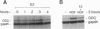Abstract
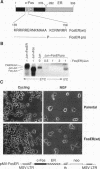
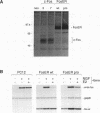
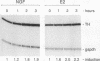
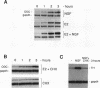
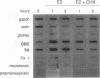
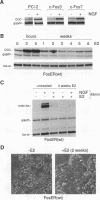
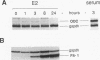
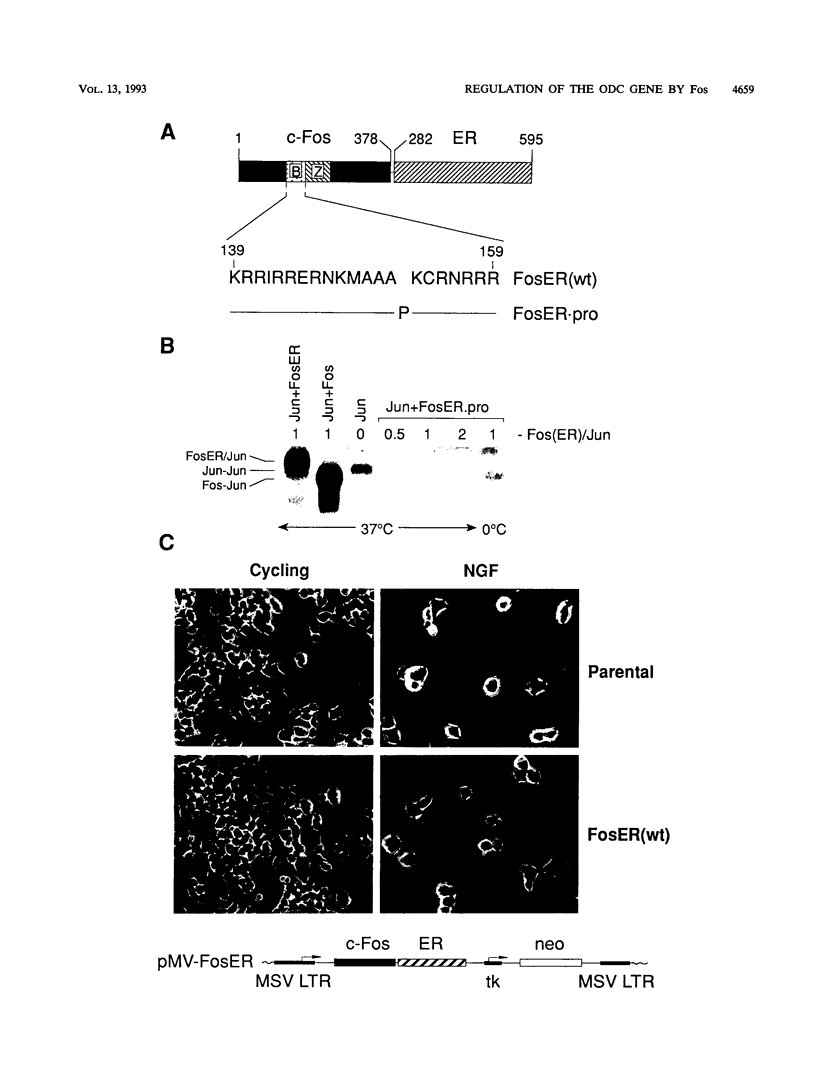
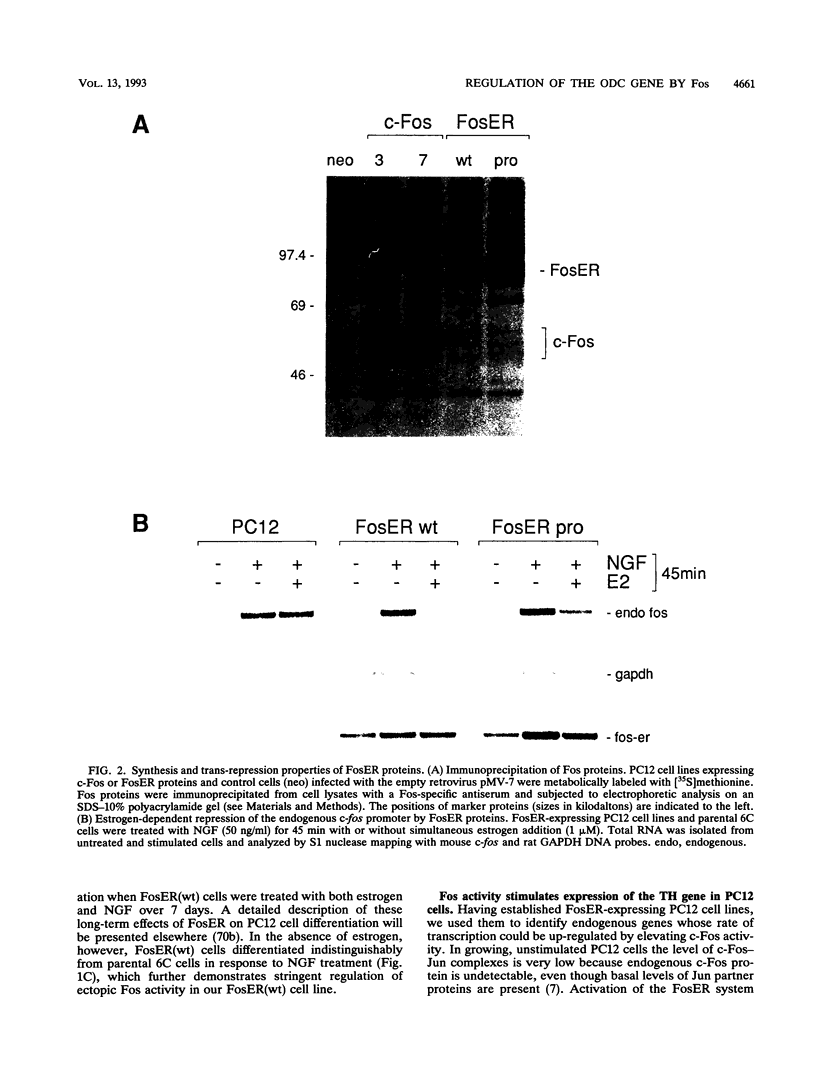
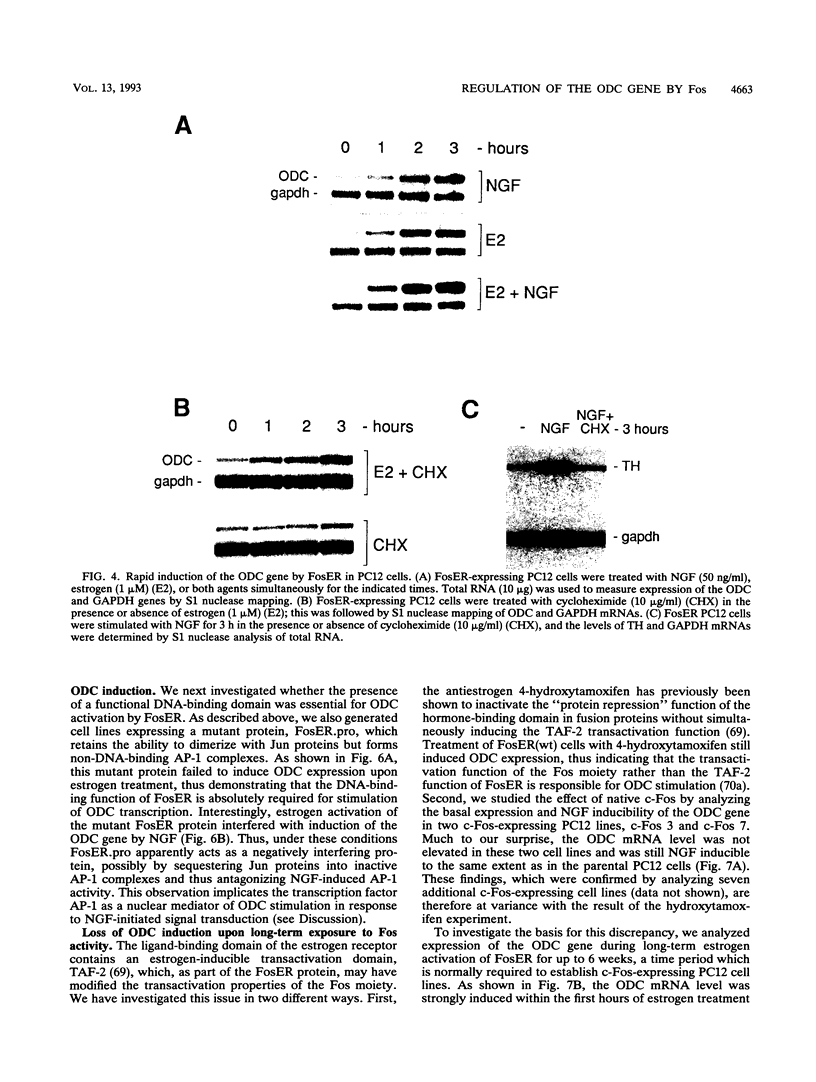
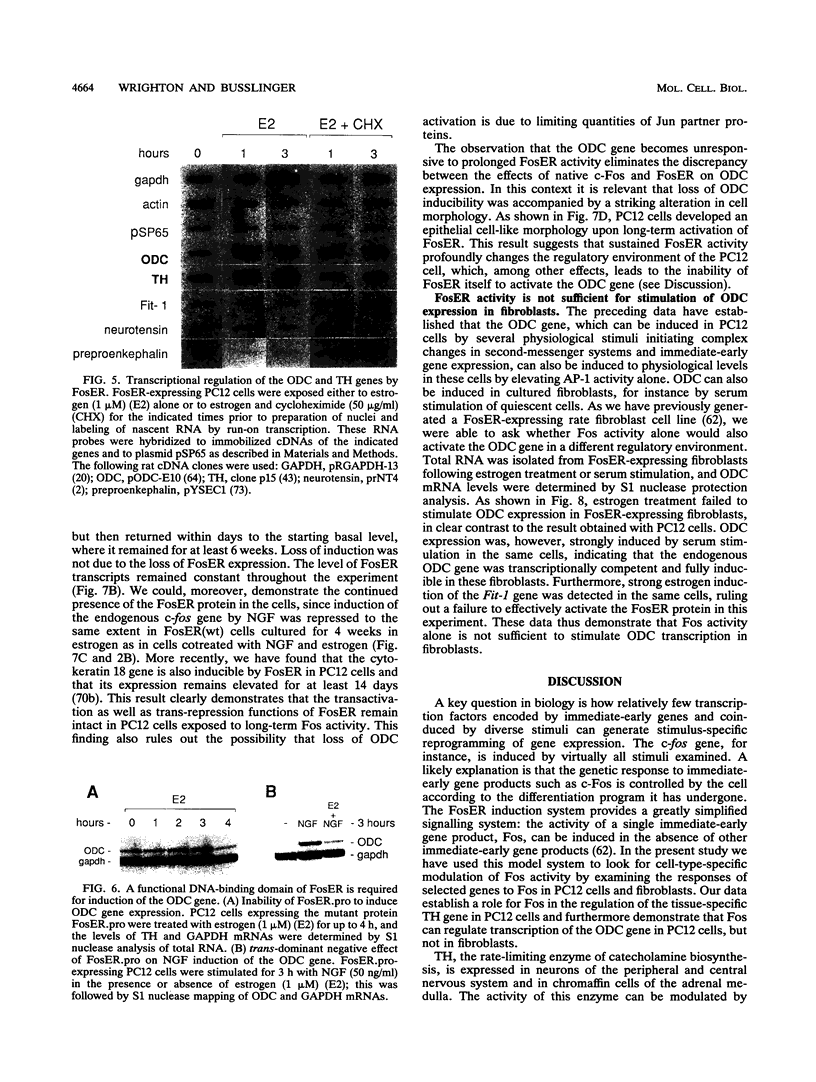
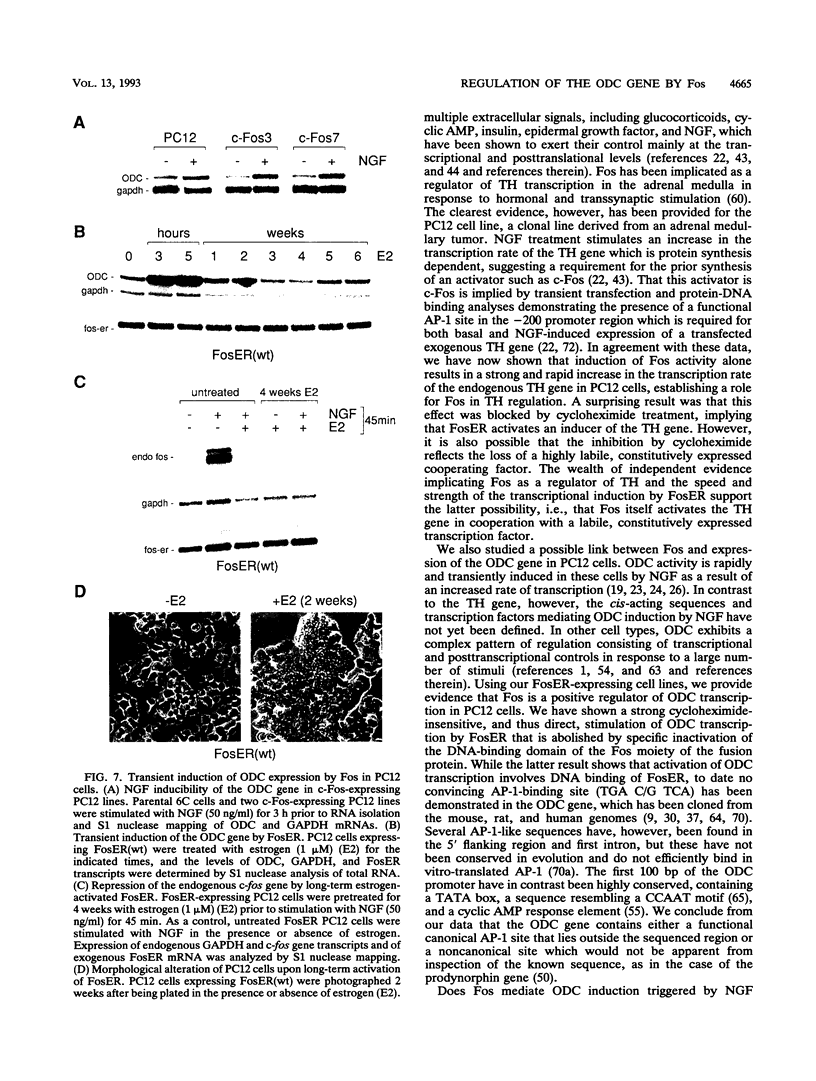
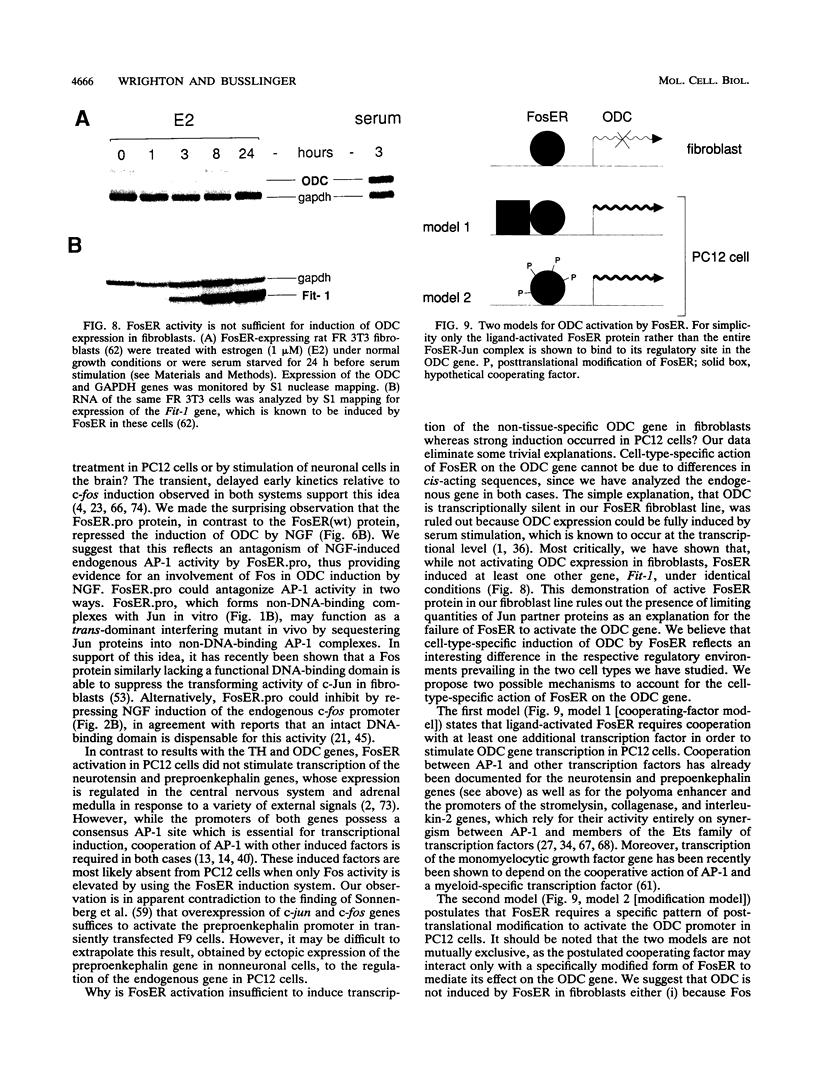
We have established rat PC12 pheochromocytoma cell lines stably expressing the estrogen-activatable transcription factor FosER to identify genes that can be regulated by c-Fos in this neuronal cell type. Induction of ectopic c-Fos activity in PC12 cells increased the mRNA levels of the ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) and tyrosine hydroxylase genes with similar kinetics and to the same maximal level as nerve growth factor treatment. In both cases the rate of transcription initiation was increased. Induction of the ODC gene occurred even in the absence of protein synthesis, indicating direct regulation by FosER. ODC expression, however, was not induced by a mutant FosER protein containing a proline insertion in the basic region of the c-Fos moiety, demonstrating the requirement for a functional DNA-binding domain. These data show that FosER, and by extrapolation c-Fos, can directly activate transcription of the endogenous ODC gene in PC12 cells by binding to cis-regulatory sequences. Activation of the ODC gene was unexpectedly transient, as transcripts returned to the basal level after prolonged exposure of PC12 cells to FosER activity. Furthermore, ODC transcription was not at all induced by FosER in rat fibroblasts. To account for this cell-specific action of FosER, we propose that stimulation of the ODC gene by FosER requires either (i) cooperation with another transcription factor(s) or (ii) a specific pattern of modification which is present in PC12 cells but not in otherwise unstimulated fibroblasts. One or both of these mechanisms may be employed by cells to achieve selective gene activation in response to apparently stereotyped induction of c-fos.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrahamsen M. S., Morris D. R. Cell type-specific mechanisms of regulating expression of the ornithine decarboxylase gene after growth stimulation. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5525–5528. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander M. J., Miller M. A., Dorsa D. M., Bullock B. P., Melloni R. H., Jr, Dobner P. R., Leeman S. E. Distribution of neurotensin/neuromedin N mRNA in rat forebrain: unexpected abundance in hippocampus and subiculum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5202–5206. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Karin M. The role of Jun, Fos and the AP-1 complex in cell-proliferation and transformation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Dec 10;1072(2-3):129–157. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(91)90011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai A., Baudry M., Staubli U., Lynch G., Gall C. Induction of ornithine decarboxylase by subseizure stimulation in the hippocampus in vivo. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1990 Feb;7(2):167–169. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(90)90094-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barber J. R., Verma I. M. Modification of fos proteins: phosphorylation of c-fos, but not v-fos, is stimulated by 12-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate and serum. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2201–2211. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartel D. P., Sheng M., Lau L. F., Greenberg M. E. Growth factors and membrane depolarization activate distinct programs of early response gene expression: dissociation of fos and jun induction. Genes Dev. 1989 Mar;3(3):304–313. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.3.304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bothwell M. A., Schechter A. L., Vaughn K. M. Clonal variants of PC12 pheochromocytoma cells with altered response to nerve growth factor. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):857–866. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90449-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brabant M., McConlogue L., van Daalen Wetters T., Coffino P. Mouse ornithine decarboxylase gene: cloning, structure, and expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2200–2204. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busslinger M., Moschonas N., Flavell R. A. Beta + thalassemia: aberrant splicing results from a single point mutation in an intron. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):289–298. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90412-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caubet J. F. c-fos proto-oncogene expression in the nervous system during mouse development. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2269–2272. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu R., Boyle W. J., Meek J., Smeal T., Hunter T., Karin M. The c-Fos protein interacts with c-Jun/AP-1 to stimulate transcription of AP-1 responsive genes. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):541–552. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90076-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comb M., Birnberg N. C., Seasholtz A., Herbert E., Goodman H. M. A cyclic AMP- and phorbol ester-inducible DNA element. 