Abstract
Background
Patterns of biodiversity in the subterranean realm are typically different from those encountered on the Earth’s surface. The Dinaric karst of Croatia, Slovenia and Bosnia and Herzegovina is a global hotspot of subterranean biodiversity. How this was achieved and why this is so remain largely unresolved despite a long tradition of research. To obtain insights into the colonisation of the Dinaric Karst and the effects of the subterranean realm on its inhabitants, we studied the tertiary relict Congeria, a unique cave-dwelling bivalve (Dreissenidae), using a combination of biogeographical, molecular, morphological, and paleontological information.
Results
Phylogenetic and molecular clock analyses using both nuclear and mitochondrial markers have shown that the surviving Congeria lineage has actually split into three distinct species, i.e., C. kusceri, C. jalzici sp. nov. and C. mulaomerovici sp. nov., by vicariant processes in the late Miocene and Pliocene. Despite millions of years of independent evolution, analyses have demonstrated a great deal of shell similarity between modern Congeria species, although slight differences in hinge plate structure have enabled the description of the two new species. Ancestral plesiomorphic shell forms seem to have been conserved during the processes of cave colonisation and subsequent lineage isolation. In contrast, shell morphology is divergent within one of the lineages, probably due to microhabitat differences.
Conclusions
Following the turbulent evolution of the Dreissenidae during the Tertiary and major radiations in Lake Pannon, species of Congeria went extinct. One lineage survived, however, by adopting a unique life history strategy that suited it to the underground environment. In light of our new data, an alternative scenario for its colonisation of the karst is proposed. The extant Congeria comprises three sister species that, to date, have only been found to live in 15 caves in the Dinaric karst. Inter-specific morphological stasis and intra-specific ecophenotypic plasticity of the congerid shell demonstrate the contrasting ways in which evolution in the underground environments shapes its inhabitants.
Keywords: Dinaric Karst, Subterranean habitats, Cave bivalve, Congeria, Dreissenidae, New species, Ecophenotypic plasticity
Background
Subterranean habitats are often colonised, either actively or passively, by unusual and highly distinctive animals, which in many cases are remnants of the surface fauna that once lived above them. These animals are often referred to as living fossils, or relict species. Congeria kusceri Bole, 1962, the only known troglobiotic bivalve [1], is a good example of this.
During the Tertiary, most of Europe was covered by a vast aquatic ecosystem of swamps and lakes spreading from the Swiss molasse Basin to Lake Aral in Central Asia. Within this system, known as the Paratethys, a spectacular radiation of many molluscs and other animal taxa occurred [2]. Here, the Dreissenidae Gray, 1840, a family of freshwater bivalves, flourished and diversified [3]. All of the five dreissenid genera [4] evolved in the Neogene lake systems of the Paratethys but only three have survived until the present day: Mytilopsis Conrad, 1857, Dreissena van Beneden, 1835 and Congeria Partsch, 1835. Many different Congeria species inhabited the Paratethys. Harzhauser & Mandic [3] identified 16 species and 11 subspecies, while Kochansky-Devide & Sliskovic [5] identified ~30 species from Miocene deposits in Croatia and Bosnia and Herzegovina alone. By the end of the Miocene, however, all but one had become extinct. Congeria kusceri, the only species known to have survived this dramatic period, is restricted today to but a few caves in the Dinaric Karst.
The Dinaric Karst extends for about 56,000 km2 along an 800 km arc from Trieste, Italy in the north, throughout most of Slovenia (SI), Croatia (HR) and Bosnia and Herzegovina (BA) to Albania in the south and is intersected by a network of caves, pits, underground lakes, rivers and streams containing one of the most complex and diverse subterranean faunas in the world [6,7]. It has been argued that the causes of such high subterranean biodiversity in the Dinarides lie in its complex geological history and intensive karstification that enabled multiple entries into the subterranean realm [8]. Congeria species, unlike other cave animals, have a rich fossil record, and can provide new insights into the timeframe, sources and causes leading to the biodiversity hotspot within the Dinaric Karst.
Congeria kusceri was first discovered in the 1930’s in deposits of empty shells, but a living population was not found until 20 years later in Žira cave in Popovo polje, southern Herzegovina, allowing J. Bole to describe the species in 1962. Later, additional living populations were found in distant areas of the Dinarides [9,10]. Recent extensive field researches have resulted in the discovery of a total of 15 known Congeria populations (Jalžić & Bilandžija, unpublished). Because of such a small number of sites, habitat destruction, and declines in population numbers, the species is listed as vulnerable (VU) in the Red List of European freshwater molluscs [11] and, in Croatia, C. kusceri is assessed as critically endangered (CR) [12].
It is currently assumed that there is only one species of stygobiotic bivalve - Congeria kusceri - that has a wide, holodinaric, distribution. Subterranean habitats are, however, subjected to fragmentation, leading potentially to lineage isolation and speciation. Conversely, the extreme character of the subterranean karst environment drives convergent adaptations in its inhabitants, resulting in cryptic morphologies and possibly masking real diversities [13,14]. Accordingly, widely-distributed cave animals have split into a number of lineages with small fragmented ranges [15], as demonstrated by molecular studies of several groundwater Dinaric taxa – the olm, Proteus anguinus Lorenti, 1768 [16], the cave shrimp, Troglocaris[17,18] and the water louse Asellus aquaticus (Linnaeus, 1758) [19].
In this study we have gathered biogeographical and paleontological data and used both molecular and morphological analyses to address several questions. We deal with contentious issues regarding the phylogenetic position and affinities of Congeria within the Dreissenidae. We have examined the question of Congeria lineage diversifications in separate parts of the Dinaric Karst, and explored the evolutionary history that ultimately caused a shift, uniquely amongst bivalves, towards a subterranean way of life. Finally, we have reported the effects of the underground environment on Congeria shell morphology. For the first time, therefore, this study combines several approaches to provide a new understanding of the evolutionary biology of Congeria and uncovers speciation events leading to the description of new Congeria species.
Results
Biogeography
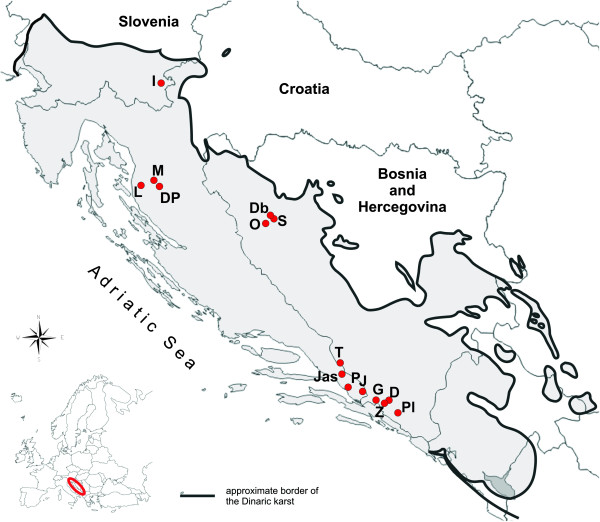
Congeria is restricted to only 15 caves (Figure 1) which belong to four geographic regions, each hydrologically isolated from the others: one is in the Kupa River basin, Bela Krajina region (SI), three in the Lika River basin, Lika region (HR) and three in the Sana River basin in north-western Bosnia (BA). The remaining eight populations occur in the Neretva River basin in southern Dalmatia (HR) and Herzegovina (BA).
Figure 1.
A map of the Dinaric Karst showing all known localities where living populations of Congeria occur. (i). Bela Krajina Region, (SI): I, Izvir Jamske Školjke. (ii). Lika Region, (HR): M, Markov Ponor; L, Lukina jama–Trojama Cave System; Dp, Dankov Ponor. (iii), north-western Bosnia, (BA): O, Oko; S, Suvaja; Db, Dabarska Pećina. (iv), Neretva Basin, southern Dalmatia (HR) and Herzegovina (BA): T, Tihaljina; Jas, Jasena Ponor; P, Pukotina u Tunelu Polje Jezero–Peračko Blato; J, Jama u Predolcu; G, Gradnica; Z, Žira; D, Doljašnica; Pl, Plitica.
Phylogenetic analyses
The final dataset consisting of all four concatenated gene markers contained 3847 nucleotides. Of these, 1033 sites were variable and 636 were parsimony informative. MP analysis resulted in 294 equally parsimonious trees (length 1598). Five runs of ML analysis computed in Garli resulted in the same topology, and the log-likelihood scores were similar in each run. Independent Bayesian runs converged to the stationary distribution. Inspection in Tracer showed acceptable ESS (effective sample size) values and good mixing of chains.
