Abstract
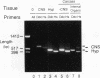
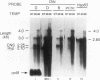
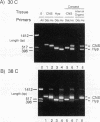
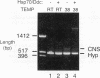
The Drosophila dopa decarboxylase gene, Ddc, is expressed in the hypoderm and in a small number of cells in the central nervous system (CNS). The unique Ddc primary transcript is alternatively spliced in these two tissues. We investigated whether Ddc splicing in the CNS is a general property of the CNS or a unique property of the cells that normally express Ddc by expressing the Ddc primary transcript ubiquitously under the control of an Hsp70 heat shock promoter. Under basal expression conditions, Ddc splicing shows normal tissue specificity, indicating that the regulation of Ddc splicing in the CNS is tissue specific rather than cell specific. Previous studies have shown that severe heat shock blocks mRNA splicing in cultured Drosophila melanogaster cells. Our results show that splicing of the heat shock-inducible Hsp83 transcript is very resistant to heat shock. In contrast, under either mild or severe heat shock, the splicing specificity of the heat shock-induced Ddc primary transcript is affected, leading to the accumulation of inappropriately high levels of the CNS splice form in non-CNS tissues. The chromosomal Ddc transcript is similarly affected. These results show unexpected heterogeneity in the splicing of individual mRNAs as a response to heat shock and suggest that the Ddc CNS-specific splicing pathway is the default.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Artavanis-Tsakonas S., Schedl P., Mirault M. E., Moran L., Lis J. Genes for the 70,000 dalton heat shock protein in two cloned D. melanogaster DNA segments. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):9–18. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90290-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beall C. J., Hirsh J. Regulation of the Drosophila dopa decarboxylase gene in neuronal and glial cells. Genes Dev. 1987 Jul;1(5):510–520. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.5.510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black D. L. Activation of c-src neuron-specific splicing by an unusual RNA element in vivo and in vitro. Cell. 1992 May 29;69(5):795–807. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90291-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black D. L. Does steric interference between splice sites block the splicing of a short c-src neuron-specific exon in non-neuronal cells? Genes Dev. 1991 Mar;5(3):389–402. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.3.389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackman R. K., Meselson M. Interspecific nucleotide sequence comparisons used to identify regulatory and structural features of the Drosophila hsp82 gene. J Mol Biol. 1986 Apr 20;188(4):499–515. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(86)80001-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond U. Heat shock but not other stress inducers leads to the disruption of a sub-set of snRNPs and inhibition of in vitro splicing in HeLa cells. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3509–3518. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03227.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray S. J., Johnson W. A., Hirsh J., Heberlein U., Tjian R. A cis-acting element and associated binding factor required for CNS expression of the Drosophila melanogaster dopa decarboxylase gene. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):177–188. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02798.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cote G. J., Nguyen I. N., Lips C. J., Berget S. M., Gagel R. F. Validation of an in vitro RNA processing system for CT/CGRP precursor mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 11;19(13):3601–3606. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.13.3601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cote G. J., Stolow D. T., Peleg S., Berget S. M., Gagel R. F. Identification of exon sequences and an exon binding protein involved in alternative RNA splicing of calcitonin/CGRP. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 May 11;20(9):2361–2366. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.9.2361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eveleth D. D., Gietz R. D., Spencer C. A., Nargang F. E., Hodgetts R. B., Marsh J. L. Sequence and structure of the dopa decarboxylase gene of Drosophila: evidence for novel RNA splicing variants. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2663–2672. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04549.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hortsch M., Bieber A. J., Patel N. H., Goodman C. S. Differential splicing generates a nervous system-specific form of Drosophila neuroglian. Neuron. 1990 May;4(5):697–709. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90196-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. A., Hirsh J. Binding of a Drosophila POU-domain protein to a sequence element regulating gene expression in specific dopaminergic neurons. Nature. 1990 Feb 1;343(6257):467–470. doi: 10.1038/343467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. A., McCormick C. A., Bray S. J., Hirsh J. A neuron-specific enhancer of the Drosophila dopa decarboxylase gene. Genes Dev. 1989 May;3(5):676–686. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.5.676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay R. J., Russnak R. H., Jones D., Mathias C., Candido E. P. Expression of intron-containing C. elegans heat shock genes in mouse cells demonstrates divergence of 3' splice site recognition sequences between nematodes and vertebrates, and an inhibitory effect of heat shock on the mammalian splicing apparatus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 May 11;15(9):3723–3741. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.9.3723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konrad K. D., Marsh J. L. Developmental expression and spatial distribution of dopa decarboxylase in Drosophila. Dev Biol. 1987 Jul;122(1):172–185. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90343-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld K., Saint R. B., Beachy P. A., Harte P. J., Peattie D. A., Hogness D. S. Structure and expression of a family of Ultrabithorax mRNAs generated by alternative splicing and polyadenylation in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1989 Feb;3(2):243–258. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.2.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laski F. A., Rio D. C., Rubin G. M. Tissue specificity of Drosophila P element transposition is regulated at the level of mRNA splicing. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):7–19. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90480-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lis J. T., Simon J. A., Sutton C. A. New heat shock puffs and beta-galactosidase activity resulting from transformation of Drosophila with an hsp70-lacZ hybrid gene. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):403–410. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90173-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundell M. J., Hirsh J. The zfh-2 gene product is a potential regulator of neuron-specific dopa decarboxylase gene expression in Drosophila. Dev Biol. 1992 Nov;154(1):84–94. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90050-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T. Mechanisms of alternative pre-mRNA splicing. Science. 1991 Jan 4;251(4989):33–34. doi: 10.1126/science.1824726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez R., Mathey-Prevot B., Bernards A., Baltimore D. Neuronal pp60c-src contains a six-amino acid insertion relative to its non-neuronal counterpart. Science. 1987 Jul 24;237(4813):411–415. doi: 10.1126/science.2440106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastick G. S., Scholnick S. B. Repression and activation of the Drosophila dopa decarboxylase gene in glia. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;12(12):5659–5666. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.12.5659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie S. L., Henikoff S., Meselson M. Localization of RNA from heat-induced polysomes at puff sites in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1117–1121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan B. A., Johnson W. A., Hirsh J. Regulated splicing produces different forms of dopa decarboxylase in the central nervous system and hypoderm of Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3335–3342. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04648.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawa H., Kotani H., Nakanishi S. Tissue-specific generation of two preprotachykinin mRNAs from one gene by alternative RNA splicing. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):729–734. doi: 10.1038/312729a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connell P. O., Rosbash M. Sequence, structure, and codon preference of the Drosophila ribosomal protein 49 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 11;12(13):5495–5513. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.13.5495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prieto A. L., Crossin K. L., Cunningham B. A., Edelman G. M. Localization of mRNA for neural cell adhesion molecule (N-CAM) polypeptides in neural and nonneural tissues by in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9579–9583. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyper J. M., Bolen J. B. Identification of a novel neuronal C-SRC exon expressed in human brain. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2035–2040. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raychaudhuri G., Haynes S. R., Beyer A. L. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein complexes and proteins in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):847–855. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinow S., White K. Characterization and spatial distribution of the ELAV protein during Drosophila melanogaster development. J Neurobiol. 1991 Jul;22(5):443–461. doi: 10.1002/neu.480220503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld M. G., Amara S. G., Evans R. M. Alternative RNA processing: determining neuronal phenotype. Science. 1984 Sep 21;225(4668):1315–1320. doi: 10.1126/science.6089345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoni M. J., Barthels D., Vopper G., Boned A., Goridis C., Wille W. Differential exon usage involving an unusual splicing mechanism generates at least eight types of NCAM cDNA in mouse brain. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):385–392. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03389.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholnick S. B., Bray S. J., Morgan B. A., McCormick C. A., Hirsh J. CNS and hypoderm regulatory elements of the Drosophila melanogaster dopa decarboxylase gene. Science. 1986 Nov 21;234(4779):998–1002. doi: 10.1126/science.3095924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholnick S. B., Morgan B. A., Hirsh J. The cloned dopa decarboxylase gene is developmentally regulated when reintegrated into the Drosophila genome. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):37–45. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90134-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shukla R. R., Dominski Z., Zwierzynski T., Kole R. Inactivation of splicing factors in HeLa cells subjected to heat shock. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20377–20383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebel C. W., Rio D. C. Regulated splicing of the Drosophila P transposable element third intron in vitro: somatic repression. Science. 1990 Jun 8;248(4960):1200–1208. doi: 10.1126/science.2161558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spradling A., Penman S., Pardue M. L. Analysis of drosophila mRNA by in situ hybridization: sequences transcribed in normal and heat shocked cultured cells. Cell. 1975 Apr;4(4):395–404. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90160-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stroeher V. L., Gaiser J. C., Garber R. L. Alternative RNA splicing that is spatially regulated: generation of transcripts from the Antennapedia gene of Drosophila melanogaster with different protein-coding regions. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4143–4154. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tissières A., Mitchell H. K., Tracy U. M. Protein synthesis in salivary glands of Drosophila melanogaster: relation to chromosome puffs. J Mol Biol. 1974 Apr 15;84(3):389–398. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90447-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utans U., Behrens S. E., Lührmann R., Kole R., Krämer A. A splicing factor that is inactivated during in vivo heat shock is functionally equivalent to the [U4/U6.U5] triple snRNP-specific proteins. Genes Dev. 1992 Apr;6(4):631–641. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.4.631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yost H. J., Lindquist S. Heat shock proteins affect RNA processing during the heat shock response of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):1062–1068. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.1062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yost H. J., Lindquist S. RNA splicing is interrupted by heat shock and is rescued by heat shock protein synthesis. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):185–193. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90382-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yost H. J., Lindquist S. Translation of unspliced transcripts after heat shock. Science. 1988 Dec 16;242(4885):1544–1548. doi: 10.1126/science.3201243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]