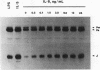
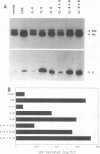
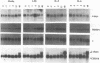
Abstract
Interleukin-5 (IL-5) and IL-6 have both been reported to act as B-cell differentiation factors by stimulating activated B cells to secrete antibody. However, it has not been possible to directly compare the effects of these two lymphokines because of the lack of a suitable B-cell line capable of responding to both. We have identified a clonal, inducible B-cell lymphoma, CH12, that has this property. Both IL-5 and IL-6 can independently stimulate increases in steady-state levels of immunoglobulin and J-chain mRNA and proteins, and they both induce the differentiation of CH12 into high-rate antibody-secreting cells. Nevertheless, there are significant differences in the activities of these two lymphokines. First, while IL-6 acts only as a differentiation factor, IL-5 also augments the proliferation of CH12 cells. Second, the differentiation stimulated by IL-5 but not by IL-6 is partially inhibited by IL-4. Inhibition of IL-5-induced differentiation was not at the level of IL-5 receptor expression, since IL-4 did not inhibit IL-5-induced proliferation. Third, IL-5 but not IL-6 stimulated increased mouse mammary tumor proviral gene expression in CH12 cells. These results demonstrate that while both IL-5 and IL-6 may act as differentiation factors for B cells, they induce differentiation by using at least partially distinct molecular pathways. Our results also establish that B cells characteristic of a single stage of development can independently respond to IL-4, IL-5, and IL-6.
Full text
PDF

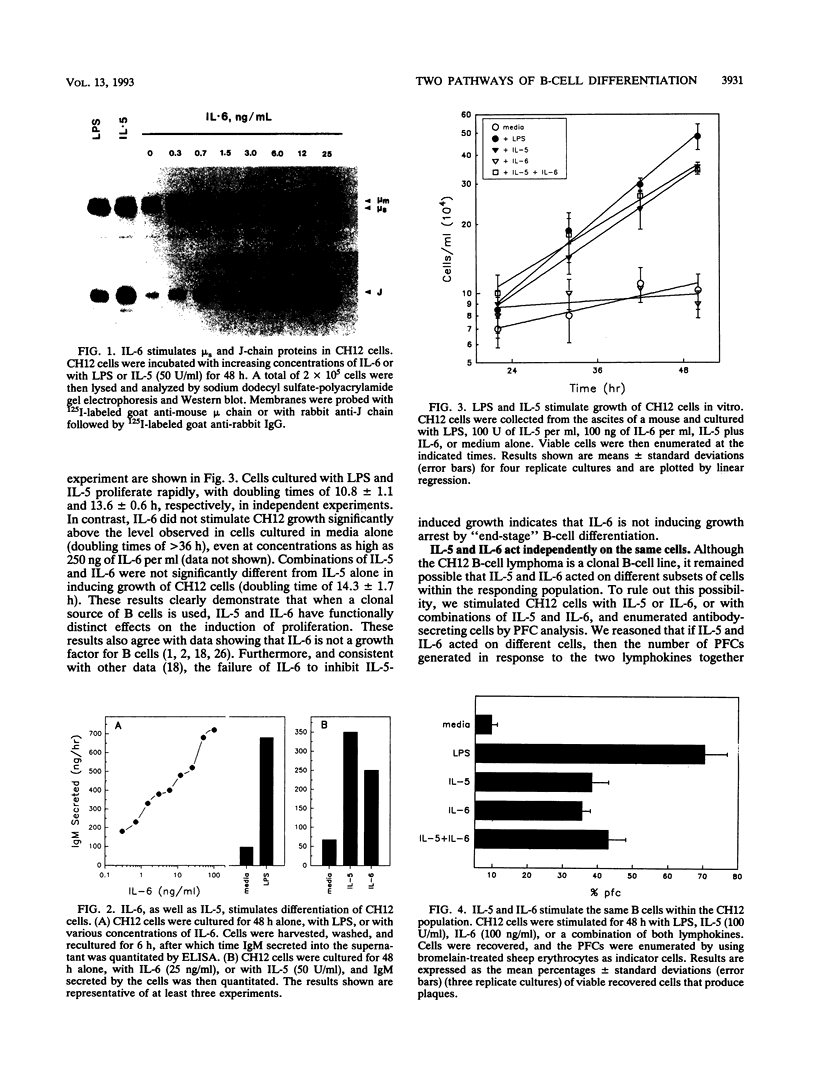





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alderson M. R., Pike B. L. Recombinant human interleukin 6 (B cell stimulatory factor 2) enhances immunoglobulin secretion by single murine hapten-specific B cells in the absence of cell division. Int Immunol. 1989;1(1):20–28. doi: 10.1093/intimm/1.1.18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beagley K. W., Eldridge J. H., Lee F., Kiyono H., Everson M. P., Koopman W. J., Hirano T., Kishimoto T., McGhee J. R. Interleukins and IgA synthesis. Human and murine interleukin 6 induce high rate IgA secretion in IgA-committed B cells. J Exp Med. 1989 Jun 1;169(6):2133–2148. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.6.2133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertolini J. N., Sanderson C. J., Benson E. M. Human interleukin-5 induces staphylococcal A Cowan 1 strain-activated human B cells to secrete IgM. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Feb;23(2):398–402. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckler A. J., Rothstein T. L., Sonenshein G. E. Two-step stimulation of B lymphocytes to enter DNA synthesis: synergy between anti-immunoglobulin antibody and cytochalasin on expression of c-myc and a G1-specific gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1371–1375. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffman R. L., Seymour B. W., Lebman D. A., Hiraki D. D., Christiansen J. A., Shrader B., Cherwinski H. M., Savelkoul H. F., Finkelman F. D., Bond M. W. The role of helper T cell products in mouse B cell differentiation and isotype regulation. Immunol Rev. 1988 Feb;102:5–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1988.tb00739.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croft M., Swain S. L. B cell response to fresh and effector T helper cells. Role of cognate T-B interaction and the cytokines IL-2, IL-4, and IL-6. J Immunol. 1991 Jun 15;146(12):4055–4064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeKruyff R. H., Mosmann R. R., Umetsu D. T. Induction of antibody synthesis by CD4+ T cells: IL 5 is essential for induction of antigen-specific antibody responses by TH2 but not TH1 clones. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Oct;20(10):2219–2227. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830201010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eardley D. D., Koshland M. E. Glycosylphosphatidylinositol: a candidate system for interleukin-2 signal transduction. Science. 1991 Jan 4;251(4989):78–81. doi: 10.1126/science.1824727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano T., Teranishi T., Lin B., Onoue K. Human helper T cell factor(s). IV. Demonstration of a human late-acting B cell differentiation factor acting on Staphylococcus aureus Cowan I-stimulated B cells. J Immunol. 1984 Aug;133(2):798–802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs M. V., McEvilly R. J., Koch R. J., Cardenas G. J., Noonan D. J. Interleukin-6 production by murine B cells and B cell lines. Cell Immunol. 