Abstract
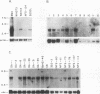
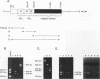
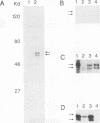
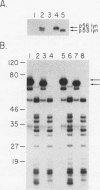
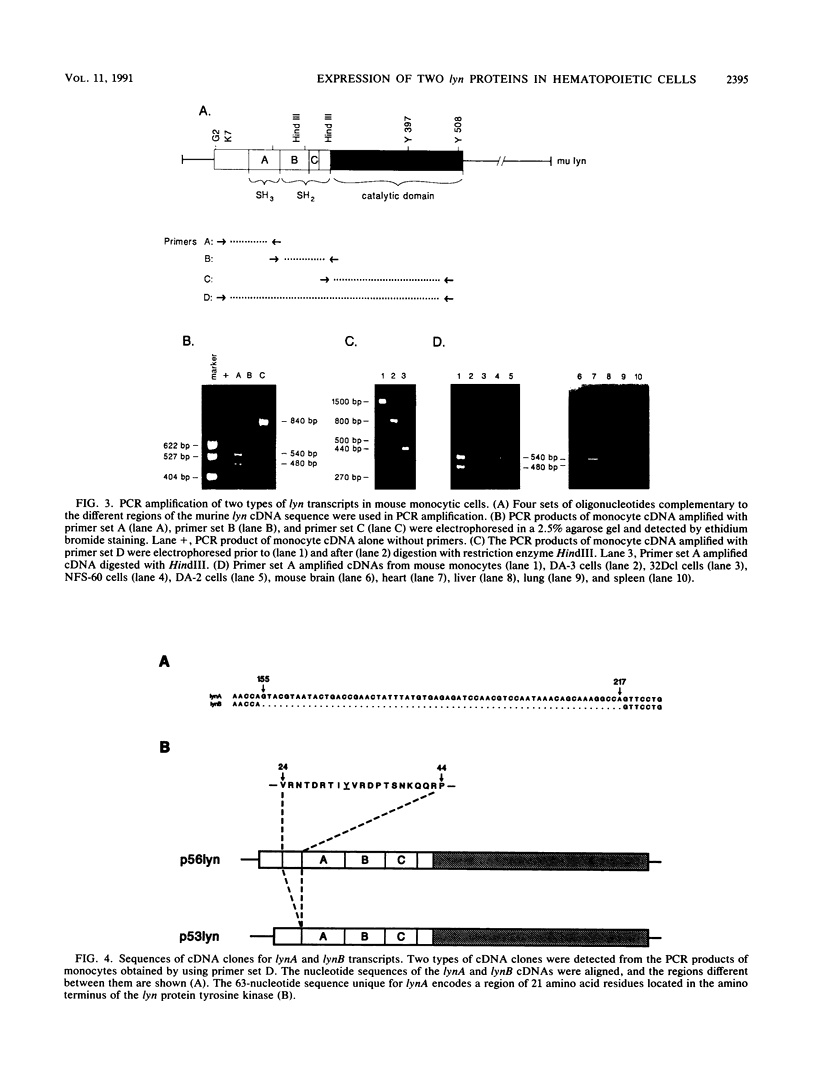
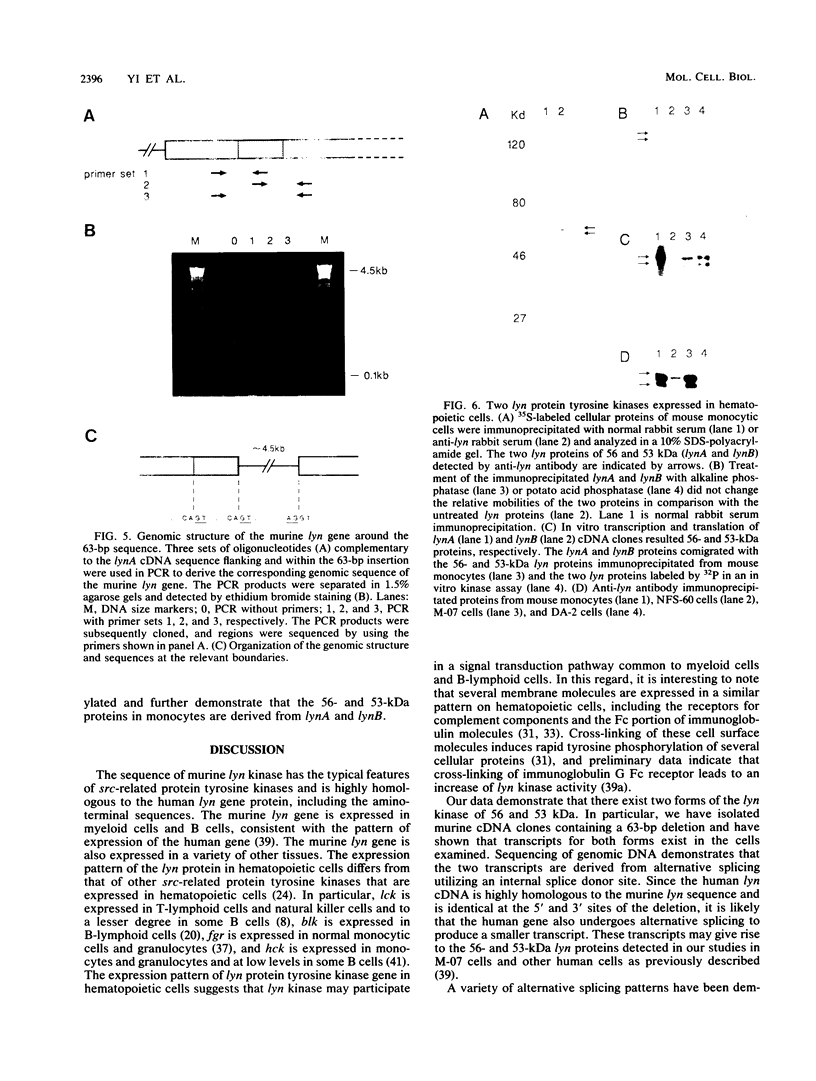
cDNAs for the murine lyn protein tyrosine kinase gene were cloned from mouse bone marrow-derived monocytic cells. Comparison of the human and murine genes demonstrated a 94% homology in peptide sequence. Comparable to the human gene, murine lyn was found to be expressed in myeloid and B-lymphoid lineage cells. During the cloning, two types of cDNAs were obtained that differed by the presence (lynA) or absence (lynB) of 63 bp within the amino-terminal coding region of the gene. The genomic structure of the murine lyn gene demonstrates that the two types of lyn transcripts are derived from alternative splicing utilizing an internal splice donor site. Transcripts for both forms were found to be expressed in myeloid cells. lyn-specific antisera detected comparable levels of proteins of 56 and 53 kDa in hematopoietic cells. these 56- and 53-kDa proteins comigrated with proteins produced by in vitro translation or in vivo expression of the lynA and lynB cDNAs, respectively. The two forms had comparable in vitro kinase activities in immunoprecipitates and showed similar peptide patterns, with partial V8 digestion of the in vitro-phosphorylated proteins. The potential significance of the two lyn proteins is discussed.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler H. T., Reynolds P. J., Kelley C. M., Sefton B. M. Transcriptional activation of lck by retrovirus promoter insertion between two lymphoid-specific promoters. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4113–4122. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4113-4122.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avanzi G. C., Lista P., Giovinazzo B., Miniero R., Saglio G., Benetton G., Coda R., Cattoretti G., Pegoraro L. Selective growth response to IL-3 of a human leukaemic cell line with megakaryoblastic features. Br J Haematol. 1988 Jul;69(3):359–366. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1988.tb02374.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitbart R. E., Andreadis A., Nadal-Ginard B. Alternative splicing: a ubiquitous mechanism for the generation of multiple protein isoforms from single genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:467–495. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.002343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke M. P., Perlmutter R. M. Expression of a novel form of the fyn proto-oncogene in hematopoietic cells. New Biol. 1989 Oct;1(1):66–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R. Trans-activation of human immunodeficiency virus occurs via a bimodal mechanism. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):973–982. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90696-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiseman E., Bolen J. B. src-related tyrosine protein kinases as signaling components in hematopoietic cells. Cancer Cells. 1990 Oct;2(10):303–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman M. A., Dush M. K., Martin G. R. Rapid production of full-length cDNAs from rare transcripts: amplification using a single gene-specific oligonucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8998–9002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garvin A. M., Pawar S., Marth J. D., Perlmutter R. M. Structure of the murine lck gene and its rearrangement in a murine lymphoma cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3058–3064. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihle J. N., Pepersack L., Rebar L. Regulation of T cell differentiation: in vitro induction of 20 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase in splenic lymphocytes from athymic mice by a unique lymphokine. J Immunol. 