1986 Sep 25-Oct 1Nature. 323(6086):353–356. doi: 10.1038/323353a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comb M., Mermod N., Hyman S. E., Pearlberg J., Ross M. E., Goodman H. M. Proteins bound at adjacent DNA elements act synergistically to regulate human proenkephalin cAMP inducible transcription. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3793–3805. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03264.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Miller A. D., Zokas L., Verma I. M. Viral and cellular fos proteins: a comparative analysis. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90219-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Morgan J. I. Superinduction of c-fos by nerve growth factor in the presence of peripherally active benzodiazepines. Science. 1985 Sep 20;229(4719):1265–1268. doi: 10.1126/science.4035354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doucas V., Spyrou G., Yaniv M. Unregulated expression of c-Jun or c-Fos proteins but not Jun D inhibits oestrogen receptor activity in human breast cancer derived cells. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2237–2245. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07760.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dragunow M., Robertson H. A. Kindling stimulation induces c-fos protein(s) in granule cells of the rat dentate gyrus. Nature. 1987 Oct 1;329(6138):441–442. doi: 10.1038/329441a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinstein S. C., Dana S. L., McConlogue L., Shooter E. M., Coffino P. Nerve growth factor rapidly induces ornithine decarboxylase mRNA in PC12 rat pheochromocytoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5761–5765. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fort P., Marty L., Piechaczyk M., el Sabrouty S., Dani C., Jeanteur P., Blanchard J. M. Various rat adult tissues express only one major mRNA species from the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate-dehydrogenase multigenic family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1431–1442. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gius D., Cao X. M., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Cohen D. R., Curran T., Sukhatme V. P. Transcriptional activation and repression by Fos are independent functions: the C terminus represses immediate-early gene expression via CArG elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4243–4255. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gizang-Ginsberg E., Ziff E. B. Nerve growth factor regulates tyrosine hydroxylase gene transcription through a nucleoprotein complex that contains c-Fos. Genes Dev. 1990 Apr;4(4):477–491. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.4.477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Greene L. A., Ziff E. B. Nerve growth factor and epidermal growth factor induce rapid transient changes in proto-oncogene transcription in PC12 cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14101–14110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. A., McGuire J. C. Induction of ornithine decarboxylase by nerve growth factor dissociated from effects on survival and neurite outgrowth. Nature. 1978 Nov 9;276(5684):191–194. doi: 10.1038/276191a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudine M., Peretz M., Weintraub H. Transcriptional regulation of hemoglobin switching in chicken embryos. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Mar;1(3):281–288. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.3.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guroff G., Dickens G., End D. The induction of ornithine decarboxylase by nerve growth factor and epidermal growth factor in PC12 cells. J Neurochem. 1981 Aug;37(2):342–349. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb00461.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutman A., Wasylyk B. The collagenase gene promoter contains a TPA and oncogene-responsive unit encompassing the PEA3 and AP-1 binding sites. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2241–2246. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07394.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halazonetis T. D., Georgopoulos K., Greenberg M. E., Leder P. c-Jun dimerizes with itself and with c-Fos, forming complexes of different DNA binding affinities. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):917–924. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90147-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herschman H. R. Extracellular signals, transcriptional responses and cellular specificity. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Nov;14(11):455–458. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90105-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickok N. J., Wahlfors J., Crozat A., Halmekytö M., Alhonen L., Jänne J., Jänne O. A. Human ornithine decarboxylase-encoding loci: nucleotide sequence of the expressed gene and characterization of a pseudogene. Gene. 1990 Sep 14;93(2):257–263. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90233-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt J. T., Gopal T. V., Moulton A. D., Nienhuis A. W. Inducible production of c-fos antisense RNA inhibits 3T3 cell proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4794–4798. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt S. P., Pini A., Evan G. Induction of c-fos-like protein in spinal cord neurons following sensory stimulation. Nature. 