Abstract
We identified a putative Saccharomyces cerevisiae homolog of a phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C (PI-PLC) gene, PLC1, which encodes a protein most similar to the delta class of PI-PLC enzymes. The PLC1 gene was isolated during a study of yeast strains that exhibit defects in chromosome segregation. plc1-1 cells showed a 10-fold increase in aberrant chromosome segregation compared with the wild type. Molecular analysis revealed that PLC1 encodes a predicted protein of 101 kDa with approximately 50 and 26% identity to the highly conserved X and Y domains of PI-PLC isozymes from humans, bovines, rats, and Drosophila melanogaster. The putative yeast protein also contains a consensus EF-hand domain that is predicted to bind calcium. Interestingly, the temperature-sensitive and chromosome missegregation phenotypes exhibited by plc1-1 cells were partially suppressed by exogenous calcium.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antebi A., Fink G. R. The yeast Ca(2+)-ATPase homologue, PMR1, is required for normal Golgi function and localizes in a novel Golgi-like distribution. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Jun;3(6):633–654. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.6.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bairoch A., Cox J. A. EF-hand motifs in inositol phospholipid-specific phospholipase C. FEBS Lett. 1990 Sep 3;269(2):454–456. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81214-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter M. A., Grafton G., Bunce C. M., Lord J. M., Michell R. H., Brown G. The role of inositol transport in cellular differentiation. Biochem Soc Trans. 1991 Apr;19(2):86S–86S. doi: 10.1042/bst019086s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berben G., Dumont J., Gilliquet V., Bolle P. A., Hilger F. The YDp plasmids: a uniform set of vectors bearing versatile gene disruption cassettes for Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast. 1991 Jul;7(5):475–477. doi: 10.1002/yea.320070506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol phosphates and cell signalling. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):197–205. doi: 10.1038/341197a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloomquist B. T., Shortridge R. D., Schneuwly S., Perdew M., Montell C., Steller H., Rubin G., Pak W. L. Isolation of a putative phospholipase C gene of Drosophila, norpA, and its role in phototransduction. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):723–733. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., LaCroute F., Fink G. R. A positive selection for mutants lacking orotidine-5'-phosphate decarboxylase activity in yeast: 5-fluoro-orotic acid resistance. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;197(2):345–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00330984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bristol A., Hall S. M., Kriz R. W., Stahl M. L., Fan Y. S., Byers M. G., Eddy R. L., Shows T. B., Knopf J. L. Phospholipase C-148: chromosomal location and deletion mapping of functional domains. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1988;53(Pt 2):915–920. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1988.053.01.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G., Vollrath D., Davis R. W. Separation of large DNA molecules by contour-clamped homogeneous electric fields. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1582–1585. doi: 10.1126/science.3538420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collingridge G. Synaptic plasticity. The role of NMDA receptors in learning and memory. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):604–605. doi: 10.1038/330604a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis E. A., Rhee S. G., Billah M. M., Hannun Y. A. Role of phospholipase in generating lipid second messengers in signal transduction. FASEB J. 1991 Apr;5(7):2068–2077. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.7.1901288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desai D. M., Newton M. E., Kadlecek T., Weiss A. Stimulation of the phosphatidylinositol pathway can induce T-cell activation. Nature. 1990 Nov 1;348(6296):66–69. doi: 10.1038/348066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Divecha N., Banfić H., Irvine R. F. The polyphosphoinositide cycle exists in the nuclei of Swiss 3T3 cells under the control of a receptor (for IGF-I) in the plasma membrane, and stimulation of the cycle increases nuclear diacylglycerol and apparently induces translocation of protein kinase C to the nucleus. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3207–3214. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04883.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domdey H., Apostol B., Lin R. J., Newman A., Brody E., Abelson J. Lariat structures are in vivo intermediates in yeast pre-mRNA splicing. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):611–621. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90468-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engebrecht J., Hirsch J., Roeder G. S. Meiotic gene conversion and crossing over: their relationship to each other and to chromosome synapsis and segregation. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):927–937. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90267-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng D. F., Doolittle R. F. Progressive sequence alignment as a prerequisite to correct phylogenetic trees. J Mol Evol. 1987;25(4):351–360. doi: 10.1007/BF02603120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerring S. L., Spencer F., Hieter P. The CHL 1 (CTF 1) gene product of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is important for chromosome transmission and normal cell cycle progression in G2/M. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4347–4358. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07884.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gietz D., St Jean A., Woods R. A., Schiestl R. H. Improved method for high efficiency transformation of intact yeast cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Mar 25;20(6):1425–1425. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.6.1425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt-Clermont P. J., Machesky L. M., Baldassare J. J., Pollard T. D. The actin-binding protein profilin binds to PIP2 and inhibits its hydrolysis by phospholipase C. Science. 1990 Mar 30;247(4950):1575–1578. doi: 10.1126/science.2157283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt-Clermont P. J., Machesky L. M., Doberstein S. K., Pollard T. D. Mechanism of the interaction of human platelet profilin with actin. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;113(5):1081–1089. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.5.1081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H., Smith D. Altered fidelity of mitotic chromosome transmission in cell cycle mutants of S. cerevisiae. Genetics. 1985 Jul;110(3):381–395. doi: 10.1093/genetics/110.3.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepler P. K. Calcium transients during mitosis: observations in flux. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):2567–2573. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.2567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hieter P., Mann C., Snyder M., Davis R. W. Mitotic stability of yeast chromosomes: a colony color assay that measures nondisjunction and chromosome loss. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):381–392. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90152-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill J. E., Myers A. M., Koerner T. J., Tzagoloff A. Yeast/E. coli shuttle vectors with multiple unique restriction sites. Yeast. 1986 Sep;2(3):163–167. doi: 10.1002/yea.320020304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman C. S., Winston F. A ten-minute DNA preparation from yeast efficiently releases autonomous plasmids for transformation of Escherichia coli. Gene. 1987;57(2-3):267–272. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90131-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma Y., Takenawa T., Emori Y., Sorimachi H., Suzuki K. Tissue- and cell type-specific expression of mRNAs for four types of inositol phospholipid-specific phospholipase C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Oct 16;164(1):406–412. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91734-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyt M. A., Totis L., Roberts B. T. S. cerevisiae genes required for cell cycle arrest in response to loss of microtubule function. Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):507–517. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90014-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huisman O., Raymond W., Froehlich K. U., Errada P., Kleckner N., Botstein D., Hoyt M. A. A Tn10-lacZ-kanR-URA3 gene fusion transposon for insertion mutagenesis and fusion analysis of yeast and bacterial genes. Genetics. 1987 Jun;116(2):191–199. doi: 10.1093/genetics/116.2.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iida H., Sakaguchi S., Yagawa Y., Anraku Y. Cell cycle control by Ca2+ in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 5;265(34):21216–21222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamm K. E., Stull J. T. Regulation of smooth muscle contractile elements by second messengers. Annu Rev Physiol. 