Abstract
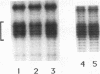
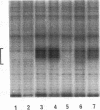
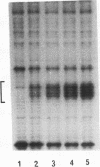
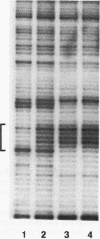
RNA polymerase II transcription is influenced both by how rapidly a gene is induced and by the rate at which continuous reinitiation occurs after induction. We show here that in vitro the rates of these two critical steps need not be the same. For activator GAL-AH-dependent HeLa transcription, the rate of assembling a preinitiation complex is significantly slower than the rate of reinitiation. Although reinitiation is rapid, it still requires ATP hydrolysis. This unexpected uncoupling of the rates of initiation and reinitiation implies that in regulating mammalian promoter activity, one must consider separately the controls on initiation during induction and the controls on the subsequent reinitiation events.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bunick D., Zandomeni R., Ackerman S., Weinmann R. Mechanism of RNA polymerase II--specific initiation of transcription in vitro: ATP requirement and uncapped runoff transcripts. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):877–886. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90449-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buratowski S., Hahn S., Guarente L., Sharp P. A. Five intermediate complexes in transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):549–561. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90578-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey M., Leatherwood J., Ptashne M. A potent GAL4 derivative activates transcription at a distance in vitro. Science. 1990 Feb 9;247(4943):710–712. doi: 10.1126/science.2405489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey M., Lin Y. S., Green M. R., Ptashne M. A mechanism for synergistic activation of a mammalian gene by GAL4 derivatives. Nature. 1990 May 24;345(6273):361–364. doi: 10.1038/345361a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpousis A. J., Stefano J. E., Gralla J. D. 5' nucleotide heterogeneity and altered initiation of transcription at mutant lac promoters. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jun 5;157(4):619–633. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90502-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conaway R. C., Conaway J. W. ATP activates transcription initiation from promoters by RNA polymerase II in a reversible step prior to RNA synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):2962–2968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Martin P. L., Shastry B. S., Roeder R. G. Eukaryotic gene transcription with purified components. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:582–598. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01039-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gralla J. D. Promoter recognition and mRNA initiation by Escherichia coli E sigma 70. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:37–54. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85006-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., Roeder R. G. Functional steps in transcription initiation and reinitiation from the major late promoter in a HeLa nuclear extract. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3452–3461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoopes B. C., LeBlanc J. F., Hawley D. K. Kinetic analysis of yeast TFIID-TATA box complex formation suggests a multi-step pathway. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 5;267(16):11539–11547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inostroza J. A., Mermelstein F. H., Ha I., Lane W. S., Reinberg D. Dr1, a TATA-binding protein-associated phosphoprotein and inhibitor of class II gene transcription. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):477–489. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90172-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang Y., Smale S. T., Gralla J. D. A common ATP requirement for open complex formation and transcription at promoters containing initiator or TATA elements. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 25;268(9):6535–6540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T. Assembly and disassembly of the Drosophila RNA polymerase II complex during transcription. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 15;265(5):2624–2631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure W. R. Mechanism and control of transcription initiation in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:171–204. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.001131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisterernst M., Roeder R. G. Family of proteins that interact with TFIID and regulate promoter activity. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):557–567. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90530-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisterernst M., Roy A. L., Lieu H. M., Roeder R. G. Activation of class II gene transcription by regulatory factors is potentiated by a novel activity. Cell. 1991 Sep 6;66(5):981–993. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90443-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
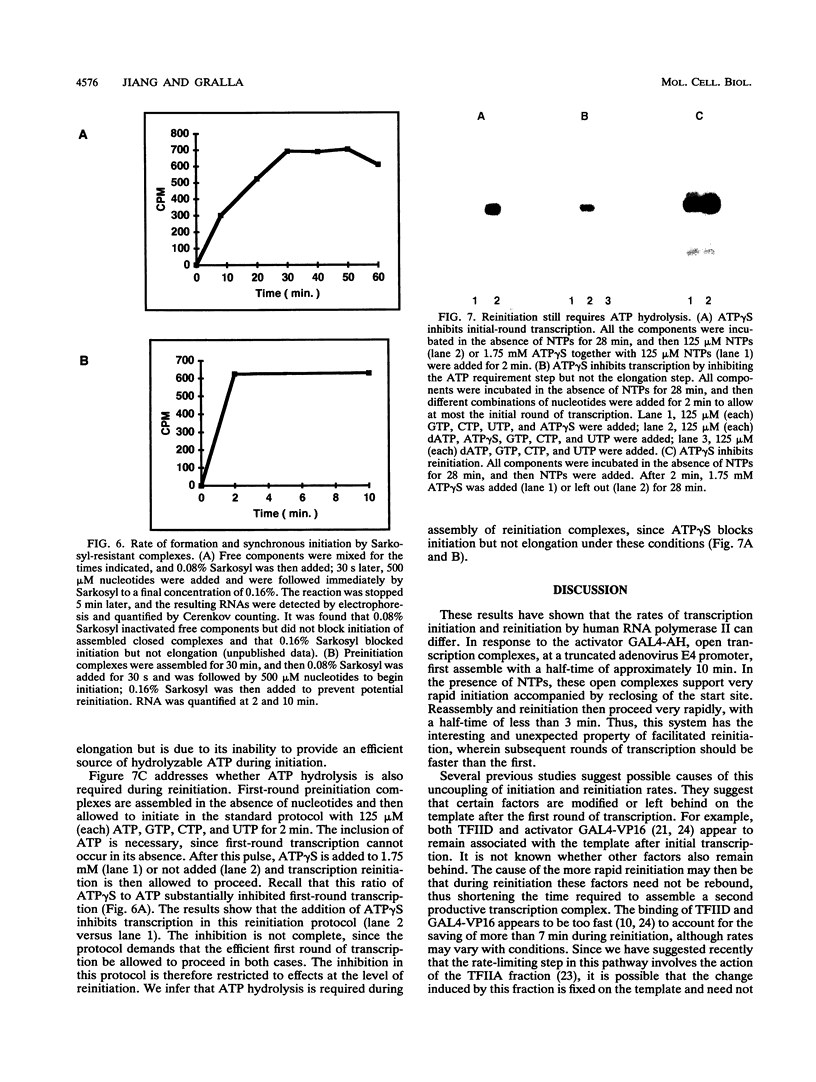
- Peterson M. G., Tjian R. Transcription. The tell-tail trigger. Nature. 1992 Aug 20;358(6388):620–621. doi: 10.1038/358620a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinberg D., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription in mammalian RNA polymerase II. Functional analysis of initiation factors IIA and IID and identification of a new factor operating at sequences downstream of the initiation site. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3322–3330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder R. G. The complexities of eukaryotic transcription initiation: regulation of preinitiation complex assembly. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Nov;16(11):402–408. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90164-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Energy requirement for specific transcription initiation by the human RNA polymerase II system. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):5321–5326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke M. W., Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Stability of transcription complexes on class II genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):342–344. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W., Carey M., Gralla J. D. Polymerase II promoter activation: closed complex formation and ATP-driven start site opening. Science. 1992 Jan 24;255(5043):450–453. doi: 10.1126/science.1310361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W., Gralla J. D., Carey M. The acidic activator GAL4-AH can stimulate polymerase II transcription by promoting assembly of a closed complex requiring TFIID and TFIIA. Genes Dev. 1992 Sep;6(9):1716–1727. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.9.1716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J., Brou C., Wu J., Lutz Y., Moncollin V., Chambon P. The acidic transcriptional activator GAL-VP16 acts on preformed template-committed complexes. EMBO J. 1992 Jun;11(6):2229–2240. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05282.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]