1987 Aug 13;328(6131):632–634. doi: 10.1038/328632a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito E., Sonnenberg J. L., Narayanan R. Nerve growth factor-induced differentiation in PC-12 cells is blocked by fos oncogene. Oncogene. 1989 Oct;4(10):1193–1199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain J., McCaffrey P. G., Valge-Archer V. E., Rao A. Nuclear factor of activated T cells contains Fos and Jun. Nature. 1992 Apr 30;356(6372):801–804. doi: 10.1038/356801a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonat C., Rahmsdorf H. J., Park K. K., Cato A. C., Gebel S., Ponta H., Herrlich P. Antitumor promotion and antiinflammation: down-modulation of AP-1 (Fos/Jun) activity by glucocorticoid hormone. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1189–1204. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90395-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz A., Kahana C. Isolation and characterization of the mouse ornithine decarboxylase gene. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7604–7609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz A., Kahana C. Transcriptional activation of mammalian ornithine decarboxylase during stimulated growth. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2641–2643. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschmeier P. T., Housey G. M., Johnson M. D., Perkins A. S., Weinstein I. B. Construction and characterization of a retroviral vector demonstrating efficient expression of cloned cDNA sequences. DNA. 1988 Apr;7(3):219–225. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kislauskis E., Dobner P. R. Mutually dependent response elements in the cis-regulatory region of the neurotensin/neuromedin N gene integrate environmental stimuli in PC12 cells. Neuron. 1990 May;4(5):783–795. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90205-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovary K., Bravo R. The jun and fos protein families are both required for cell cycle progression in fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;11(9):4466–4472. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.9.4466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruijer W., Schubert D., Verma I. M. Induction of the proto-oncogene fos by nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7330–7334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard D. G., Ziff E. B., Greene L. A. Identification and characterization of mRNAs regulated by nerve growth factor in PC12 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3156–3167. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis E. J., Harrington C. A., Chikaraishi D. M. Transcriptional regulation of the tyrosine hydroxylase gene by glucocorticoid and cyclic AMP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3550–3554. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucibello F. C., Lowag C., Neuberg M., Müller R. trans-repression of the mouse c-fos promoter: a novel mechanism of Fos-mediated trans-regulation. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):999–1007. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90756-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz D., Goff S., Bank A. A safe packaging line for gene transfer: separating viral genes on two different plasmids. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1120–1124. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1120-1124.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milbrandt J. Nerve growth factor rapidly induces c-fos mRNA in PC12 rat pheochromocytoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4789–4793. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan J. I., Cohen D. R., Hempstead J. L., Curran T. Mapping patterns of c-fos expression in the central nervous system after seizure. Science. 1987 Jul 10;237(4811):192–197. doi: 10.1126/science.3037702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan J. I., Curran T. Stimulus-transcription coupling in neurons: role of cellular immediate-early genes. Trends Neurosci. 1989 Nov;12(11):459–462. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(89)90096-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naranjo J. R., Mellström B., Achaval M., Sassone-Corsi P. Molecular pathways of pain: Fos/Jun-mediated activation of a noncanonical AP-1 site in the prodynorphin gene. Neuron. 1991 Apr;6(4):607–617. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90063-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikura K., Murray J. M. Antisense RNA of proto-oncogene c-fos blocks renewed growth of quiescent 3T3 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):639–649. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offringa R., Gebel S., van Dam H., Timmers M., Smits A., Zwart R., Stein B., Bos J. L., van der Eb A., Herrlich P. A novel function of the transforming domain of E1a: repression of AP-1 activity. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):527–538. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuno H., Suzuki T., Yoshida T., Hashimoto Y., Curran T., Iba H. Inhibition of jun transformation by a mutated fos gene: design of an anti-oncogene. Oncogene. 1991 Sep;6(9):1491–1497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson E. N., Spizz G. Mitogens and protein synthesis inhibitors induce ornithine decarboxylase gene transcription through separate mechanisms in the BC3H1 muscle cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2792–2799. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palvimo J. J., Eisenberg L. M., Jänne O. A. Protein-DNA interactions in the cAMP responsive promoter region of the murine ornithine decarboxylase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 25;19(14):3921–3927. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.14.3921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ransone L. J., Verma I. M. Nuclear proto-oncogenes fos and jun. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:539–557. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.002543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riabowol K. T., Vosatka R. J., Ziff E. B., Lamb N. J., Feramisco J. R. Microinjection of fos-specific antibodies blocks DNA synthesis in fibroblast cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1670–1676. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüle R., Rangarajan P., Kliewer S., Ransone L. J., Bolado J., Yang N., Verma I. M., Evans R. M. Functional antagonism between oncoprotein c-Jun and the glucocorticoid receptor. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1217–1226. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90397-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenberg J. L., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Morgan J. I., Curran T. Regulation of proenkephalin by Fos and Jun. Science. 1989 Dec 22;246(4937):1622–1625. doi: 10.1126/science.2512642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterneck E., Müller C., Katz S., Leutz A. Autocrine growth induced by kinase type oncogenes in myeloid cells requires AP-1 and NF-M, a myeloid specific, C/EBP-like factor. EMBO J. 1992 Jan;11(1):115–126. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05034.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Superti-Furga G., Bergers G., Picard D., Busslinger M. Hormone-dependent transcriptional regulation and cellular transformation by Fos-steroid receptor fusion proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5114–5118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vendrell M., Zawia N. H., Serratosa J., Bondy S. C. c-fos and ornithine decarboxylase gene expression in brain as early markers of neurotoxicity. Brain Res. 1991 Mar 29;544(2):291–296. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)90067-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Wasylyk C., Flores P., Begue A., Leprince D., Stehelin D. The c-ets proto-oncogenes encode transcription factors that cooperate with c-Fos and c-Jun for transcriptional activation. Nature. 1990 Jul 12;346(6280):191–193. doi: 10.1038/346191a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk C., Gutman A., Nicholson R., Wasylyk B. The c-Ets oncoprotein activates the stromelysin promoter through the same elements as several non-nuclear oncoproteins. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1127–1134. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08053.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster N. J., Green S., Jin J. R., Chambon P. The hormone-binding domains of the estrogen and glucocorticoid receptors contain an inducible transcription activation function. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):199–207. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90552-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wen L., Huang J. K., Blackshear P. J. Rat ornithine decarboxylase gene. Nucleotide sequence, potential regulatory elements, and comparison to the mouse gene. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):9016–9021. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang-Yen H. F., Chambard J. C., Sun Y. L., Smeal T., Schmidt T. J., Drouin J., Karin M. Transcriptional interference between c-Jun and the glucocorticoid receptor: mutual inhibition of DNA binding due to direct protein-protein interaction. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1205–1215. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90396-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoon S. O., Chikaraishi D. M. Tissue-specific transcription of the rat tyrosine hydroxylase gene requires synergy between an AP-1 motif and an overlapping E box-containing dyad. Neuron. 1992 Jul;9(1):55–67. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90220-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa K., Williams C., Sabol S. L. Rat brain preproenkephalin mRNA. cDNA cloning, primary structure, and distribution in the central nervous system. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):14301–14308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zawia N. H., Bondy S. C. Electrically stimulated rapid gene expression in the brain: ornithine decarboxylase and c-fos. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1990 Apr;7(3):243–247. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(90)90034-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Daalen Wetters T., Brabant M., Coffino P. Regulation of mouse ornithine decarboxylase activity by cell growth, serum and tetradecanoyl phorbol acetate is governed primarily by sequences within the coding region of the gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Dec 11;17(23):9843–9860. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.23.9843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Kranen H. J., van de Zande L., van Kreijl C. F., Bisschop A., Wieringa B. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of rat ornithine decarboxylase cDNA. Gene. 1987;60(2-3):145–155. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90222-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Steeg H., van Oostrom C. T., Hodemaekers H. M., van Kreyl C. F. Cloning and functional analysis of the rat ornithine decarboxylase-encoding gene. Gene. 1990 Sep 14;93(2):249–256. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90232-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]