Abstract
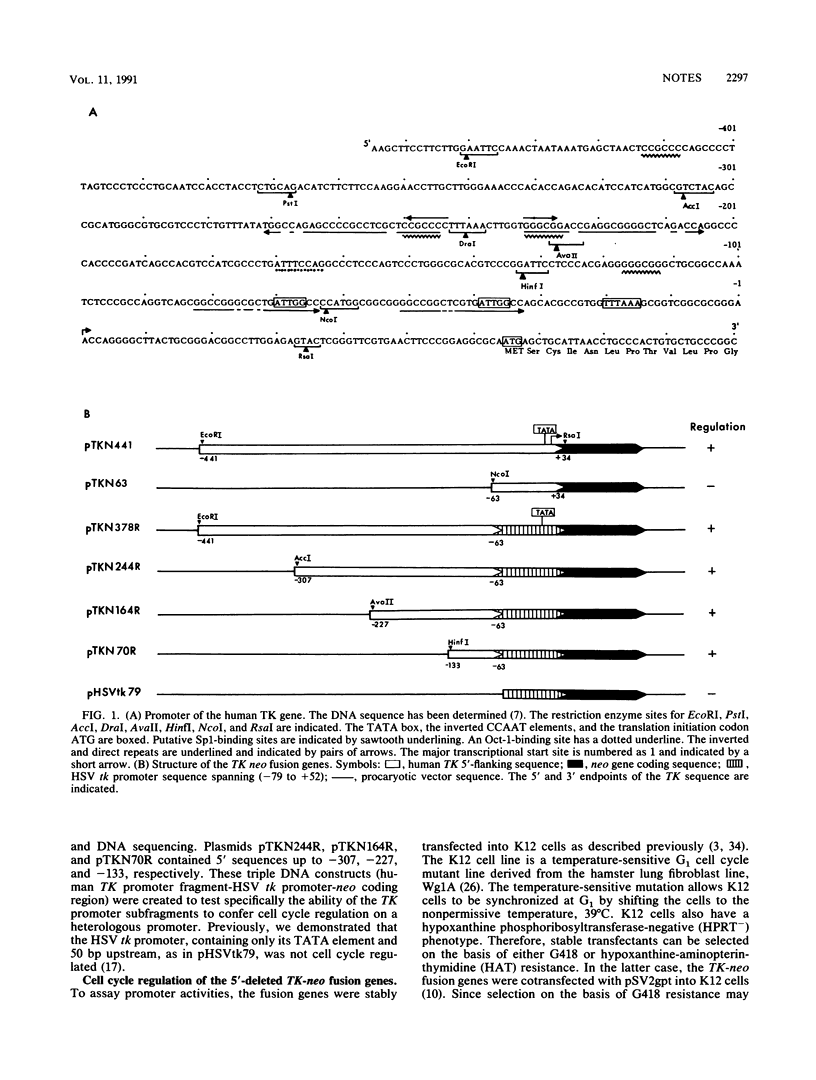
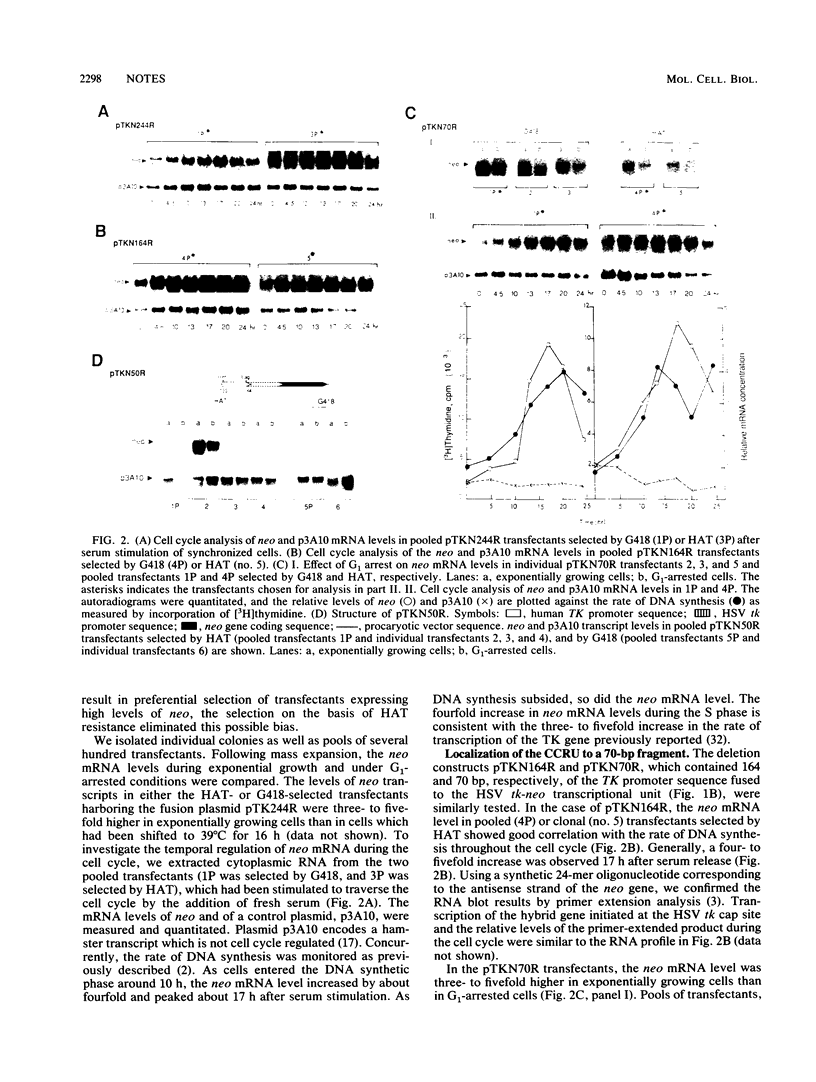
The promoter of the human thymidine kinase gene contains cis-regulatory elements responsible for its cell-cycle-regulated expression. We report here that a 70-bp region between -133 and -64 is sufficient to confer cell cycle regulation on a heterologous promoter. The 20-bp region between -64 and -83, which contains an inverted CCAAT motif, is important for transcriptional stimulation of this functional unit. The sequence of this CCAAT motif is nearly identical to the consensus sequence for the transcriptional factor CP1. We also examined the specificity and binding activities of cellular factors interacting with the 70-bp fragment. We showed that the cellular factors binding to the 70-bp region are similar during the G1, S, and G2 phases, suggesting that the cell cycle regulatory activity observed must involve processes other than factor binding to the DNA.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arcot S. S., Flemington E. K., Deininger P. L. The human thymidine kinase gene promoter. Deletion analysis and specific protein binding. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 5;264(4):2343–2349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artishevsky A., Delegeane A. M., Lee A. S. Use of a cell cycle mutant to delineate the critical period for the control of histone mRNA levels in the mammalian cell cycle. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2364–2369. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artishevsky A., Wooden S., Sharma A., Resendez E., Jr, Lee A. S. Cell-cycle regulatory sequences in a hamster histone promoter and their interactions with cellular factors. 1987 Aug 27-Sep 2Nature. 328(6133):823–827. doi: 10.1038/328823a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu R., Boyle W. J., Meek J., Smeal T., Hunter T., Karin M. The c-Fos protein interacts with c-Jun/AP-1 to stimulate transcription of AP-1 responsive genes. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):541–552. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90076-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chodosh L. A., Baldwin A. S., Carthew R. W., Sharp P. A. Human CCAAT-binding proteins have heterologous subunits. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90483-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppock D. L., Pardee A. B. Control of thymidine kinase mRNA during the cell cycle. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2925–2932. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flemington E., Bradshaw H. D., Jr, Traina-Dorge V., Slagel V., Deininger P. L. Sequence, structure and promoter characterization of the human thymidine kinase gene. Gene. 1987;52(2-3):267–277. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90053-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallinari P., La Bella F., Heintz N. Characterization and purification of H1TF2, a novel CCAAT-binding protein that interacts with a histone H1 subtype-specific consensus element. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1566–1575. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidoni D., Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Multiple specific contacts between a mammalian transcription factor and its cognate promoters. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):409–413. doi: 10.1038/312409a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross M. K., Kainz M. S., Merrill G. F. The chicken thymidine kinase gene is transcriptionally repressed during terminal differentiation: the associated decline in TK mRNA cannot account fully for the disappearance of TK enzyme activity. Dev Biol. 1987 Aug;122(2):439–451. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90308-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudas J. M., Knight G. B., Pardee A. B. Nuclear posttranscriptional processing of thymidine kinase mRNA at the onset of DNA synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4705–4709. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofbauer R., Müllner E., Seiser C., Wintersberger E. Cell cycle regulated synthesis of stable mouse thymidine kinase mRNA is mediated by a sequence within the cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 26;15(2):741–752. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.2.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holthuis J., Owen T. A., van Wijnen A. J., Wright K. L., Ramsey-Ewing A., Kennedy M. B., Carter R., Cosenza S. C., Soprano K. J., Lian J. B. Tumor cells exhibit deregulation of the cell cycle histone gene promoter factor HiNF-D. Science. 1990 Mar 23;247(4949 Pt 1):1454–1457. doi: 10.1126/science.247.4949.1454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang I., Chae C. B. S-phase-specific transcription regulatory elements are present in a replication-independent testis-specific H2B histone gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):1005–1013. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.1005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito M., Sharma A., Lee A. S., Maxson R. Cell cycle regulation of H2b histone octamer DNA-binding activity in Chinese hamster lung fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):869–873. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. K., Wells S., Lau Y. F., Lee A. S. Sequences contained within the promoter of the human thymidine kinase gene can direct cell-cycle regulation of heterologous fusion genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5894–5898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kit S., Jorgensen G. N. Formation of thymidine kinase and deoxycytidylate deaminase in synchronized cultures of chinese hamster cells temperature-sensitive for DNA synthesis. J Cell Physiol. 1976 May;88(1):57–64. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040880108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight G. B., Gudas J. M., Pardee A. B. Cell-cycle-specific interaction of nuclear DNA-binding proteins with a CCAAT sequence from the human thymidine kinase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8350–8354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaBella F., Sive H. L., Roeder R. G., Heintz N. Cell-cycle regulation of a human histone H2b gene is mediated by the H2b subtype-specific consensus element. Genes Dev. 1988 Jan;2(1):32–39. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.1.32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. A., Matkovich D. A. Genetic determinants of growth phase-dependent and adenovirus 5-responsive expression of the Chinese hamster thymidine kinase gene are contained within thymidine kinase mRNA sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2262–2266. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipson K. E., Chen S. T., Koniecki J., Ku D. H., Baserga R. S-phase-specific regulation by deletion mutants of the human thymidine kinase promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):6848–6852. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.6848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu H. T., Gibson C. W., Hirschhorn R. R., Rittling S., Baserga R., Mercer W. E. Expression of thymidine kinase and dihydrofolate reductase genes in mammalian ts mutants of the cell cycle. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3269–3274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Fire A., Cano A., Sharp P. A., Gefter M. L. DNA-dependent transcription of adenovirus genes in a soluble whole-cell extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3855–3859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melero J. A. Identification of the glucose/glycosylation-regulated proteins as those which accumulate in the temperature-sensitive cell line K12. J Cell Physiol. 1981 Oct;109(1):59–67. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041090108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resendez E., Jr, Wooden S. K., Lee A. S. Identification of highly conserved regulatory domains and protein-binding sites in the promoters of the rat and human genes encoding the stress-inducible 78-kilodalton glucose-regulated protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4579–4584. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roehl H. H., Conrad S. E. Identification of a G1-S-phase-regulated region in the human thymidine kinase gene promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3834–3837. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharff D. J., Delegeane A. M., Lee A. S. Characterization of a cell cycle mutant derived from hamster fibroblast: reversion analysis. J Cell Biol. 1982 Mar;92(3):629–633. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.3.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma A., Bos T. J., Pekkala-Flagan A., Vogt P. K., Lee A. S. Interaction of cellular factors related to the Jun oncoprotein with the promoter of a replication-dependent hamster histone H3.2 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):491–495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simanis V., Nurse P. The cell cycle control gene cdc2+ of fission yeast encodes a protein kinase potentially regulated by phosphorylation. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):261–268. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90390-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart C. J., Ito M., Conrad S. E. Evidence for transcriptional and post-transcriptional control of the cellular thymidine kinase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1156–1163. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travali S., Lipson K. E., Jaskulski D., Lauret E., Baserga R. Role of the promoter in the regulation of the thymidine kinase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1551–1557. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang M. L., Lee A. S. Polymerization of vector DNA after transfection into hamster fibroblast cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jan 27;110(2):593–601. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91191-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]