Abstract
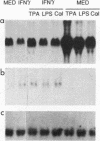
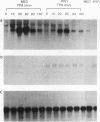
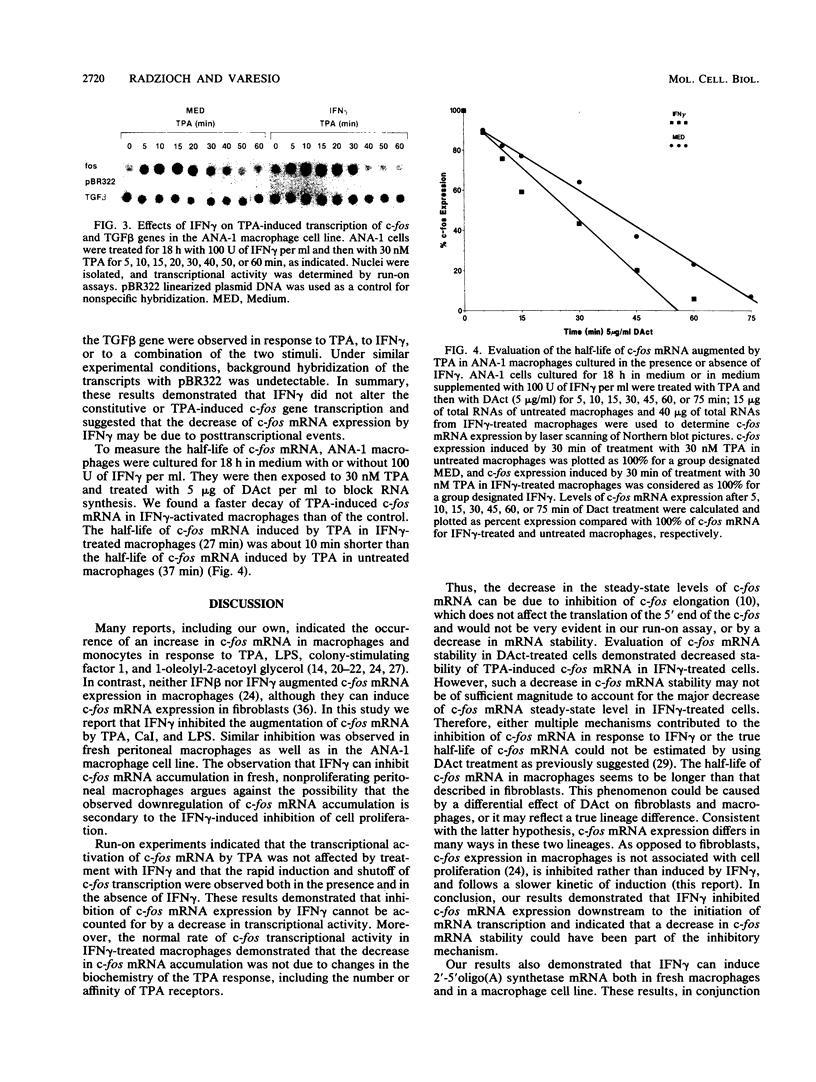
Treatment of macrophages with interferon-gamma (IFN gamma) strongly decreased the induction of c-fos mRNA by 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA), lipopolysaccharide, or calcium ionophore A23187 in macrophages. Under the same experimental conditions, IFN gamma induced oligo(A) synthetase mRNA and did not affect the constitutive expression of transforming growth factor beta mRNA, indicating that IFN gamma did not induce general degradation of mRNAs. Run-on experiments indicated that c-fos was constitutively transcribed at low levels and that TPA augmented c-fos transcription. IFN gamma did not inhibit constitutive or TPA-induced c-fos transcription. However, IFN gamma decreased c-fos mRNA stability, as assessed by measuring the half-life of c-fos mRNA in actinomycin D-treated cells. These results indicated that IFN gamma inhibited c-fos mRNA induction by TPA at the posttranscriptional level.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. O., Hamilton T. A. Molecular transductional mechanisms by which IFN gamma and other signals regulate macrophage development. Immunol Rev. 1987 Jun;97:5–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1987.tb00514.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasi E., Herberman R. B., Varesio L. Requirement for protein synthesis for induction of macrophage tumoricidal activity by IFN-alpha and IFN-beta but not by IFN-gamma. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):3226–3228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang R. J., Lee S. H. Effects of interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha on the expression of an Ia antigen on a murine macrophage cell line. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 1;137(9):2853–2856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choubey D., Snoddy J., Chaturvedi V., Toniato E., Opdenakker G., Thakur A., Samanta H., Engel D. A., Lengyel P. Interferons as gene activators. Indications for repeated gene duplication during the evolution of a cluster of interferon-activatable genes on murine chromosome 1. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):17182–17189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox G. W., Mathieson B. J., Gandino L., Blasi E., Radzioch D., Varesio L. Heterogeneity of hematopoietic cells immortalized by v-myc/v-raf recombinant retrovirus infection of bone marrow or fetal liver. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1989 Oct 4;81(19):1492–1496. doi: 10.1093/jnci/81.19.1492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Peters G., Van Beveren C., Teich N. M., Verma I. M. FBJ murine osteosarcoma virus: identification and molecular cloning of biologically active proviral DNA. J Virol. 1982 Nov;44(2):674–682. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.2.674-682.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faltynek C. R., Kung H. F. The biochemical mechanisms of action of the interferons. Biofactors. 1988 Oct;1(3):227–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figueiredo F., Koerner T. J., Adams D. O. Molecular mechanisms regulating the expression of class II histocompatibility molecules on macrophages. Effects of inductive and suppressive signals on gene transcription. J Immunol. 1989 Dec 1;143(11):3781–3786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fort P., Rech J., Vie A., Piechaczyk M., Bonnieu A., Jeanteur P., Blanchard J. M. Regulation of c-fos gene expression in hamster fibroblasts: initiation and elongation of transcription and mRNA degradation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 24;15(14):5657–5667. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.14.5657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gusella G. L., Ayroldi E., Espinoza-Delgado I., Varesio L. Lipopolysaccharide, but not IFN-gamma, down-regulates c-fms mRNA proto-oncogene expression in murine macrophages. J Immunol. 1990 May 1;144(9):3574–3580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harel-Bellan A., Brini A. T., Farrar W. L. IFN-gamma inhibits c-myc gene expression by impairing the splicing process in a colony-stimulating factor dependent murine myeloid cell line. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 1;141(3):1012–1017. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Introna M., Hamilton T. A., Kaufman R. E., Adams D. O., Bast R. C., Jr Treatment of murine peritoneal macrophages with bacterial lipopolysaccharide alters expression of c-fos and c-myc oncogenes. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 15;137(8):2711–2715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. M., Varesio L., Herberman R. B., Pestka S. Interferon activates macrophages to produce plasminogen activator. J Interferon Res. 1982;2(3):377–386. doi: 10.1089/jir.1982.2.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebleu B., Sen G. C., Shaila S., Cabrer B., Lengyel P. Interferon, double-stranded RNA, and protein phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3107–3111. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lengyel P. Biochemistry of interferons and their actions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:251–282. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKay R. J., Pace J. L., Jarpe M. A., Russell S. W. Macrophage activation-associated proteins. Characterization of stimuli and conditions needed for expression of proteins 47b, 71/73, and 120. J Immunol. 1989 Mar 1;142(5):1639–1645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Curran T., Müller D., Guilbert L. Induction of c-fos during myelomonocytic differentiation and macrophage proliferation. Nature. 1985 Apr 11;314(6011):546–548. doi: 10.1038/314546a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Müller D., Guilbert L. Differential expression of c-fos in hematopoietic cells: correlation with differentiation of monomyelocytic cells in vitro. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1887–1890. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02063.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S., Langer J. A., Zoon K. C., Samuel C. E. Interferons and their actions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:727–777. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radzioch D., Bottazzi B., Varesio L. Augmentation of c-fos mRNA expression by activators of protein kinase C in fresh, terminally differentiated resting macrophages. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):595–599. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radzioch D., Clayton M., Varesio L. Interferon-alpha, -beta, and -gamma augment the levels of rRNA precursors in peritoneal macrophages but not in macrophage cell lines and fibroblasts. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 1;139(3):805–812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radzioch D., Varesio L. Protein kinase C inhibitors block the activation of macrophages by IFN-beta but not by IFN-gamma. J Immunol. 1988 Feb 15;140(4):1259–1263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sariban E., Luebbers R., Kufe D. Transcriptional and posttranscriptional control of c-fos gene expression in human monocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):340–346. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sariban E., Mitchell T., Griffin J., Kufe D. W. Effects of interferon-gamma on proto-oncogene expression during induction of human monocytic differentiation. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 15;138(6):1954–1958. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shyu A. B., Greenberg M. E., Belasco J. G. The c-fos transcript is targeted for rapid decay by two distinct mRNA degradation pathways. Genes Dev. 1989 Jan;3(1):60–72. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.1.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannenbaum C. S., Hamilton T. A. Lipopolysaccharide-induced gene expression in murine peritoneal macrophages is selectively suppressed by agents that elevate intracellular cAMP. J Immunol. 1989 Feb 15;142(4):1274–1280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorens B., Mermod J. J., Vassalli P. Phagocytosis and inflammatory stimuli induce GM-CSF mRNA in macrophages through posttranscriptional regulation. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):671–679. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90245-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varesio L., Clayton M., Radzioch D., Bonvini E. Selective inhibition of 28S ribosomal RNA in macrophages activated by interferon-gamma or -beta. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 1;138(7):2332–2337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wan Y. J., Levi B. Z., Ozato K. Induction of c-fos gene expression by interferons. J Interferon Res. 1988 Feb;8(1):105–112. doi: 10.1089/jir.1988.8.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber B., Horiguchi J., Luebbers R., Sherman M., Kufe D. Posttranscriptional stabilization of c-fms mRNA by a labile protein during human monocytic differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):769–775. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]