1989;51:299–313. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.51.030189.001503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennelly P. J., Krebs E. G. Consensus sequences as substrate specificity determinants for protein kinases and protein phosphatases. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15555–15558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. W., Sim S. S., Kim U. H., Nishibe S., Wahl M. I., Carpenter G., Rhee S. G. Tyrosine residues in bovine phospholipase C-gamma phosphorylated by the epidermal growth factor receptor in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):3940–3943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshland D., Hieter P. Visual assay for chromosome ploidy. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:351–372. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55024-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretsinger R. H. Calcium coordination and the calmodulin fold: divergent versus convergent evolution. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1987;52:499–510. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1987.052.01.057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriz R., Lin L. L., Sultzman L., Ellis C., Heldin C. H., Pawson T., Knopf J. Phospholipase C isozymes: structural and functional similarities. Ciba Found Symp. 1990;150:112–127. doi: 10.1002/9780470513927.ch8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuppe A., Evans L. M., McMillen D. A., Griffith O. H. Phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C of Bacillus cereus: cloning, sequencing, and relationship to other phospholipases. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):6077–6083. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.6077-6083.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin D. E., Bartlett-Heubusch E. Mutants in the S. cerevisiae PKC1 gene display a cell cycle-specific osmotic stability defect. J Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;116(5):1221–1229. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.5.1221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin D. E., Fields F. O., Kunisawa R., Bishop J. M., Thorner J. A candidate protein kinase C gene, PKC1, is required for the S. cerevisiae cell cycle. Cell. 1990 Jul 27;62(2):213–224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90360-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li R., Murray A. W. Feedback control of mitosis in budding yeast. Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):519–531. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90015-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majerus P. W., Ross T. S., Cunningham T. W., Caldwell K. K., Jefferson A. B., Bansal V. S. Recent insights in phosphatidylinositol signaling. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):459–465. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90442-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maslanski J. A., Leshko L., Busa W. B. Lithium-sensitive production of inositol phosphates during amphibian embryonic mesoderm induction. Science. 