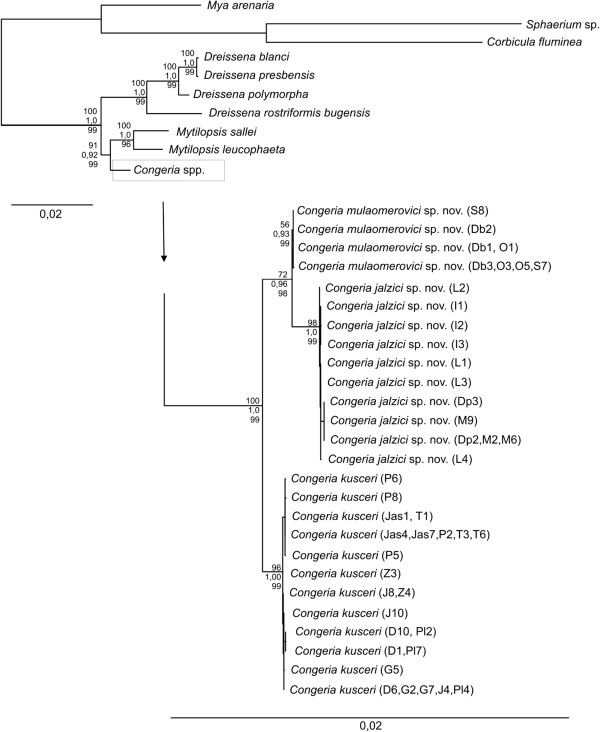
MP, ML and Bayesian concatenated trees were well resolved with most main branches showing high statistical support (>95% MP and ML bootstrap values and >98% BPP). Lower bootstrap and posterior probabilities were associated with the north-western Bosnian populations, probably due to lower resolution in the sequences at this shallow phylogenetic level (Figure 2).
Figure 2.
Maximum likelihood phylogram based on combined nuclear (18S and 28S rRNA) and mitochondrial (COI and 16S rRNA) gene fragments. Numbers on the nodes indicate ML bootstrap values (uppermost value), Bayesian posterior probabilities (in the middle) and MP bootstrap values (lowest value). Abbreviations next to Congeria branches stand for localities. See Figure 1 legend for locality abbreviations.
All genetic markers and phylogenetic reconstruction methods employed supported the Dreissenidae as well as the three extant genera as monophyletic clades. Within the family, the first split isolated Dreissena, leaving Mytilopsis and Congeria as sister groups. The only exceptions to this overall topology were due to conflicting phylogenetic signals in the 16S and 18S rRNA trees, but without good statistical support.
Congeria was, thus, always monophyletic and divided into three subclades, although in some cases not with high support. Each of the subclades was restricted to a distinct geographic region: one subclade comprised populations from the Lika and Kupa River basins, another comprised individuals from the Sana River basin and the third comprised all southern populations from the Neretva River basin.
Divergence dating
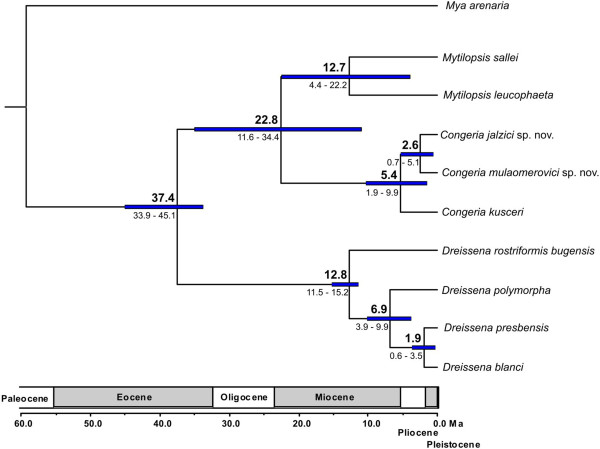
Separate molecular clock analyses using either the lognormal or exponential clock models, different prior distributions on the mean of the branch rates and on calibration nodes gave concordant divergence times in all but one instance (see below), demonstrating that the results are robust and not dominated by the choice of models and priors. The crown node of the family was estimated at 37.4 million years ago (MYA) (mean node age), which corresponds to the Priabonian Age and the occurrence of the first identifiable dreissenid fossils. The timing of the first split within Dreissena was set with lognormal prior placing a minimum hard bound at 11.6 MYA, when the genus first appeared in the fossil record. Accordingly, the first split, between D. rostriformis bugensis and the remaining three Dreissena spp., was estimated at 12.7 MYA. Dreissena polymorpha branched off next at 6.9 MYA. Finally, D. blanci and D. presbensis separated at 1.9 MYA (Figure 3).
Figure 3.
Age estimates of evolutionary divergence events within Dreissenidae. Maximum clade credibility chronogram based on BEAST analysis (lognormal clock model) of concatenated sequences of four genes (18S, 28S and 16S rRNA and COI). Mean divergence ages are shown above the nodes and 95% highest posterior density intervals (95% HPD ) are given in parentheses below nodes and denoted by blue horizontal bars. Major geological periods are indicated in million years on the time scale bellow the tree. Bayesian posterior probabilities were 1.0 for all nodes except for Mytilopsis + Congeria node (0.99) and C. jalzici + C. mulaomerovici node (0.99).
The split between Congeria and Mytilopsis lineages was estimated to have occurred between 22.6 MYA, and the two Mytilopsis species split between 12.7 MYA. The estimates of the splits within Congeria differed according to the molecular clock model used. The exponential clock model placed these divergence events deeper in the past than the lognormal clock model did.
Descriptions of the new species
DREISSENOIDEA Gray in Turton, 1840
Dreissenidae Gray in Turton, 1840
Congeria Partsch, 1835
Type species, Congeria subglobosa Partsch, 1835, subsequent designation by Pilsbry, 1911. [=Enocephalus Münster, 1831 (nomen nudum)].
Congeria jalzici sp. nov. Morton & Bilandžija, 2013. (Figures 4, 6A and 6B, 7A and D)
Figure 4.
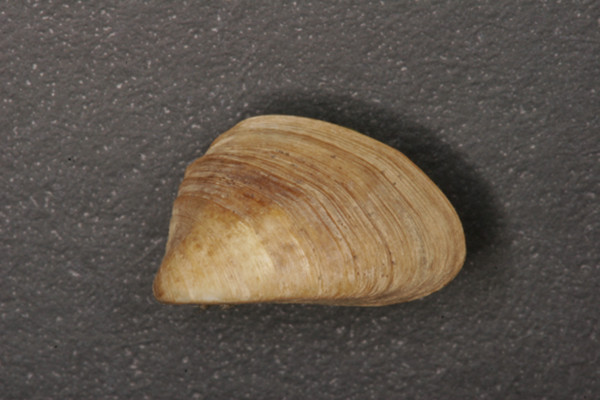

Congeria jalzici sp. nov. The holotype from Markov Ponor, Lipovo polje, Lika, Croatia. Croatian Natural History Museum, Zagreb, Croatia (Reg. No.: 10346).
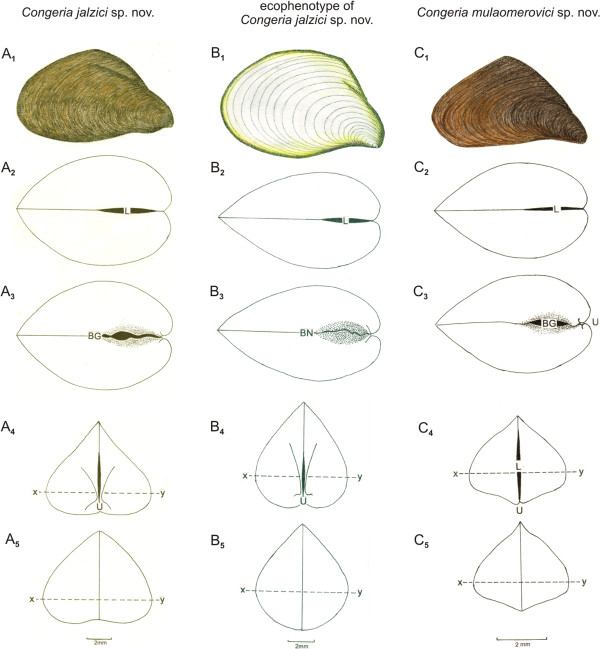
Figure 6.
Shells of Congeria. A shell of (A) Congeria jalzici sp. nov. from Markov Ponor, (B) the ecophenotype of Congeria jalzici sp. nov. from the Lukina Jama-Trojama Cave System, and (C) Congeria mulaomerovici sp. nov. from Oko. 1, right lateral view; 2, dorsal view; 3, ventral view; 4, anterior view; 5, posterior view. (x---y indicates the greatest shell width). Abbreviations: BG - Byssal gape; BN - Byssal notch; L - Ligament; U - Umbo. x-----y equals the greatest width of the shell.
Figure 7.
