Abstract
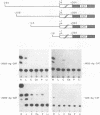
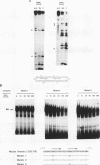
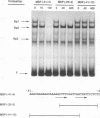
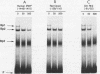
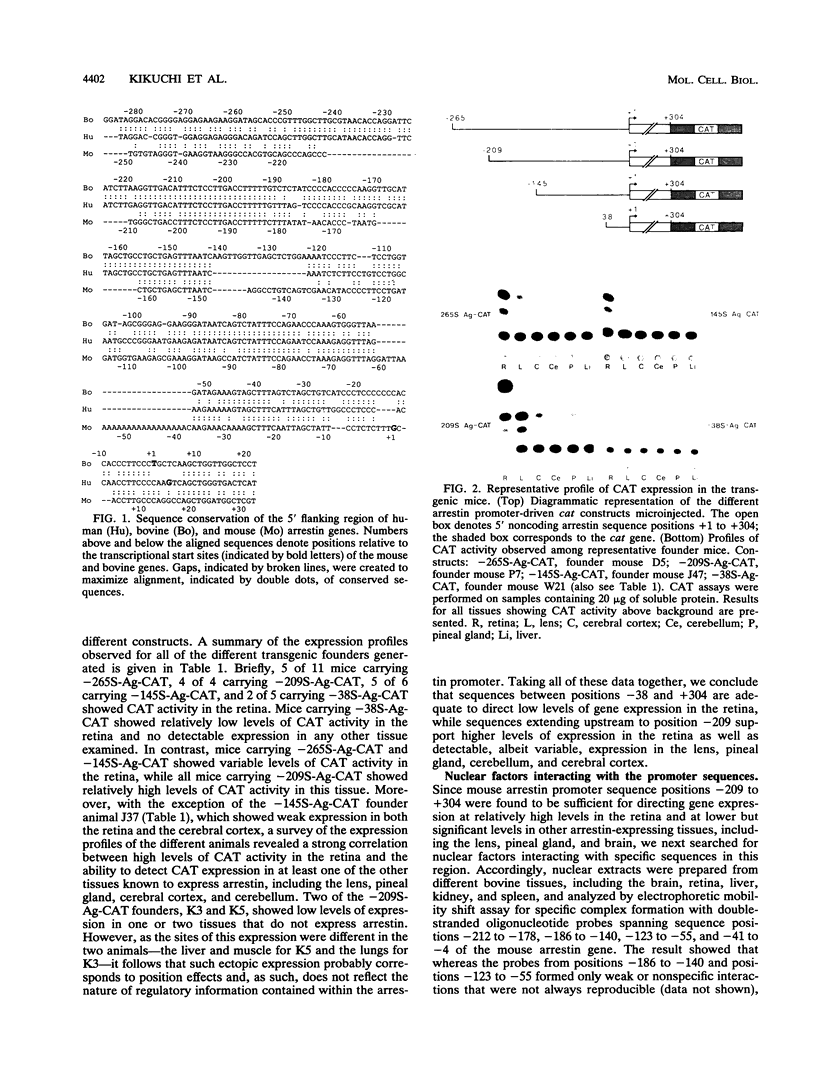
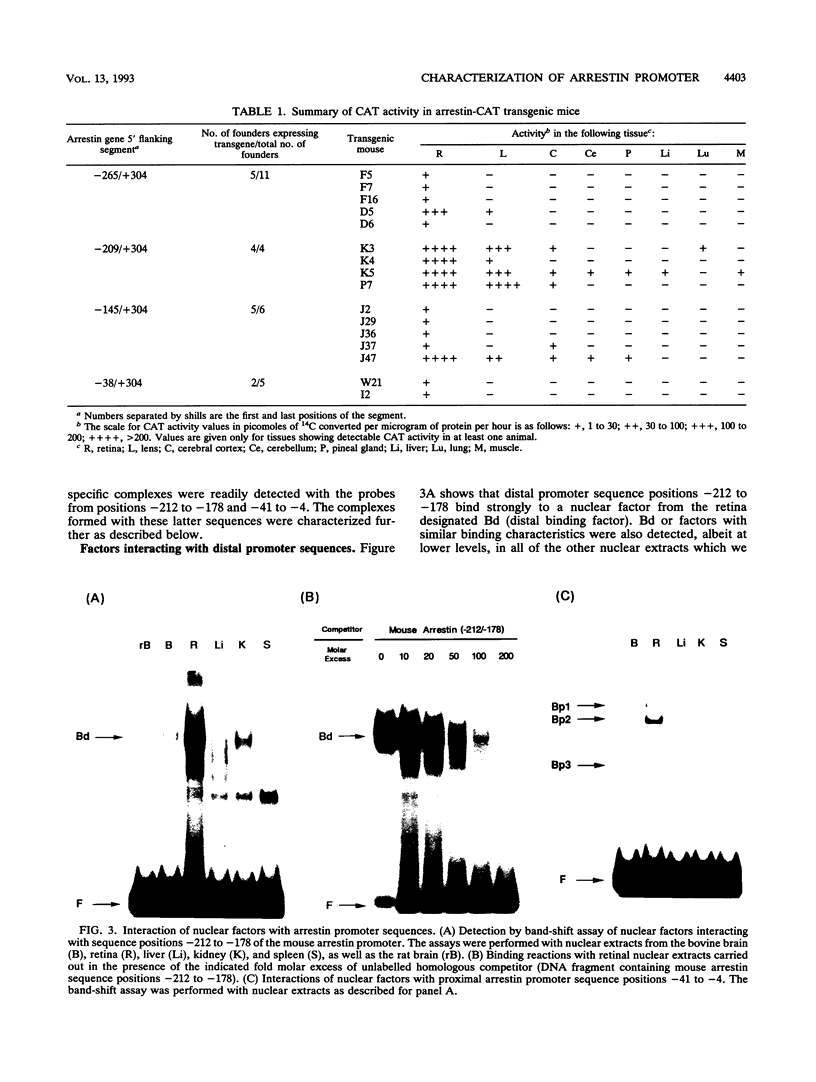
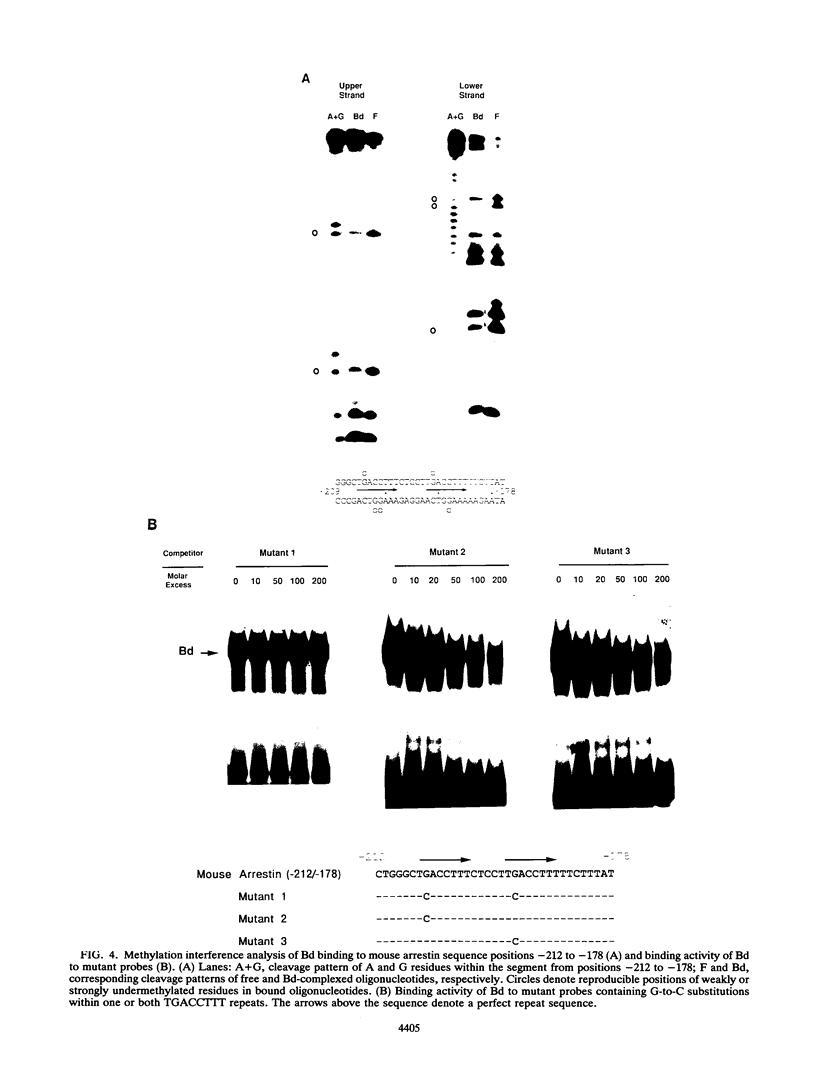
Regulatory sequences and nuclear factors governing tissue-restricted expression of the mouse arrestin gene were investigated. The results showed that while proximal promoter sequence positions -38 to +304 are sufficient to direct low levels of retina-specific gene expression, sequences extending upstream to position -209 support higher levels of expression in the retina, as well as detectable expression in the lens, pineal gland, and brain. Within the interval between positions -209 and -38, a broadly expressed nuclear factor, Bd, binds to sequences centered between positions -205 and -185, a region which contains two direct repeats of the hexamer, TGACCT. The proximal promoter binds three apparently retina-specific nuclear factors, Bp1, Bp2, and Bp3, through overlapping sequences centered between positions -25 and -15. Bp1 and Bp3 also recognize a closely related sequence found in the promoter regions of several other vertebrate photoreceptor-specific genes. Moreover, the consensus binding site for Bp1, designated PCE I, is identical to RCS I, an element known to play a critical role eliciting photoreceptor-specific gene expression in Drosophila melanogaster. The results suggest that PCE I and RCS I are functionally as well as structurally similar and that, despite marked differences in the fly and vertebrate visual systems, the transcriptional machinery involved in photoreceptor-specific gene expression has been strongly evolutionarily conserved.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albini A., Toffenetti J., Zhu Z., Chader G. J., Noonan D. M. Hypomethylation of the interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein (IRBP) promotor and first exon is linked to expression of the gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 11;18(17):5181–5187. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.17.5181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker N. E., Mlodzik M., Rubin G. M. Spacing differentiation in the developing Drosophila eye: a fibrinogen-related lateral inhibitor encoded by scabrous. Science. 1990 Dec 7;250(4986):1370–1377. doi: 10.1126/science.2175046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett N., Sitaramayya A. Inactivation of photoexcited rhodopsin in retinal rods: the roles of rhodopsin kinase and 48-kDa protein (arrestin). Biochemistry. 1988 Mar 8;27(5):1710–1715. doi: 10.1021/bi00405a049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloomquist B. T., Shortridge R. D., Schneuwly S., Perdew M., Montell C., Steller H., Rubin G., Pak W. L. Isolation of a putative phospholipase C gene of Drosophila, norpA, and its role in phototransduction. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):723–733. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitman M. L., Clapoff S., Rossant J., Tsui L. C., Glode L. M., Maxwell I. H., Bernstein A. Genetic ablation: targeted expression of a toxin gene causes microphthalmia in transgenic mice. Science. 