Abstract
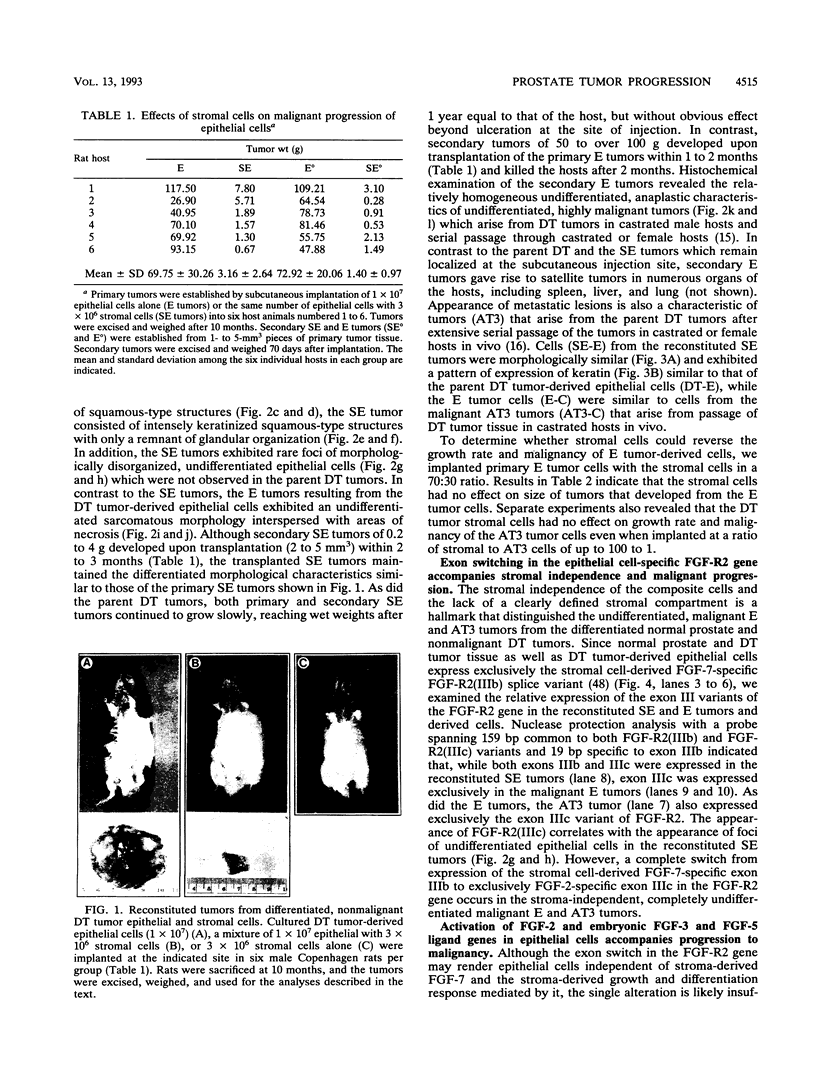
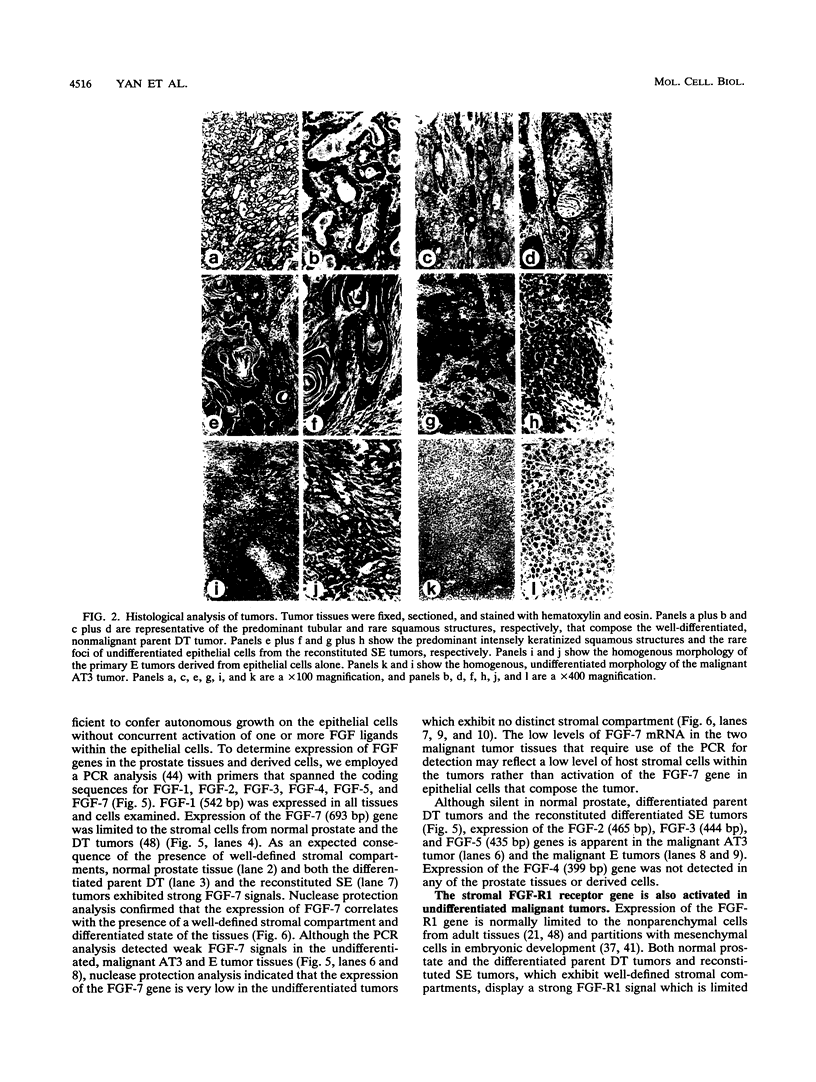
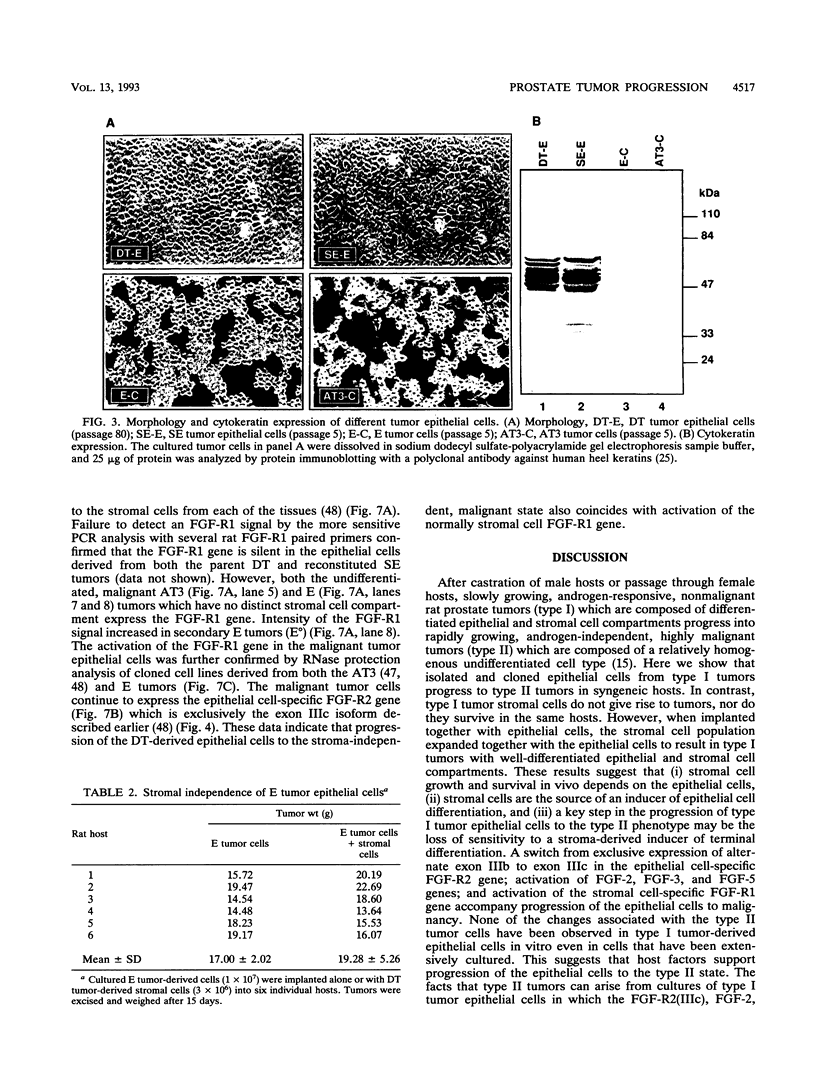
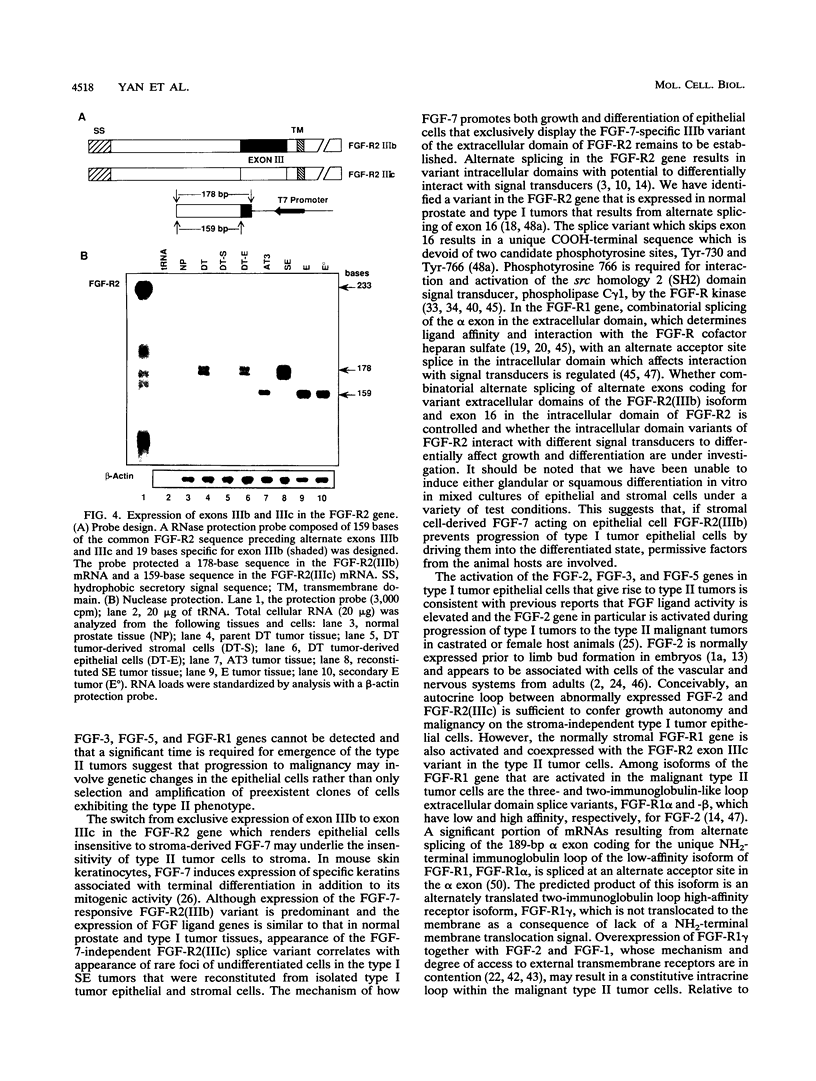
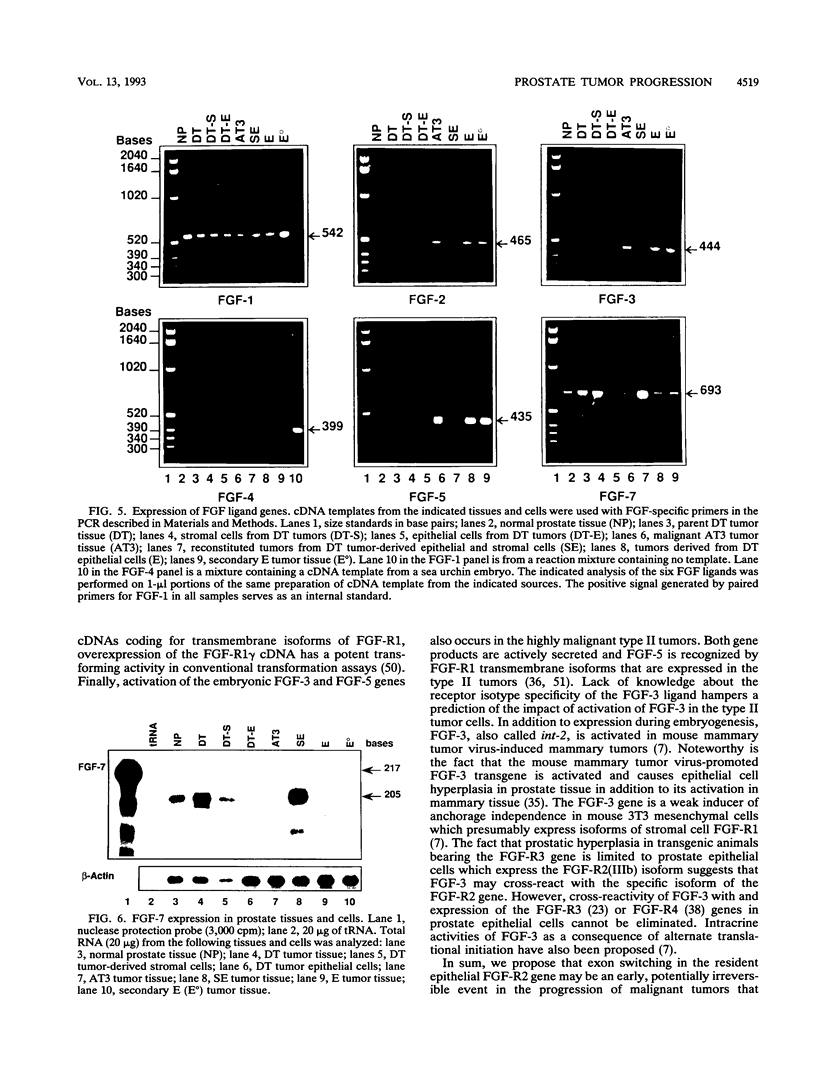
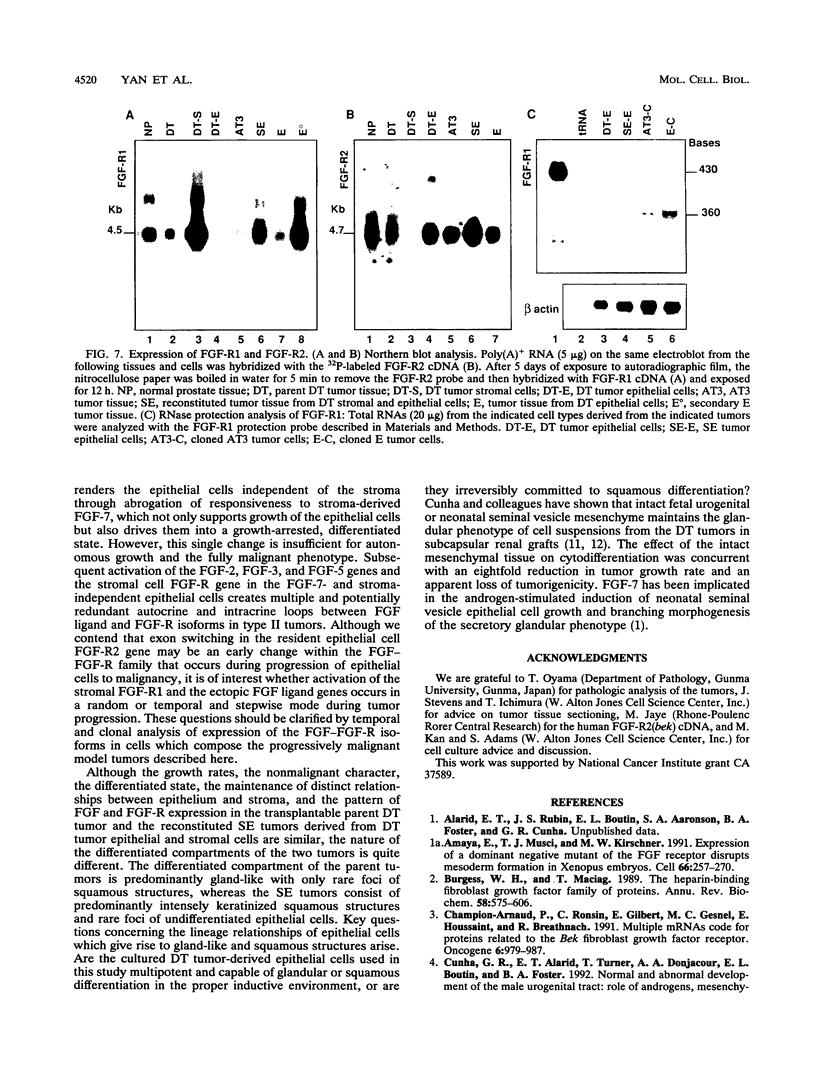
Stroma and the heparin-binding fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family influence normal epithelial cell growth and differentiation in embryonic and adult tissues. The role of stromal cells and the expression of isoforms of the FGF ligand and receptor family were examined during malignant progression of epithelial cells from a differentiated, slowly growing, nonmalignant model rat prostate tumor. In syngeneic hosts, a mixture of stromal and epithelial cells resulted in nonmalignant tumors which were differentiated and slowly growing. In the absence of the stromal cells, epithelial cells progressed to malignant tumors which were independent of the stroma and undifferentiated. The independence of the malignant epithelial cells from stromal cells was accompanied by a switch from exclusive expression of exon IIIb to exclusive expression of exon IIIc in the FGF receptor 2 (FGF-R2) gene. The FGF-R2(IIIb) isoform displays high affinity for stromal cell-derived FGF-7, whereas the FGF-R2(IIIc) isoform does not recognize FGF-7 but has high affinity for the FGF-2 member of the FGF ligand family. The switch from expression of exclusively exon IIIb to exclusively exon IIIc in the resident FGF-R2 gene was followed by activation of the FGF-2 ligand gene, the normally stromal cell FGF-R1 gene, and embryonic FGF-3 and FGF-5 ligand genes in malignant epithelial cells. Multiple autocrine and potentially intracrine ligand-receptor loops resulting from these alterations within the FGF-FGF-R family may underlie the autonomy of malignant tumor cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amaya E., Musci T. J., Kirschner M. W. Expression of a dominant negative mutant of the FGF receptor disrupts mesoderm formation in Xenopus embryos. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):257–270. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90616-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess W. H., Maciag T. The heparin-binding (fibroblast) growth factor family of proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:575–606. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.003043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champion-Arnaud P., Ronsin C., Gilbert E., Gesnel M. C., Houssaint E., Breathnach R. Multiple mRNAs code for proteins related to the BEK fibroblast growth factor receptor. Oncogene. 1991 Jun;6(6):979–987. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunha G. R., Bigsby R. M., Cooke P. S., Sugimura Y. Stromal-epithelial interactions in adult organs. Cell Differ. 1985 Sep;17(3):137–148. doi: 10.1016/0045-6039(85)90481-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunha G. R., Donjacour A. A., Cooke P. S., Mee S., Bigsby R. M., Higgins S. J., Sugimura Y. The endocrinology and developmental biology of the prostate. Endocr Rev. 1987 Aug;8(3):338–362. doi: 10.1210/edrv-8-3-338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson C., Acland P., Smith R., Dixon M., Deed R., MacAllan D., Walther W., Fuller-Pace F., Kiefer P., Peters G. Characterization of int-2: a member of the fibroblast growth factor family. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1990;13:87–96. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1990.supplement_13.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch P. W., Rubin J. S., Miki T., Ron D., Aaronson S. A. Human KGF is FGF-related with properties of a paracrine effector of epithelial cell growth. Science. 1989 Aug 18;245(4919):752–755. doi: 10.1126/science.2475908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franks L. M., Riddle P. N., Carbonell A. W., Gey G. O. A comparative study of the ultrastructure and lack of growth capacity of adult human prostate epithelium mechanically separated from its stroma. J Pathol. 1970 Feb;100(2):113–119. doi: 10.1002/path.1711000206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori Y., Odagiri H., Nakatani H., Miyagawa K., Naito K., Sakamoto H., Katoh O., Yoshida T., Sugimura T., Terada M. K-sam, an amplified gene in stomach cancer, is a member of the heparin-binding growth factor receptor genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5983–5987. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi N., Cunha G. R. Mesenchyme-induced changes in the neoplastic characteristics of the Dunning prostatic adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 1991 Sep 15;51(18):4924–4930. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi N., Cunha G. R., Wong Y. C. Influence of male genital tract mesenchymes on differentiation of Dunning prostatic adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 1990 Aug 1;50(15):4747–4754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hou J. Z., Kan M. K., McKeehan K., McBride G., Adams P., McKeehan W. L. Fibroblast growth factor receptors from liver vary in three structural domains. Science. 1991 Feb 8;251(4994):665–668. doi: 10.1126/science.1846977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hébert J. M., Basilico C., Goldfarb M., Haub O., Martin G. R. Isolation of cDNAs encoding four mouse FGF family members and characterization of their expression patterns during embryogenesis. Dev Biol. 1990 Apr;138(2):454–463. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(90)90211-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacs J. T. Development and characteristics of the available animal model systems for the study of prostatic cancer. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1987;239:513–576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacs J. T., Heston W. D., Weissman R. M., Coffey D. S. Animal models of the hormone-sensitive and -insensitive prostatic adenocarcinomas, Dunning R-3327-H, R-3327-HI, and R-3327-AT. Cancer Res. 1978 Nov;38(11 Pt 2):4353–4359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaye M., Schlessinger J., Dionne C. A. Fibroblast growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases: molecular analysis and signal transduction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Jun 10;1135(2):185–199. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(92)90136-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. E., Lu J., Chen H., Werner S., Williams L. T. The human fibroblast growth factor receptor genes: a common structural arrangement underlies the mechanisms for generating receptor forms that differ in their third immunoglobulin domain. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;11(9):4627–4634. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.9.4627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kan M., Huang J. S., Mansson P. E., Yasumitsu H., Carr B., McKeehan W. L. Heparin-binding growth factor type 1 (acidic fibroblast growth factor): a potential biphasic autocrine and paracrine regulator of hepatocyte regeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7432–7436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kan M., Wang F., Xu J., Crabb J. W., Hou J., McKeehan W. L. An essential heparin-binding domain in the fibroblast growth factor receptor kinase. Science. 1993 Mar 26;259(5103):1918–1921. doi: 10.1126/science.8456318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kan M., Yan G. C., Xu J., Nakahara M., Hou J. Receptor phenotype underlies differential response of hepatocytes and nonparenchymal cells to heparin-binding fibroblast growth factor type 1 (aFGF) and type 2 (bFGF). In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1992 Jul-Aug;28A(7-8):515–520. doi: 10.1007/BF02634135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandel J., Bossy-Wetzel E., Radvanyi F., Klagsbrun M., Folkman J., Hanahan D. Neovascularization is associated with a switch to the export of bFGF in the multistep development of fibrosarcoma. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1095–1104. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90033-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keegan K., Johnson D. E., Williams L. T., Hayman M. J. Isolation of an additional member of the fibroblast growth factor receptor family, FGFR-3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1095–1099. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klagsbrun M., Edelman E. R. Biological and biochemical properties of fibroblast growth factors. Implications for the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Arteriosclerosis. 1989 May-Jun;9(3):269–278. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.9.3.269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansson P. E., Adams P., Kan M., McKeehan W. L. Heparin-binding growth factor gene expression and receptor characteristics in normal rat prostate and two transplantable rat prostate tumors. Cancer Res. 1989 May 1;49(9):2485–2494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchese C., Rubin J., Ron D., Faggioni A., Torrisi M. R., Messina A., Frati L., Aaronson S. A. Human keratinocyte growth factor activity on proliferation and differentiation of human keratinocytes: differentiation response distinguishes KGF from EGF family. J Cell Physiol. 