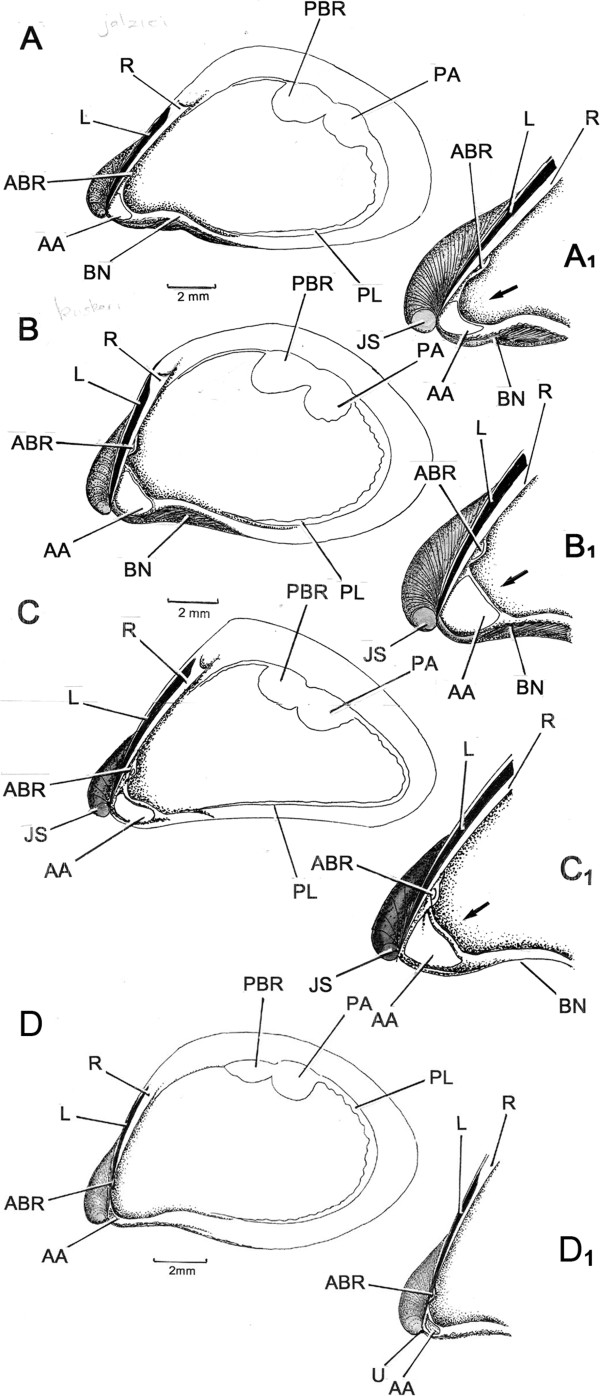
Internal shell structures. Internal views of the shells of A, Congeria jalzici sp. nov., B, Congeria kusceri, C, Congeria mulaomerovici sp. nov., and D, the ecophenotype of Congeria jalzici sp. nov. from the Lukina Jama-Trojama Cave System. Aı, Bı, Cı, and Dı are details of the hinge plates of the four specimens with the arrows pointing to the septa on which is inserted the anterior adductor muscles. Abbreviations: AA - Anterior adductor muscle scar; ABR - Anterior retractor muscle scar; BN - Byssal notch; JS - Juvenile shell; L - Ligament; PA - Posterior adductor muscle scar; PBR - Posterior byssal retractor muscle scar; PL - Pallial line; R - Resilifer; U - Umbo.
Material examined
HOLOTYPE. General Collection of Recent Molluscs, Croatian Natural History Museum, Zagreb (CNHM, Reg. No.: 10346). Locality: Markov Ponor, Lipovo Polje, Lika, Croatia (Co-ordinates: WGS84 x = 44°45′57″: y = 15°10′53″). Leg: B. Jalžić and H. Bilandžija, 2008–2009. Shell length: 11.7 mm; height: 7.0 mm; width: 8.0 mm (Figure 4).
PARATYPES: Specimens 1–3, General Collection of Recent Molluscs, Croatian Natural History Museum, Zagreb (CNHM, Reg. No.: 10347); Specimens 4–6, The Natural History Museum, London (Reg. No’s.: NHMUK 20110180–20110182). Locality: Markov Ponor, Lipovo Polje, Lika, Croatia (Co-ordinates: WGS84 x = 44°45′57″: y = 15°10′53″). Leg: B. Jalžić and H. Bilandžija, 2008–2009 (Table 1).
Table 1.
Shell dimensions of Congeria jalzici sp. nov.
| Shell length | Shell height | Shell width (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| 11.4 |
6.7 |
6.8 |
| 10.2 |
5.9 |
6.8 |
| 11.1 |
6.6 |
6.9 |
| 11.5 |
6.4 |
7.3 |
| 11.0 |
6.7 |
7.1 |
| 10.7 | 6.3 | 6.9 |
VOUCHER MATERIAL: Specimens 1 & 2, ecophenotypes of Congeria jalzici sp.nov.: General Collection of Recent Molluscs, Croatian Natural History Museum, Zagreb (CNHM, Reg. No.: 10348); Specimens 3 & 4, The Natural History Museum, London (Reg. No’s.: NHMUK 20110183 & 20110184). Locality: Lukina Jama – Trojama Cave System, Northern Velebit, Lika, Croatia. (Co-ordinates: WGS84 x = 44°46′04″: y = 15°01′52″). Leg: B. Jalžić, 2010 (Table 2).
Table 2.
Shell dimensions of Congeria jalzici sp. nov. ecophenotypes
| Shell length | Shell height | Shell width (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| 11.6 |
7.6 |
6.0 |
| 12.4 |
7.4 |
6.7 |
| 11.5 |
7.3 |
6.2 |
| 10.9 | 6.7 | 6.4 |
Description
Shell small, up to 13 mm in length, approximately equivalve, and distinctly inequilateral. Shell generally wider than it is tall, but often only slightly so. Periostracum brown. Distinctly heteromyarian with the swollen posterior face generally round; anterior narrowly rounded with the beaks pointed downwards. Postero- and antero-ventrally convex, although typically concave mid to antero-ventrally around a distinct byssal notch. Valve margins uniform, except ventrally around byssal notch where they are sinusoidal to varying degrees. An external, opisthodetic, ligament. Anterior adductor muscle scar situated on a small septum whose internal face is characteristically and smoothly rounded. Apophysis tiny, situated dorsal to the septum and located (partially hidden) under the resilifer and bears the tiny scar of the anterior byssal retractor muscle.
Remarks
As with its sister species, Congeria kusceri, the shell of Congeria jalzici sp. nov. is variable in form, but the septum is small and distinctively concave. Hence, the anterior adductor muscle scar of the former is much larger and has a near straight internal margin aligned with the straight septum margin.
The ecophenotype of Congeria jalzici sp. nov. from the Lukina Jama – Trojama Cave System is different, in terms of shell form, from the specimens obtained from the type locality. It has a near transparent shell, with the periostracum only obvious as a yellow – light brown marginal fringe. Its internal shell septum is even smaller than that of conspecifics from Markov Ponor and the shell has a less triangular form in cross-section.
Etymology
Congeria jalzici sp. nov. is named after Branko Jalžić, Croatian Natural History Museum, in honour of his achievements in the field of cave biology in the Dinarides and in appreciation of his invaluable help during this research.
Congeria mulaomerovici sp. nov. Morton & Bilandžija, 2013. (Figures 5, 6C, 7C)
Figure 5.
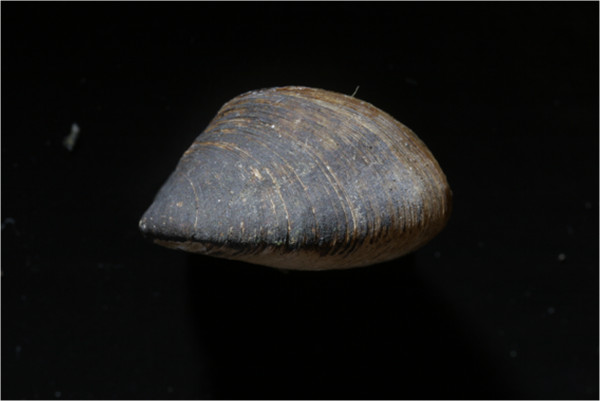

Congeria mulaomerovici sp. nov. The holotype from Oko, Lušci Palanka, north-western Bosnia, Bosnia and Herzegovina. The National Museum of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina (Reg. No.: 470).
Material examined
HOLOTYPE. Collection of Molluscs, The National Museum of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Sarajevo (Reg. No.: 470). Locality: Oko, Lušci Palanka, north-western Bosnia, Bosnia and Herzegovina (Co-ordinates: WGS84 x = 44°42′08″: y = 16°28′04″). Leg: B. Jalžić, 2011. Shell length: 11.8 mm; height: 6.8 mm; width: 8.0 mm (Figure 5).
PARATYPES: Specimens 1–3, The National Museum of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Sarajevo (Reg. No.: 471); Specimens 4–6, The Natural History Museum, London (Reg. No’s.: NHMUK: 20110469/1,2,3); Specimens 7–9, General Collection of Recent Molluscs, Zoology Department, Croatian Natural History Museum, Zagreb (CNHM, Reg. No.: 10348). Locality: Oko, Lušci Palanka, Bosnia and Herzegovina. Leg: B. Jalžić, 2011 (Table 3).
Table 3.
Shell dimensions of Congeria mulaomerovici sp. nov.
| Shell length | Shell height | Shell width (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| 12.0 |
7.3 |
7.6 |
| 10.9 |
7.2 |
6.6 |
| 10.8 |
6.7 |
6.3 |
| 10.6 |
6.7 |
6.4 |
| 11.2 |
7.1 |
7.1 |
| 10.4 |
6.1 |
6.7 |
| 10.2 |
6.2 |
6.1 |
| 10.4 |
6.4 |
6.5 |
| 10.0 | 6.2 | 6.0 |
Description
Shell small, up to 12 mm in length, approximately equivalve but distinctly and acutely inequilateral. Shell usually wider than it is tall, but often only slightly so. Periostracum uniformly brown. Distinctly heteromyarian with the postero-dorsal slope straight and, hence, sharply pointed; anteriorly also pointedly rounded. Ventrally flattened, although somewhat concave antero-ventrally around a slight byssal notch. Valve margins uniform, except ventrally around the byssal notch where they are slightly sinusoidal to varying degrees. The beaks point downwards. An external, opisthodetic, ligament. Anterior adductor muscle scar situated on a small septum whose internal face is smoothly sinusoidal. Apophysis small, situated dorsal to the septum and located (partially hidden) under the resilifer and bears the tiny scar of the anterior byssal retractor muscle.