1987 Dec 11;238(4833):1563–1565. doi: 10.1126/science.3685993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitman M. L., Tsuda M., Usukura J., Kikuchi T., Zucconi A., Khoo W., Shinohara T. Expression of S-antigen in retina, pineal gland, lens, and brain is directed by 5'-flanking sequences. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):15505–15510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brent G. A., Moore D. D., Larsen P. R. Thyroid hormone regulation of gene expression. Annu Rev Physiol. 1991;53:17–35. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.53.030191.000313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan C. C., Li Q., Kikuchi T., Shinohara T., Nussenblatt R. B. Enhancement of S-antigen and its mRNA in the irides of uveitic patients. J Autoimmun. 1992 Dec;5(6):719–732. doi: 10.1016/0896-8411(92)90188-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):889–895. doi: 10.1126/science.3283939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faure J. P. Autoimmunity and the retina. Curr Top Eye Res. 1980;2:215–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fortini M. E., Rubin G. M. Analysis of cis-acting requirements of the Rh3 and Rh4 genes reveals a bipartite organization to rhodopsin promoters in Drosophila melanogaster. Genes Dev. 1990 Mar;4(3):444–463. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.3.444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukada Y., Yoshizawa T., Saito T., Ohguro H., Akino T. Binding of GTP to transducin is not inhibited by arrestin and phosphorylated rhodopsin. FEBS Lett. 1990 Feb 26;261(2):419–422. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80606-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaul U., Mardon G., Rubin G. M. A putative Ras GTPase activating protein acts as a negative regulator of signaling by the Sevenless receptor tyrosine kinase. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):1007–1019. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90073-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski K., Carneiro M., Schibler U. Tissue-specific in vitro transcription from the mouse albumin promoter. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):767–776. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90519-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S., Chambon P. Nuclear receptors enhance our understanding of transcription regulation. Trends Genet. 1988 Nov;4(11):309–314. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90108-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hafen E., Basler K., Edstroem J. E., Rubin G. M. Sevenless, a cell-specific homeotic gene of Drosophila, encodes a putative transmembrane receptor with a tyrosine kinase domain. Science. 