Abstract
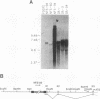
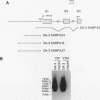
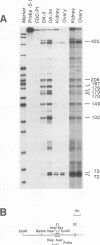
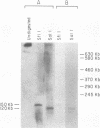
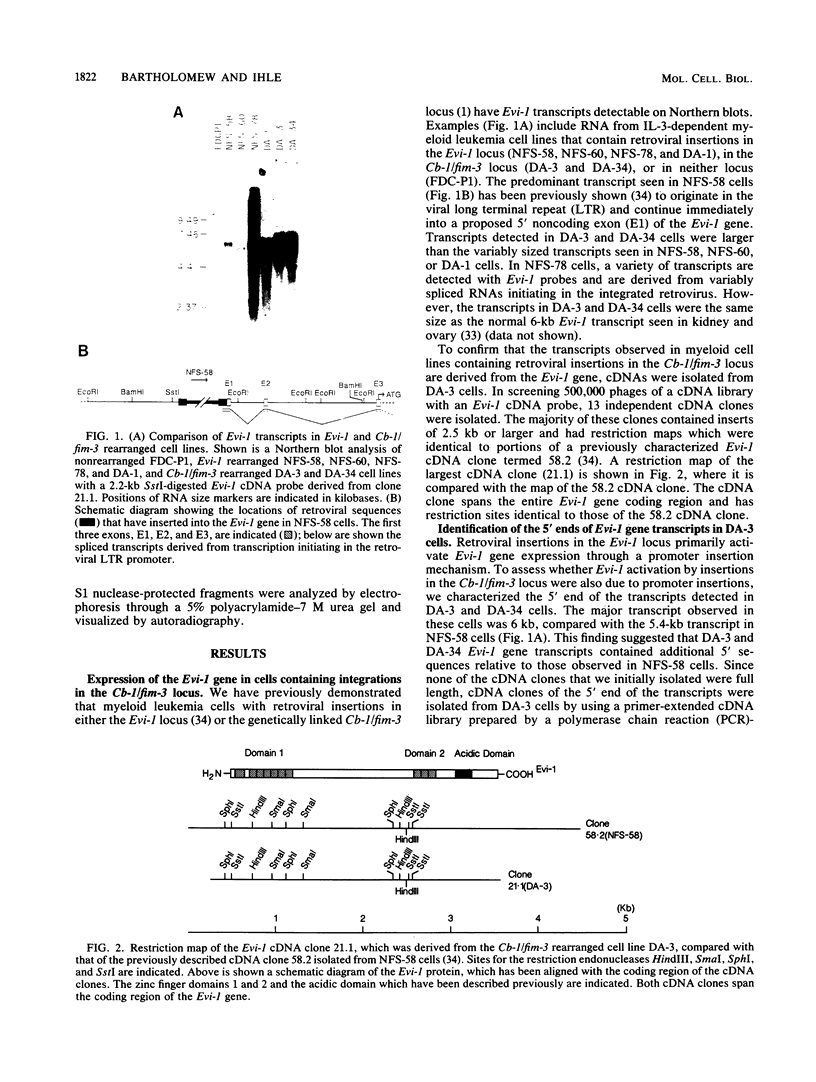
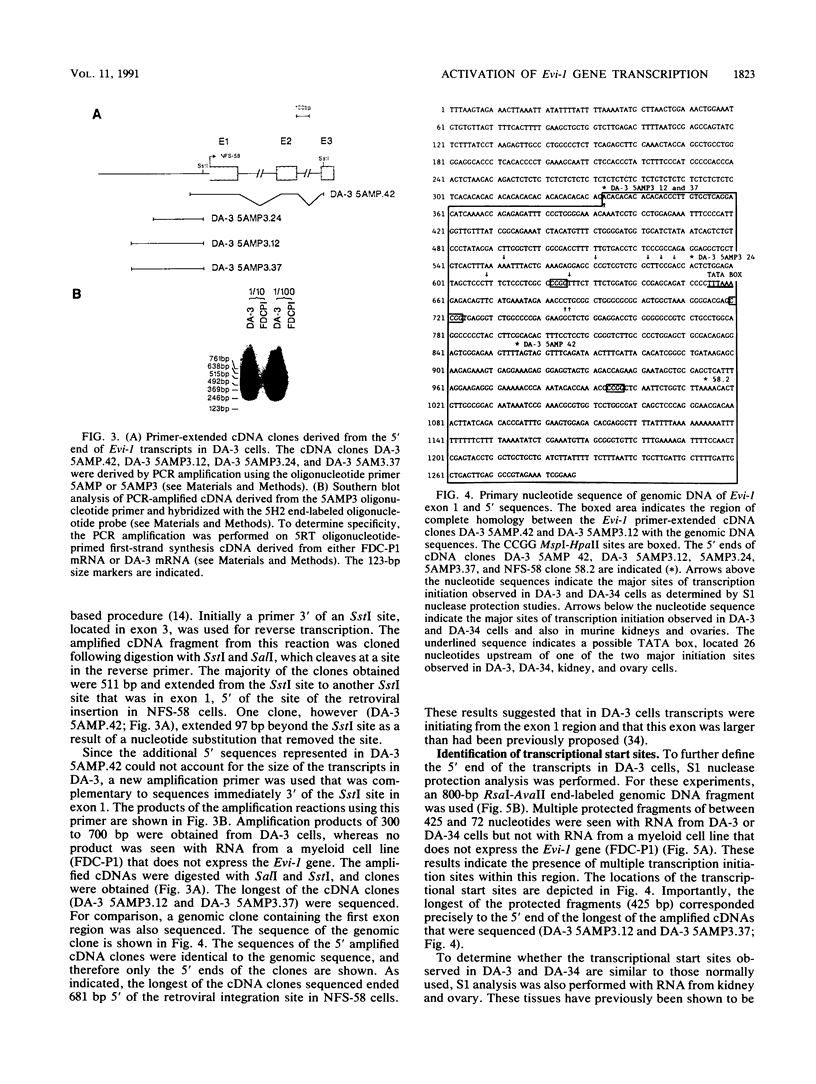
The inappropriate production of the Evi-1 zinc finger protein occurs in retrovirus-induced murine myeloid leukemias and human acute myelogenous leukemias. In murine leukemias, expression of the Evi-1 gene is associated with retroviral insertions either in the Evi-1 locus, which is immediately 5' of the coding region of the gene, or in the genetically linked Cb-1/fim-3 locus. In these studies, we demonstrate by chromosomal walking and pulse field electrophoresis that the Cb-1/fim-3 locus is located 90 kb 5' of the Evi-1 locus. Primary structure analysis of Evi-1 cDNA clones from a Cb-1/fim-3 rearranged cell line (DA-3) demonstrates that transcription initiates 5' of the Evi-1 locus and that the first noncoding exon of the gene is 681 bp larger than previously defined. S1 nuclease protection studies reveal multiple transcription initiation sites within this region. Comparable transcriptional initiation sites were identified in RNA from kidney and ovary, in which the gene is normally expressed, suggesting that retroviral insertions in the Cb-1/fim-3 locus activate transcription from the normal promoter. In one myeloid cell line (DA-3), a single long terminal repeat (LTR) is present in the Cb-1/fim-3 locus. No stable transcripts were detectable from this LTR. In cells with retroviral insertions in the Cb-1/fim-3 locus, one allele of the Evi-1 locus becomes hypermethylated in the 5' region of the gene. Together, these results are most consistent with an LTR-mediated, long-range cis activation of Evi-1 gene expression.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
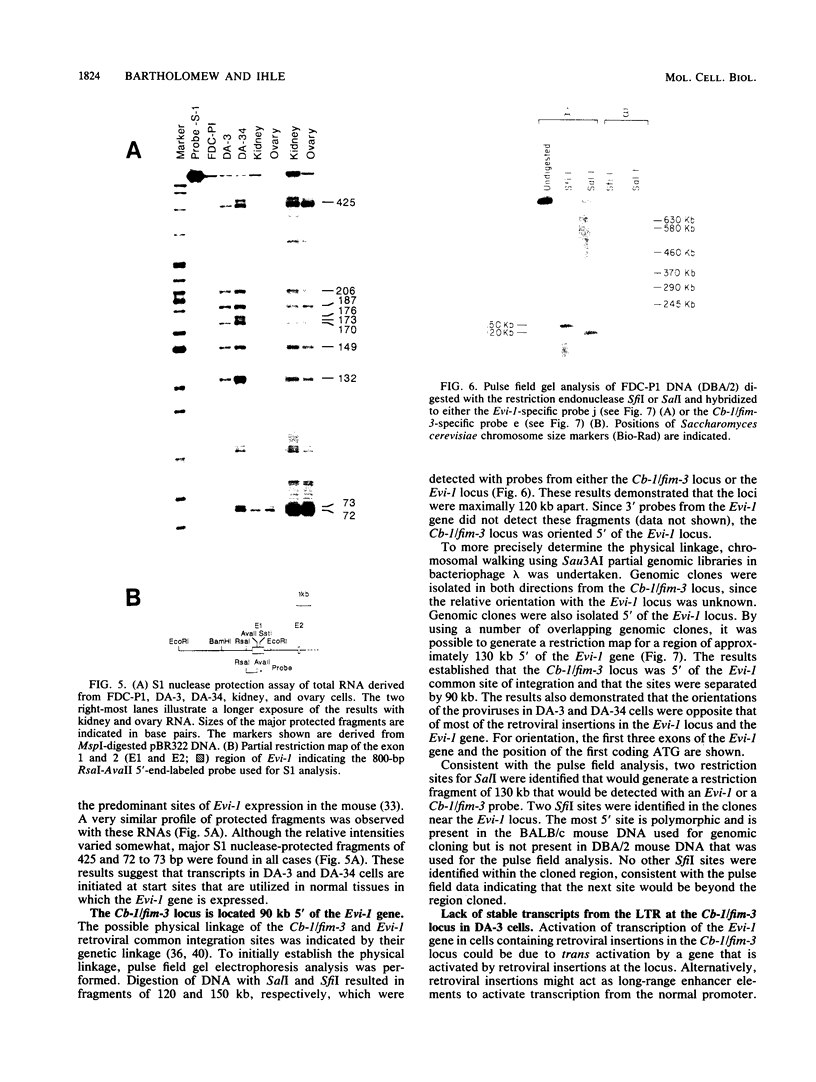
- Bartholomew C., Morishita K., Askew D., Buchberg A., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Ihle J. N. Retroviral insertions in the CB-1/Fim-3 common site of integration activate expression of the Evi-1 gene. Oncogene. 1989 May;4(5):529–534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein R., Pinto M. R., Behr A., Mendelow B. Chromosome 3 abnormalities in acute nonlymphocytic leukemia (ANLL) with abnormal thrombopoiesis: report of three patients with a "new" inversion anomaly and a further case of homologous translocation. Blood. 1982 Sep;60(3):613–617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. P. CpG-rich islands and the function of DNA methylation. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):209–213. doi: 10.1038/321209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bitter M. A., Neilly M. E., Le Beau M. M., Pearson M. G., Rowley J. D. Rearrangements of chromosome 3 involving bands 3q21 and 3q26 are associated with normal or elevated platelet counts in acute nonlymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 1985 Dec;66(6):1362–1370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordereaux D., Fichelson S., Sola B., Tambourin P. E., Gisselbrecht S. Frequent involvement of the fim-3 region in Friend murine leukemia virus-induced mouse myeloblastic leukemias. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):4043–4045. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.4043-4045.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordereaux D., Fichelson S., Tambourin P., Gisselbrecht S. Alternative splicing of the Evi-1 zinc finger gene generates mRNAs which differ by the number of zinc finger motifs. Oncogene. 1990 Jun;5(6):925–927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croce C. M., Nowell P. C. Molecular basis of human B cell neoplasia. Blood. 1985 Jan;65(1):1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dexter T. M., Garland J., Scott D., Scolnick E., Metcalf D. Growth of factor-dependent hemopoietic precursor cell lines. J Exp Med. 1980 Oct 1;152(4):1036–1047. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.4.1036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhar R., McClements W. L., Enquist L. W., Vande Woude G. F. Nucleotide sequences of integrated Moloney sarcoma provirus long terminal repeats and their host and viral junctions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3937–3941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doerfler W. DNA methylation and gene activity. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:93–124. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.000521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favaloro J., Treisman R., Kamen R. Transcription maps of polyoma virus-specific RNA: analysis by two-dimensional nuclease S1 gel mapping. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):718–749. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman M. A., Dush M. K., Martin G. R. Rapid production of full-length cDNAs from rare transcripts: amplification using a single gene-specific oligonucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8998–9002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasser S. M., Laemmli U. K. Cohabitation of scaffold binding regions with upstream/enhancer elements of three developmentally regulated genes of D. melanogaster. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):521–530. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90877-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geliebter J., Zeff R. A., Schulze D. H., Pease L. R., Weiss E. H., Mellor A. L., Flavell R. A., Nathenson S. G. Interaction between Kb and Q4 gene sequences generates the Kbm6 mutation. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):645–652. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henglein B., Synovzik H., Groitl P., Bornkamm G. W., Hartl P., Lipp M. Three breakpoints of variant t(2;8) translocations in Burkitt's lymphoma cells fall within a region 140 kilobases distal from c-myc. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2105–2113. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann B. G., Barlow D. P., Lehrach H. A large inverted duplication allows homologous recombination between chromosomes heterozygous for the proximal t complex inversion. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):813–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90078-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes K. L., Palaszynski E., Fredrickson T. N., Morse H. C., 3rd, Ihle J. N. Correlation of cell-surface phenotype with the establishment of interleukin 3-dependent cell lines from wild-mouse murine leukemia virus-induced neoplasms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6687–6691. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihle J. N., Keller J., Greenberger J. S., Henderson L., Yetter R. A., Morse H. C., 3rd Phenotypic characteristics of cell lines requiring interleukin 3 for growth. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1377–1383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jähner D., Jaenisch R. Retrovirus-induced de novo methylation of flanking host sequences correlates with gene inactivity. Nature. 1985 Jun 13;315(6020):594–597. doi: 10.1038/315594a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koehne C. F., Lazo P. A., Alves K., Lee J. S., Tsichlis P. N., O'Donnell P. V. The Mlvi-1 locus involved in the induction of rat T-cell lymphomas and the pvt-1/Mis-1 locus are identical. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2366–2369. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2366-2369.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazo P. A., Lee J. S., Tsichlis P. N. Long-distance activation of the Myc protooncogene by provirus insertion in Mlvi-1 or Mlvi-4 in rat T-cell lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):170–173. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsugi T., Morishita K., Ihle J. N. Identification, nuclear localization, and DNA-binding activity of the zinc finger protein encoded by the Evi-1 myeloid transforming gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1259–1264. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meehan R. R., Lewis J. D., McKay S., Kleiner E. L., Bird A. P. Identification of a mammalian protein that binds specifically to DNA containing methylated CpGs. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):499–507. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90430-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Wang C., Tjian R. Positive and negative regulation of transcription in vitro: enhancer-binding protein AP-2 is inhibited by SV40 T antigen. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):847–861. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90512-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morishita K., Parganas E., Bartholomew C., Sacchi N., Valentine M. B., Raimondi S. C., Le Beau M. M., Ihle J. N. The human Evi-1 gene is located on chromosome 3q24-q28 but is not rearranged in three cases of acute nonlymphocytic leukemias containing t(3;5)(q25;q34) translocations. Oncogene Res. 1990;5(3):221–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morishita K., Parganas E., Douglass E. C., Ihle J. N. Unique expression of the human Evi-1 gene in an endometrial carcinoma cell line: sequence of cDNAs and structure of alternatively spliced transcripts. Oncogene. 1990 Jul;5(7):963–971. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morishita K., Parganas E., Parham D. M., Matsugi T., Ihle J. N. The Evi-1 zinc finger myeloid transforming gene is normally expressed in the kidney and in developing oocytes. Oncogene. 