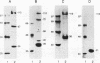Abstract
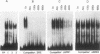
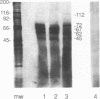
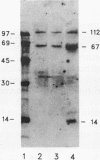
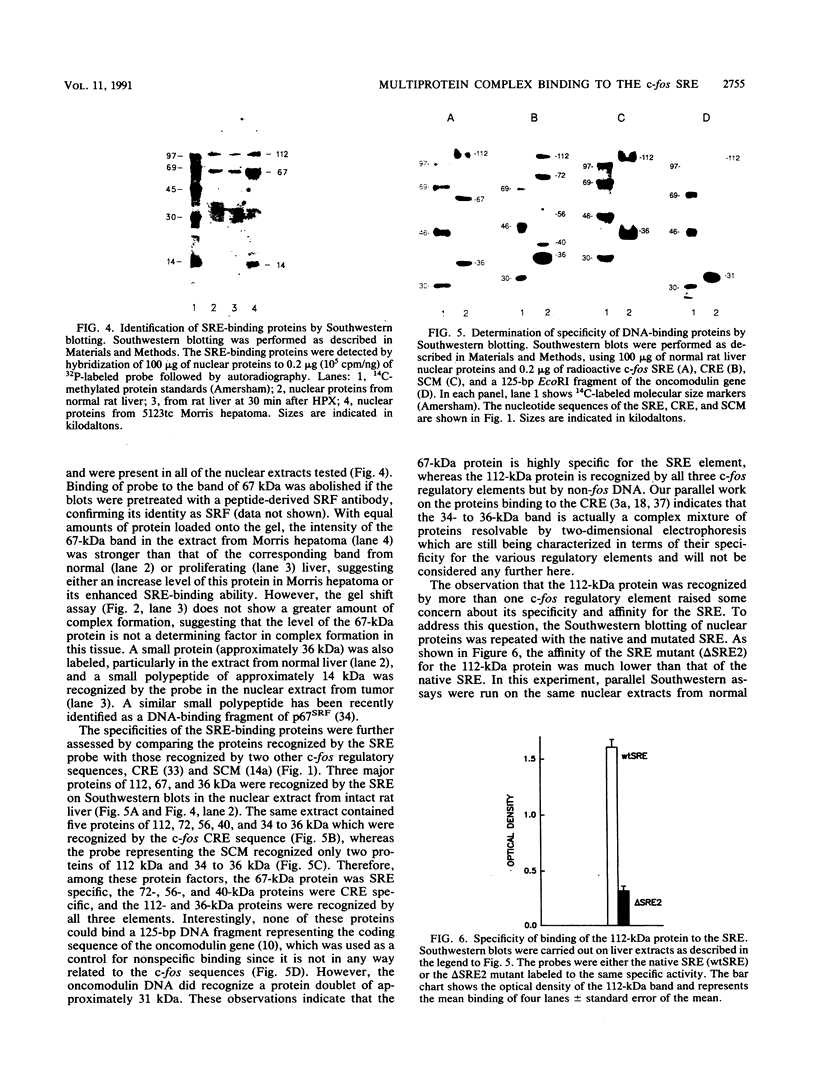
The serum response element (SRE) is essential for serum and growth factor stimulation of the c-fos gene. We have examined the nuclear proteins, obtained from tissues with elevated expression of the c-fos gene (proliferating rat liver and hepatocarcinoma), that bind to the SRE sequence. A synthetic oligonucleotide containing the SRE sequence from the mouse c-fos gene promoter (-299 to -322) was radioactively labeled, used as a probe for the mobility shift assay and Southwestern (DNA-protein) blotting, and also used for sequence-specific affinity chromatography. We have identified a group of nuclear proteins of molecular sizes 36, 45, 62, 67, 72, and 112 kDa capable of interacting with the SRE sequence. The 36-, 67-, and 112-kDa proteins have DNA-binding properties, but the presence of the others in the SRE-protein complex could be the result of protein-protein interaction. All of these protein factors were present in nuclei obtained from intact and proliferating rat liver as well as from 5123tc Morris hepatoma. The DNA-binding activity (on Southwestern blots) of the 67- and 112-kDa proteins was not affected by alkaline phosphatase treatment, but the ability of the dephosphorylated nuclear proteins to form the complex with the SRE sequence under gel shift assay conditions was severely impaired. The same alkaline phosphatase treatment completely abolished the DNA-binding properties of the c-fos cyclic AMP-responsive element-specific proteins. Therefore, transcriptional activation of the c-fos gene at the SRE must require the presence of a multiprotein complex the formation of which is governed by phosphorylation. The binding of the 67- and 62-kDa proteins to the c-fos SRE has been previously reported; however, the 36-. 45-, 72-, and 112-kDa proteins are novel factors involved in the multifaceted regulation of c-fos gene expression in vivo.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bandyopadhyay S. K., Bancroft C. Calcium induction of the mRNAs for prolactin and c-fos is independent of protein kinase C activity. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14216–14219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boxer L. M., Prywes R., Roeder R. G., Kedes L. The sarcomeric actin CArG-binding factor is indistinguishable from the c-fos serum response factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):515–522. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corral M., Tichonicky L., Guguen-Guillouzo C., Corcos D., Raymondjean M., Paris B., Kruh J., Defer N. Expression of c-fos oncogene during hepatocarcinogenesis, liver regeneration and in synchronized HTC cells. Exp Cell Res. 1985 Oct;160(2):427–434. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(85)90190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S. Modularity in promoters and enhancers. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90393-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisch T. M., Prywes R., Roeder R. G. c-fos sequence necessary for basal expression and induction by epidermal growth factor, 12-O-tetradecanoyl phorbol-13-acetate and the calcium ionophore. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3490–3502. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukumoto Y., Kaibuchi K., Oku N., Hori Y., Takai Y. Activation of the c-fos serum-response element by the activated c-Ha-ras protein in a manner independent of protein kinase C and cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):774–780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillen M. F., Banville D., Rutledge R. G., Narang S., Seligy V. L., Whitfield J. F., MacManus J. P. A complete complementary DNA for the oncodevelopmental calcium-binding protein, oncomodulin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):5308–5312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman M. Z. The c-fos serum response element responds to protein kinase C-dependent and -independent signals but not to cyclic AMP. Genes Dev. 1988 Apr;2(4):394–402. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.4.394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman M. Z., Wilson R. N., Weinberg R. A. Multiple protein-binding sites in the 5'-flanking region regulate c-fos expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4305–4316. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Hermanowski A. L., Ziff E. B. Effect of protein synthesis inhibitors on growth factor activation of c-fos, c-myc, and actin gene transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1050–1057. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes T. E., Kitchen A. M., Cochran B. H. Inducible binding of a factor to the c-fos regulatory region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1272–1276. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera R. E., Shaw P. E., Nordheim A. Occupation of the c-fos serum response element in vivo by a multi-protein complex is unaltered by growth factor induction. Nature. 1989 Jul 6;340(6228):68–70. doi: 10.1038/340068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Tjian R. Affinity purification of sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5889–5893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruijer W., Skelly H., Botteri F., van der Putten H., Barber J. R., Verma I. M., Leffert H. L. Proto-oncogene expression in regenerating liver is simulated in cultures of primary adult rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):7929–7933. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwast-Welfeld J., de Belle I., Walker P. R., Isaacs R. J., Whitfield J. F., Sikorska M. Changes in cyclic adenosine monophosphate-responsive element binding proteins in rat hepatomas. Cancer Res. 1991 Jan 15;51(2):528–535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi B. Z., Kasik J. W., Burke P. A., Prywes R., Roeder R. G., Appella E., Ozato K. Neonatal induction of a nuclear protein that binds to the c-fos enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2262–2266. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manak J. R., de Bisschop N., Kris R. M., Prywes R. Casein kinase II enhances the DNA binding activity of serum response factor. Genes Dev. 1990 Jun;4(6):955–967. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.6.955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Curran T., Verma I. M. c-fos protein can induce cellular transformation: a novel mechanism of activation of a cellular oncogene. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):51–60. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90073-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minty A., Kedes L. Upstream regions of the human cardiac actin gene that modulate its transcription in muscle cells: presence of an evolutionarily conserved repeated motif. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2125–2136. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohun T., Garrett N., Treisman R. Xenopus cytoskeletal actin and human c-fos gene promoters share a conserved protein-binding site. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):667–673. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04806.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman C., Treisman R. Analysis of serum response element function in vitro. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1988;53(Pt 2):719–726. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1988.053.01.082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prywes R., Dutta A., Cromlish J. A., Roeder R. G. Phosphorylation of serum response factor, a factor that binds to the serum response element of the c-FOS enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7206–7210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prywes R., Fisch T. M., Roeder R. G. Transcriptional regulation of c-fos. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1988;53(Pt 2):739–748. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1988.053.01.084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prywes R., Roeder R. G. Inducible binding of a factor to the c-fos enhancer. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):777–784. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90520-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prywes R., Roeder R. G. Purification of the c-fos enhancer-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3482–3489. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. Gene regulation by proteins acting nearby and at a distance. Nature. 1986 Aug 21;322(6081):697–701. doi: 10.1038/322697a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radzioch D., Bottazzi B., Varesio L. Augmentation of c-fos mRNA expression by activators of protein kinase C in fresh, terminally differentiated resting macrophages. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):595–599. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan W. A., Jr, Franza B. R., Jr, Gilman M. Z. Two distinct cellular phosphoproteins bind to the c-fos serum response element. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1785–1792. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03572.