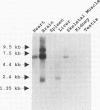
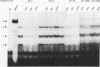
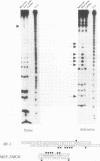
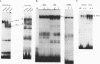
Abstract
The AT-rich element MEF-2 plays an important role in the maintenance of the muscle-specific expression of a number of cardiac and skeletal muscle genes. In the MLC-2 gene, an AT-rich element (HF-1b) which contains a consensus MEF-2 site is required for cardiac tissue-specific expression. The present study reports the isolation and characterization of a cDNA which encodes a novel C2H2 zinc finger (HF-1b) that binds in a sequence-specific manner to the HF-1b/MEF-2 site in the MLC-2 promoter. A number of independent criteria suggest that this HF-1b zinc finger protein is a component of the endogenous HF-1b/MEF-2 binding activity in cardiac muscle cells and that it can serve as a transcriptional activator of the MLC-2 promoter in transient assays. These studies suggest that, in addition to the previously reported RSRF proteins, structurally divergent transcriptional factors can bind to MEF-2-like sites in muscle promoters. These results underscore the complexity of the regulation of the muscle gene program via these AT-rich elements in cardiac and skeletal muscle.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blackwell T. K., Weintraub H. Differences and similarities in DNA-binding preferences of MyoD and E2A protein complexes revealed by binding site selection. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1104–1110. doi: 10.1126/science.2174572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun T., Bober E., Winter B., Rosenthal N., Arnold H. H. Myf-6, a new member of the human gene family of myogenic determination factors: evidence for a gene cluster on chromosome 12. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):821–831. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08179.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buskin J. N., Hauschka S. D. Identification of a myocyte nuclear factor that binds to the muscle-specific enhancer of the mouse muscle creatine kinase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2627–2640. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers A. E., Kotecha S., Towers N., Mohun T. J. Muscle-specific expression of SRF-related genes in the early embryo of Xenopus laevis. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):4981–4991. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05605.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chien K. R. Molecular advances in cardiovascular biology. Science. 1993 May 14;260(5110):916–917. doi: 10.1126/science.8493528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chien K. R., Zhu H., Knowlton K. U., Miller-Hance W., van-Bilsen M., O'Brien T. X., Evans S. M. Transcriptional regulation during cardiac growth and development. Annu Rev Physiol. 1993;55:77–95. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.55.030193.000453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courey A. J., Holtzman D. A., Jackson S. P., Tjian R. Synergistic activation by the glutamine-rich domains of human transcription factor Sp1. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):827–836. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90606-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courey A. J., Tjian R. Analysis of Sp1 in vivo reveals multiple transcriptional domains, including a novel glutamine-rich activation motif. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):887–898. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90144-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cserjesi P., Olson E. N. Myogenin induces the myocyte-specific enhancer binding factor MEF-2 independently of other muscle-specific gene products. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):4854–4862. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.4854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmondson D. G., Cheng T. C., Cserjesi P., Chakraborty T., Olson E. N. Analysis of the myogenin promoter reveals an indirect pathway for positive autoregulation mediated by the muscle-specific enhancer factor MEF-2. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;12(9):3665–3677. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.9.3665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmondson D. G., Olson E. N. A gene with homology to the myc similarity region of MyoD1 is expressed during myogenesis and is sufficient to activate the muscle differentiation program. Genes Dev. 1989 May;3(5):628–640. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.5.628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch M., Levine M. Complementary patterns of even-skipped and fushi tarazu expression involve their differential regulation by a common set of segmentation genes in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1987 Nov;1(9):981–995. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.9.981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgopoulos K., Moore D. D., Derfler B. Ikaros, an early lymphoid-specific transcription factor and a putative mediator for T cell commitment. Science. 1992 Oct 30;258(5083):808–812. doi: 10.1126/science.1439790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gossett L. A., Kelvin D. J., Sternberg E. A., Olson E. N. A new myocyte-specific enhancer-binding factor that recognizes a conserved element associated with multiple muscle-specific genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5022–5033. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson S. A., Spencer M., Sen A., Kumar C., Siddiqui M. A., Chien K. R. Structure, organization, and expression of the rat cardiac myosin light chain-2 gene. Identification of a 250-base pair fragment which confers cardiac-specific expression. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):18142–18148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horlick R. A., Benfield P. A. The upstream muscle-specific enhancer of the rat muscle creatine kinase gene is composed of multiple elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2396–2413. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horlick R. A., Hobson G. M., Patterson J. H., Mitchell M. T., Benfield P. A. Brain and muscle creatine kinase genes contain common TA-rich recognition protein-binding regulatory elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4826–4836. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iannello R. C., Mar J. H., Ordahl C. P. Characterization of a promoter element required for transcription in myocardial cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 15;266(5):3309–3316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. E., Wold B. J., Hauschka S. D. Muscle creatine kinase sequence elements regulating skeletal and cardiac muscle expression in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3393–3399. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Carner K. R., Masiarz F. R., Tjian R. Isolation of cDNA encoding transcription factor Sp1 and functional analysis of the DNA binding domain. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1079–1090. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90594-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsley C., Winoto A. Cloning of GT box-binding proteins: a novel Sp1 multigene family regulating T-cell receptor gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4251–4261. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowlton K. U., Baracchini E., Ross R. S., Harris A. N., Henderson S. A., Evans S. M., Glembotski C. C., Chien K. R. Co-regulation of the atrial natriuretic factor and cardiac myosin light chain-2 genes during alpha-adrenergic stimulation of neonatal rat ventricular cells. Identification of cis sequences within an embryonic and a constitutive contractile protein gene which mediate inducible expression. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7759–7768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassar A. B., Buskin J. N., Lockshon D., Davis R. L., Apone S., Hauschka S. D., Weintraub H. MyoD is a sequence-specific DNA binding protein requiring a region of myc homology to bind to the muscle creatine kinase enhancer. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):823–831. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90935-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassar A. B., Davis R. L., Wright W. E., Kadesch T., Murre C., Voronova A., Baltimore D., Weintraub H. Functional activity of myogenic HLH proteins requires hetero-oligomerization with E12/E47-like proteins in vivo. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):305–315. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90620-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. J., Ross R. S., Rockman H. A., Harris A. N., O'Brien T. X., van Bilsen M., Shubeita H. E., Kandolf R., Brem G., Price J. Myosin light chain-2 luciferase transgenic mice reveal distinct regulatory programs for cardiac and skeletal muscle-specific expression of a single contractile protein gene. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 5;267(22):15875–15885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons G. E., Mühlebach S., Moser A., Masood R., Paterson B. M., Buckingham M. E., Perriard J. C. Developmental regulation of creatine kinase gene expression by myogenic factors in embryonic mouse and chick skeletal muscle. Development. 1991 Nov;113(3):1017–1029. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.3.1017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miner J. H., Wold B. Herculin, a fourth member of the MyoD family of myogenic regulatory genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1089–1093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minty A., Kedes L. Upstream regions of the human cardiac actin gene that modulate its transcription in muscle cells: presence of an evolutionarily conserved repeated motif. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2125–2136. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Baltimore D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Vaessin H., Caudy M., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N., Cabrera C. V., Buskin J. N., Hauschka S. D., Lassar A. B. Interactions between heterologous helix-loop-helix proteins generate complexes that bind specifically to a common DNA sequence. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):537–544. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90434-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nardelli J., Gibson T. J., Vesque C., Charnay P. Base sequence discrimination by zinc-finger DNA-binding domains. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):175–178. doi: 10.1038/349175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navankasattusas S., Zhu H., Garcia A. V., Evans S. M., Chien K. R. A ubiquitous factor (HF-1a) and a distinct muscle factor (HF-1b/MEF-2) form an E-box-independent pathway for cardiac muscle gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;12(4):1469–1479. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.4.1469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson C., Shen L. P., Meister A., Fodor E., Rutter W. J. Pan: a transcriptional regulator that binds chymotrypsin, insulin, and AP-4 enhancer motifs. Genes Dev. 1990 Jun;4(6):1035–1043. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.6.1035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson E. N. MyoD family: a paradigm for development? Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1454–1461. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott M. O., Bober E., Lyons G., Arnold H., Buckingham M. Early expression of the myogenic regulatory gene, myf-5, in precursor cells of skeletal muscle in the mouse embryo. Development. 1991 Apr;111(4):1097–1107. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.4.1097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmacek M. S., Vora A. J., Shen T., Barr E., Jung F., Leiden J. M. Identification and characterization of a cardiac-specific transcriptional regulatory element in the slow/cardiac troponin C gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 May;12(5):1967–1976. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.5.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock R., Treisman R. Human SRF-related proteins: DNA-binding properties and potential regulatory targets. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12A):2327–2341. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12a.2327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes S. J., Konieczny S. F. Identification of MRF4: a new member of the muscle regulatory factor gene family. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2050–2061. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruppert J. M., Kinzler K. W., Wong A. J., Bigner S. H., Kao F. T., Law M. L., Seuanez H. N., O'Brien S. J., Vogelstein B. The GLI-Kruppel family of human genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3104–3113. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sartorelli V., Webster K. A., Kedes L. Muscle-specific expression of the cardiac alpha-actin gene requires MyoD1, CArG-box binding factor, and Sp1. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1811–1822. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanojević D., Hoey T., Levine M. Sequence-specific DNA-binding activities of the gap proteins encoded by hunchback and Krüppel in Drosophila. Nature. 1989 Sep 28;341(6240):331–335. doi: 10.1038/341331a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturm R., Baumruker T., Franza B. R., Jr, Herr W. A 100-kD HeLa cell octamer binding protein (OBP100) interacts differently with two separate octamer-related sequences within the SV40 enhancer. Genes Dev. 1987 Dec;1(10):1147–1160. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.10.1147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman J., Desplan C. The products of the Drosophila gap genes hunchback and Krüppel bind to the hunchback promoters. Nature. 1989 Sep 28;341(6240):335–337. doi: 10.1038/341335a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinson C. R., LaMarco K. L., Johnson P. F., Landschulz W. H., McKnight S. L. In situ detection of sequence-specific DNA binding activity specified by a recombinant bacteriophage. Genes Dev. 1988 Jul;2(7):801–806. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.7.801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu Y. T., Breitbart R. E., Smoot L. B., Lee Y., Mahdavi V., Nadal-Ginard B. Human myocyte-specific enhancer factor 2 comprises a group of tissue-restricted MADS box transcription factors. Genes Dev. 1992 Sep;6(9):1783–1798. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.9.1783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu H., Garcia A. V., Ross R. S., Evans S. M., Chien K. R. A conserved 28-base-pair element (HF-1) in the rat cardiac myosin light-chain-2 gene confers cardiac-specific and alpha-adrenergic-inducible expression in cultured neonatal rat myocardial cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):2273–2281. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.2273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuo P., Stanojević D., Colgan J., Han K., Levine M., Manley J. L. Activation and repression of transcription by the gap proteins hunchback and Krüppel in cultured Drosophila cells. Genes Dev. 1991 Feb;5(2):254–264. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.2.254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]