Abstract
Eukaryotic initiation factor 4F (eIF-4F) is a three-subunit complex that binds the 5' cap structure (m7GpppX, where X is any nucleotide) of eukaryotic mRNAs. This factor facilitates ribosome binding by unwinding the secondary structure in the mRNA 5' noncoding region. The limiting component of the 4F complex is believed to be the 24-kDa cap-binding phosphoprotein, eIF-4E. In this report, we describe the phosphorylation of eIF-4E in response to expression of the tyrosine kinase oncoproteins pp60v-src and pp60c-src527F. The results suggest that eIF-4E functions as a downstream target of the phosphorylation cascade induced by tyrosine-specific protein kinases as well as by effectors of the mitogenic response.
Full text
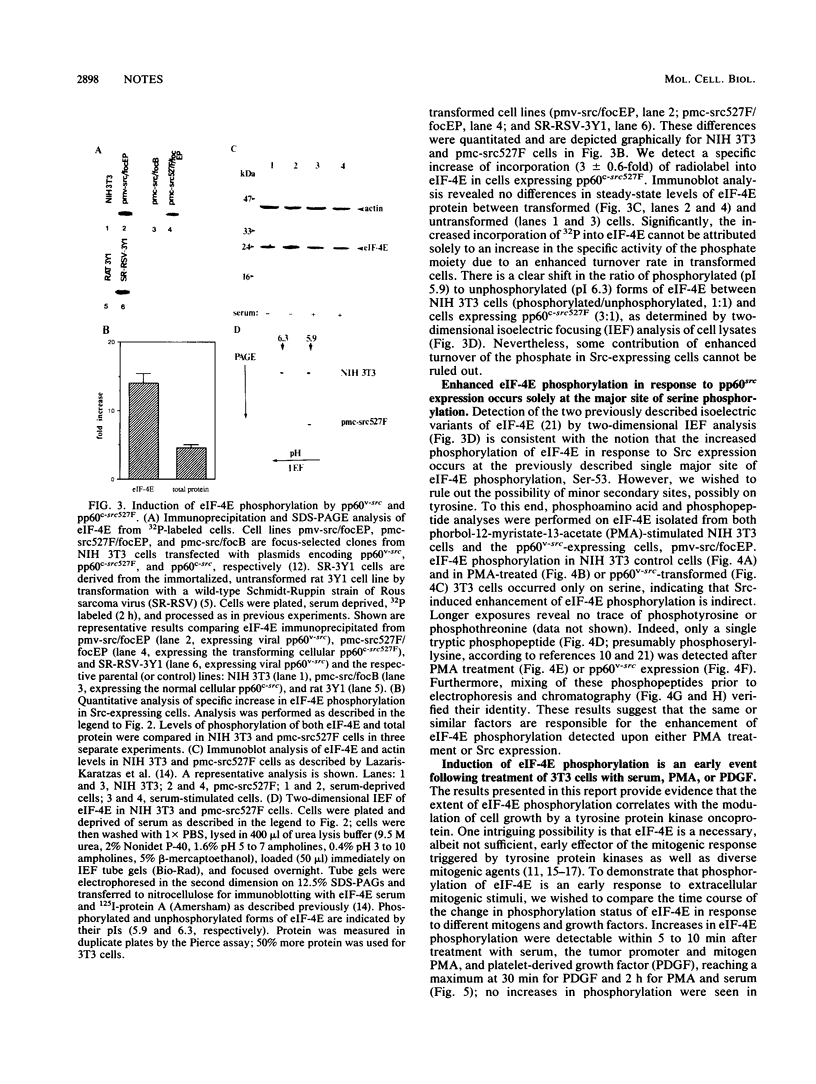
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blenis J., Erikson R. L. Regulation of a ribosomal protein S6 kinase activity by the Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein, serum, or phorbol ester. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7621–7625. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonneau A. M., Sonenberg N. Involvement of the 24-kDa cap-binding protein in regulation of protein synthesis in mitosis. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 15;262(23):11134–11139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks R. F. Continuous protein synthesis is required to maintain the probability of entry into S phase. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):311–317. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90209-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan R., Milburn S. C., Hershey J. W. Regulated phosphorylation and low abundance of HeLa cell initiation factor eIF-4F suggest a role in translational control. Heat shock effects on eIF-4F. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 5;262(1):380–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutta A., Stoeckle M. Y., Hanafusa H. Serum and v-src increase the level of a CCAAT-binding factor required for transcription from a retroviral long terminal repeat. Genes Dev. 1990 Feb;4(2):243–254. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.2.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edery I., Altmann M., Sonenberg N. High-level synthesis in Escherichia coli of functional cap-binding eukaryotic initiation factor eIF-4E and affinity purification using a simplified cap-analog resin. Gene. 1988 Dec 30;74(2):517–525. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90184-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershey J. W. Protein phosphorylation controls translation rates. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 15;264(35):20823–20826. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiremath L. S., Webb N. R., Rhoads R. E. Immunological detection of the messenger RNA cap-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 5;260(13):7843–7849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagus R., Anderson W. F., Safer B. The regulation of initiation of mammalian protein synthesis. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1981;25:127–185. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60484-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaspar R. L., Rychlik W., White M. W., Rhoads R. E., Morris D. R. Simultaneous cytoplasmic redistribution of ribosomal protein L32 mRNA and phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor 4E after mitogenic stimulation of Swiss 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):3619–3622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kmiecik T. E., Shalloway D. Activation and suppression of pp60c-src transforming ability by mutation of its primary sites of tyrosine phosphorylation. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):65–73. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90756-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozma S. C., Ferrari S., Thomas G. Unmasking a growth factor/oncogene-activated S6 phosphorylation cascade. Cell Signal. 