Remarks
As with its sister species, Congeria kusceri and Congeria jalzici sp. nov., the shell of Congeria mulaomerovici sp. nov. is variable in overall form but is more distinctively pyramidal dorsally. Further, the septum is sinusoidal, such that the anterior adductor muscle scar is bean-shaped.
Etymology
Congeria mulaomerovici sp. nov. is named after Dr. Jasminko Mulaomerović, Centre for Karst and Speleology, Sarajevo, an eminent researcher of the karst in Bosnia and Herzegovina, and in appreciation of his support during our research.
A comparison of shell form
Congeria jalzici sp. nov. Seen from the right (Figure 6A1), the shell is antero-dorsally keeled and deeply convex at the midpoint around the keel. Seen from the dorsal aspect (Figure 6A2), the shell is posteriorly pointed and laterally inflated. The ventral valve margins (Figure 6A3) are straight posteriorly, anteriorly they are sinusoidal around a large byssal gape (BG). The separated umbones (U) are clearly obvious when seen from the anterior aspect (Figure 6A4). The shell is flattened ventrally and the greatest shell width (x---y) is situated close to the ventral side making the shell of C. jalzici sp. nov. distinctly mytiliform. From the posterior aspect (Figure 6A5), the shell is more rounded laterally and concave centrally.
Ecophenotype of Congeria jalzici sp. nov.. The shell of C. jalzici sp. nov. from the Lukina Jama – Trojama Cave System is distinctly less antero-dorsally keeled than conspecifics from the type locality (Figure 6B1) and therefore less concave at the mid antero-dorsal point. It is also posteriorly more rounded, less anteriorly convex and concave postero-ventrally around the byssal notch. Seen from the dorsal and ventral aspect (Figure 6B2, 6B3), the shell is like its type locality conspecifics except there is not a byssal gape although there is a shallow byssal notch (BN). In cross-section (Figure 6B4), the left and right valves are not indented as in type conspecifics but are more smoothly rounded to create a more drop-shaped form. The shell is less flattened ventrally, except at the valve margins, which are concave anteriorly. The greatest shell width (x---y) is situated at a point more dorsally than in type locality conspecifics and thus is not mytiliform. From the posterior aspect (Figure 6B5), the shell is distinctly rounded laterally and is not flattened ventrally as in type locality conspecifics. The shell of this population of C. jalzici sp. nov. is clearly not adapted to flowing waters as are conspecifics from the type locality.
Congeria kusceri. The shell of Congeria kusceri has been described by Morton et al. (1998, Figures seven-sixteen).
Congeria mulaomerovici sp. nov.. The shell of C. mulaomerovici sp. nov. is somewhat antero-dorsally keeled but at a point more anteriorly than in C. jalzici sp. nov. (Figure 6C1). It is dorsally peaked, almost pyramidal. Seen from the dorsal aspect (Figure 6C2), the shell is posteriorly pointed and laterally inflated. The ventral valve margins (Figure 6C3) are slightly curved posteriorly, anteriorly they are somewhat sinusoidal around a large byssal gape (BG). The right valve overlaps the left somewhat posterior and, especially, anteriorly such that the umbones (U) are distinctly unequally situated, the left more anterior than the right. The umbones are also less separated than in C. jalzici sp. nov.. The valves are slightly laterally indented in cross-section (Figure 6C4, 6C5) and the shell is ventrally keeled. As a consequence, the greatest shell width (x---y) is situated more dorsally than in C. jalzici sp. nov. so that the whole form of the shell is less mytiliform.
A comparison of hinge plates
Congeria jalzici sp. nov. (Figure 7A). Internally, the shell possesses a large posterior adductor muscle scar (PA), internal to which is the scar of the posterior byssal retractor muscle (PBR). There is a thick pallial line (PL), especially posteriorly and a small, bean-shaped anterior adductor muscle scar (AA) located on a shell shelf or septum, internal to the downwardly directed umbones. The long thin ligament is situated on a resilifer and extends approximately half way up the anterior slope of the shell. Underneath the resilifer, just above the shell shelf is a tiny apophysis on which is located the scar of the anterior byssal retractor muscle (ABR). There is a deep byssal notch (BN). The shell shelf (Figure 7A1) has a distinctively curved inner margin (arrowed).
The ecophenotype of Congeria jalzici sp. nov. (Figure 7D). The shell is altogether more delicate than in C. jalzici sp. nov. from its type locality. Similarly, the internal muscle scars are smaller and more delicate – indeed they are difficult to discern in such a thin, near-translucent, shell but their arrangement is approximately the same. In the ecophenotype of C. jalzici sp. nov., the shell septum is extremely delicate, but has the same form, a distinctively curved inner margin (Figure 7D1). The scar of the tiny anterior adductor muscle (AA) is located just internal to the umbo (U). The apophysis with its scar of the anterior byssal retractor muscle (ABR) is similarly proportionally smaller than in C. jalzici sp. nov. from its type locality.
Congeria kusceri (Figure 7B). The arrangement of the internal muscle scars are approximately the same as in C. jalzici sp. nov.. In C. kusceri, however, the shell septum is proportionally larger than in C. jalzici sp. nov., as are the scars of the anterior adductor muscle (AA) and the anterior byssal retractor muscle (ABR) situated on its also proportionally larger apophysis. The shell septum of C. kusceri (Figure 7B1) has a straight inner margin (arrowed) and the apophysis is located much closer to the shell septum.
Congeria mulaomerovici sp. nov. (Figure 7C). The shell is more steeply pointed dorsally and is distinctively more pointed posteriorly than in both C. kusceri and C. jalzici sp. nov., but the byssal notch is small. The arrangement of the internal muscle scars is approximately the same as in the previous two species. In C. mulaomerovici sp. nov., however, the shell septum is approximately mid way in size between the other two Congeria species as is the scar of the anterior adductor muscle (AA). The apophysis with its scar of the anterior byssal retractor muscle (ABR) is approximately the same size as in C. kusceri but, of all the three species it is located the closest to the shell septum and, in fact, partially beneath it (Figure 7C1). The shell shelf has a sinusoidal inner margin (arrowed).
Discussion
The Dreissenidae is an excellent candidate group to study evolutionary processes that shape close relatives into biologically and ecologically diverse sets of species. Here we have focused on the most rare and exceptional taxon in the family - Congeria - a Tertiary relict that underwent significant changes in morphology, biology and ecology to be the only survivor of a once widespread and diverse genus.
Phylogenetic relationships
Our results have shown that each of the three extant dreissenid genera form a monophyletic group. Although our Mytilopsis species representation is far from exhaustive, this confirms previous taxonomic understandings [20]. The sister relationship of Congeria and Mytilopsis is evident from both molecular and morphological characters. The presence of an apophysis is a common feature that separates them both from Dreissena but it has also been used as an argument to merge these two genera into one, that is, Congeria[21]. An apophysis is, however, the ancestral feature of the Dreissenidae and its sole use to infer dreissenid relationships has led to conclusions such as the polyphyletic origin of Dreissena. This view was most recently supported by Sket [22], who formally proposed the placement of Congeria kusceri into Mytilopsis. In a detailed study of the morphology of C. kusceri, however, Morton et al. [1] provided additional evidence to distinguish the species from others comprising Mytilopsis. Further, many aspects of the biology and ecology of C. kusceri are unique. In addition to its distinctive reproductive strategy, C. kusceri exhibits a wholly characteristic life history that involves extreme longevity (decades) [1] unlike the short lived (2–3 years), opportunistic, non-brooding, representatives of Dreissena and Mytilopsis[23,24]. Furthermore, our molecular clock analysis placed the timing of divergence between these two extant lineages at 22.6 MYA, arguing in favour of a special and distinctive placement for Congeria.
The results have demonstrated that instead of only one holodinaric species, as was previously thought, Congeria comprises at least three distinct species: C. kusceri, C. jalzici sp. nov. and C. mulaomerovici sp. nov.. Separate lineages have formed in the geographically and hydrologically isolated regions of the Dinaric Karst. Along with fragmentation of karstic underground habitats, both the sessile lifestyle and the reproductive strategy of C. kusceri[25] would not facilitate dispersal, so it is argued that speciation occurred after vicariant isolation of lineages in separate hydrological basins. Within the C. jalzici sp. nov. lineage, however, the isolated Slovenian population lacks any obvious genetic distinction, but shows slight and consistent differences in shell. Even if undiscovered populations exist between the Bela Krajina and Lika regions, it is unlikely that there is any gene flow present, because several hydrological basins and the divide between the Black Sea and the Adriatic Sea catchments separate these two populations. Without the possibility of communication, the most likely explanation for such a common genetic similarity would be a relatively recent split.
