Abstract
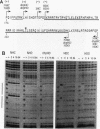
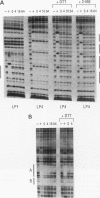
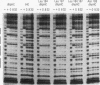
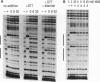
The human HoxB5 (Hox-2.1) gene product is a sequence-specific DNA binding protein. Cooperative interactions stabilize in vitro DNA binding of the HoxB5 protein to tandem binding sites by at least 100-fold relative to binding to a single site. The HoxB5 homeodomain is sufficient for sequence-specific DNA binding but not for cooperative DNA binding. Here we report that the additional protein sequence required for cooperativity is a small domain adjacent to the homeodomain on the amino-terminal side. We further show that cooperative DNA binding is under redox regulation. The HoxB5 protein binds to DNA in vitro both when oxidized or reduced but binds cooperatively only when oxidized. Mutational analysis has revealed that the cysteine residue in the turn between homeodomain helices 2 and 3 is necessary for cooperative binding and redox regulation. The enhanced DNA binding of oxidized HoxB5 protein is the opposite of the redox regulation reported for other mammalian transcription factors such as Fos, Jun, USF, NF-kappa B, c-Myb, and v-Rel, in which oxidation of cysteine residues inhibits DNA binding. Thus, specific oxidation of nuclear proteins is a potential regulatory mechanism that can act to either decrease or increase their DNA binding activity.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abate C., Patel L., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Curran T. Redox regulation of fos and jun DNA-binding activity in vitro. Science. 1990 Sep 7;249(4973):1157–1161. doi: 10.1126/science.2118682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arcioni L., Simeone A., Guazzi S., Zappavigna V., Boncinelli E., Mavilio F. The upstream region of the human homeobox gene HOX3D is a target for regulation by retinoic acid and HOX homeoproteins. EMBO J. 1992 Jan;11(1):265–277. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05049.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baier L. J., Hannibal M. C., Hanley E. W., Nabel G. J. Lymphoid expression and TATAA binding of a human protein containing an Antennapedia homeodomain. Blood. 1991 Aug 15;78(4):1047–1055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannister A. J., Cook A., Kouzarides T. In vitro DNA binding activity of Fos/Jun and BZLF1 but not C/EBP is affected by redox changes. Oncogene. 1991 Jul;6(7):1243–1250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cappel R. E., Gilbert H. F. Thiol/disulfide exchange between 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase and glutathione. A thermodynamically facile dithiol oxidation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12204–12212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demple B., Amábile-Cuevas C. F. Redox redux: the control of oxidative stress responses. Cell. 1991 Nov 29;67(5):837–839. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90355-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desplan C., Theis J., O'Farrell P. H. The sequence specificity of homeodomain-DNA interaction. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):1081–1090. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90123-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dessain S., Gross C. T., Kuziora M. A., McGinnis W. Antp-type homeodomains have distinct DNA binding specificities that correlate with their different regulatory functions in embryos. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):991–1002. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05138.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubendorff J. W., Studier F. W. Controlling basal expression in an inducible T7 expression system by blocking the target T7 promoter with lac repressor. J Mol Biol. 1991 May 5;219(1):45–59. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90856-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galang C. K., Hauser C. A. Cooperative DNA binding of the highly conserved human Hox 2.1 homeodomain gene product. New Biol. 1992 May;4(5):558–568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham A., Papalopulu N., Krumlauf R. The murine and Drosophila homeobox gene complexes have common features of organization and expression. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):367–378. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90912-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grueneberg D. A., Natesan S., Alexandre C., Gilman M. Z. Human and Drosophila homeodomain proteins that enhance the DNA-binding activity of serum response factor. Science. 1992 Aug 21;257(5073):1089–1095. doi: 10.1126/science.257.5073.1089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guehmann S., Vorbrueggen G., Kalkbrenner F., Moelling K. Reduction of a conserved Cys is essential for Myb DNA-binding. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 May 11;20(9):2279–2286. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.9.2279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi S., Scott M. P. What determines the specificity of action of Drosophila homeodomain proteins? Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):883–894. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90492-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland P. W., Hogan B. L. Expression of homeo box genes during mouse development: a review. Genes Dev. 1988 Jul;2(7):773–782. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.7.773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E., Henzel W., Deisseroth A. An isoform of protein disulfide isomerase isolated from chronic myelogenous leukemia cells alters complex formation between nuclear proteins and regulatory regions of interferon-inducible genes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):14412–14417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson F. B., Krasnow M. A. Differential regulation of transcription preinitiation complex assembly by activator and repressor homeo domain proteins. Genes Dev. 1992 Nov;6(11):2177–2189. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.11.2177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones F. S., Chalepakis G., Gruss P., Edelman G. M. Activation of the cytotactin promoter by the homeobox-containing gene Evx-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2091–2095. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones F. S., Prediger E. A., Bittner D. A., De Robertis E. M., Edelman G. M. Cell adhesion molecules as targets for Hox genes: neural cell adhesion molecule promoter activity is modulated by cotransfection with Hox-2.5 and -2.4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2086–2090. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Tjian R. Affinity purification of sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5889–5893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamphuis I. G., Kalk K. H., Swarte M. B., Drenth J. Structure of papain refined at 1.65 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 25;179(2):233–256. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90467-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kissinger C. R., Liu B. S., Martin-Blanco E., Kornberg T. B., Pabo C. O. Crystal structure of an engrailed homeodomain-DNA complex at 2.8 A resolution: a framework for understanding homeodomain-DNA interactions. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):579–590. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90453-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar S., Rabson A. B., Gélinas C. The RxxRxRxxC motif conserved in all Rel/kappa B proteins is essential for the DNA-binding activity and redox regulation of the v-Rel oncoprotein. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;12(7):3094–3106. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.7.3094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughon A. DNA binding specificity of homeodomains. Biochemistry. 1991 Dec 3;30(48):11357–11367. doi: 10.1021/bi00112a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBowitz J. H., Clerc R. G., Brenowitz M., Sharp P. A. The Oct-2 protein binds cooperatively to adjacent octamer sites. Genes Dev. 1989 Oct;3(10):1625–1638. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.10.1625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M., Hoey T. Homeobox proteins as sequence-specific transcription factors. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):537–540. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90209-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow B., Schütz G. CAT constructions with multiple unique restriction sites for the functional analysis of eukaryotic promoters and regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5490–5490. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mavilio F., Simeone A., Giampaolo A., Faiella A., Zappavigna V., Acampora D., Poiana G., Russo G., Peschle C., Boncinelli E. Differential and stage-related expression in embryonic tissues of a new human homoeobox gene. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):664–668. doi: 10.1038/324664a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride A. A., Klausner R. D., Howley P. M. Conserved cysteine residue in the DNA-binding domain of the bovine papillomavirus type 1 E2 protein confers redox regulation of the DNA-binding activity in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7531–7535. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis W., Krumlauf R. Homeobox genes and axial patterning. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):283–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90471-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molitor J. A., Ballard D. W., Greene W. C. Kappa B-specific DNA binding proteins are differentially inhibited by enhancer mutations and biological oxidation. New Biol. 1991 Oct;3(10):987–996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M., Affolter M., Leupin W., Otting G., Wüthrich K., Gehring W. J. Isolation and sequence-specific DNA binding of the Antennapedia homeodomain. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4299–4304. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03328.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odenwald W. F., Garbern J., Arnheiter H., Tournier-Lasserve E., Lazzarini R. A. The Hox-1.3 homeo box protein is a sequence-specific DNA-binding phosphoprotein. Genes Dev. 1989 Feb;3(2):158–172. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.2.158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkuma Y., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G., Desplan C. Binding site-dependent direct activation and repression of in vitro transcription by Drosophila homeodomain proteins. Cell. 1990 May 4;61(3):475–484. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90529-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkuma Y., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G., Desplan C. Engrailed, a homeodomain protein, can repress in vitro transcription by competition with the TATA box-binding protein transcription factor IID. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2289–2293. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otting G., Qian Y. Q., Müller M., Affolter M., Gehring W., Wüthrich K. Secondary structure determination for the Antennapedia homeodomain by nuclear magnetic resonance and evidence for a helix-turn-helix motif. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4305–4309. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03329.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pognonec P., Kato H., Roeder R. G. The helix-loop-helix/leucine repeat transcription factor USF can be functionally regulated in a redox-dependent manner. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 5;267(34):24563–24567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pöpperl H., Featherstone M. S. An autoregulatory element of the murine Hox-4.2 gene. EMBO J. 1992 Oct;11(10):3673–3680. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05452.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian Y. Q., Otting G., Furukubo-Tokunaga K., Affolter M., Gehring W. J., Wüthrich K. NMR structure determination reveals that the homeodomain is connected through a flexible linker to the main body in the Drosophila Antennapedia protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10738–10742. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki H., Yamamoto M., Kuroiwa A. Cell type dependent transcription regulation by chick homeodomain proteins. Mech Dev. 1992 Mar;37(1-2):25–36. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(92)90012-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. P., Tamkun J. W., Hartzell G. W., 3rd The structure and function of the homeodomain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jul 28;989(1):25–48. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(89)90033-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. P. Vertebrate homeobox gene nomenclature. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):551–553. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90588-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shashikant C. S., Utset M. F., Violette S. M., Wise T. L., Einat P., Einat M., Pendleton J. W., Schughart K., Ruddle F. H. Homeobox genes in mouse development. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 1991;1(3):207–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder G. H., Cennerazzo M. J., Karalis A. J., Field D. Electrostatic influence of local cysteine environments on disulfide exchange kinetics. Biochemistry. 1981 Nov 10;20(23):6509–6519. doi: 10.1021/bi00526a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stehle T., Ahmed S. A., Claiborne A., Schulz G. E. Structure of NADH peroxidase from Streptococcus faecalis 10C1 refined at 2.16 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1991 Oct 20;221(4):1325–1344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storz G., Tartaglia L. A., Ames B. N. Transcriptional regulator of oxidative stress-inducible genes: direct activation by oxidation. Science. 1990 Apr 13;248(4952):189–194. doi: 10.1126/science.2183352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartaglia L. A., Gimeno C. J., Storz G., Ames B. N. Multidegenerate DNA recognition by the OxyR transcriptional regulator. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 25;267(3):2038–2045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toledano M. B., Leonard W. J. Modulation of transcription factor NF-kappa B binding activity by oxidation-reduction in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4328–4332. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tournier-Lasserve E., Odenwald W. F., Garbern J., Trojanowski J., Lazzarini R. A. Remarkable intron and exon sequence conservation in human and mouse homeobox Hox 1.3 genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2273–2278. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verrijzer C. P., van Oosterhout J. A., van der Vliet P. C. The Oct-1 POU domain mediates interactions between Oct-1 and other POU proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):542–551. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vershon A. K., Johnson A. D. A short, disordered protein region mediates interactions between the homeodomain of the yeast alpha 2 protein and the MCM1 protein. Cell. 1993 Jan 15;72(1):105–112. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90054-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Violette S. M., Shashikant C. S., Salbaum J. M., Belting H. G., Wang J. C., Ruddle F. H. Repression of the beta-amyloid gene in a Hox-3.1-producing cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):3805–3809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.3805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams S. C., Cantwell C. A., Johnson P. F. A family of C/EBP-related proteins capable of forming covalently linked leucine zipper dimers in vitro. Genes Dev. 1991 Sep;5(9):1553–1567. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolberger C., Vershon A. K., Liu B., Johnson A. D., Pabo C. O. Crystal structure of a MAT alpha 2 homeodomain-operator complex suggests a general model for homeodomain-DNA interactions. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):517–528. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90526-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C. V., Cho K. W., Oliver G., De Robertis E. M. Vertebrate homeodomain proteins: families of region-specific transcription factors. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Feb;14(2):52–56. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90043-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xanthoudakis S., Curran T. Identification and characterization of Ref-1, a nuclear protein that facilitates AP-1 DNA-binding activity. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):653–665. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05097.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xanthoudakis S., Miao G., Wang F., Pan Y. C., Curran T. Redox activation of Fos-Jun DNA binding activity is mediated by a DNA repair enzyme. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3323–3335. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05411.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan Y. L., Fields S. Properties of the DNA-binding domain of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae STE12 protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;11(12):5910–5918. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.12.5910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]