Abstract
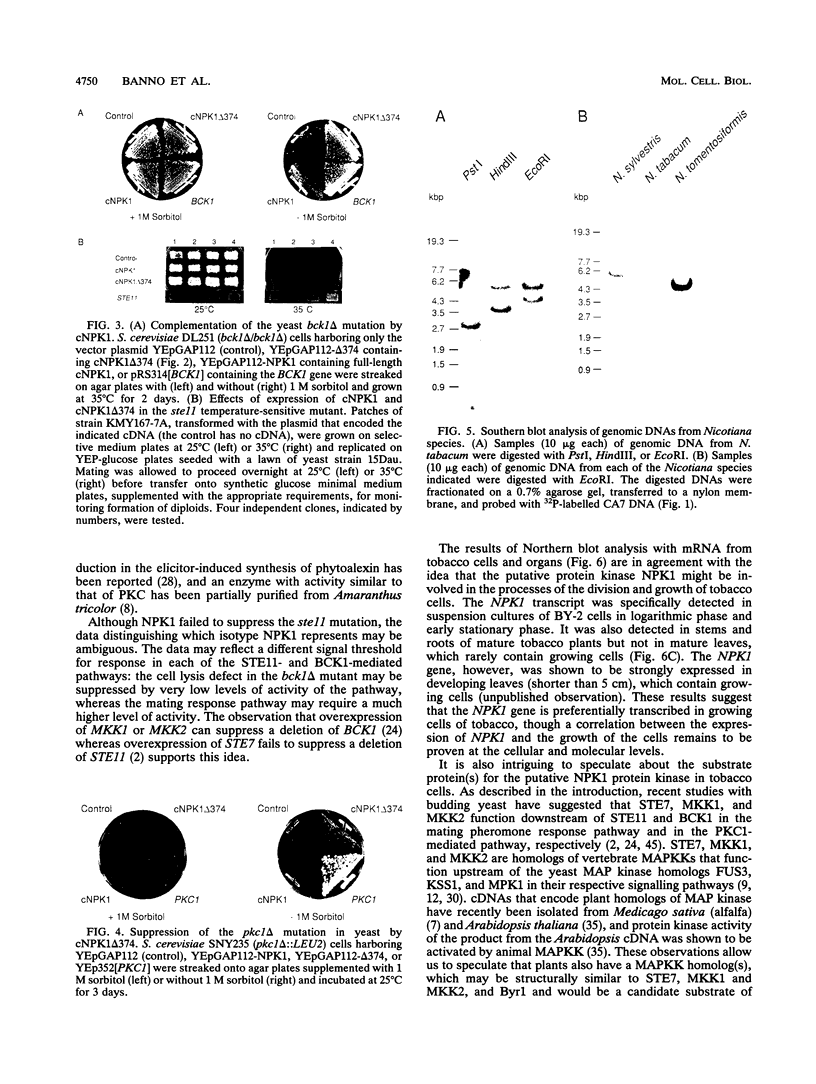
We have isolated a cDNA (cNPK1) that encodes a predicted protein kinase of 690 amino acids from suspension cultures of tobacco cells. The deduced sequence is closely related to those of the protein kinases encoded by the STE11 and BCK1 genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and the byr2 gene of Schizosaccharomyces pombe. STE11 and Byr2 function in the yeast mating pheromone response pathways, and BCK1 acts downstream of the yeast protein kinase C homolog encoded by the PKC1 gene, which is essential for normal growth and division of yeast cells. Overexpression in yeast cells of a truncated form of cNPK1, which encodes only the putative catalytic domain, replaced the growth control functions of BCK1 and PKC1 but not the mating pheromone response function of STE11. Thus, the catalytic domain of NPK1 specifically activates the signal transduction pathway mediated by BCK1 in yeast. In tobacco cells in suspension culture, the NPK1 gene is transcribed during logarithmic phase and early stationary phase but not during late stationary phase. In a tobacco plant, it is also transcribed in stems and roots but not in mature leaves, which rarely contain growing cells. The present results suggest that a signal transduction pathway mediated by this BCK1- and STE11-related protein kinase is also conserved in plants and that a function of NPK1 is controlled at least in part at a transcriptional level.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banuett F. Ustilago maydis, the delightful blight. Trends Genet. 1992 May;8(5):174–180. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(92)90220-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cairns B. R., Ramer S. W., Kornberg R. D. Order of action of components in the yeast pheromone response pathway revealed with a dominant allele of the STE11 kinase and the multiple phosphorylation of the STE7 kinase. Genes Dev. 1992 Jul;6(7):1305–1318. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.7.1305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaleff D. T., Tatchell K. Molecular cloning and characterization of the STE7 and STE11 genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1878–1886. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colasanti J., Tyers M., Sundaresan V. Isolation and characterization of cDNA clones encoding a functional p34cdc2 homologue from Zea mays. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3377–3381. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crews C. M., Alessandrini A., Erikson R. L. The primary structure of MEK, a protein kinase that phosphorylates the ERK gene product. Science. 1992 Oct 16;258(5081):478–480. doi: 10.1126/science.1411546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent P., Haser W., Haystead T. A., Vincent L. A., Roberts T. M., Sturgill T. W. Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase by v-Raf in NIH 3T3 cells and in vitro. Science. 1992 Sep 4;257(5075):1404–1407. doi: 10.1126/science.1326789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duerr B., Gawienowski M., Ropp T., Jacobs T. MsERK1: a mitogen-activated protein kinase from a flowering plant. Plant Cell. 1993 Jan;5(1):87–96. doi: 10.1105/tpc.5.1.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Errede B., Gartner A., Zhou Z., Nasmyth K., Ammerer G. MAP kinase-related FUS3 from S. cerevisiae is activated by STE7 in vitro. Nature. 1993 Mar 18;362(6417):261–264. doi: 10.1038/362261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feiler H. S., Jacobs T. W. Cell division in higher plants: a cdc2 gene, its 34-kDa product, and histone H1 kinase activity in pea. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5397–5401. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira P. C., Hemerly A. S., Villarroel R., Van Montagu M., Inzé D. The Arabidopsis functional homolog of the p34cdc2 protein kinase. Plant Cell. 1991 May;3(5):531–540. doi: 10.1105/tpc.3.5.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartner A., Nasmyth K., Ammerer G. Signal transduction in Saccharomyces cerevisiae requires tyrosine and threonine phosphorylation of FUS3 and KSS1. Genes Dev. 1992 Jul;6(7):1280–1292. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.7.1280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M. Protein kinase catalytic domain sequence database: identification of conserved features of primary structure and classification of family members. Methods Enzymol. 1991;200:38–62. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)00126-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto J., Hirabayashi T., Hayano Y., Hata S., Ohashi Y., Suzuka I., Utsugi T., Toh-e A., Kikuchi Y. Isolation and characterization of cDNA clones encoding cdc2 homologues from Oryza sativa: a functional homologue and cognate variants. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 May;233(1-2):10–16. doi: 10.1007/BF00587555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hata S., Kouchi H., Suzuka I., Ishii T. Isolation and characterization of cDNA clones for plant cyclins. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2681–2688. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07811.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemerly A., Bergounioux C., Van Montagu M., Inzé D., Ferreira P. Genes regulating the plant cell cycle: isolation of a mitotic-like cyclin from Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3295–3299. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirayama T., Imajuku Y., Anai T., Matsui M., Oka A. Identification of two cell-cycle-controlling cdc2 gene homologs in Arabidopsis thaliana. Gene. 1991 Sep 15;105(2):159–165. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90146-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt H., Páy A., Györgyey J., Bakó L., Németh K., Bögre L., Schweyen R. J., Heberle-Bors E., Dudits D. Complementation of a yeast cell cycle mutant by an alfalfa cDNA encoding a protein kinase homologous to p34cdc2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1636–1640. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Housey G. M., Johnson M. D., Hsiao W. L., O'Brian C. A., Murphy J. P., Kirschmeier P., Weinstein I. B. Overproduction of protein kinase C causes disordered growth control in rat fibroblasts. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):343–354. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80027-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe L. R., Leevers S. J., Gómez N., Nakielny S., Cohen P., Marshall C. J. Activation of the MAP kinase pathway by the protein kinase raf. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):335–342. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90361-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irie K., Takase M., Lee K. S., Levin D. E., Araki H., Matsumoto K., Oshima Y. MKK1 and MKK2, which encode Saccharomyces cerevisiae mitogen-activated protein kinase-kinase homologs, function in the pathway mediated by protein kinase C. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 May;13(5):3076–3083. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.5.3076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosako H., Nishida E., Gotoh Y. cDNA cloning of MAP kinase kinase reveals kinase cascade pathways in yeasts to vertebrates. EMBO J. 1993 Feb;12(2):787–794. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05713.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurosaki F., Tsurusawa Y., Nishi A. Breakdown of Phosphatidylinositol during the Elicitation of Phytoalexin Production in Cultured Carrot Cells. Plant Physiol. 1987 Nov;85(3):601–604. doi: 10.1104/pp.85.3.601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyriakis J. M., App H., Zhang X. F., Banerjee P., Brautigan D. L., Rapp U. R., Avruch J. Raf-1 activates MAP kinase-kinase. Nature. 1992 Jul 30;358(6385):417–421. doi: 10.1038/358417a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange-Carter C. A., Pleiman C. M., Gardner A. M., Blumer K. J., Johnson G. L. A divergence in the MAP kinase regulatory network defined by MEK kinase and Raf. Science. 1993 Apr 16;260(5106):315–319. doi: 10.1126/science.8385802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. S., Irie K., Gotoh Y., Watanabe Y., Araki H., Nishida E., Matsumoto K., Levin D. E. A yeast mitogen-activated protein kinase homolog (Mpk1p) mediates signalling by protein kinase C. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 May;13(5):3067–3075. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.5.3067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. S., Levin D. E. Dominant mutations in a gene encoding a putative protein kinase (BCK1) bypass the requirement for a Saccharomyces cerevisiae protein kinase C homolog. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):172–182. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin D. E., Bartlett-Heubusch E. Mutants in the S. cerevisiae PKC1 gene display a cell cycle-specific osmotic stability defect. J Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;116(5):1221–1229. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.5.1221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin D. E., Fields F. O., Kunisawa R., Bishop J. M., Thorner J. A candidate protein kinase C gene, PKC1, is required for the S. cerevisiae cell cycle. Cell. 1990 Jul 27;62(2):213–224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90360-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh L., Neiman A. M., Herskowitz I. Signal transduction during pheromone response in yeast. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:699–728. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.003411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muramatsu M., Kaibuchi K., Arai K. A protein kinase C cDNA without the regulatory domain is active after transfection in vivo in the absence of phorbol ester. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):831–836. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neiman A. M., Stevenson B. J., Xu H. P., Sprague G. F., Jr, Herskowitz I., Wigler M., Marcus S. Functional homology of protein kinases required for sexual differentiation in Schizosaccharomyces pombe and Saccharomyces cerevisiae suggests a conserved signal transduction module in eukaryotic organisms. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Jan;4(1):107–120. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.1.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Intracellular signaling by hydrolysis of phospholipids and activation of protein kinase C. Science. 1992 Oct 23;258(5082):607–614. doi: 10.1126/science.1411571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitschke K., Fleig U., Schell J., Palme K. Complementation of the cs dis2-11 cell cycle mutant of Schizosaccharomyces pombe by a protein phosphatase from Arabidopsis thaliana. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1327–1333. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05177.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onouchi H., Yokoi K., Machida C., Matsuzaki H., Oshima Y., Matsuoka K., Nakamura K., Machida Y. Operation of an efficient site-specific recombination system of Zygosaccharomyces rouxii in tobacco cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec 11;19(23):6373–6378. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.23.6373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes N., Connell L., Errede B. STE11 is a protein kinase required for cell-type-specific transcription and signal transduction in yeast. Genes Dev. 1990 Nov;4(11):1862–1874. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.11.1862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts T. M. Cell biology. A signal chain of events. Nature. 1992 Dec 10;360(6404):534–535. doi: 10.1038/360534a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman F. Getting started with yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:3–21. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94004-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson B. J., Rhodes N., Errede B., Sprague G. F., Jr Constitutive mutants of the protein kinase STE11 activate the yeast pheromone response pathway in the absence of the G protein. Genes Dev. 1992 Jul;6(7):1293–1304. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.7.1293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi Y., Kuroda H., Tanaka T., Machida Y., Takebe I., Nagata T. Isolation of an auxin-regulated gene cDNA expressed during the transition from G0 to S phase in tobacco mesophyll protoplasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9279–9283. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda T., Cameron S., Sass P., Zoller M., Wigler M. Three different genes in S. cerevisiae encode the catalytic subunits of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Cell. 1987 Jul 17;50(2):277–287. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90223-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres L., Martín H., García-Saez M. I., Arroyo J., Molina M., Sánchez M., Nombela C. A protein kinase gene complements the lytic phenotype of Saccharomyces cerevisiae lyt2 mutants. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Nov;5(11):2845–2854. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01993.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda L., Inoue Y. H., Yoo M. A., Mizuno M., Hata M., Lim Y. M., Adachi-Yamada T., Ryo H., Masamune Y., Nishida Y. A protein kinase similar to MAP kinase activator acts downstream of the raf kinase in Drosophila. Cell. 1993 Feb 12;72(3):407–414. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90117-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Xu H. P., Riggs M., Rodgers L., Wigler M. byr2, a Schizosaccharomyces pombe gene encoding a protein kinase capable of partial suppression of the ras1 mutant phenotype. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3554–3563. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J., Harrison J. K., Vincent L. A., Haystead C., Haystead T. A., Michel H., Hunt D. F., Lynch K. R., Sturgill T. W. Molecular structure of a protein-tyrosine/threonine kinase activating p42 mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase: MAP kinase kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 1;90(1):173–177. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.1.173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida S., Ikeda E., Uno I., Mitsuzawa H. Characterization of a staurosporine- and temperature-sensitive mutant, stt1, of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: STT1 is allelic to PKC1. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Feb;231(3):337–344. doi: 10.1007/BF00292700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Z., Gartner A., Cade R., Ammerer G., Errede B. Pheromone-induced signal transduction in Saccharomyces cerevisiae requires the sequential function of three protein kinases. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2069–2080. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]