1991 Feb;132(2):442–450. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(91)90041-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaji H., Parkhouse R. M. Intracellular J chain in mouse plasmacytomas secreting IgA, IgM and IgG. Nature. 1974 May 3;249(452):45–47. doi: 10.1038/249045a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D., Leder P. Cell-specific regulation of the c-myc gene by lymphocyte mitogens and platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King L. B., Corley R. B. Characterization of a presecretory phase in B-cell differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2814–2818. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King L. B., Corley R. B. Lipopolysaccharide and dexamethasone induce mouse mammary tumor proviral gene expression and differentiation in B lymphocytes through distinct regulatory pathways. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4211–4220. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King L. B., Lund F. E., White D. A., Sharma S., Corley R. B. Molecular events in B lymphocyte differentiation. Inducible expression of the endogenous mouse mammary tumor proviral gene, Mtv-9. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 15;144(8):3218–3227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T., Hirano T. Molecular regulation of B lymphocyte response. Annu Rev Immunol. 1988;6:485–512. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.06.040188.002413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T., Yoshizaki K., Kimoto M., Okada M., Kuritani T., Kikutani H., Shimizu K., Nakagawa T., Nakagawa N., Miki Y. B cell growth and differentiation factors and mechanism of B cell activation. Immunol Rev. 1984 Apr;78:97–118. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1984.tb00478.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitani A., Hara M., Hirose T., Harigai M., Suzuki K., Kawakami M., Kawaguchi Y., Hidaka T., Kawagoe M., Nakamura H. Autostimulatory effects of IL-6 on excessive B cell differentiation in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: analysis of IL-6 production and IL-6R expression. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Apr;88(1):75–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb03042.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. T., Vitetta E. S. Virgin T cells do not provide help for antigen-specific B cells in the absence of IL-4, IL-5, and IL-6. Int Immunol. 1991 Sep;3(9):907–916. doi: 10.1093/intimm/3.9.907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund F. E., Corley R. B. Regulated expression of mouse mammary tumor proviral genes in cells of the B lineage. J Exp Med. 1991 Dec 1;174(6):1439–1450. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.6.1439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund F. E., Randall T. D., Woodland D. L., Corley R. B. MHC class II limits the functional expression of endogenous superantigens in B cells. J Immunol. 1993 Jan 1;150(1):78–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. Establishment of an interleukin 6 (IL 6)/B cell stimulatory factor 2-dependent cell line and preparation of anti-IL 6 monoclonal antibodies. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Jun;18(6):951–956. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden H. J., Koshland M. E. Interleukin 2- and interleukin 5-induced changes in the binding of regulatory factors to the J-chain gene promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11027–11031. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Dec 16;65(1-2):55–63. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90303-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muraguchi A., Hirano T., Tang B., Matsuda T., Horii Y., Nakajima K., Kishimoto T. The essential role of B cell stimulatory factor 2 (BSF-2/IL-6) for the terminal differentiation of B cells. J Exp Med. 1988 Feb 1;167(2):332–344. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.2.332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima K., Wall R. Interleukin-6 signals activating junB and TIS11 gene transcription in a B-cell hybridoma. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1409–1418. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi K., Howard M., Muraguchi A., Farrar J., Takatsu K., Hamaoka T., Paul W. E. Soluble factors involved in B cell differentiation: identification of two distinct T cell-replacing factors (TRF). J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2219–2224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovnic M., Corley R. B. Quantitation of cell surface molecules on a differentiating, Ly-1+ B cell lymphoma. J Immunol. 