Effects on morphology
Over half of the known Congeria sites contain only empty shell deposits that were flushed to the surface by underground water currents. In order to be able to assign this material to any of the three Congeria species, we had to focus on finding distinctive shell characters. Shell morphometric measurements (Additional file 1) have, however, demonstrated that no single dimension differed significantly between all three species and the two species that are genetically and geographically most distant are most similar morphometrically. Shell morphology is, moreover, intra-specifically variable in all three species of Congeria, and C. jalzici sp. nov. is particularly remarkable in terms of a demonstrable shell plasticity. That is, two populations of this species, living in the same hydrological system (Figure 8), have significantly different shell morphologies. In the flowing waters of Markov Ponor, C. jalzici sp. nov. is characterised by a heteromyarian, ventrally flattened, shell whereas conspecifics from the Lukina Jama–Trojama Cave System at −1421 m below ground, are extremely delicate with ventrally concave shells and a reduced apophysis. In contrast to all other known Congeria localities where strong currents form during high water levels, the waters of the deep karst aquifer in the Lukina Jama–Trojama Cave System seem to be static and to rise and fall only slowly. The shape of Congeria shell and also the fact that tubes of Marifugia cavatica Absolon & Hrabe, 1930, grow perpendicular to the walls of the cave (B. Jalžić, personal information) point to this conclusion. The example of C. jalzici sp. nov. shows how the dreissenid shell is, to a great extent, shaped by environmental conditions and can be misleading, when viewed alone, in interpreting phylogenetic relationships within the family.
Figure 8.
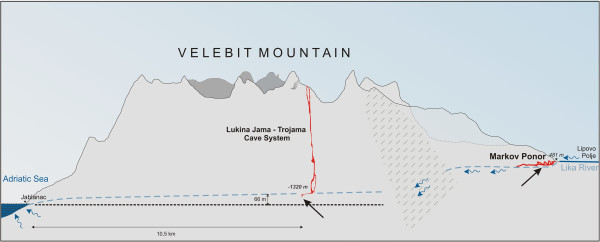
A cross section through Velebit Mountain, Lika, Croatia. The Markov Ponor and Lukina Jama – Trojama Cave System are hydrologicaly connected via underground conduits.
Finally, subtle differences between the three Congeria species have been identified in terms of hinge plate morphology. These include the sizes of shell septum and the anterior adductor muscle scar, the form of the inner margin and the position of the apophysis. These characters, although also showing variability, were consistent in all cave populations comprising one phylogenetic lineage (including the ecophenotype of C. jalzici sp. nov.). Interestingly, Schütt [21] distinguished a number of dreissenid species also on the detailed structure of the hinge plate/resilifer/apophysis. Despite the difference in opinion with regard to the generic placement of these taxa, it is evident from both Schütt’s and our studies that the only useful shell characters for distinguishing between these species of Dreissenidae relate to the hinge plate.
Divergence dating and evolutionary history
Our molecular clock estimates of divergence events within the Dreissenidae differ from those published previously [20,26,27]. All previous studies have utilised a strict clock for the timing of speciation events. In recent years, however, new methods have been developed that account for rate variation and assume uncorrelated rates of evolution [28,29], and these have been applied in the present study.
Although a wide uniform prior of 33.9-55.8 MYA was used to calibrate the origin of the Dreissenidae, the posterior estimates narrowed the divergence time to 37.4 MYA. This age estimate corresponds to the time frame of the formation of the Paratethys Sea [30] as well as the occurrence of the first certain dreissenid fossils [31]. Our study was not designed for divergence dating within Dreissena and the species coverage of this genus is incomplete in our dataset (for associated problems see Wilke [32]), but there is some correlation between our Dreissena divergence estimates and those reported in studies of Stepien et al. [20,26,27]. Their divergence ranges vary slightly from study to study, but they collectively place the split between D. rostriformis bugensis and D. polymorpha at around 10–15 MYA, which is consistent with the fossil record and supports our calibration choices. Our estimates of the divergence of D. polymorpha and the Balkan D. blanci/D. presbensis clade at 6.9 MYA is more ancient then reported by Stepien et al. [27]. The occurrence of D. polymorpha in lower Pliocene deposits from the southernmost remnants of Lake Pannon [3], suggest that this species followed the immigration route into the eastern Paratethys, presumably through the Dacian Basin [2], rather later. This implies that the common ancestor of the Balkan clade started migration towards the central Balkans during the late Miocene. Sometime during the Pliocene it settled in Lake Ohrid, which became the source of today’s Dreissena biodiversity in the region [33]. This is in accordance with the late Miocene/early Pliocene timeframe of changes in distributions of Dreissena lineages [27]. The divergence between the two Balkan clades of Dreissena happened after ancestors of D. blanci invaded the southern Ionian region from Lake Ohrid [33] around 1.9 MYA, according to our estimates.
Our results show a divergence time of 22.6 MYA for the split between the ancestors of the extant Mytilopsis species from the Americas and the ancestors of stygobiotic Congeria spp. This estimate roughly corresponds to the Oligocene/Miocene boundary and follows after the isolation and the establishment of the Paratethys as an independent biogeographic unit in Late Oligocene [2]. This is in accordance with Nutall [4], who proposed that founder populations of extant Mytilopsis lineages invaded the New World in the Late Oligocene. Another possible scenario is a gene flow blockade between Mytilopsis populations from both sides of the Atlantic as a result of the isolation of the Paratethys. Following this event, the New World Mytilopsis evolved independently of their relatives that remained in Europe. After the split with Congeria, that occurred in the long-lived Lake Pannon about 11.6 MYA [3], the European lineages of Mytilopsis became extinct.
According to the exponential clock model, the first split within the extant lineages of Congeria happened around 8 MYA, what approximately corresponds to the ages of the holodinaric groups of Troglocaris and Proteus, although 7.5-8.5 MYA was the lowest estimate of the inferred ranges for these taxa [34]. The lognormal clock gave different estimates and the discrepancy is probably due to the fact that the exponential model assumes most branch rates are small. Due to their generation times, reproductive strategies and pronounced adaptability that enabled high invasiveness, most dreissenids would not be expected to have slow mutation rates. The lognormal clock therefore probably gives better estimates. The lognormal clock estimate of 5.4 MYA corresponds approximately with the disappearance of Congeria from the fossil record, which coincided with large paleogeographical changes in the region involving the final disappearance of both Lake Pannon and the bordering Dinaride Lake System [3]. Although the Dinaride Lake System is more frequently suggested as the source of stygobiotic Congeria ancestors [1,22] the adjacent Lake Pannon offers another possible alternative.
Lake Pannon was a long-lasting lake where Congeria originated and went through an exceptional radiation [2,3]. Its disappearance gradually progressed from north to south, and by the late Miocene/early Pliocene it occupied only the extreme south of its previous range, an area bordering the Dinaric Karst. Part of the Lake Pannon fauna has survived to the present day by immigration into other regions before the lake finally vanished. For example, Lake Pannon is considered to be the source of the Ponto-Caspian fauna and it also had an impact on the fauna of Balkan lakes such as Lake Ohrid [2]. According to one of the biogeographical scenarios presented by Albrecht et al. [35], the ancestor of endemic Balkan Dreissena migrated from the Pannon basin into central Balkan lakes that are situated even further from Lake Pannon than the neighbouring Dinarides. The origin of Asselus aquaticus (Linnaeus, 1758) lineages is also considered to be the western Pannonian region, from where it colonised the rest of Europe including the Dinaric Karst around 4–5 MYA [36]. It is, therefore, possible that the ancestral stock of the subterranean Congeria lineages invaded the Dinaric Karst from Lake Pannon. If so, this must have happened prior to the first divergence event that separated today’s north-western and south-eastern lineages. Perhaps it coincided with the split of the “Dinaro-Caucasian” lineage of Troglocaris into Dinaric and Caucasian clades, which was estimated at 6–11 MYA [17], implying that there must have been a faunal interchange between the Dinaric water systems and the Paratethyan basins of Central Europe up to that time period.
The second divergence event occurred in the northern portion of the present distribution and separated the northern Bosnian populations of Congeria mulaomerovici sp. nov. from Congeria jalzici sp. nov. at about 2.5 MYA according to the lognormal clock. This occurred much later than the isolation of the northern Bosnian populations from the remaining Proteus (4.4-5.4 MYA) and Troglocaris anophthalmus (Kollar, 1848) lineages (3.7-5.3 MYA) [17,34]. Along with divergence time estimates of various Dinaric groundwater taxa, the phylogeographical patterns are incongruent as well [15,16,18,34]. The disparities may be the result of dissimilarities in biology of these animals and/or a complex geological history of the Dinaric Karst. Progressive karstification alters hydrological relationships over time and consequently the distributions of phylogenetic lineages are often not concordant with present day hydrological regimes, for example in Asellus aquaticus[19], Troglocaris anophthalmus[18] and Congeria jalzici sp. nov..
On the other hand, the disparities in the divergence estimates may be a result of availability and employment of different molecular clock methodologies. In comparison to the other groundwater Dinaric taxa, hard-shelled dreissenids have a rich fossil record that can possibly enable more reliable time divergence dating. Unfortunately, plasticity of the dreissenid shell makes linking of cave Congeria lineages with any of the fossil species highly speculative so the questions regarding the last surface ancestor and its colonisation of the underground remain to be answered. Further studies are needed to resolve these issues and to create an integrated picture of the processes that shaped the subterranean biodiversity of the Dinaric Karst.