1990 Sep;5(9):1419–1423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morishita K., Parker D. S., Mucenski M. L., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Ihle J. N. Retroviral activation of a novel gene encoding a zinc finger protein in IL-3-dependent myeloid leukemia cell lines. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):831–840. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91175-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mucenski M. L., Taylor B. A., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A. Chromosomal location of Evi-1, a common site of ecotropic viral integration in AKXD murine myeloid tumors. Oncogene Res. 1988 Feb;2(3):219–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohki K., Nagayama A. Establishment and characterization of factor-dependent macrophage cell lines. J Leukoc Biol. 1988 Dec;44(6):465–473. doi: 10.1002/jlb.44.6.465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raimondi S. C., Dubé I. D., Valentine M. B., Mirro J., Jr, Watt H. J., Larson R. A., Bitter M. A., Le Beau M. M., Rowley J. D. Clinicopathologic manifestations and breakpoints of the t(3;5) in patients with acute nonlymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia. 1989 Jan;3(1):42–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sola B., Simon D., Mattéi M. G., Fichelson S., Bordereaux D., Tambourin P. E., Guenet J. L., Gisselbrecht S. Fim-1, Fim-2/c-fms, and Fim-3, three common integration sites of Friend murine leukemia virus in myeloblastic leukemias, map to mouse chromosomes 13, 18, and 3, respectively. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):3973–3978. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.3973-3978.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varmus H. E., Quintrell N., Ortiz S. Retroviruses as mutagens: insertion and excision of a nontransforming provirus alter expression of a resident transforming provirus. Cell. 1981 Jul;25(1):23–36. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90228-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver R. F., Weissmann C. Mapping of RNA by a modification of the Berk-Sharp procedure: the 5' termini of 15 S beta-globin mRNA precursor and mature 10 s beta-globin mRNA have identical map coordinates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1175–1193. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westaway D., Payne G., Varmus H. E. Proviral deletions and oncogene base-substitutions in insertionally mutagenized c-myc alleles may contribute to the progression of avian bursal tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):843–847. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T., Admon A., Lüscher B., Tjian R. Cloning and expression of AP-2, a cell-type-specific transcription factor that activates inducible enhancer elements. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1557–1569. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. Y., Supakar P. C., Khan R., Ehrlich K. C., Ehrlich M. Related sites in human and herpesvirus DNA recognized by methylated DNA-binding protein from human placenta. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 25;17(4):1459–1474. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.4.1459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]