1990 Aug;144(2):326–332. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041440219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeehan W. L., Adams P. S., Fast D. Different hormonal requirements for androgen-independent growth of normal and tumor epithelial cells from rat prostate. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1987 Feb;23(2):147–152. doi: 10.1007/BF02623596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeehan W. L., Adams P. S. Heparin-binding growth factor/prostatropin attenuates inhibition of rat prostate tumor epithelial cell growth by transforming growth factor type beta. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1988 Mar;24(3):243–246. doi: 10.1007/BF02623554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeehan W. L., Adams P. S., Rosser M. P. Direct mitogenic effects of insulin, epidermal growth factor, glucocorticoid, cholera toxin, unknown pituitary factors and possibly prolactin, but not androgen, on normal rat prostate epithelial cells in serum-free, primary cell culture. Cancer Res. 1984 May;44(5):1998–2010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeehan W. L. Growth factor receptors and prostate cell growth. Cancer Surv. 1991;11:165–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki T., Bottaro D. P., Fleming T. P., Smith C. L., Burgess W. H., Chan A. M., Aaronson S. A. Determination of ligand-binding specificity by alternative splicing: two distinct growth factor receptors encoded by a single gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):246–250. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki T., Fleming T. P., Bottaro D. P., Rubin J. S., Ron D., Aaronson S. A. Expression cDNA cloning of the KGF receptor by creation of a transforming autocrine loop. Science. 1991 Jan 4;251(4989):72–75. doi: 10.1126/science.1846048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadi M., Dionne C. A., Li W., Li N., Spivak T., Honegger A. M., Jaye M., Schlessinger J. Point mutation in FGF receptor eliminates phosphatidylinositol hydrolysis without affecting mitogenesis. Nature. 1992 Aug 20;358(6388):681–684. doi: 10.1038/358681a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadi M., Honegger A. M., Rotin D., Fischer R., Bellot F., Li W., Dionne C. A., Jaye M., Rubinstein M., Schlessinger J. A tyrosine-phosphorylated carboxy-terminal peptide of the fibroblast growth factor receptor (Flg) is a binding site for the SH2 domain of phospholipase C-gamma 1. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):5068–5078. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.5068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller W. J., Lee F. S., Dickson C., Peters G., Pattengale P., Leder P. The int-2 gene product acts as an epithelial growth factor in transgenic mice. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):907–913. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08188.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornitz D. M., Leder P. Ligand specificity and heparin dependence of fibroblast growth factor receptors 1 and 3. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16305–16311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr-Urtreger A., Givol D., Yayon A., Yarden Y., Lonai P. Developmental expression of two murine fibroblast growth factor receptors, flg and bek. Development. 1991 Dec;113(4):1419–1434. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.4.1419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partanen J., Mäkelä T. P., Eerola E., Korhonen J., Hirvonen H., Claesson-Welsh L., Alitalo K. FGFR-4, a novel acidic fibroblast growth factor receptor with a distinct expression pattern. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1347–1354. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07654.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peehl D. M., Wong S. T., Bazinet M., Stamey T. A. In vitro studies of human prostatic epithelial cells: attempts to identify distinguishing features of malignant cells. Growth Factors. 1989;1(3):237–250. doi: 10.3109/08977198908998000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters K. G., Werner S., Chen G., Williams L. T. Two FGF receptor genes are differentially expressed in epithelial and mesenchymal tissues during limb formation and organogenesis in the mouse. Development. 1992 Jan;114(1):233–243. doi: 10.1242/dev.114.1.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell P. P., Klagsbrun M. Three forms of rat basic fibroblast growth factor are made from a single mRNA and localize to the nucleus. J Cell Physiol. 1991 Aug;148(2):202–210. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041480204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renko M., Quarto N., Morimoto T., Rifkin D. B. Nuclear and cytoplasmic localization of different basic fibroblast growth factor species. J Cell Physiol. 1990 Jul;144(1):108–114. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041440114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi E., Kan M., Xu J., Wang F., Hou J., McKeehan W. L. Control of fibroblast growth factor receptor kinase signal transduction by heterodimerization of combinatorial splice variants. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):3907–3918. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.3907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westermann R., Grothe C., Unsicker K. Basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), a multifunctional growth factor for neuroectodermal cells. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1990;13:97–117. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1990.supplement_13.10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu J., Nakahara M., Crabb J. W., Shi E., Matuo Y., Fraser M., Kan M., Hou J., McKeehan W. L. Expression and immunochemical analysis of rat and human fibroblast growth factor receptor (flg) isoforms. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 5;267(25):17792–17803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan G. C., Nikolaropoulos S., Wang F., McKeehan W. L. Sequence of rat keratinocyte growth factor (heparin-binding growth factor type 7) In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1991 Jun;27A(6):437–438. doi: 10.1007/BF02631140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan G., Wang F., Fukabori Y., Sussman D., Hou J., McKeehan W. L. Expression and transforming activity of a variant of the heparin-binding fibroblast growth factor receptor (flg) gene resulting from splicing of the alpha exon at an alternate 3'-acceptor site. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Mar 16;183(2):423–430. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)90498-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhan X., Bates B., Hu X. G., Goldfarb M. The human FGF-5 oncogene encodes a novel protein related to fibroblast growth factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3487–3495. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]