Conclusions
In conclusion, Congeria is a distinct member of the Dreissenidae that is separated from its closest extant relatives - Mytilopsis - by ~22-23 million years of independent evolution. The exact origin of the subterranean Congeria lineage is problematic because the innate plasticity of the dreissenid shell, as demonstrated in this study, does not allow the cave Congeria lineage to be related to the fossil dressenids of either the Lake Pannon or the Dinaride Lake Systems. Isolation in the Dinaric Karst underground has driven the speciation of the three allopatric lineages of Congeria: C. kusceri, C. jalzici sp. nov., and C. mulaomerovici sp. nov., herein identified morphologically and genetically. Inter-specific morphological stasis of shell forms has not been interrupted during the colonisation of caves or subsequent speciations. Instead, a plesiomorphic shell form has been retained and remained relatively unaffected by the millions of years that the tree species have spent in isolation from each other. The divergent shell form within a single lineage illustrated by the ecophenotype of C. jalzici sp. nov. has possibly arisen as an adaptation to a specific subterranean microhabitat.
The tasks of understanding the evolutionary history of Congeria spp., especially their origin and colonisation of the subterranean habitats as well as how genotypic and ecophenotypic components interact, provide new interdisciplinary challenges.
Methods
Taxon sampling and identification
Samples of Congeria from all 15 caves (Figure 1) known to harbour living populations have been examined. Individuals were partly collected between 2008 and 2011. Others were obtained from the Croatian Natural History Museum, and the University of Ljubljana. Dreissena polymorpha Pallas, 1771 was collected from Lake Jarun, Zagreb, Croatia. Dreissena rostriformis bugensis (Andrusov, 1897) was obtained from Ijsselmeer, Lelystadt, The Netherlands, and Mytilopsis sallei (Récluz, 1849) was obtained from Hong Kong, China.
DNA extraction, amplification cloning and sequencing
The fragments of two mitochondrial (COI and 16S rRNA) and two nuclear (28S and 18S rRNA) genes were sequenced from one individual of Dreissena polymorpha, Dreissena rostriformis bugensis, Mytilopsis sallei and 44 different Congeria specimens from 15 locations including, for the first time, the type locality of C. kusceri, Žira ponor. DNA was extracted using DNeasy Blood & Tissue kit (Qiagen) or i-genomic DNA extraction kit (Intron). The primers, PCR reaction components and cycling conditions are indicated in Additional file 2. PCR products were separated by electrophoresis in 0.5 to 1.5% agarose gels, excised from the gel and purified using QIAquick Gel Extraction Kit (Qiagen) or MEGAquick-spin PCR & Agarose Gel DNA Extraction System (Intron). DNA fragments were cloned into either pGEM-T or pGEM-T Easy Vector Systems (Promega) or were sequenced directly using an ABI PRISM 3100 automatic sequencer (Applied Biosystem).
PCR products were sequenced on both strands and inspected manually for ambiguities. The resulting sequences have been deposited in GenBank. Sequences from Dreissena blanci (Westerlund, 1890), Dreissena presbensis Kobelt, 1915, Mytilopsis leucophaeta (Conrad, 1831) and three selected outgroups were retrieved from GenBank. Accession numbers are listed in Table 4. Outgroups were chosen according to Park & O’Foighil [37] and Taylor et al. [38]. Since there is no consensus regarding the group most closely related to the Dreissenidae, Mya arenaria Linnaeus, 1758, Corbicula fluminea (O.F. Müller, 1774) and Sphaerium striatinum (Lamarck, 1818) were selected as outgroups.
Table 4.
List of species and GenBank Accession numbers of sequences used in this study
| Species | Source | Specimen | 18S rRNA | 28S rRNA | 16S rRNA | COI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Congeria kusceri |
Plitica, Popovo polje, BA |
Pl2 |
JX099472 |
JX099493 |
JX099451 |
JX099431 |
| Pl4 |
|
JX524681 |
JX524654 |
JX524708 |
||
| Pl7 |
|
JX524682 |
JX524655 |
JX524709 |
||
|
Congeria kusceri |
Žira, Popovo polje, BA |
Z3 |
JX099475 |
JX099496 |
JX099454 |
JX099434 |
| Z4 |
|
JX524686 |
JX524659 |
JX524713 |
||
|
Congeria kusceri |
Doljašnica, Popovo polje, BA |
D1 |
|
JX524664 |
JX524637 |
JX524692 |
| D6 |
|
JX524665 |
JX524638 |
JX524691 |
||
| D10 |
JX099460 |
JX099481 |
JX099439 |
JX099419 |
||
|
Congeria kusceri |
Gradnica, Neum, BA |
G2 |
|
JX524666 |
JX524639 |
JX524693 |
| G5 |
JX099461 |
JX099482 |
JX099440 |
JX099420 |
||
| G7 |
|
JX524667 |
JX524640 |
JX524694 |
||
|
Congeria kusceri |
Jama u Predolcu, Metković, HR |
J4 |
|
JX524669 |
JX524642 |
JX524696 |
| J8 |
|
JX524670 |
JX524643 |
JX524697 |
||
| J10 |
JX099464 |
JX099485 |
JX099443 |
JX099423 |
||
|
Congeria kusceri |
Pukotina u Tunelu Polje Jezero-Peračko Blato, Ploče, HR |
P2 |
|
JX524679 |
JX524652 |
JX524706 |
| P5 |
|
JX524680 |
JX524653 |
JX524707 |
||
| P6 |
JX099470 |
JX099491 |
JX099449 |
JX099429 |
||
| P8 |
JX099471 |
JX099493 |
JX099450 |
JX099430 |
||
|
Congeria kusceri |
Jasena, Vrgorac, HR |
Jas1 |
JX099465 |
JX099486 |
JX099444 |
JX099424 |
| Jas4 |
|
JX524671 |
JX524644 |
JX524698 |
||
| Jas7 |
|
JX524672 |
JX524645 |
JX524699 |
||
|
Congeria kusceri |
Tihaljina, Ljubuški, BA |
T1 |
JX099474 |
JX099495 |
JX099453 |
JX099433 |
| T3 |
|
JX524684 |
JX524657 |
JX524711 |
||
| T6 |
|
JX524685 |
JX524658 |
JX524712 |
||
|
Congeria mulaomerovici sp.nov. |
Oko, Lušci Palanka, Northern Bosnia, BA |
O1 |
JX099469 |
JX099490 |
JX099448 |
JX099428 |
| O3 |
|
JX524677 |
JX524650 |
JX524704 |
||
| O5 |
|
JX524678 |
JX524651 |
JX524705 |
||
|
Congeria mulaomerovici sp.nov. |
Suvaja, Lušci Palanka, Northern Bosnia, BA |
S7 |
|
JX524683 |
JX524656 |
JX524710 |
| S8 |
JX099473 |
JX099494 |
JX099452 |
JX099432 |
||
|
Congeria mulaomerovici sp.nov. |
Dabarska Pećina, Sanski Most, Northern Bosnia, BA |
DB1 |
JX099459 |
JX099480 |
JX099438 |
JX099418 |
| DB2 |
|
JX524660 |
JX524633 |
JX524687 |
||
| DB3 |
|
JX524661 |
JX524634 |
JX524688 |
||
|
Congeria jalzici sp.nov. |
Markov Ponor, Lipovo Polje, Lika, HR |
M2 |
|
JX524675 |
JX524648 |
JX524702 |
| M6 |
|
JX524676 |
JX524649 |
JX524703 |
||
| M9 |
JX099468 |
JX099489 |
JX099447 |
JX099427 |
||
|
Congeria jalzici sp.nov. |
Dankov Ponor, Lipovo Polje, Lika, HR |
DP2 |
|
JX524662 |
JX524635 |
JX524689 |
| DP3 |
JX473583 |
JX524663 |
JX524636 |
JX524690 |
||
|
Congeria jalzici sp.nov. |
Lukina Jama – Trojama Cave System, Northern Velebit, Lika, HR |
L1 |
JX099466 |
JX099487 |
JX099445 |
JX099425 |
| L2 |
|
JX524673 |
JX524646 |
JX524700 |
||
| L3 |
|
JX524674 |
JX524647 |
JX524701 |
||
| L4 |
JX099467 |
JX099488 |
JX099446 |
JX099426 |
||
|
Congeria jalzici sp.nov. |
Izvir Jamske Školjke, Metlika, Bela Krajina, SI |
I1 |
JX099462 |
JX099483 |
JX099441 |
JX099421 |
| I2 |
JX099463 |
JX099484 |
JX099442 |
JX099422 |
||
| I3 |
|
JX524668 |
JX524641 |
JX524695 |
||
|
Mytilopsis sallei |
Lam Tsuen River, Shatin, Hong Kong, China |
|
JX099476 |
JX099497 |
JX099455 |
JX099435 |
|
JX099477 |
|
JX099456 |
|
|||
|
Mytilopsis leucophaeata |
GenBank |
|
AF305704 |
EF414468 |
EF414448 |
HM100258 |
|
Dreissena polymorpha |
Jarun Lake, Zagreb, HR |
|
JX099478 |
JX099499 |
JX099458 |
JX099437 |
|
Dreissena bugensis |
Ijsselmeer, Lelystadt, The Netherlands |
|
JX099479 |
JX099498 |
JX099457 |
JX099436 |
|
Dreissena presbensis |
GenBank |
|
- |
EF414469 |
EF414449 |
EF414491 |
|
Dreissena blanci |
GenBank |
|
- |
EF414471 |
EF414459 |
EF414483 |
|
Sphaerium spp. |
GenBank |
|
S. corneum |
S. corneum |
S. striatinum |
S. striatinum |
|
AM774537 |
AM779711 |
AF152041 |
AF120667 |
|||
|
Mya arenaria |
GenBank |
|
AF120560 |
FM999792 |
AY377618 |
AF68 |
| Corbicula fluminea | GenBank | AF120557 | DQ343848 | AF038999 | U47647 |
DNA sequence alignment
Sequences were aligned using the ClustalW option in BioEdit [39], and the resulting alignments were inspected manually and tested using Gblocks Server [40,41]. The regions identified as problematic and aligned poorly were excluded from subsequent analyses. The COI fragment showed significant variation, which was confirmed with the test for substitution saturation [42] implemented in Dambe [43]. Since there were no topological differences between the analyses ran with or without the 3rd codon position, the COI 3rd codon position was included in all phylogenetic analyses.
