Abstract
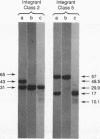
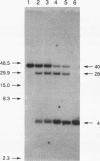
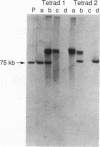
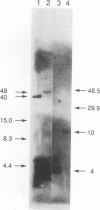
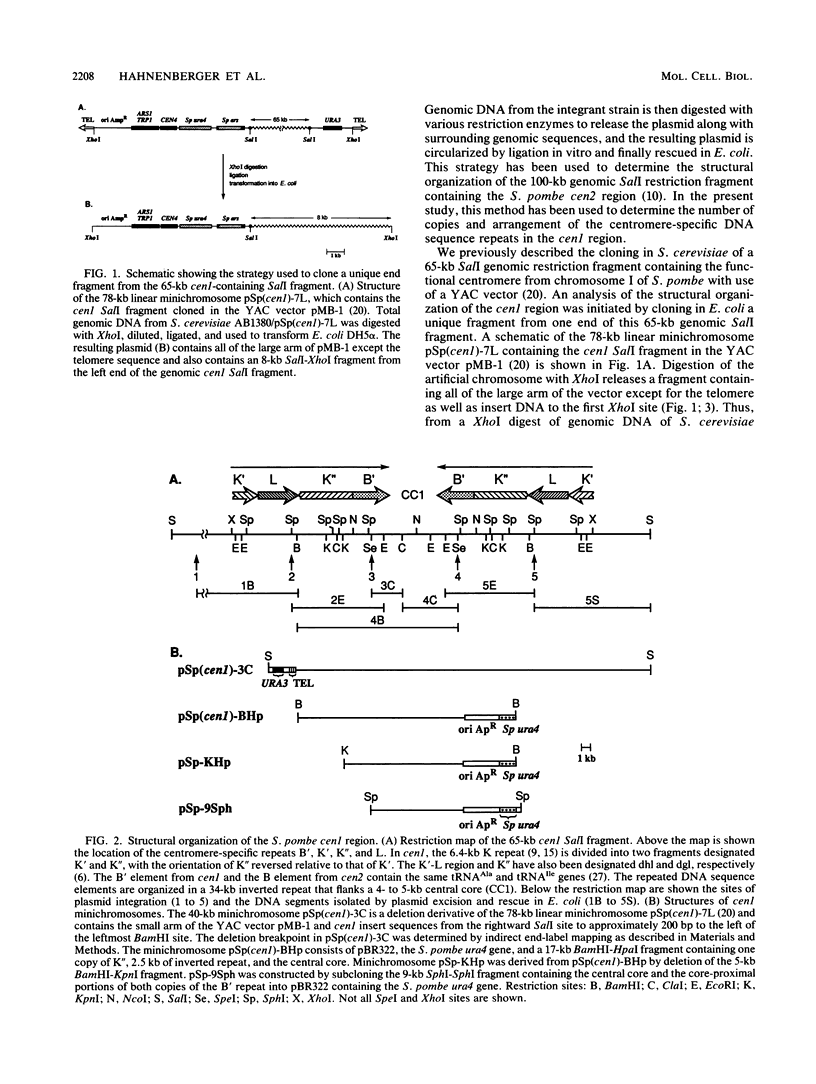
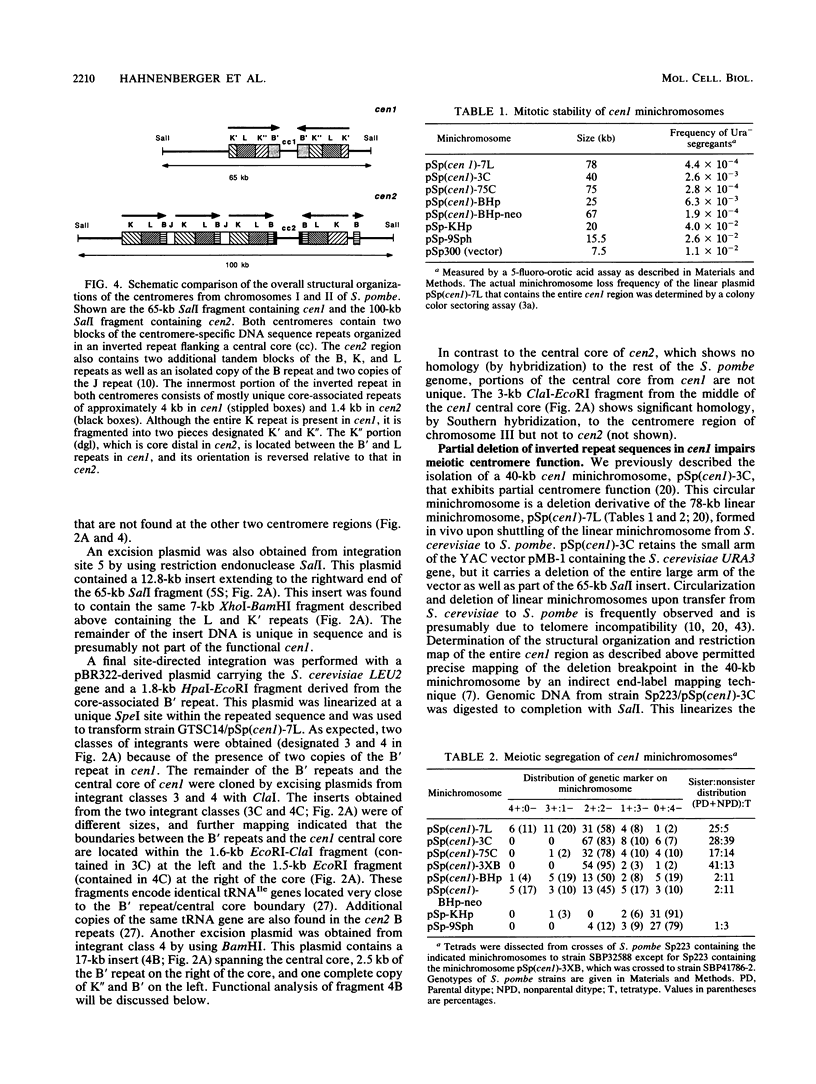
We have determined the structural organization and functional roles of centromere-specific DNA sequence repeats in cen1, the centromere region from chromosome I of the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. cen1 is composed of various classes of repeated sequences designated K', K"(dgl), L, and B', arranged in a 34-kb inverted repeat surrounding a 4- to 5-kb nonhomologous central core. Artificial chromosomes containing various portions of the cen1 region were constructed and assayed for mitotic and meiotic centromere function in S. pombe. Deleting K' and L from the distal portion of one arm of the inverted repeat had no effect on mitotic centromere function but resulted in greatly increased precocious sister chromatid separation in the first meiotic division. A centromere completely lacking K' and L, but containing the central core, one copy of B' and K" in one arm, and approximately 2.5 kb of the core-proximal portion of B' in the other arm, was also fully functional mitotically but again did not maintain sister chromatid attachment in meiosis I. However, deletion of K" from this minichromosome resulted in complete loss of centromere function. Thus, one copy of at least a portion of the K" (dgl) repeat is absolutely required but is not sufficient for S. pombe centromere function. The long centromeric inverted-repeat region must be relatively intact to maintain sister chromatid attachment in meiosis I.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beach D. H., Klar A. J. Rearrangements of the transposable mating-type cassettes of fission yeast. EMBO J. 1984 Mar;3(3):603–610. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01855.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., LaCroute F., Fink G. R. A positive selection for mutants lacking orotidine-5'-phosphate decarboxylase activity in yeast: 5-fluoro-orotic acid resistance. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;197(2):345–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00330984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D. T., Carle G. F., Olson M. V. Cloning of large segments of exogenous DNA into yeast by means of artificial chromosome vectors. Science. 1987 May 15;236(4803):806–812. doi: 10.1126/science.3033825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbon J., Clarke L. Centromere structure and function in budding and fission yeasts. New Biol. 1990 Jan;2(1):10–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carle G. F., Frank M., Olson M. V. Electrophoretic separations of large DNA molecules by periodic inversion of the electric field. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):65–68. doi: 10.1126/science.3952500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chikashige Y., Kinoshita N., Nakaseko Y., Matsumoto T., Murakami S., Niwa O., Yanagida M. Composite motifs and repeat symmetry in S. pombe centromeres: direct analysis by integration of NotI restriction sites. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):739–751. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90789-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke L., Amstutz H., Fishel B., Carbon J. Analysis of centromeric DNA in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8253–8257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke L., Baum M. P. Functional analysis of a centromere from fission yeast: a role for centromere-specific repeated DNA sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):1863–1872. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.1863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke L., Carbon J. Genomic substitutions of centromeres in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nature. 1983 Sep 1;305(5929):23–28. doi: 10.1038/305023a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke L., Carbon J. The structure and function of yeast centromeres. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:29–55. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.000333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke L. Centromeres of budding and fission yeasts. Trends Genet. 1990 May;6(5):150–154. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90149-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cottarel G., Shero J. H., Hieter P., Hegemann J. H. A 125-base-pair CEN6 DNA fragment is sufficient for complete meiotic and mitotic centromere functions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3342–3349. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cumberledge S., Carbon J. Mutational analysis of meiotic and mitotic centromere function in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1987 Oct;117(2):203–212. doi: 10.1093/genetics/117.2.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishel B., Amstutz H., Baum M., Carbon J., Clarke L. Structural organization and functional analysis of centromeric DNA in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):754–763. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald-Hayes M., Clarke L., Carbon J. Nucleotide sequence comparisons and functional analysis of yeast centromere DNAs. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):235–244. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90108-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald-Hayes M. Yeast centromeres. Yeast. 1987 Sep;3(3):187–200. doi: 10.1002/yea.320030306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaudet A., Fitzgerald-Hayes M. Mutations in CEN3 cause aberrant chromosome segregation during meiosis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 Mar;121(3):477–489. doi: 10.1093/genetics/121.3.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahnenberger K. M., Baum M. P., Polizzi C. M., Carbon J., Clarke L. Construction of functional artificial minichromosomes in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):577–581. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegemann J. H., Shero J. H., Cottarel G., Philippsen P., Hieter P. Mutational analysis of centromere DNA from chromosome VI of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2523–2535. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hieter P., Mann C., Snyder M., Davis R. W. Mitotic stability of yeast chromosomes: a colony color assay that measures nondisjunction and chromosome loss. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):381–392. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90152-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hieter P., Pridmore D., Hegemann J. H., Thomas M., Davis R. W., Philippsen P. Functional selection and analysis of yeast centromeric DNA. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):913–921. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90287-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jabs E. W., Goble C. A., Cutting G. R. Macromolecular organization of human centromeric regions reveals high-frequency, polymorphic macro DNA repeats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):202–206. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohli J., Hottinger H., Munz P., Strauss A., Thuriaux P. Genetic Mapping in SCHIZOSACCHAROMYCES POMBE by Mitotic and Meiotic Analysis and Induced Haploidization. Genetics. 1977 Nov;87(3):471–489. doi: 10.1093/genetics/87.3.471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrew J., Diehl B., Fitzgerald-Hayes M. Single base-pair mutations in centromere element III cause aberrant chromosome segregation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):530–538. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Szostak J. W. Construction of artificial chromosomes in yeast. Nature. 1983 Sep 15;305(5931):189–193. doi: 10.1038/305189a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakaseko Y., Adachi Y., Funahashi S., Niwa O., Yanagida M. Chromosome walking shows a highly homologous repetitive sequence present in all the centromere regions of fission yeast. EMBO J. 1986 May;5(5):1011–1021. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04316.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng R., Carbon J. Mutational and in vitro protein-binding studies on centromere DNA from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4522–4534. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niwa O., Matsumoto T., Chikashige Y., Yanagida M. Characterization of Schizosaccharomyces pombe minichromosome deletion derivatives and a functional allocation of their centromere. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):3045–3052. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08455.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr-Weaver T. L., Szostak J. W., Rothstein R. J. Yeast transformation: a model system for the study of recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6354–6358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panzeri L., Landonio L., Stotz A., Philippsen P. Role of conserved sequence elements in yeast centromere DNA. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1867–1874. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03862.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polizzi C., Clarke L. The chromatin structure of centromeres from fission yeast: differentiation of the central core that correlates with function. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;112(2):191–201. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.2.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharon G., Simchen G. Centromeric regions control autonomous segregation tendencies in single-division meiosis of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1990 Jul;125(3):487–494. doi: 10.1093/genetics/125.3.487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharon G., Simchen G. Mixed segregation of chromosomes during single-division meiosis of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1990 Jul;125(3):475–485. doi: 10.1093/genetics/125.3.475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer M. F. Highly repeated sequences in mammalian genomes. Int Rev Cytol. 1982;76:67–112. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61789-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschumper G., Carbon J. Copy number control by a yeast centromere. Gene. 1983 Aug;23(2):221–232. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90054-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]