18 amino acid fragment from the serendipity delta zinc finger protein. FEBS Lett. 1991 Mar 11;280(1):167–170. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80229-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palazzolo M. J., Hamilton B. A., Ding D. L., Martin C. H., Mead D. A., Mierendorf R. C., Raghavan K. V., Meyerowitz E. M., Lipshitz H. D. Phage lambda cDNA cloning vectors for subtractive hybridization, fusion-protein synthesis and Cre-loxP automatic plasmid subcloning. Gene. 1990 Mar 30;88(1):25–36. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90056-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peabody D. S. Translation initiation at non-AUG triplets in mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 25;264(9):5031–5035. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirrotta V., Bickel S., Mariani C. Developmental expression of the Drosophila zeste gene and localization of zeste protein on polytene chromosomes. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12B):1839–1850. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12b.1839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prats A. C., De Billy G., Wang P., Darlix J. L. CUG initiation codon used for the synthesis of a cell surface antigen coded by the murine leukemia virus. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jan 20;205(2):363–372. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90347-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prats H., Kaghad M., Prats A. C., Klagsbrun M., Lélias J. M., Liauzun P., Chalon P., Tauber J. P., Amalric F., Smith J. A. High molecular mass forms of basic fibroblast growth factor are initiated by alternative CUG codons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):1836–1840. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.1836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson H. M., Preston C. R., Phillis R. W., Johnson-Schlitz D. M., Benz W. K., Engels W. R. A stable genomic source of P element transposase in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1988 Mar;118(3):461–470. doi: 10.1093/genetics/118.3.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinow S., White K. Characterization and spatial distribution of the ELAV protein during Drosophila melanogaster development. J Neurobiol. 1991 Jul;22(5):443–461. doi: 10.1002/neu.480220503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M., Spradling A. C. Genetic transformation of Drosophila with transposable element vectors. Science. 1982 Oct 22;218(4570):348–353. doi: 10.1126/science.6289436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saris C. J., Domen J., Berns A. The pim-1 oncogene encodes two related protein-serine/threonine kinases by alternative initiation at AUG and CUG. EMBO J. 1991 Mar;10(3):655–664. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07994.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortridge R. D., Yoon J., Lending C. R., Bloomquist B. T., Perdew M. H., Pak W. L. A Drosophila phospholipase C gene that is expressed in the central nervous system. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12474–12480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steller H., Pirrotta V. Expression of the Drosophila white gene under the control of the hsp70 heat shock promoter. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 30;4(13B):3765–3772. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04146.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugihara H., Andrisani V., Salvaterra P. M. Drosophila choline acetyltransferase uses a non-AUG initiation codon and full length RNA is inefficiently translated. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 15;265(35):21714–21719. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thambi N. C., Quan F., Wolfgang W. J., Spiegel A., Forte M. Immunological and molecular characterization of Go alpha-like proteins in the Drosophila central nervous system. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18552–18560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton K. A., Yedvobnick B., Finnerty V. G., Artavanis-Tsakonas S. opa: a novel family of transcribed repeats shared by the Notch locus and other developmentally regulated loci in D. melanogaster. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):55–62. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90308-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoon J., Shortridge R. D., Bloomquist B. T., Schneuwly S., Perdew M. H., Pak W. L. Molecular characterization of Drosophila gene encoding G0 alpha subunit homolog. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18536–18543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Sousa S. M., Hoveland L. L., Yarfitz S., Hurley J. B. The Drosophila Go alpha-like G protein gene produces multiple transcripts and is expressed in the nervous system and in ovaries. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18544–18551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Pompa J. L., Garcia J. R., Ferrús A. Genetic analysis of muscle development in Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 1989 Feb;131(2):439–454. doi: 10.1016/s0012-1606(89)80016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]