1992 Apr 10;256(5054):243–245. doi: 10.1126/science.1314424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrew J. T., Xiao Z. X., Fitzgerald-Hayes M. Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutants defective in chromosome segregation. Yeast. 1989 Jul-Aug;5(4):271–284. doi: 10.1002/yea.320050407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisenhelder J., Suh P. G., Rhee S. G., Hunter T. Phospholipase C-gamma is a substrate for the PDGF and EGF receptor protein-tyrosine kinases in vivo and in vitro. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1109–1122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90048-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortimer R. K., Schild D. Genetic map of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, edition 9. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Sep;49(3):181–213. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.3.181-213.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishibe S., Wahl M. I., Hernández-Sotomayor S. M., Tonks N. K., Rhee S. G., Carpenter G. Increase of the catalytic activity of phospholipase C-gamma 1 by tyrosine phosphorylation. Science. 1990 Nov 30;250(4985):1253–1256. doi: 10.1126/science.1700866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The molecular heterogeneity of protein kinase C and its implications for cellular regulation. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):661–665. doi: 10.1038/334661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohya Y., Ohsumi Y., Anraku Y. Genetic study of the role of calcium ions in the cell division cycle of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a calcium-dependent mutant and its trifluoperazine-dependent pseudorevertants. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;193(3):389–394. doi: 10.1007/BF00382073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paravicini G., Cooper M., Friedli L., Smith D. J., Carpentier J. L., Klig L. S., Payton M. A. The osmotic integrity of the yeast cell requires a functional PKC1 gene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;12(11):4896–4905. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.11.4896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payrastre B., Nievers M., Boonstra J., Breton M., Verkleij A. J., Van Bergen en Henegouwen P. M. A differential location of phosphoinositide kinases, diacylglycerol kinase, and phospholipase C in the nuclear matrix. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 15;267(8):5078–5084. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payrastre B., van Bergen en Henegouwen P. M., Breton M., den Hartigh J. C., Plantavid M., Verkleij A. J., Boonstra J. Phosphoinositide kinase, diacylglycerol kinase, and phospholipase C activities associated to the cytoskeleton: effect of epidermal growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;115(1):121–128. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.1.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poenie M., Alderton J., Tsien R. Y., Steinhardt R. A. Changes of free calcium levels with stages of the cell division cycle. Nature. 