Phylogenetic analyses
The final dataset consisted of 1736 bp of the 18S rRNA gene, 1046 bp of the 28S rRNA, 470 bp of the 16S rRNA and 595 bp of the COI gene fragment. The best-fit partitioning schemes as well as nucleotide substitution models for each partition were calculated using the PartitionFinder [44]. “Branchlengths” were set to unlinked allowing branch length to be estimated independently for each subset, “search” to all in order to analyse all possible partitioning schemes, and “models” were set to mrbayes or to all, depending on whether the results were used for setting up Bayesian or ML analyses, respectively.
The rate heterogeneity test performed in PAUP [45] showed significant incongruence between different partitions. The phylogenetic analyses were, therefore, performed for each gene fragment separately. Inspection of the results revealed inconsistencies in the positions of Dreissena spp. in the 18S rRNA tree and the position of Mytilopsis spp. in the 16S gene tree. Since none of the conflicting branches had good posterior probabilities or bootstrap support, concatenated trees were constructed using Bayesian, MP and ML methods.
Maximum parsimony (MP) analyses were conducted in MEGA 5 [46]. The trees were obtained using the default settings. All sites were equally weighted and gaps were partially deleted (sites were deleted if gaps were present in more than 5% of the sequences). The resulting phylogeny was tested by 5,000 bootstrap replications.
Several independent Bayesian searches were run in MrBayes version 3.1.2 [47] for altogether 10 million generations with a sampling density of 1/100. The starting tree was random and partitioning scheme and substitution model type fixed according to results in PartitionFinder while model parameter values were estimated. First 17% of the generations that had average standard deviation of the split frequencies above 0,01 were discarded as burn in. Additionally, mixing of chains and ESS values were checked using Tracer [48]. Bayesian posterior probabilities (BPP) were estimated from the 50% majority-rule consensus tree.
Five replicates of maximum likelihood (ML) searches were performed in Garli [49]. Partitions and model types were set as determined in PartitionFinder while model parameter values were estimated by the program. All program settings were default except “streefname” which was set to random enabling multiple searches with random starting trees, “modweight” which was set to 0.003 according to developer’s instructions in order to ensure that partitioned models are properly optimised and during 200 bootstrap replicates “genthreshfortopoterm”, the first part of termination condition, was set to 10,000. Bootstrap consensus trees were obtained in Geneious Basic.
Divergence times were calculated on a reduced dataset using the relaxed clock in Beast 1.6.2. The dataset consisted of one sequence from the putative type locality of each Congeria lineage. Mya arenaria was included as an outgroup. The dataset was partitioned by different gene fragments, and substitution models were unlinked. To ensure that the dataset was robust enough for the divergence dating and that posterior ranges were not dominated by prior choices, we used both lognormal and exponential clocks, explored different prior distributions on various parameters (calibration nodes and means of the branch rates) and ran the analysis using sampling from the prior only. The Birth-death model was used as a tree prior.
Based on fossil data, we set up two points to calibrate the tree. The first undisputed dreissenid fossil is from the Priabonian Age (33.9–37.2 MYA), but there is also a questionable record from the Ypressian Age (48.6–55.8 MYA) [31]. We, therefore, used uniform prior spanning entire Eocene (55.8–33.9 MYA) to calibrate the family node. The origin of Dreissena was used as a second calibration point. Dreissena has a clear morphological feature, the lack of a shell apophysis for the attachment of the anterior byssal retractor muscle, which distinguishes it from other, both extant and fossil, genera. Although this feature has previously been considered a polyphyletic trait (references in Müller et al., 1999, e.g., Papp, 1950; 1985; Lueger, 1980; Taylor in Gray, 1988), our and other genetic studies [27,35] clearly demonstrate that Dreissena and, therefore, the loss of the apophysis, is of monophyletic origin. Dreissena first appeared in Lake Pannon 11.6 MYA [3]. Accordingly, we used lognormal prior with the onset of 11.6 MYA and a standard deviation of 0.75 to include the beginning of the Sarmatian Period (12.7 MYA) within the 95% of the prior probability density, because part of the Lake Pannon fauna, including dreissenids, originated in the Samartian Paratethyan Lakes [2,50].
With the final settings, we ran three independent runs and a total of 60 million generations, which after 15% burn in, yielded 51 million trees. We compared independent chains in Tracer to ensure that the chains had reached stationarity and converged to the same posterior distribution. There was no significant difference between the runs, and LogCombiner was thus used to pool all estimates into one file.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
HB conceived and designed the study, performed field work, carried out the molecular genetic studies, participated in the phylogenetic and morphological analysis, performed molecular clock analysis and drafted the manuscript. BM performed the morphological studies and statistical analysis and drafted the manuscript. MP participated in the phylogenetic analysis, HĆ conceived, designed and coordinated the study. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Supplementary Material
Shell morphometrics. The file contains details of the methods and results of morphometric shell measurements.
The PCR primers, reactions and conditions used in this study. The file contains details on the PCR primers, reaction components and cycling conditions used in the study.
Contributor Information
Helena Bilandžija, Email: hbilandz@irb.hr.
Brian Morton, Email: prof_bmorton@hotmail.co.uk.
Martina Podnar, Email: martina.podnar@hpm.hr.
Helena Ćetković, Email: cetkovic@irb.hr.
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by Croatian MSES grants 098–0982913–2874 (H. Ćetković). Part of the fieldwork was financed by the Croatian State Institute for Nature Protection. We are indebted to Branko Jalžić and many members of Croatian Biospeleological Society and other caving clubs in Croatia for their assistance and help with fieldwork. Nikola Tvrtković and Markica Vuica are thanked for logistical support. Boris Sket, Peter Trontelj and Valerija Zakšek (University of Ljubljana) are thanked for providing us with part of the Congeria material. We are grateful to Andrej Hudoklin, Martin Ilenić and Boris Sket for enabling the collections in Slovenia. In Bosnia and Herzegovina we benefited from the help of Jasminko Mulaomerović, Ivo Lučić, the Zelena brda caving club (Trebinje) especially Dubravko Kurtović, Dejan Janković and Miroslav Đokić - Đole as well as Zlatko Grizelj, Zoran Weber and Ivan Bebek who helped us during fieldtrips in western Herzegovina. Abraham bij de Vaate, Waterfauna Hydrobiologisch Adviesbureau, The Netherlands, is thanked for providing specimens of Dreissena rostriformis bugensis. G.E. Dinesen, Technical University, Denmark, and K F. Leung, Environmental Protection Department, Hong Kong SAR Government, Hong Kong, are especially thanked for statistical help. Mirna Imešek and Inga Patarčić are acknowledged for their laboratory help. Darko Bakšić gave permission to use and change his Velebit profile figure. William R. Jeffery, Branko Jalžić, Matija Harcet and two anonymous reviewers gave useful comments on earlier versions of this manuscript.