1987 Apr 3;236(4797):55–63. doi: 10.1126/science.2882603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrickson W., Schleif R. A dimer of AraC protein contacts three adjacent major groove regions of the araI DNA site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3129–3133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwung Y. P., Crowe D. T., Wang L. H., Tsai S. Y., Tsai M. J. The COUP transcription factor binds to an upstream promoter element of the rat insulin II gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2070–2077. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyde D. R., Mecklenburg K. L., Pollock J. A., Vihtelic T. S., Benzer S. Twenty Drosophila visual system cDNA clones: one is a homolog of human arrestin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1008–1012. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalb V. F., Jr, Bernlohr R. W. A new spectrophotometric assay for protein in cell extracts. Anal Biochem. 1977 Oct;82(2):362–371. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90173-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krämer H., Cagan R. L., Zipursky S. L. Interaction of bride of sevenless membrane-bound ligand and the sevenless tyrosine-kinase receptor. Nature. 1991 Jul 18;352(6332):207–212. doi: 10.1038/352207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühn H., Wilden U. Deactivation of photoactivated rhodopsin by rhodopsin-kinase and arrestin. J Recept Res. 1987;7(1-4):283–298. doi: 10.3109/10799898709054990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mlodzik M., Hiromi Y., Weber U., Goodman C. S., Rubin G. M. The Drosophila seven-up gene, a member of the steroid receptor gene superfamily, controls photoreceptor cell fates. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):211–224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90737-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montell C., Rubin G. M. Molecular characterization of the Drosophila trp locus: a putative integral membrane protein required for phototransduction. Neuron. 1989 Apr;2(4):1313–1323. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90069-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montell C., Rubin G. M. The Drosophila ninaC locus encodes two photoreceptor cell specific proteins with domains homologous to protein kinases and the myosin heavy chain head. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):757–772. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90413-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Tousa J. E., Baehr W., Martin R. L., Hirsh J., Pak W. L., Applebury M. L. The Drosophila ninaE gene encodes an opsin. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):839–850. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90343-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinohara T., Dietzschold B., Craft C. M., Wistow G., Early J. J., Donoso L. A., Horwitz J., Tao R. Primary and secondary structure of bovine retinal S antigen (48-kDa protein). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):6975–6979. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.6975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinohara T., Kikuchi T., Tsuda M., Yamaki K. A family of retinal S-antigens (arrestins) and their genes: comparative analysis of human, mouse, rat, bovine and Drosophila. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1992 Nov;103(3):505–509. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(92)90361-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. P., Shieh B. H., Zuker C. S. Isolation and structure of an arrestin gene from Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1003–1007. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takao M., Yasui A., Tokunaga F. Isolation and sequence determination of the chicken rhodopsin gene. Vision Res. 1988;28(4):471–480. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(88)90169-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda M., Kikuchi T., Yamaki K., Shinohara T. The mouse S-antigen gene. Comparison with human and Drosophila. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Aug 15;200(1):95–101. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb21053.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H., Tsai S. Y., Cook R. G., Beattie W. G., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. COUP transcription factor is a member of the steroid receptor superfamily. Nature. 1989 Jul 13;340(6229):163–166. doi: 10.1038/340163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Macke J. P., Merbs S. L., Zack D. J., Klaunberg B., Bennett J., Gearhart J., Nathans J. A locus control region adjacent to the human red and green visual pigment genes. Neuron. 1992 Sep;9(3):429–440. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90181-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaki K., Takahashi Y., Sakuragi S., Matsubara K. Molecular cloning of the S-antigen cDNA from bovine retina. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Feb 13;142(3):904–910. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91499-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaki K., Tsuda M., Kikuchi T., Chen K. H., Huang K. P., Shinohara T. Structural organization of the human S-antigen gene. cDNA, amino acid, intron, exon, promoter, in vitro transcription, retina, and pineal gland. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 5;265(34):20757–20762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama T., Liou G. I., Caldwell R. B., Overbeek P. A. Photoreceptor-specific activity of the human interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein (IRBP) promoter in transgenic mice. Exp Eye Res. 1992 Aug;55(2):225–233. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(92)90186-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. W. Visual cells and the concept of renewal. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1976 Sep;15(9):700–725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zack D. J., Bennett J., Wang Y., Davenport C., Klaunberg B., Gearhart J., Nathans J. Unusual topography of bovine rhodopsin promoter-lacZ fusion gene expression in transgenic mouse retinas. Neuron. 1991 Feb;6(2):187–199. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90355-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuckerman R., Cheasty J. E. A 48 kDa protein arrests cGMP phosphodiesterase activation in retinal rod disk membranes. FEBS Lett. 1986 Oct 20;207(1):35–41. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]