Abstract
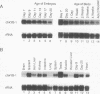
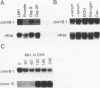
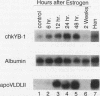
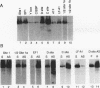
A cDNA expression library constructed from day 9 embryonic liver was screened with a previously identified protein binding site in the flanking region of the liver-specific, estrogen-dependent avian apoVLDLII gene. Two of the clones isolated were shown to encode the chicken homolog of the Y-box binding protein, YB-1 (dbpb), which we have designated chkYB-1. This protein was originally identified in avian extracts by virtue of its ability to bind to two reverse CCAAT motifs in the Rous sarcoma virus enhancer. Since its identification, additional nucleic acid binding properties have been ascribed to its homologs, or closely related proteins, in other species. We have determined the sequence of chkYB-1, investigated its ability to bind to sites known to be involved in tissue-specific expression in the liver, and examined factors influencing its hepatic expression. These studies have demonstrated that the level of chkYB-1 mRNA in the liver decreases steadily throughout embryogenesis and for several weeks posthatching until adult levels are attained. We present several lines of evidence that YB-1 expression in the liver is positively associated with DNA synthesis or cell proliferation. Its binding characteristics indicate that the protein can interact specifically with a number of binding sites for liver-enriched or specific factors. In addition, although it is not particularly asymmetric in terms of base composition, we find a marked preference in binding to the pyrimidine-rich strand of these sites regardless of the presence or polarity of an intact CCAAT box. The increased levels of expression of YB-1 during proliferation combined with its binding characteristics suggest that it may be involved in the reduced expression of liver-specific genes observed at early stages of development or during liver regeneration.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almendral J. M., Sommer D., Macdonald-Bravo H., Burckhardt J., Perera J., Bravo R. Complexity of the early genetic response to growth factors in mouse fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2140–2148. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkenmeier E. H., Gwynn B., Howard S., Jerry J., Gordon J. I., Landschulz W. H., McKnight S. L. Tissue-specific expression, developmental regulation, and genetic mapping of the gene encoding CCAAT/enhancer binding protein. Genes Dev. 1989 Aug;3(8):1146–1156. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.8.1146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgmeyer U., Nowock J., Sippel A. E. The TGGCA-binding protein: a eukaryotic nuclear protein recognizing a symmetrical sequence on double-stranded linear DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 25;12(10):4295–4311. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.10.4295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brissette L., Young I., Narindrasorasak S., Kisilevsky R., Deeley R. Differential induction of the serum amyloid A gene family in response to an inflammatory agent and to amyloid-enhancing factor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 15;264(32):19327–19332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch J. B. Identification and sequence analysis of the 5' end of the major chicken vitellogenin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):1117–1135. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.1117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch J. B., Weintraub H. Temporal order of chromatin structural changes associated with activation of the major chicken vitellogenin gene. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):65–76. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90335-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caput D., Beutler B., Hartog K., Thayer R., Brown-Shimer S., Cerami A. Identification of a common nucleotide sequence in the 3'-untranslated region of mRNA molecules specifying inflammatory mediators. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1670–1674. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavrier P., Zerial M., Lemaire P., Almendral J., Bravo R., Charnay P. A gene encoding a protein with zinc fingers is activated during G0/G1 transition in cultured cells. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):29–35. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02780.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chodosh L. A., Baldwin A. S., Carthew R. W., Sharp P. A. Human CCAAT-binding proteins have heterologous subunits. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90483-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen I., Reynolds W. F. The Xenopus YB3 protein binds the B box element of the class III promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Sep 11;19(17):4753–4759. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.17.4753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colgan V., Elbrecht A., Goldman P., Lazier C. B., Deeley R. The avian apoprotein II very low density lipoprotein gene. Methylation patterns of 5' and 3' flanking regions during development and following induction by estrogen. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14453–14460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa R. H., Grayson D. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Multiple hepatocyte-enriched nuclear factors function in the regulation of transthyretin and alpha 1-antitrypsin genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1415–1425. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa R. H., Grayson D. R., Xanthopoulos K. G., Darnell J. E., Jr A liver-specific DNA-binding protein recognizes multiple nucleotide sites in regulatory regions of transthyretin, alpha 1-antitrypsin, albumin, and simian virus 40 genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3840–3844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deschamps S., Viel A., Garrigos M., Denis H., le Maire M. mRNP4, a major mRNA-binding protein from Xenopus oocytes is identical to transcription factor FRG Y2. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):13799–13802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Descombes P., Chojkier M., Lichtsteiner S., Falvey E., Schibler U. LAP, a novel member of the C/EBP gene family, encodes a liver-enriched transcriptional activator protein. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1541–1551. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Descombes P., Schibler U. A liver-enriched transcriptional activator protein, LAP, and a transcriptional inhibitory protein, LIP, are translated from the same mRNA. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):569–579. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90531-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Didier D. K., Schiffenbauer J., Woulfe S. L., Zacheis M., Schwartz B. D. Characterization of the cDNA encoding a protein binding to the major histocompatibility complex class II Y box. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7322–7326. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn A., Bollekens J., Staub A., Benoist C., Mathis D. A multiplicity of CCAAT box-binding proteins. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):863–872. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90513-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elbrecht A., Lazier C. B., Protter A. A., Williams D. L. Independent developmental programs for two estrogen-regulated genes. Science. 1984 Aug 10;225(4662):639–641. doi: 10.1126/science.6740331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faber M., Sealy L. Rous sarcoma virus enhancer factor I is a ubiquitous CCAAT transcription factor highly related to CBF and NF-Y. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 25;265(36):22243–22254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firulli A. B., Maibenco D. C., Kinniburgh A. J. The identification of a tandem H-DNA structure in the c-myc nuclease sensitive promoter element. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 May 29;185(1):264–270. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80985-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman M. A., Dush M. K., Martin G. R. Rapid production of full-length cDNAs from rare transcripts: amplification using a single gene-specific oligonucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8998–9002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gai X. X., Lipson K. E., Prystowsky M. B. Unusual DNA binding characteristics of an in vitro translation product of the CCAAT binding protein mYB-1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Feb 11;20(3):601–606. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.3.601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. I., Burns A. T., Christmann J. L., Deeley R. G. Cloning of a double-stranded cDNA that codes for a portion of chicken preproalbumin. A general method for isolating a specific DNA sequence from partially purified mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 10;253(23):8629–8639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greuel B. T., Sealy L., Majors J. E. Transcriptional activity of the Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat correlates with binding of a factor to an upstream CCAAT box in vitro. Virology. 1990 Jul;177(1):33–43. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90457-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa S. L., Doetsch P. W., Hamilton K. K., Martin A. M., Okenquist S. A., Lenz J., Boss J. M. DNA binding properties of YB-1 and dbpA: binding to double-stranded, single-stranded, and abasic site containing DNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Sep 25;19(18):4915–4920. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.18.4915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoodless P. A., Roy R. N., Ryan A. K., Haché R. J., Vasa M. Z., Deeley R. G. Developmental regulation of specific protein interactions with an enhancerlike binding site far upstream from the avian very-low-density apolipoprotein II gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):154–164. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoodless P. A., Ryan A. K., Schrader T. J., Deeley R. G. Characterization of liver-enriched proteins binding to a developmentally demethylated site flanking the avian apoVLDLII gene. DNA Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;11(10):755–765. doi: 10.1089/dna.1992.11.755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Eukaryotic transcriptional regulatory proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:799–839. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.004055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. G., Krah R., Tafuri S. R., Wolffe A. P. DNA gyrase, CS7.4, and the cold shock response in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1992 Sep;174(18):5798–5802. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.18.5798-5802.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost J. P., Keller R., Dierks-Ventling C. Deoxyribonucleic acid and ribonucleic acid synthesis during phosvitin induction by 17beta-estradiol in immature chicks. J Biol Chem. 1973 Aug 10;248(15):5262–5266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaguchi T., Nomura K., Hirayama Y., Kitagawa T. Establishment and characterization of a chicken hepatocellular carcinoma cell line, LMH. Cancer Res. 1987 Aug 15;47(16):4460–4464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolluri R., Kinniburgh A. J. Full length cDNA sequence encoding a nuclease-sensitive element DNA binding protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Sep 11;19(17):4771–4771. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.17.4771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolluri R., Torrey T. A., Kinniburgh A. J. A CT promoter element binding protein: definition of a double-strand and a novel single-strand DNA binding motif. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 11;20(1):111–116. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.1.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Teana A., Brandi A., Falconi M., Spurio R., Pon C. L., Gualerzi C. O. Identification of a cold shock transcriptional enhancer of the Escherichia coli gene encoding nucleoid protein H-NS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10907–10911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., Adashi E. Y., Graves B. J., McKnight S. L. Isolation of a recombinant copy of the gene encoding C/EBP. Genes Dev. 1988 Jul;2(7):786–800. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.7.786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landsman D. RNP-1, an RNA-binding motif is conserved in the DNA-binding cold shock domain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jun 11;20(11):2861–2864. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.11.2861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau L. F., Nathans D. Expression of a set of growth-related immediate early genes in BALB/c 3T3 cells: coordinate regulation with c-fos or c-myc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1182–1186. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenz J., Okenquist S. A., LoSardo J. E., Hamilton K. K., Doetsch P. W. Identification of a mammalian nuclear factor and human cDNA-encoded proteins that recognize DNA containing apurinic sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3396–3400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X. Y., Mantovani R., Hooft van Huijsduijnen R., Andre I., Benoist C., Mathis D. Evolutionary variation of the CCAAT-binding transcription factor NF-Y. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Mar 11;20(5):1087–1091. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.5.1087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantovani R., Pessara U., Tronche F., Li X. Y., Knapp A. M., Pasquali J. L., Benoist C., Mathis D. Monoclonal antibodies to NF-Y define its function in MHC class II and albumin gene transcription. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3315–3322. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05410.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mischoulon D., Rana B., Bucher N. L., Farmer S. R. Growth-dependent inhibition of CCAAT enhancer-binding protein (C/EBP alpha) gene expression during hepatocyte proliferation in the regenerating liver and in culture. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;12(6):2553–2560. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.6.2553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller C. R., Maire P., Schibler U. DBP, a liver-enriched transcriptional activator, is expressed late in ontogeny and its tissue specificity is determined posttranscriptionally. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):279–291. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90808-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller C. R. The down-regulation of albumin transcription during regeneration is due to the loss of HNF-1 and the D-site transcription factors. DNA Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;11(7):559–566. doi: 10.1089/dna.1992.11.559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray M. T., Schiller D. L., Franke W. W. Sequence analysis of cytoplasmic mRNA-binding proteins of Xenopus oocytes identifies a family of RNA-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):11–15. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obokata J., Ohme M., Hayashida N. Nucleotide sequence of a cDNA clone encoding a putative glycine-rich protein of 19.7 kDa in Nicotiana sylvestris. Plant Mol Biol. 1991 Oct;17(4):953–955. doi: 10.1007/BF00037080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozer J., Faber M., Chalkley R., Sealy L. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA clone for the CCAAT transcription factor EFIA reveals a novel structural motif. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 25;265(36):22143–22152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poli V., Mancini F. P., Cortese R. IL-6DBP, a nuclear protein involved in interleukin-6 signal transduction, defines a new family of leucine zipper proteins related to C/EBP. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):643–653. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90459-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramji D. P., Tadros M. H., Hardon E. M., Cortese R. The transcription factor LF-A1 interacts with a bipartite recognition sequence in the promoter regions of several liver-specific genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Mar 11;19(5):1139–1146. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.5.1139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymondjean M., Cereghini S., Yaniv M. Several distinct "CCAAT" box binding proteins coexist in eukaryotic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):757–761. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder K., Lau L. F., Nathans D. A gene activated by growth factors is related to the oncogene v-jun. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1487–1491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabath D. E., Podolin P. L., Comber P. G., Prystowsky M. B. cDNA cloning and characterization of interleukin 2-induced genes in a cloned T helper lymphocyte. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 25;265(21):12671–12678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakura H., Maekawa T., Imamoto F., Yasuda K., Ishii S. Two human genes isolated by a novel method encode DNA-binding proteins containing a common region of homology. Gene. 1988 Dec 20;73(2):499–507. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90514-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoro C., Mermod N., Andrews P. C., Tjian R. A family of human CCAAT-box-binding proteins active in transcription and DNA replication: cloning and expression of multiple cDNAs. Nature. 1988 Jul 21;334(6179):218–224. doi: 10.1038/334218a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sealey L., Chalkley R. At least two nuclear proteins bind specifically to the Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):787–798. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Clerc R. G., LeBowitz J. H. Molecular cloning of sequence-specific DNA binding proteins using recognition site probes. Biotechniques. 1989 Mar;7(3):252–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitkovsky D. D., Royer-Pokora B., Delius H., Kisseljov F., Jenkins N. A., Gilbert D. J., Copeland N. G., Royer H. D. Tissue restricted expression and chromosomal localization of the YB-1 gene encoding a 42 kD nuclear CCAAT binding protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Feb 25;20(4):797–803. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.4.797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tafuri S. R., Wolffe A. P. DNA binding, multimerization, and transcription stimulation by the Xenopus Y box proteins in vitro. New Biol. 1992 Apr;4(4):349–359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tafuri S. R., Wolffe A. P. Xenopus Y-box transcription factors: molecular cloning, functional analysis and developmental regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):9028–9032. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.9028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinson C. R., LaMarco K. L., Johnson P. F., Landschulz W. H., McKnight S. L. In situ detection of sequence-specific DNA binding activity specified by a recombinant bacteriophage. Genes Dev. 1988 Jul;2(7):801–806. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.7.801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willimsky G., Bang H., Fischer G., Marahiel M. A. Characterization of cspB, a Bacillus subtilis inducible cold shock gene affecting cell viability at low temperatures. J Bacteriol. 1992 Oct;174(20):6326–6335. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.20.6326-6335.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiskocil R., Bensky P., Dower W., Goldberger R. F., Gordon J. I., Deeley R. G. Coordinate regulation of two estrogen-dependent genes in avian liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4474–4478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wistow G. Cold shock and DNA binding. Nature. 1990 Apr 26;344(6269):823–824. doi: 10.1038/344823c0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P., Tafuri S., Ranjan M., Familari M. The Y-box factors: a family of nucleic acid binding proteins conserved from Escherichia coli to man. New Biol. 1992 Apr;4(4):290–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan C., Tamm I. Molecular cloning and characterization of interferon alpha/beta response element binding factors of the murine (2'-5')oligoadenylate synthetase ME-12 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):144–148. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Oliveira D. E., Seurinck J., Inzé D., Van Montagu M., Botterman J. Differential expression of five Arabidopsis genes encoding glycine-rich proteins. Plant Cell. 1990 May;2(5):427–436. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.5.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]