Abstract
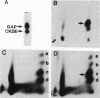
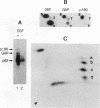
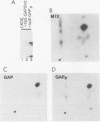
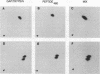
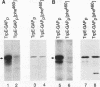
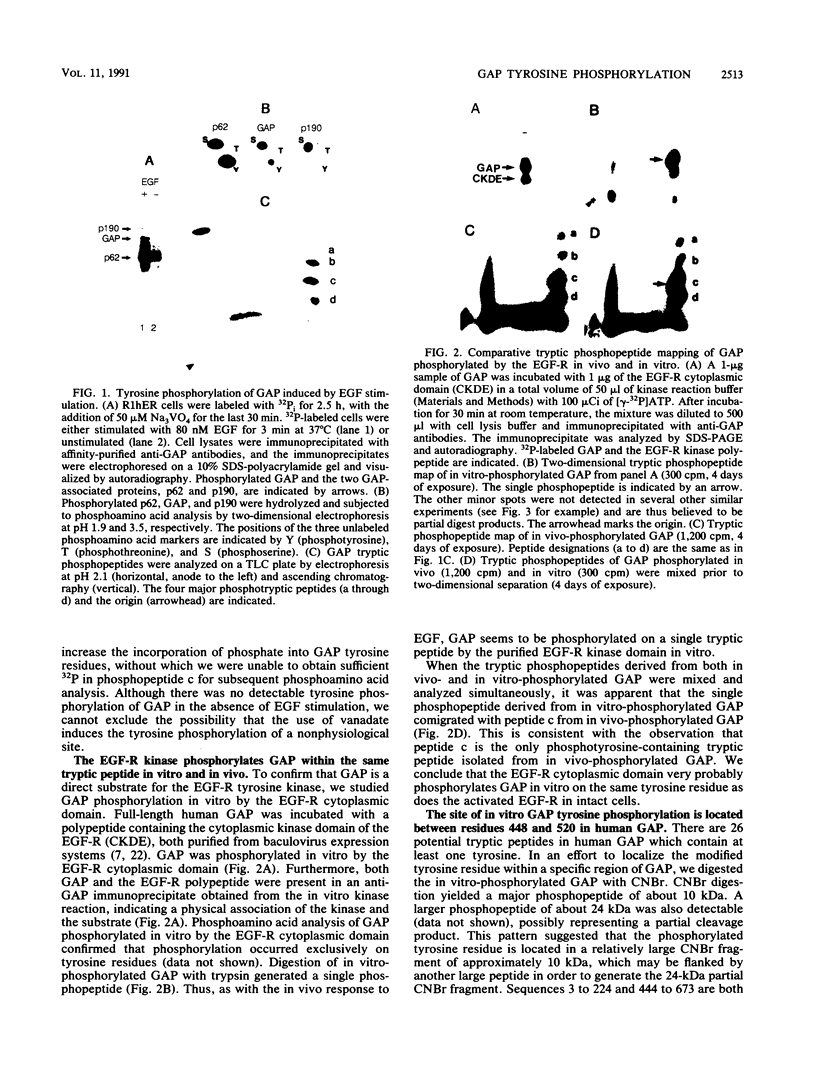
GTPase-activating protein (GAP) stimulates the ability of p21ras to hydrolyze GTP to GDP. Since GAP is phosphorylated by a variety of activated or oncogenic protein-tyrosine kinases, it may couple tyrosine kinases to the Ras signaling pathway. The epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor cytoplasmic domain phosphorylated human GAP in vitro within a single tryptic phosphopeptide. The same GAP peptide was also apparently phosphorylated on tyrosine in EGF-stimulated rat fibroblasts. Circumstantial evidence suggested that residue 460 might be the site of GAP tyrosine phosphorylation. This possibility was confirmed by phosphorylation of a synthetic peptide corresponding to the predicted tryptic peptide containing Tyr-460. Alteration of Tyr-460 to phenylalanine by site-directed mutagenesis diminished the in vitro phosphorylation of a bacterial GAP polypeptide by the EGF receptor. We conclude that Tyr-460 is a site of GAP tyrosine phosphorylation by the EGF receptor in vitro and likely in vivo. GAP Tyr-460 is located immediately C terminal to the second GAP SH2 domain, suggesting that its phosphorylation might have a role in regulating protein-protein interactions.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adari H., Lowy D. R., Willumsen B. M., Der C. J., McCormick F. Guanosine triphosphatase activating protein (GAP) interacts with the p21 ras effector binding domain. Science. 1988 Apr 22;240(4851):518–521. doi: 10.1126/science.2833817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D., Koch C. A., Grey L., Ellis C., Moran M. F., Pawson T. Binding of SH2 domains of phospholipase C gamma 1, GAP, and Src to activated growth factor receptors. Science. 1990 Nov 16;250(4983):979–982. doi: 10.1126/science.2173144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calés C., Hancock J. F., Marshall C. J., Hall A. The cytoplasmic protein GAP is implicated as the target for regulation by the ras gene product. Nature. 1988 Apr 7;332(6164):548–551. doi: 10.1038/332548a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Sefton B. M., Hunter T. Detection and quantification of phosphotyrosine in proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1983;99:387–402. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)99075-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis C., Moran M., McCormick F., Pawson T. Phosphorylation of GAP and GAP-associated proteins by transforming and mitogenic tyrosine kinases. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):377–381. doi: 10.1038/343377a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Sefton B. M. Neither arginine nor histidine can carry out the function of lysine-295 in the ATP-binding site of p60src. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;6(3):751–757. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.3.751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. R., Morrison D. K., Wong G., McCormick F., Williams L. T. PDGF beta-receptor stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of GAP and association of GAP with a signaling complex. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):125–133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90220-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. R., Whitman M., Schaffhausen B., Pallas D. C., White M., Cantley L., Roberts T. M. Common elements in growth factor stimulation and oncogenic transformation: 85 kd phosphoprotein and phosphatidylinositol kinase activity. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1021–1029. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90168-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazlauskas A., Ellis C., Pawson T., Cooper J. A. Binding of GAP to activated PDGF receptors. Science. 1990 Mar 30;247(4950):1578–1581. doi: 10.1126/science.2157284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. W., Sim S. S., Kim U. H., Nishibe S., Wahl M. I., Carpenter G., Rhee S. G. Tyrosine residues in bovine phospholipase C-gamma phosphorylated by the epidermal growth factor receptor in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):3940–3943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kypta R. M., Goldberg Y., Ulug E. T., Courtneidge S. A. Association between the PDGF receptor and members of the src family of tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):481–492. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo K., Hurley T. R., Sefton B. M. Transfer of proteins to membranes facilitates both cyanogen bromide cleavage and two-dimensional proteolytic mapping. Oncogene. 