1987 May 1;138(9):3075–3082. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall T. D., Brewer J. W., Corley R. B. Direct evidence that J chain regulates the polymeric structure of IgM in antibody-secreting B cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 5;267(25):18002–18007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall T. D., Parkhouse R. M., Corley R. B. J chain synthesis and secretion of hexameric IgM is differentially regulated by lipopolysaccharide and interleukin 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 1;89(3):962–966. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.3.962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen R., Takatsu K., Harada N., Takahashi T., Bottomly K. T cell-dependent hapten-specific and polyclonal B cell responses require release of interleukin 5. J Immunol. 1988 Feb 1;140(3):705–712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma S., King L. B., Corley R. B. Molecular events during B lymphocyte differentiation. Induction of endogenous mouse mammary tumor proviral envelope transcripts after B cell stimulation. J Immunol. 1988 Oct 1;141(7):2510–2518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain S. L., Dutton R. W., McKenzie D., Helstrom H., English M. Role of antigen in the B cell response. Specific antigen and the lymphokine IL-5 synergize to drive B cell lymphoma proliferation and differentiation to Ig secretion. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 15;140(12):4224–4230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain S. L., Dutton R. W. Production of a B cell growth-promoting activity, (DL)BCGF, from a cloned T cell line and its assay on the BCL1 B cell tumor. J Exp Med. 1982 Dec 1;156(6):1821–1834. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.6.1821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain S. L., McKenzie D. T., Dutton R. W., Tonkonogy S. L., English M. The role of IL4 and IL5: characterization of a distinct helper T cell subset that makes IL4 and IL5 (Th2) and requires priming before induction of lymphokine secretion. Immunol Rev. 1988 Feb;102:77–105. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1988.tb00742.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain S. L. Role of BCGFII in the differentiation to antibody secretion normal and tumor B cells. J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):3934–3943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takatsu K., Tominaga A., Harada N., Mita S., Matsumoto M., Takahashi T., Kikuchi Y., Yamaguchi N. T cell-replacing factor (TRF)/interleukin 5 (IL-5): molecular and functional properties. Immunol Rev. 1988 Feb;102:107–135. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1988.tb00743.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tigges M. A., Casey L. S., Koshland M. E. Mechanism of interleukin-2 signaling: mediation of different outcomes by a single receptor and transduction pathway. Science. 1989 Feb 10;243(4892):781–786. doi: 10.1126/science.2492678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Damme J., Opdenakker G., Simpson R. J., Rubira M. R., Cayphas S., Vink A., Billiau A., Van Snick J. Identification of the human 26-kD protein, interferon beta 2 (IFN-beta 2), as a B cell hybridoma/plasmacytoma growth factor induced by interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor. J Exp Med. 1987 Mar 1;165(3):914–919. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.3.914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Snick J., Cayphas S., Vink A., Uyttenhove C., Coulie P. G., Rubira M. R., Simpson R. J. Purification and NH2-terminal amino acid sequence of a T-cell-derived lymphokine with growth factor activity for B-cell hybridomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9679–9683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Snick J. Interleukin-6: an overview. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:253–278. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.001345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xia X., Lee H. K., Clark S. C., Choi Y. S. Recombinant interleukin (IL) 2-induced human B cell differentiation is mediated by autocrine IL6. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Dec;19(12):2275–2281. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830191215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshizaki K., Nakagawa T., Kaieda T., Muraguchi A., Yamamura Y., Kishimoto T. Induction of proliferation and Ig production in human B leukemic cells by anti-immunoglobulins and T cell factors. J Immunol. 1982 Mar;128(3):1296–1301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]