1985 May 9;315(6015):147–149. doi: 10.1038/315147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr The role of phosphoinositide metabolism in signal transduction in secretory cells. J Exp Biol. 1988 Sep;139:135–150. doi: 10.1242/jeb.139.1.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhee S. G., Choi K. D. Regulation of inositol phospholipid-specific phospholipase C isozymes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):12393–12396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhee S. G., Suh P. G., Ryu S. H., Lee S. Y. Studies of inositol phospholipid-specific phospholipase C. Science. 1989 May 5;244(4904):546–550. doi: 10.1126/science.2541501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross C. A., MacCumber M. W., Glatt C. E., Snyder S. H. Brain phospholipase C isozymes: differential mRNA localizations by in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2923–2927. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
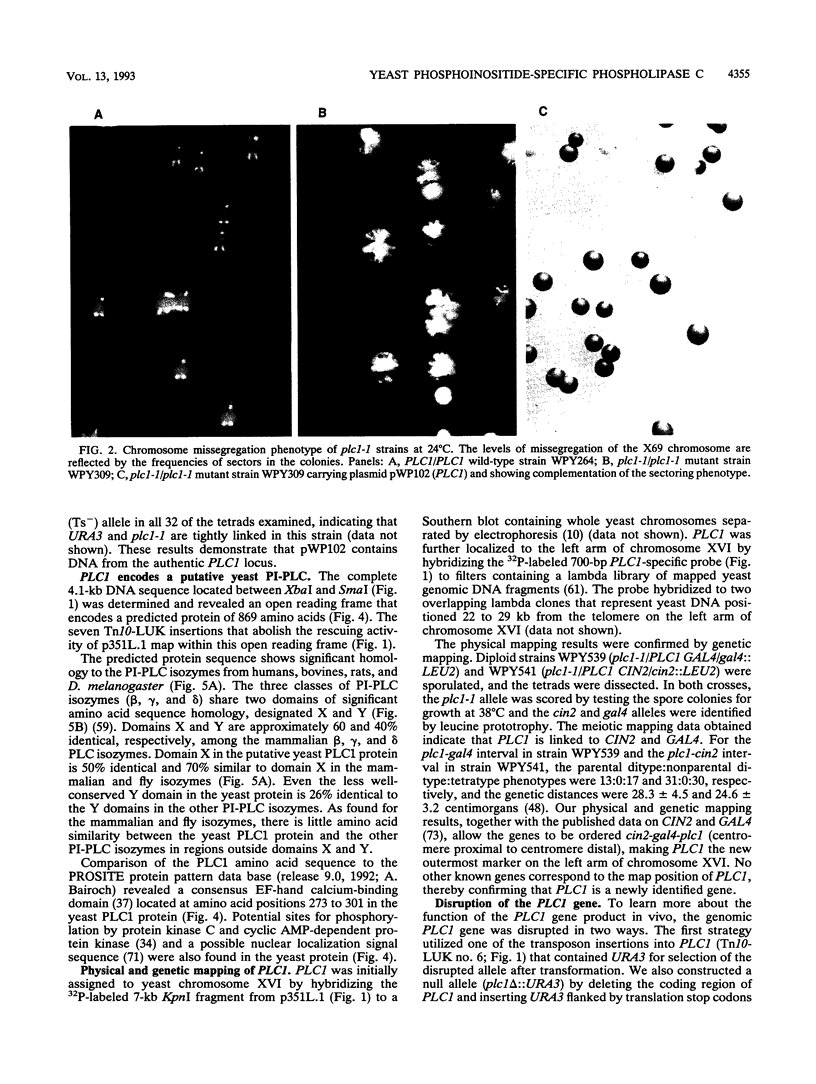
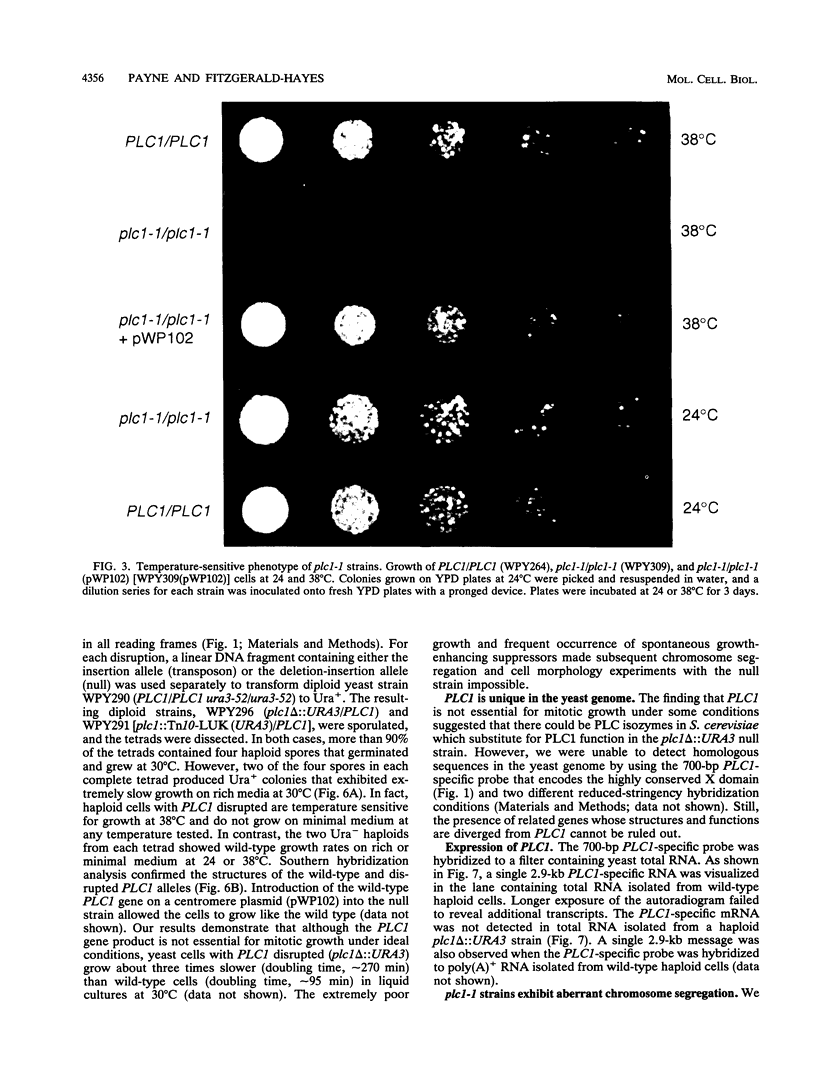
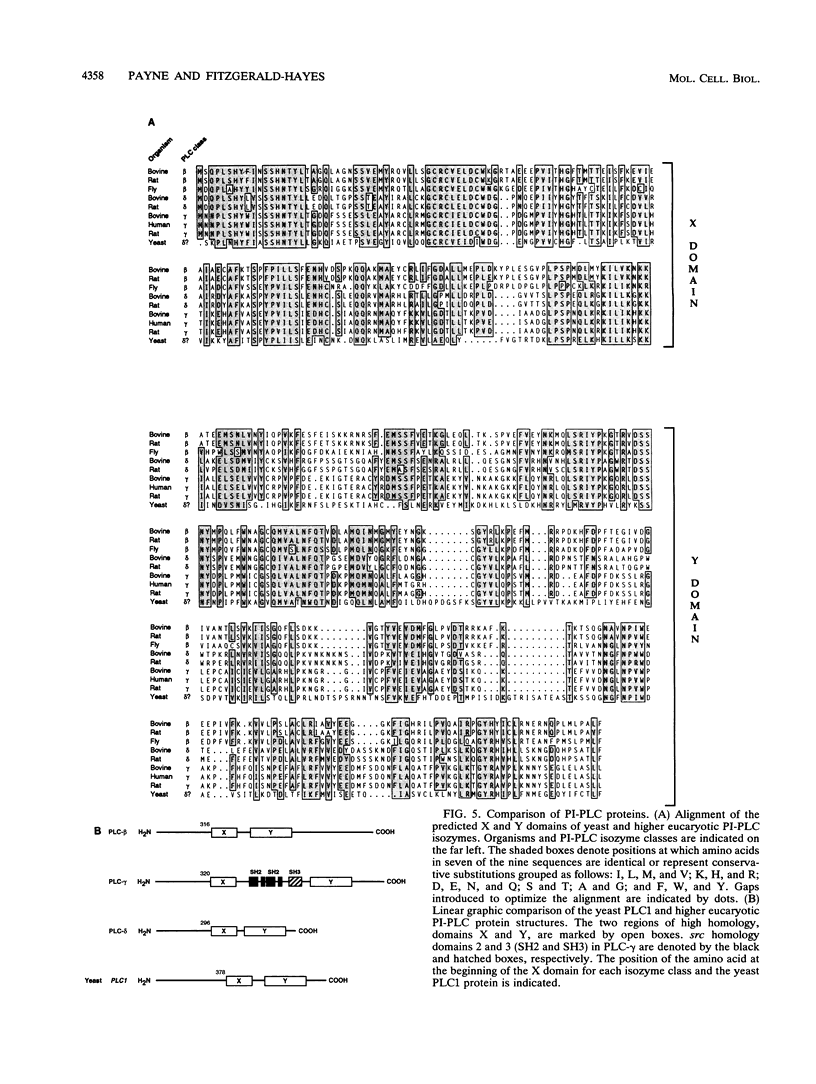
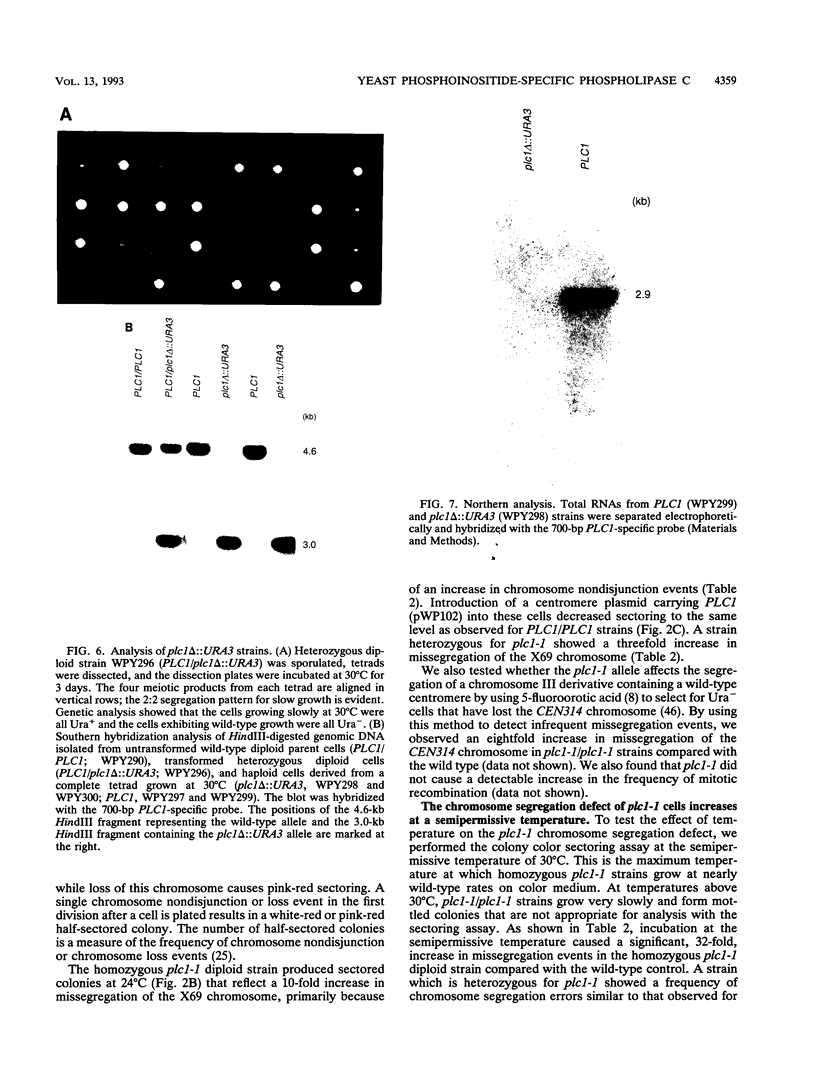
- Rothstein R. J. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiestl R. H., Gietz R. D. High efficiency transformation of intact yeast cells using single stranded nucleic acids as a carrier. Curr Genet. 1989 Dec;16(5-6):339–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00340712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneuwly S., Burg M. G., Lending C., Perdew M. H., Pak W. L. Properties of photoreceptor-specific phospholipase C encoded by the norpA gene of Drosophila melanogaster. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 25;266(36):24314–24319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selinger Z., Minke B. Inositol lipid cascade of vision studied in mutant flies. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1988;53(Pt 1):333–341. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1988.053.01.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shariff A., Luna E. J. Diacylglycerol-stimulated formation of actin nucleation sites at plasma membranes. Science. 1992 Apr 10;256(5054):245–247. doi: 10.1126/science.1373523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortridge R. D., Yoon J., Lending C. R., Bloomquist B. T., Perdew M. H., Pak W. L. A Drosophila phospholipase C gene that is expressed in the central nervous system. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12474–12480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver P. A. How proteins enter the nucleus. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):489–497. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90233-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smrcka A. V., Hepler J. R., Brown K. O., Sternweis P. C. Regulation of polyphosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C activity by purified Gq. Science. 1991 Feb 15;251(4995):804–807. doi: 10.1126/science.1846707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stearns T., Hoyt M. A., Botstein D. Yeast mutants sensitive to antimicrotubule drugs define three genes that affect microtubule function. Genetics. 