1989;1(3):219–225. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(89)90039-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazaris-Karatzas A., Montine K. S., Sonenberg N. Malignant transformation by a eukaryotic initiation factor subunit that binds to mRNA 5' cap. Nature. 1990 Jun 7;345(6275):544–547. doi: 10.1038/345544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marino M. W., Pfeffer L. M., Guidon P. T., Jr, Donner D. B. Tumor necrosis factor induces phosphorylation of a 28-kDa mRNA cap-binding protein in human cervical carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8417–8421. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morley S. J., Traugh J. A. Differential stimulation of phosphorylation of initiation factors eIF-4F, eIF-4B, eIF-3, and ribosomal protein S6 by insulin and phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10611–10616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morley S. J., Traugh J. A. Phorbol esters stimulate phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factors 3, 4B, and 4F. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 15;264(5):2401–2404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray B. K., Brendler T. G., Adya S., Daniels-McQueen S., Miller J. K., Hershey J. W., Grifo J. A., Merrick W. C., Thach R. E. Role of mRNA competition in regulating translation: further characterization of mRNA discriminatory initiation factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):663–667. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads R. E. Cap recognition and the entry of mRNA into the protein synthesis initiation cycle. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Feb;13(2):52–56. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozen F., Edery I., Meerovitch K., Dever T. E., Merrick W. C., Sonenberg N. Bidirectional RNA helicase activity of eucaryotic translation initiation factors 4A and 4F. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1134–1144. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rychlik W., Russ M. A., Rhoads R. E. Phosphorylation site of eukaryotic initiation factor 4E. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10434–10437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar G., Edery I., Gallo R., Sonenberg N. Preferential stimulation of rabbit alpha globin mRNA translation by a cap-binding protein complex. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Nov 22;783(2):122–129. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(84)90003-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenberg N. Cap-binding proteins of eukaryotic messenger RNA: functions in initiation and control of translation. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1988;35:173–207. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60614-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenberg N., Morgan M. A., Merrick W. C., Shatkin A. J. A polypeptide in eukaryotic initiation factors that crosslinks specifically to the 5'-terminal cap in mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4843–4847. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenberg N., Trachsel H., Hecht S., Shatkin A. J. Differential stimulation of capped mRNA translation in vitro by cap binding protein. Nature. 1980 May 29;285(5763):331–333. doi: 10.1038/285331a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veillette A., Horak I. D., Bolen J. B. Post-translational alterations of the tyrosine kinase p56lck in response to activators of protein kinase C. Oncogene Res. 1988 May;2(4):385–401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veillette A., Horak I. D., Horak E. M., Bookman M. A., Bolen J. B. Alterations of the lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase (p56lck) during T-cell activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4353–4361. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]