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P., Visvader J., Ferland L., Mellon P. L., Verma I. M. Induction of proto-oncogene fos transcription through the adenylate cyclase pathway: characterization of a cAMP-responsive element. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1529–1538. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröter H., Mueller C. G., Meese K., Nordheim A. Synergism in ternary complex formation between the dimeric glycoprotein p67SRF, polypeptide p62TCF and the c-fos serum response element. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1123–1130. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08218.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw P. E., Frasch S., Nordheim A. Repression of c-fos transcription is mediated through p67SRF bound to the SRE. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2567–2574. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08395.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw P. E., Schröter H., Nordheim A. The ability of a ternary complex to form over the serum response element correlates with serum inducibility of the human c-fos promoter. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):563–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90579-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorska M., MacManus J. P., Walker P. R., Whitfield J. F. The protein kinases of rat liver nuclei. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Apr 29;93(4):1196–1203. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90616-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorska M., Whitfield J. F., Walker P. R. The regulatory and catalytic subunits of cAMP-dependent protein kinases are associated with transcriptionally active chromatin during changes in gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):3005–3011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva C. M., Tully D. B., Petch L. A., Jewell C. M., Cidlowski J. A. Application of a protein-blotting procedure to the study of human glucocorticoid receptor interactions with DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):1744–1748. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stumpo D. J., Stewart T. N., Gilman M. Z., Blackshear P. J. Identification of c-fos sequences involved in induction by insulin and phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 5;263(4):1611–1614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson N. L., Mead J. E., Braun L., Goyette M., Shank P. R., Fausto N. Sequential protooncogene expression during rat liver regeneration. Cancer Res. 1986 Jun;46(6):3111–3117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Identification and purification of a polypeptide that binds to the c-fos serum response element. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2711–2717. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02564.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Identification of a protein-binding site that mediates transcriptional response of the c-fos gene to serum factors. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):567–574. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90882-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Transient accumulation of c-fos RNA following serum stimulation requires a conserved 5' element and c-fos 3' sequences. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):889–902. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90285-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda T., Fukumoto Y., Hamamori Y., Yamashita T., Takai Y. Involvement of two intracellular messenger systems, protein kinase C and cyclic AMP, in the regulation of c-fos gene expression in human promyelocytic leukemia (HL-60) cells. J Biochem. 1987 Dec;102(6):1579–1583. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visvader J., Sassone-Corsi P., Verma I. M. Two adjacent promoter elements mediate nerve growth factor activation of the c-fos gene and bind distinct nuclear complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9474–9478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh K. Cross-binding of factors to functionally different promoter elements in c-fos and skeletal actin genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2191–2201. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. K., Huang D. P., Chiu D. K., Chiu J. F. The expression of oncogenes in human developing liver and hepatomas. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Feb 13;142(3):932–938. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91503-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]