1990 Feb;124(2):251–262. doi: 10.1093/genetics/124.2.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinhardt R. A., Alderton J. Intracellular free calcium rise triggers nuclear envelope breakdown in the sea urchin embryo. Nature. 1988 Mar 24;332(6162):364–366. doi: 10.1038/332364a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. J., Chae H. Z., Rhee S. G., Exton J. H. Activation of the beta 1 isozyme of phospholipase C by alpha subunits of the Gq class of G proteins. Nature. 1991 Apr 11;350(6318):516–518. doi: 10.1038/350516a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tombes R. M., Borisy G. G. Intracellular free calcium and mitosis in mammalian cells: anaphase onset is calcium modulated, but is not triggered by a brief transient. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):627–636. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twigg J., Patel R., Whitaker M. Translational control of InsP3-induced chromatin condensation during the early cell cycles of sea urchin embryos. Nature. 1988 Mar 24;332(6162):366–369. doi: 10.1038/332366a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl M. I., Nishibe S., Suh P. G., Rhee S. G., Carpenter G. Epidermal growth factor stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-II independently of receptor internalization and extracellular calcium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1568–1572. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl M., Carpenter G. Selective phospholipase C activation. Bioessays. 1991 Mar;13(3):107–113. doi: 10.1002/bies.950130303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldo G. L., Boyer J. L., Morris A. J., Harden T. K. Purification of an AlF4- and G-protein beta gamma-subunit-regulated phospholipase C-activating protein. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 5;266(22):14217–14225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinert T. A., Hartwell L. H. The RAD9 gene controls the cell cycle response to DNA damage in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Science. 1988 Jul 15;241(4863):317–322. doi: 10.1126/science.3291120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoko-o T., Matsui Y., Yagisawa H., Nojima H., Uno I., Toh-e A. The putative phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C gene, PLC1, of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae is important for cell growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):1804–1808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.1804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida S., Ikeda E., Uno I., Mitsuzawa H. Characterization of a staurosporine- and temperature-sensitive mutant, stt1, of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: STT1 is allelic to PKC1. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Feb;231(3):337–344. doi: 10.1007/BF00292700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshioka T., Inoue H. Inositol phospholipid in visual excitation. Neurosci Res Suppl. 1987;6:S15–S24. doi: 10.1016/0921-8696(87)90004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]