References
- Morton B, Velkovrh F, Sket B. Biology and anatomy of the “living fossil” Congeria kusceri (Bivalvia: Dreissenidae) from subterranean rivers and caves in the Dinaric karst of the former Yugoslavia. J Zool. 1998;245:147–174. [Google Scholar]
- Müller P, Geary DH, Magyar I. The endemic molluscs of the Late Miocene Lake Pannon: their origin, evolution, and family-level taxonomy. Lethaia. 1999;32:47–60. [Google Scholar]
- Harzhauser M, Mandic O. In: The Zebra Mussel in Europe. van der Velde G, Rajagopal S, Bij de Vaate A, editor. Weikersheim: Backhuys Publishers, Leiden/Margraf Publishers; 2010. Neogene dreissenids in Central Europe: evolutionary shifts and diversity changes; pp. 11–29. [Google Scholar]
- Nuttall CP. Review of the Caenozoic heterodont bivalve superfamily Dreissenacea. Palaeontology. 1990;33:707–737. [Google Scholar]
- Kochansky-Devide V, Sliskovic T. Miocenske kongerije Hrvatske, Bosne i Hercegovine. Zagreb: Jugoslavenska Akademija Znanosti i Umjetnosti; 1978. p. 19. [Google Scholar]
- Culver DC, Sket B. Hotspots of subterranean biodiversity in caves and wells. J Cave Karst Stud. 2000;62:11–17. [Google Scholar]
- Deharveng L, Gibert J, Culver DC. In: Encyclopedia of Caves. 2. White WB, Culver DC, editor. New York: Academic Press; 2011. Diversity patterns in Europe; pp. 219–228. [Google Scholar]
- Sket B. High biodiversity in hypogean waters and its endangerment - The situation in Slovenia, the Dinaric Karst, and Europe. Crustaceana. 1999;72:767–779. doi: 10.1163/156854099503951. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Sket B. Presenetljive novosti v jamski favni Bosanske Krajine. Naše jame. 1970;11:93–99. [Google Scholar]
- Jalžić B. The first finding of a live stygobiont bivalve Congeria in the Lika region, Croatia. Nat Croat. 2001;10:213–220. [Google Scholar]
- Cuttelod A, Seddon M, Neubert E. European Red List of Non-Marine Molluscs. Luxembourg: Publications Office of the European Union; 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bilandžija H, Jalžić B. In: Red Book of Croatian Cave Dwelling Fauna. Ozimec R, Zagreb KL, editor. Republic of Croatia: Ministry of Culture, State Institute for Nature Protection; 2009. Dinaric cave clam, Congeria kusceri Bole; pp. 67–68. [Google Scholar]
- Culver DC, Pipan T. The biology of caves and other subterranean habitats. USA: Oxford University Press; 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Bilandžija H, Ćetković H, Jeffery WR. Evolution of albinism in cave planthoppers by a convergent defect in the first step of melanin biosynthesis. Evol Dev. 2012;14:196–203. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-142X.2012.00535.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trontelj P, Douady CJ, Fišer C, Gibert J, Gorički Š, Lefébure T, Sket B, Zakšek V. A molecular test for cryptic diversity in ground water: how large are the ranges of macro-stygobionts? Freshwater Biol. 2009;54:727–744. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2427.2007.01877.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Gorički Š, Trontelj P. Structure and evolution of the mitochondrial control region and flanking sequences in the European cave salamander Proteus anguinus. Gene. 2006;378:31–41. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2006.04.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakšek V, Sket B, Trontelj P. Phylogeny of the cave shrimp Troglocaris: Evidence of a young connection between Balkans and Caucasus. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2007;42:223–235. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2006.07.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakšek V, Sket B, Gottstein S, Franjević D, Trontelj P. The limits of cryptic diversity in groundwater: phylogeography of the cave shrimp Troglocaris anophthalmus (Crustacea: Decapoda: Atyidae) Mol Ecol. 2009;18:931–946. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2008.04061.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verovnik R, Sket B, Trontelj P. Phylogeography of subterranean and surface populations of water lice Asellus aquaticus (Crustacea: Isopoda) Mol Ecol. 2004;13:1519–1532. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2004.02171.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stepien C, Morton B, Dabrowska K, Guarnera R, Radja T, Radja B. Genetic diversity and evolutionary relationships of the troglodytic “living fossil” Congeria kusceri (Bivalvia: Dreissenidae) Mol Ecol. 2001;10:1873–1879. doi: 10.1046/j.0962-1083.2001.01329.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schütt H. Proceedings of the Tenth International Malacological Congress. Tubingen; 1991. The taxonomical situation in the genus Congeria Partsch; pp. 607–610. [Google Scholar]
- Sket B. Origins of the Dinaric troglobiotic mussel and its correct taxonomical classification. Congeria or Mytilopsis (Bivalvia: Dreissenidae)? Acta Biologica Slovenica. 2012;54:67–76. [Google Scholar]
- Morton B. Studies on the biology of Dreissena polymorpha Pall III. Population dynamics. Proc Malacol Soc Lond. 1969;38:471–482. [Google Scholar]
- Morton B. Life-history characteristics and sexual strategy of Mytilopsis sallei (Bivalvia, Dreissenacea), introduced into Hong-Kong. J Zool. 1989;219:469–485. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7998.1989.tb02594.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Morton B, Puljas S. Life history strategy, with ctenidial and mantle larval brooding, of the troglodytic “living fossil” Congeria kusceri (Bivalvia: Dreissenidae) from the Dinaric karst of Croatia. Biol J Linn Soc Lond. 2013;108:294–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1095-8312.2012.02020.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Stepien CA, Hubers AN, Skidmore JL. Diagnostic genetic markers and evolutionary relationships among invasive dreissenoid and corbiculoid bivalves in North America: phylogenetic signal from mitochondrial 16S rDNA. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 1999;13:31–49. doi: 10.1006/mpev.1999.0666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stepien CA, Taylor CD, Grigorovich IA, Shirman SV, Wei R, Korniushin AV, Dabrowska KA. DNA and systematic analysis of invasive and native dreissenid mussels: Is Dreissena bugensis really D rostriformis? Aquat Invaders. 2003;14:8–18. [Google Scholar]
- Drummond AJ, Ho SYW, Phillips MJ, Rambaut A. Relaxed phylogenetics and dating with confidence. PLoS Biol. 2006;4:e88. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0040088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond A, Rambaut A. BEAST: Bayesian evolutionary analysis by sampling trees. BMC Evol Biol. 2007;7:214. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-7-214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rögl F. Mediterranean and Paratethys. Facts and hypotheses of an Oligocene to Miocene paleogeography (short overview) Geol Carpathica. 1999;50:339–349. [Google Scholar]
- Benton MJ. Fossil Record 2. London: Chapman & Hall; 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Wilke T. How dependable is a non-local molecular clock? A reply to Hausdorf et al. (2003) Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2004;30:835–840. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2003.08.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilke T, Schultheiß R, Albrecht C, Bornmann N, Trajanovski S, Kevrekidis T. Native Dreissena freshwater mussels in the Balkans: in and out of ancient lakes. Biogeosciences. 2010;7:3051–3065. doi: 10.5194/bg-7-3051-2010. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Trontelj P, Gorički S, Polak S, Verovnik R, Zakšek V, Sket B. Age estimates for some subterranean taxa and lineages in the Dinaric Karst. Acta Carsologica. 2007;36:183–189. [Google Scholar]
- Albrecht C, Schultheiß R, Kevrekidis T, Streit B, Wilke T. Invaders or endemics? Molecular phylogenetics, biogeography and systematics of Dreissena in the Balkans. Freshwater Biol. 2007;52:1525–1536. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2427.2007.01784.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Verovnik R, Sket B, Trontelj P. The colonization of Europe by the freshwater crustacean Asellus aquaticus (Crustacea: Isopoda) proceeded from ancient refugia and was directed by habitat connectivity. Mol Ecol. 2005;14:4355–4369. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2005.02745.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park J-K, O’Foighil D. Sphaeriid and corbiculid clams represent separate heterodont bivalve radiations into freshwater environments. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2000;14:75–88. doi: 10.1006/mpev.1999.0691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor JD, Williams ST, Glover EA, Dyal P. A molecular phylogeny of heterodont bivalves (Mollusca: Bivalvia: Heterodonta): new analyses of 18S and 28S rRNA genes. Zool Scr. 2007;36:587–606. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-6409.2007.00299.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Hall TA BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT Nucleic acids symposium series 199995–98.Volume 4110780396
- Castresana J. Selection of conserved clocks from multiple alignments for their use in phylogenetic analysis. Mol Biol Evol. 2000;17:540–552. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a026334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talavera G, Castresana J. Improvement of phylogenies after removing divergent and ambiguously aligned blocks from protein sequence alignments. Syst Biol. 2007;56:564–577. doi: 10.1080/10635150701472164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xia X, Xie Z, Salemi M, Chen L, Wang Y. An index of substitution saturation and its application. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2003;26:1–7. doi: 10.1016/S1055-7903(02)00326-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xia X, Xie Z. DAMBE: software package for data analysis in molecular biology and evolution. J Hered. 2001;92:371–373. doi: 10.1093/jhered/92.4.371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanfear R, Calcott B, Ho SYW, Guindon S. PartitionFinder: combined selection of partitioning schemes and substitution models for phylogenetic analyses. Mol Biol Evol. 2012;29:1695–1701. doi: 10.1093/molbev/mss020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swofford D. PAUP*. Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (*and Other Methods). Version 4. Sunderland, MA: Sinauer Associates; 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S. MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol. 2011;28:2731–2739. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msr121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronquist F, Huelsenbeck JP. MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics. 2003;19:1572–1574. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btg180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rambaut A, Drummond AJ. Tracer v1. 4. 2007. Available from http://beast.bio.ed.ac.uk/Tracer.
- Zwickl DJ. Genetic algorithm approaches for the phylogenetic analysis of large biological sequence datasets under the maximum likelihood criterion. PhD thesis. : The University of Texas at Austin; 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Harzhauser M, Mandic O. Neogene lake systems of Central and South-Eastern Europe: Faunal diversity, gradients and interrelations. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol. 2008;260:417–434. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2007.12.013. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Shell morphometrics. The file contains details of the methods and results of morphometric shell measurements.
The PCR primers, reactions and conditions used in this study. The file contains details on the PCR primers, reaction components and cycling conditions used in the study.