Abstract
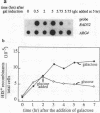
We have examined the effects of RAD52 overexpression on methyl methanesulfonate (MMS) sensitivity and spontaneous mitotic recombination rates. Cells expressing a 10-fold excess of RAD52 mRNA from the ENO1 promoter are no more resistant to MMS than are wild-type cells. Similarly, under the same conditions, the rate of mitotic recombination within a reporter plasmid does not exceed that measured in wild-type cells. This high level of expression is capable of correcting the defects of rad52 mutant cells in carrying out repair and recombination. From these observations, we conclude that wild-type amounts of Rad52 are not rate limiting for repair of MMS-induced lesions or plasmid recombination. By placing RAD52 under the control of the inducible GAL1 promoter, we find that induction results in a 12-fold increase in the fraction of recombinants within 4 h. After this time, the fraction increases less rapidly. When RAD52 expression is quickly repressed during induction, the amount of RAD52 mRNA decreases rapidly and no nascent recombinants are formed. This result suggests a short active half-life for the protein product. Induction of RAD52 in G1-arrested mutant cells also causes a rapid increase in recombinants, suggesting that replication is not necessary for plasmid recombination.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adzuma K., Ogawa T., Ogawa H. Primary structure of the RAD52 gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2735–2744. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahn B. Y., Livingston D. M. Mitotic gene conversion lengths, coconversion patterns, and the incidence of reciprocal recombination in a Saccharomyces cerevisiae plasmid system. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3685–3693. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreadis A., Hsu Y. P., Hermodson M., Kohlhaw G., Schimmel P. Yeast LEU2. Repression of mRNA levels by leucine and primary structure of the gene product. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8059–8062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beacham I. R., Schweitzer B. W., Warrick H. M., Carbon J. The nucleotide sequence of the yeast ARG4 gene. Gene. 1984 Sep;29(3):271–279. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90056-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borts R. H., Lichten M., Haber J. E. Analysis of meiosis-defective mutations in yeast by physical monitoring of recombination. Genetics. 1986 Jul;113(3):551–567. doi: 10.1093/genetics/113.3.551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brill S. J., Sternglanz R. Transcription-dependent DNA supercoiling in yeast DNA topoisomerase mutants. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):403–411. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90203-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole G. M., Schild D., Mortimer R. K. Two DNA repair and recombination genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, RAD52 and RAD54, are induced during meiosis. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):3101–3104. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.3101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esposito M. S. Evidence that spontaneous mitotic recombination occurs at the two-strand stage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4436–4440. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esposito R. E. Genetic recombination in synchronized cultures of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1968 Jun;59(2):191–210. doi: 10.1093/genetics/59.2.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabre F., Boulet A., Roman H. Gene conversion at different points in the mitotic cycle of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;195(1-2):139–143. doi: 10.1007/BF00332736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabre F. Induced intragenic recombination in yeast can occur during the G1 mitotic phase. Nature. 1978 Apr 27;272(5656):795–798. doi: 10.1038/272795a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Game J. C., Mortimer R. K. A genetic study of x-ray sensitive mutants in yeast. Mutat Res. 1974 Sep;24(3):281–292. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(74)90176-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Game J. C., Zamb T. J., Braun R. J., Resnick M., Roth R. M. The Role of Radiation (rad) Genes in Meiotic Recombination in Yeast. Genetics. 1980 Jan;94(1):51–68. doi: 10.1093/genetics/94.1.51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golin J. E., Esposito M. S. Mitotic recombination: mismatch correction and replicational resolution of Holliday structures formed at the two strand stage in Saccharomyces. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;183(2):252–263. doi: 10.1007/BF00270626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haber J. E., Hearn M. Rad52-independent mitotic gene conversion in Saccharomyces cerevisiae frequently results in chromosomal loss. Genetics. 1985 Sep;111(1):7–22. doi: 10.1093/genetics/111.1.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho K. S. The gene dosage effect of the rad52 mutation on X-ray survival curves of tetraploid yeast strains. Mutat Res. 1975 Dec;33(2-3):165–172. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(75)90191-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innis M. A., Holland M. J., McCabe P. C., Cole G. E., Wittman V. P., Tal R., Watt K. W., Gelfand D. H., Holland J. P., Meade J. H. Expression, Glycosylation, and Secretion of an Aspergillus Glucoamylase by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Science. 1985 Apr 5;228(4695):21–26. doi: 10.1126/science.228.4695.21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson J. A., Fink G. R. Gene conversion between duplicated genetic elements in yeast. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):306–311. doi: 10.1038/292306a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston M., Davis R. W. Sequences that regulate the divergent GAL1-GAL10 promoter in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1440–1448. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luria S. E., Delbrück M. Mutations of Bacteria from Virus Sensitivity to Virus Resistance. Genetics. 1943 Nov;28(6):491–511. doi: 10.1093/genetics/28.6.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAlister L., Holland M. J. Targeted deletion of a yeast enolase structural gene. Identification and isolation of yeast enolase isozymes. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):7181–7188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prakash L., Prakash S. Isolation and characterization of MMS-sensitive mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1977 May;86(1):33–55. doi: 10.1093/genetics/86.1.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prakash S., Prakash L., Burke W., Montelone B. A. Effects of the RAD52 Gene on Recombination in SACCHAROMYCES CEREVISIAE. Genetics. 1980 Jan;94(1):31–50. doi: 10.1093/genetics/94.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick M. A. Genetic control of radiation sensitivity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1969 Jul;62(3):519–531. doi: 10.1093/genetics/62.3.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick M. A., Martin P. The repair of double-strand breaks in the nuclear DNA of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and its genetic control. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Jan 16;143(2):119–129. doi: 10.1007/BF00266917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick M. A., Nitiss J., Edwards C., Malone R. E. Meiosis can induce recombination in rad52 mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1986 Jul;113(3):531–550. doi: 10.1093/genetics/113.3.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roman H., Fabre F. Gene conversion and associated reciprocal recombination are separable events in vegetative cells of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6912–6916. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Throm E., Duntze W. Mating-Type-Dependent Inhibition of Deoxyribonucleic Acid Synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1388–1390. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1388-1390.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White C. I., Haber J. E. Intermediates of recombination during mating type switching in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):663–673. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08158.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildenberg J. The relation of mitotic recombination to DNA replication in yeast pedigrees. Genetics. 1970 Oct;66(2):291–304. doi: 10.1093/genetics/66.2.291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakian V. A., Brewer B. J., Fangman W. L. Replication of each copy of the yeast 2 micron DNA plasmid occurs during the S phase. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):923–934. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90332-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]