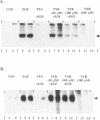
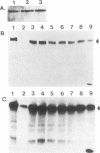
Abstract
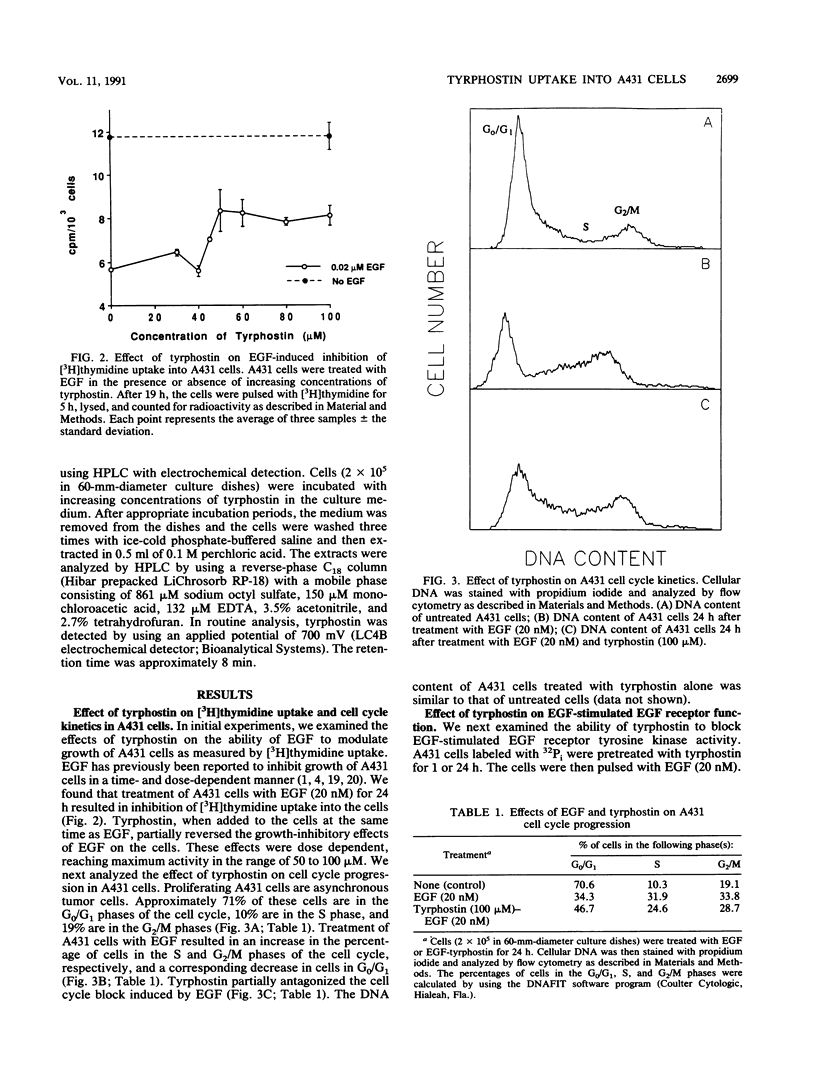
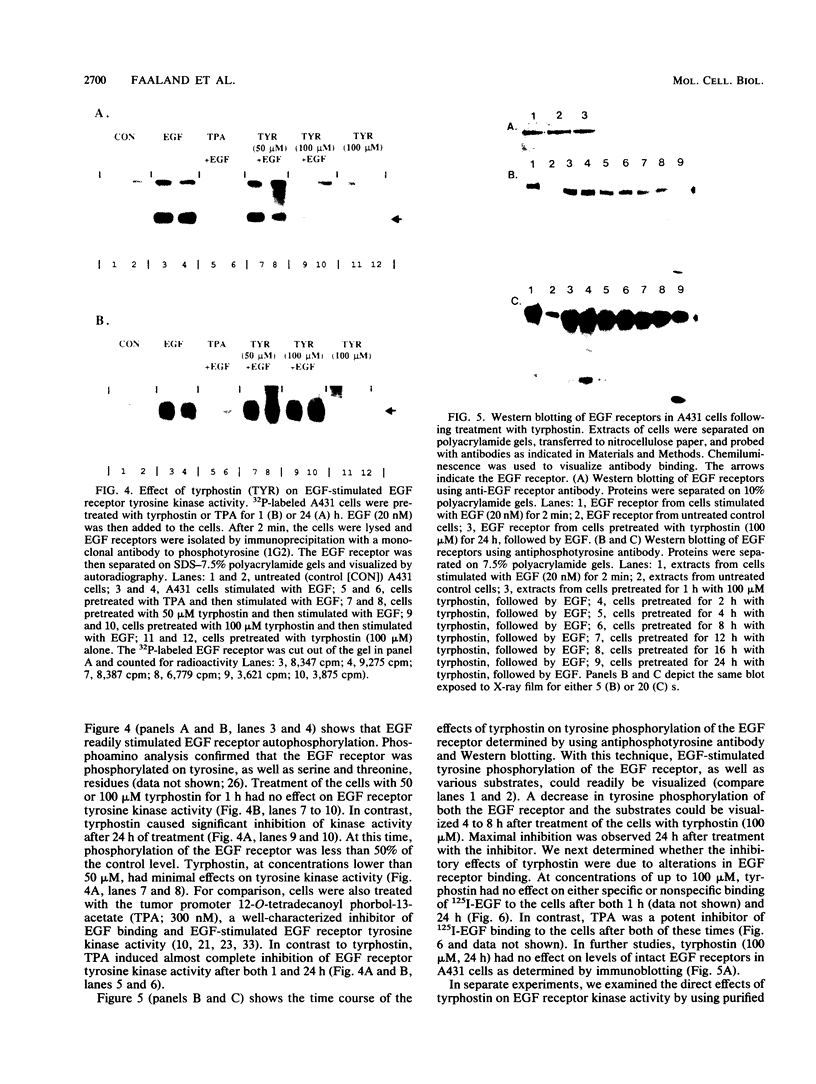
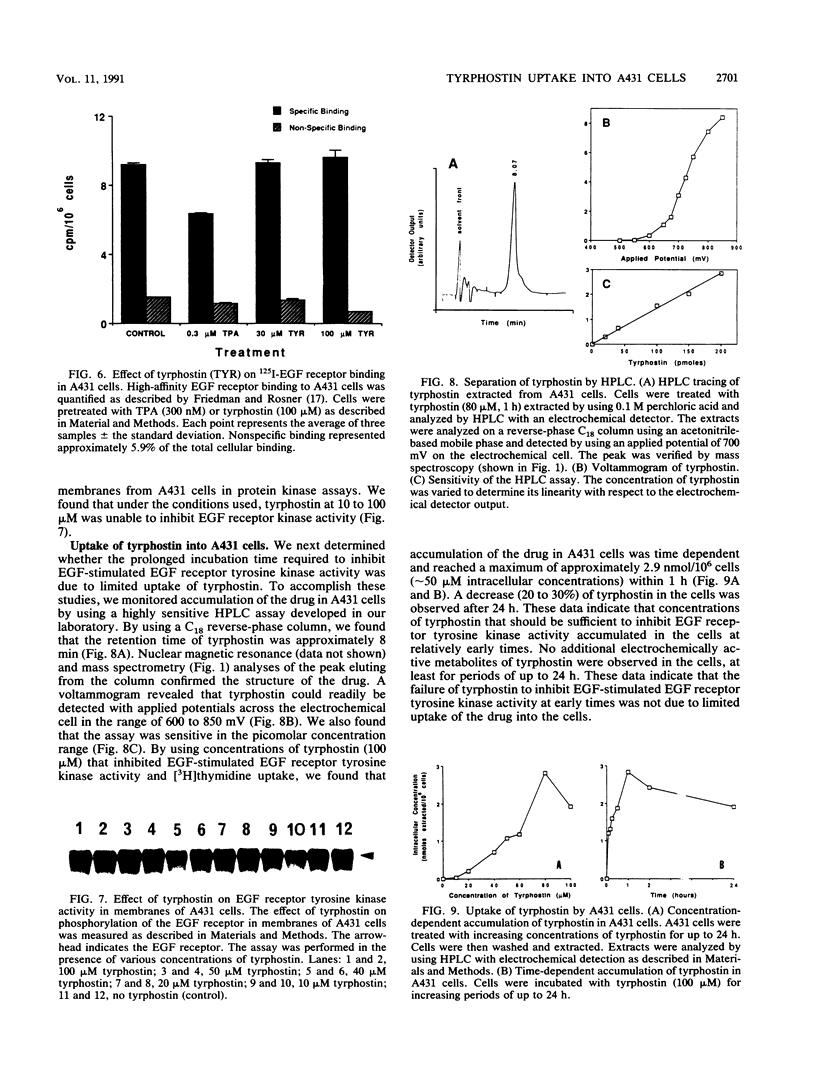
Treatment of A431 human epidermoid cells with epidermal growth factor (EGF; 20 nM) results in decreased proliferation. This is associated with blockage of the cells in the S and/or G2 phases of the cell cycle. We found that tyrphostin, a putative tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in the range of 50 to 100 microM, partially reversed the growth-inhibitory and cell cycle changes induced by EGF. By using high-pressure liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection, we found that tyrphostin was readily incorporated into A431 cells, reaching maximal levels within 1 h. Although tyrphostin (50 to 100 microM) had no effect on high-affinity binding of EGF to its receptor in A431 cells for up to 24 h, the compound partially inhibited EGF-stimulated EGF receptor tyrosine kinase activity. However, this effect was evident only after prolonged treatment of the cells (4 to 24 h) with the drug. When the peak intracellular concentration of tyrphostin occurred (1 h), no inhibition of tyrosine kinase activity was observed. After both 1 and 24 h, tyrphostin was a less effective inhibitor of tyrosine kinase activity than the potent tumor promoter 12-O-tetradecanoyl phorbol-13-acetate, which almost completely blocked EGF receptor autophosphorylation. On the basis of our data, we hypothesize that tyrphostin is not a competitive inhibitor of the EGF receptor tyrosine kinase in intact cells and that it functions by an indirect mechanism.
Full text
PDF
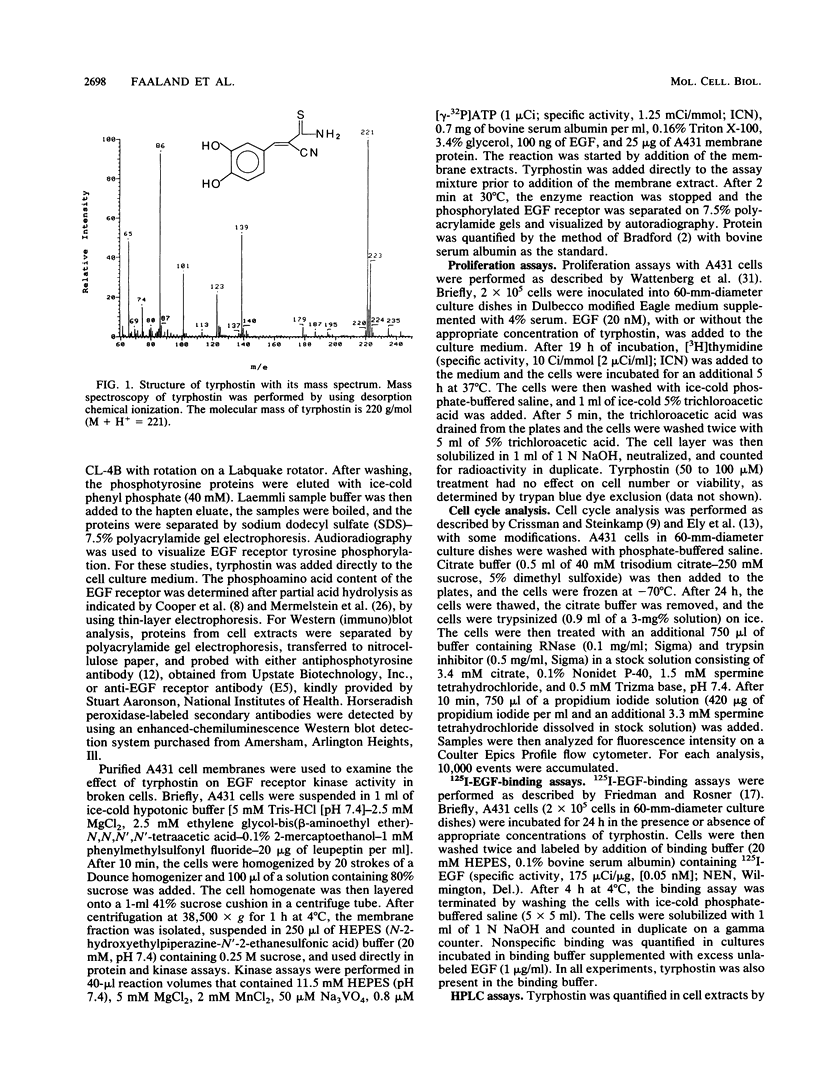


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes D. W. Epidermal growth factor inhibits growth of A431 human epidermoid carcinoma in serum-free cell culture. J Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;93(1):1–4. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buhrow S. A., Cohen S., Garbers D. L., Staros J. V. Characterization of the interaction of 5'-p-fluorosulfonylbenzoyl adenosine with the epidermal growth factor receptor/protein kinase in A431 cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7824–7827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buss J. E., Kudlow J. E., Lazar C. S., Gill G. N. Altered epidermal growth factor (EGF)-stimulated protein kinase activity in variant A431 cells with altered growth responses to EGF. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(8):2574–2578. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G. Receptors for epidermal growth factor and other polypeptide mitogens. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:881–914. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochet C., Gill G. N., Meisenhelder J., Cooper J. A., Hunter T. C-kinase phosphorylates the epidermal growth factor receptor and reduces its epidermal growth factor-stimulated tyrosine protein kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2553–2558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Ushiro H., Stoscheck C., Chinkers M. A native 170,000 epidermal growth factor receptor-kinase complex from shed plasma membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 10;257(3):1523–1531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Sefton B. M., Hunter T. Detection and quantification of phosphotyrosine in proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1983;99:387–402. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)99075-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crissman H. A., Steinkamp J. A. Rapid, simultaneous measurement of DNA, protein, and cell volume in single cells from large mammalian cell populations. J Cell Biol. 1973 Dec;59(3):766–771. doi: 10.1083/jcb.59.3.766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. J., Czech M. P. Tumor-promoting phorbol diesters cause the phosphorylation of epidermal growth factor receptors in normal human fibroblasts at threonine-654. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):1974–1978. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Parker P., Waterfield M. D. Autophosphorylation sites on the epidermal growth factor receptor. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):483–485. doi: 10.1038/311483a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Druker B. J., Mamon H. J., Roberts T. M. Oncogenes, growth factors, and signal transduction. N Engl J Med. 1989 Nov 16;321(20):1383–1391. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198911163212007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ely C. M., Leftwich J. A., Chenevix-Trench G., Hall R. E., Westin E. H. Altered regulation of c-myc in an HL-60 differentiation resistant subclone, HL-60-1E3. Cancer Res. 1987 Sep 1;47(17):4595–4600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman B. A., Rosner M. R. Growth factors modify the epidermal growth factor receptor through multiple pathways. J Cell Biochem. 1987 May;34(1):1–11. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240340102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman B. A., van Amsterdam J., Fujiki H., Rosner M. R. Phosphorylation at threonine-654 is not required for negative regulation of the epidermal growth factor receptor by non-phorbol tumor promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):812–816. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman B., Frackelton A. R., Jr, Ross A. H., Connors J. M., Fujiki H., Sugimura T., Rosner M. R. Tumor promoters block tyrosine-specific phosphorylation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):3034–3038. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.3034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazit A., Yaish P., Gilon C., Levitzki A. Tyrphostins I: synthesis and biological activity of protein tyrosine kinase inhibitors. J Med Chem. 1989 Oct;32(10):2344–2352. doi: 10.1021/jm00130a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill G. N., Buss J. E., Lazar C. S., Lifshitz A., Cooper J. A. Role of epidermal growth factor-stimulated protein kinase in control of proliferation of A431 cells. J Cell Biochem. 1982;19(3):249–257. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240190306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill G. N., Lazar C. S. Increased phosphotyrosine content and inhibition of proliferation in EGF-treated A431 cells. Nature. 1981 Sep 24;293(5830):305–307. doi: 10.1038/293305a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Ling N., Cooper J. A. Protein kinase C phosphorylation of the EGF receptor at a threonine residue close to the cytoplasmic face of the plasma membrane. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):480–483. doi: 10.1038/311480a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskin J. D., Lee E., Laskin D. L., Gallo M. A. Psoralens potentiate ultraviolet light-induced inhibition of epidermal growth factor binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8211–8215. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L. S., Weinstein I. B. Tumor-promoting phorbol esters inhibit binding of epidermal growth factor to cellular receptors. Science. 1978 Oct 20;202(4365):313–315. doi: 10.1126/science.308698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyall R. M., Zilberstein A., Gazit A., Gilon C., Levitzki A., Schlessinger J. Tyrphostins inhibit epidermal growth factor (EGF)-receptor tyrosine kinase activity in living cells and EGF-stimulated cell proliferation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14503–14509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Rhee S. G., Felder S., Mervic M., Lyall R., Levitzki A., Ullrich A., Zilberstein A., Schlessinger J. EGF induces tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-II: a potential mechanism for EGF receptor signaling. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1101–1107. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90047-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mermelstein F. H., Abidi T. F., Laskin J. D. Inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase activity in A431 human epidermoid cells following psoralen/ultraviolet light treatment. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Dec;36(6):848–855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nexł E., Hock R. A., Hollenberg M. D. Lectin-agarose immobilization, a new method for detecting soluble membrane receptors. Application to studies with epidermal growth factor-urogastrone and transcobalamin-II. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):8740–8743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northwood I. C., Davis R. J. Protein kinase C inhibition of the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine protein kinase activity is independent of the oligomeric state of the receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5746–5750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posner I., Gazit A., Gilon C., Levitzki A. Tyrphostins inhibit the epidermal growth factor receptor-mediated breakdown of phosphoinositides. FEBS Lett. 1989 Nov 6;257(2):287–291. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81554-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wattenberg E. V., Fujiki H., Rosner M. R. Heterologous regulation of the epidermal growth factor receptor by palytoxin, a non-12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-type tumor promoter. Cancer Res. 1987 Sep 1;47(17):4618–4622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber W., Bertics P. J., Gill G. N. Immunoaffinity purification of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Stoichiometry of binding and kinetics of self-phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14631–14636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteley B., Glaser L. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) promotes phosphorylation at threonine-654 of the EGF receptor: possible role of protein kinase C in homologous regulation of the EGF receptor. J Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;103(4):1355–1362. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.4.1355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaish P., Gazit A., Gilon C., Levitzki A. Blocking of EGF-dependent cell proliferation by EGF receptor kinase inhibitors. Science. 1988 Nov 11;242(4880):933–935. doi: 10.1126/science.3263702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]