1981 Jun;126(6):2184–2189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzav S., Martin-Zanca D., Barbacid M. vav, a novel human oncogene derived from a locus ubiquitously expressed in hematopoietic cells. EMBO J. 1989 Aug;8(8):2283–2290. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08354.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Possible role of flanking nucleotides in recognition of the AUG initiator codon by eukaryotic ribosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 24;9(20):5233–5252. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.20.5233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. B., Dorai T., Wang L. H., Brugge J. S. The structurally distinct form of pp60c-src detected in neuronal cells is encoded by a unique c-src mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):4142–4145. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.4142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marth J. D., Cooper J. A., King C. S., Ziegler S. F., Tinker D. A., Overell R. W., Krebs E. G., Perlmutter R. M. Neoplastic transformation induced by an activated lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase (pp56lck). Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):540–550. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marth J. D., Peet R., Krebs E. G., Perlmutter R. M. A lymphocyte-specific protein-tyrosine kinase gene is rearranged and overexpressed in the murine T cell lymphoma LSTRA. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):393–404. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90169-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez R., Mathey-Prevot B., Bernards A., Baltimore D. Neuronal pp60c-src contains a six-amino acid insertion relative to its non-neuronal counterpart. Science. 1987 Jul 24;237(4813):411–415. doi: 10.1126/science.2440106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. K., Kaplan D. R., Escobedo J. A., Rapp U. R., Roberts T. M., Williams L. T. Direct activation of the serine/threonine kinase activity of Raf-1 through tyrosine phosphorylation by the PDGF beta-receptor. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):649–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90100-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T. Non-catalytic domains of cytoplasmic protein-tyrosine kinases: regulatory elements in signal transduction. Oncogene. 1988 Nov;3(5):491–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmutter R. M., Marth J. D., Ziegler S. F., Garvin A. M., Pawar S., Cooke M. P., Abraham K. M. Specialized protein tyrosine kinase proto-oncogenes in hematopoietic cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Feb;948(3):245–262. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(89)90001-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyper J. M., Bolen J. B. Identification of a novel neuronal C-SRC exon expressed in human brain. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2035–2040. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovera G., Valtieri M., Mavilio F., Reddy E. P. Effect of Abelson murine leukemia virus on granulocytic differentiation and interleukin-3 dependence of a murine progenitor cell line. Oncogene. 1987 Mar;1(1):29–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudd C. E., Trevillyan J. M., Dasgupta J. D., Wong L. L., Schlossman S. F. The CD4 receptor is complexed in detergent lysates to a protein-tyrosine kinase (pp58) from human T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5190–5194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw A. S., Amrein K. E., Hammond C., Stern D. F., Sefton B. M., Rose J. K. The lck tyrosine protein kinase interacts with the cytoplasmic tail of the CD4 glycoprotein through its unique amino-terminal domain. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):627–636. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenoy S., Choi J. K., Bagrodia S., Copeland T. D., Maller J. L., Shalloway D. Purified maturation promoting factor phosphorylates pp60c-src at the sites phosphorylated during fibroblast mitosis. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):763–774. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90791-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart S. G., Simister N. E., Clarkson S. B., Kacinski B. M., Shapiro M., Mellman I. Human IgG Fc receptor (hFcRII; CD32) exists as multiple isoforms in macrophages, lymphocytes and IgG-transporting placental epithelium. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3657–3666. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08540.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner J. M., Brodsky M. H., Irving B. A., Levin S. D., Perlmutter R. M., Littman D. R. Interaction of the unique N-terminal region of tyrosine kinase p56lck with cytoplasmic domains of CD4 and CD8 is mediated by cysteine motifs. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):755–765. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90090-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unkeless J. C. Function and heterogeneity of human Fc receptors for immunoglobulin G. J Clin Invest. 1989 Feb;83(2):355–361. doi: 10.1172/JCI113891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veillette A., Bookman M. A., Horak E. M., Bolen J. B. The CD4 and CD8 T cell surface antigens are associated with the internal membrane tyrosine-protein kinase p56lck. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):301–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90053-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veillette A., Bookman M. A., Horak E. M., Samelson L. E., Bolen J. B. Signal transduction through the CD4 receptor involves the activation of the internal membrane tyrosine-protein kinase p56lck. Nature. 1989 Mar 16;338(6212):257–259. doi: 10.1038/338257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilks A. F. Two putative protein-tyrosine kinases identified by application of the polymerase chain reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1603–1607. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willman C. L., Stewart C. C., Griffith J. K., Stewart S. J., Tomasi T. B. Differential expression and regulation of the c-src and c-fgr protooncogenes in myelomonocytic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4480–4484. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanashi Y., Fukushige S., Semba K., Sukegawa J., Miyajima N., Matsubara K., Yamamoto T., Toyoshima K. The yes-related cellular gene lyn encodes a possible tyrosine kinase similar to p56lck. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):237–243. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanashi Y., Mori S., Yoshida M., Kishimoto T., Inoue K., Yamamoto T., Toyoshima K. Selective expression of a protein-tyrosine kinase, p56lyn, in hematopoietic cells and association with production of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6538–6542. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yi T. L., Willman C. L. Cloning of the murine c-fgr proto-oncogene cDNA and induction of c-fgr expression by proliferation and activation factors in normal bone marrow-derived monocytic cells. Oncogene. 1989 Sep;4(9):1081–1087. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler S. F., Marth J. D., Lewis D. B., Perlmutter R. M. Novel protein-tyrosine kinase gene (hck) preferentially expressed in cells of hematopoietic origin. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2276–2285. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]