1990 Jun;5(6):921–923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Bellot F., Honegger A. M., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J., Zilberstein A. Tyrosine kinase activity is essential for the association of phospholipase C-gamma with the epidermal growth factor receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):435–441. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Li N., Koch A., Mohammadi M., Hurwitz D. R., Zilberstein A., Ullrich A., Pawson T., Schlessinger J. The tyrosine phosphorylated carboxyterminus of the EGF receptor is a binding site for GAP and PLC-gamma. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4375–4380. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07887.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Rhee S. G., Felder S., Mervic M., Lyall R., Levitzki A., Ullrich A., Zilberstein A., Schlessinger J. EGF induces tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-II: a potential mechanism for EGF receptor signaling. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1101–1107. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90047-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisenhelder J., Suh P. G., Rhee S. G., Hunter T. Phospholipase C-gamma is a substrate for the PDGF and EGF receptor protein-tyrosine kinases in vivo and in vitro. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1109–1122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90048-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molloy C. J., Bottaro D. P., Fleming T. P., Marshall M. S., Gibbs J. B., Aaronson S. A. PDGF induction of tyrosine phosphorylation of GTPase activating protein. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):711–714. doi: 10.1038/342711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran M. F., Koch C. A., Anderson D., Ellis C., England L., Martin G. S., Pawson T. Src homology region 2 domains direct protein-protein interactions in signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8622–8626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. K., Kaplan D. R., Escobedo J. A., Rapp U. R., Roberts T. M., Williams L. T. Direct activation of the serine/threonine kinase activity of Raf-1 through tyrosine phosphorylation by the PDGF beta-receptor. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):649–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90100-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishibe S., Wahl M. I., Wedegaertner P. B., Kim J. W., Rhee S. G., Carpenter G., Kim J. J. Selectivity of phospholipase C phosphorylation by the epidermal growth factor receptor, the insulin receptor, and their cytoplasmic domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):424–428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T. Non-catalytic domains of cytoplasmic protein-tyrosine kinases: regulatory elements in signal transduction. Oncogene. 1988 Nov;3(5):491–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder M. A., Bishop J. M., McGrath J. P., Levinson A. D. A mutation at the ATP-binding site of pp60v-src abolishes kinase activity, transformation, and tumorigenicity. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1772–1779. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trahey M., McCormick F. A cytoplasmic protein stimulates normal N-ras p21 GTPase, but does not affect oncogenic mutants. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):542–545. doi: 10.1126/science.2821624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trahey M., Wong G., Halenbeck R., Rubinfeld B., Martin G. A., Ladner M., Long C. M., Crosier W. J., Watt K., Koths K. Molecular cloning of two types of GAP complementary DNA from human placenta. Science. 1988 Dec 23;242(4886):1697–1700. doi: 10.1126/science.3201259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90801-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel U. S., Dixon R. A., Schaber M. D., Diehl R. E., Marshall M. S., Scolnick E. M., Sigal I. S., Gibbs J. B. Cloning of bovine GAP and its interaction with oncogenic ras p21. Nature. 1988 Sep 1;335(6185):90–93. doi: 10.1038/335090a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl M. I., Nishibe S., Kim J. W., Kim H., Rhee S. G., Carpenter G. Identification of two epidermal growth factor-sensitive tyrosine phosphorylation sites of phospholipase C-gamma in intact HSC-1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):3944–3948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinmaster G., Zoller M. J., Smith M., Hinze E., Pawson T. Mutagenesis of Fujinami sarcoma virus: evidence that tyrosine phosphorylation of P130gag-fps modulates its biological activity. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):559–568. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90386-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]