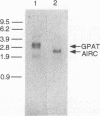
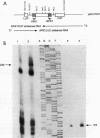
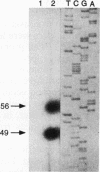
Abstract
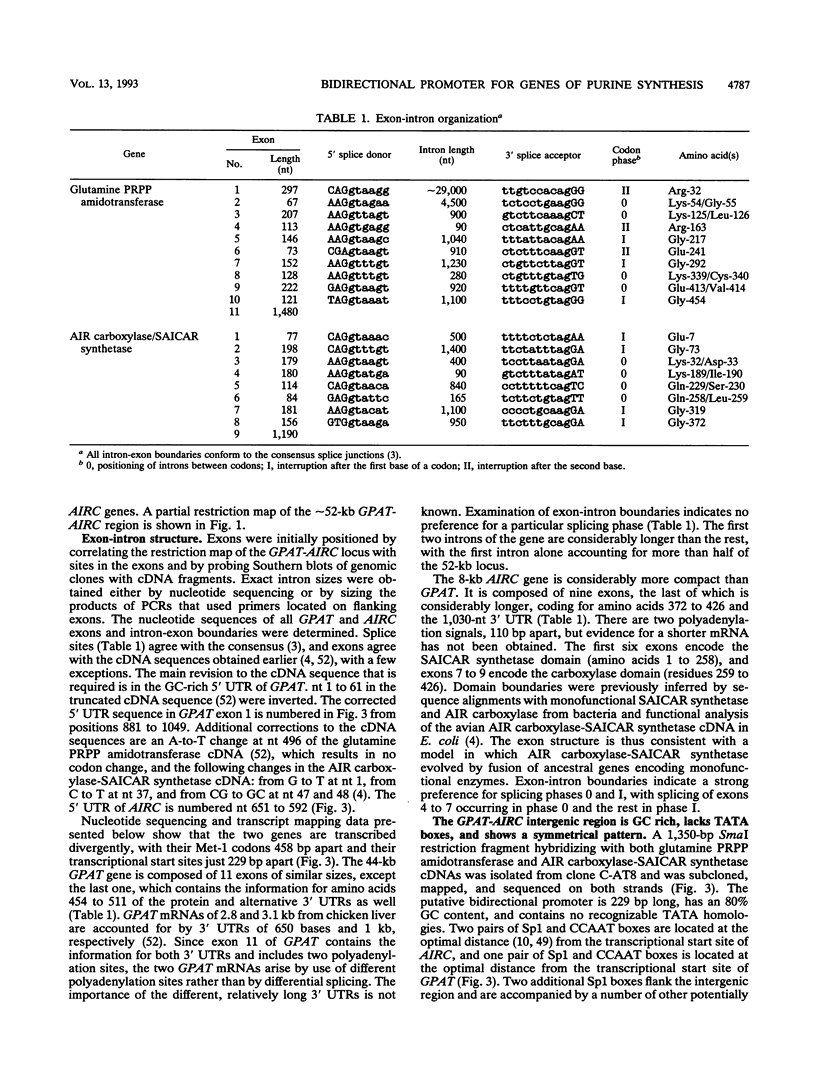
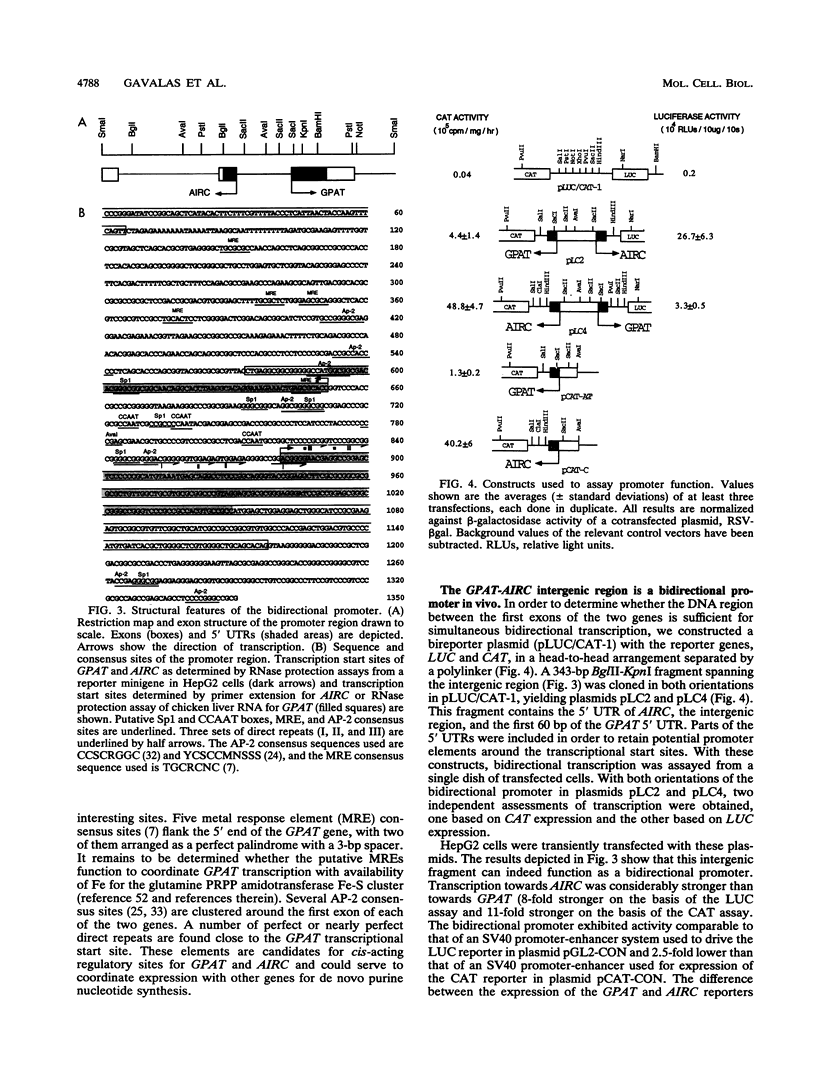
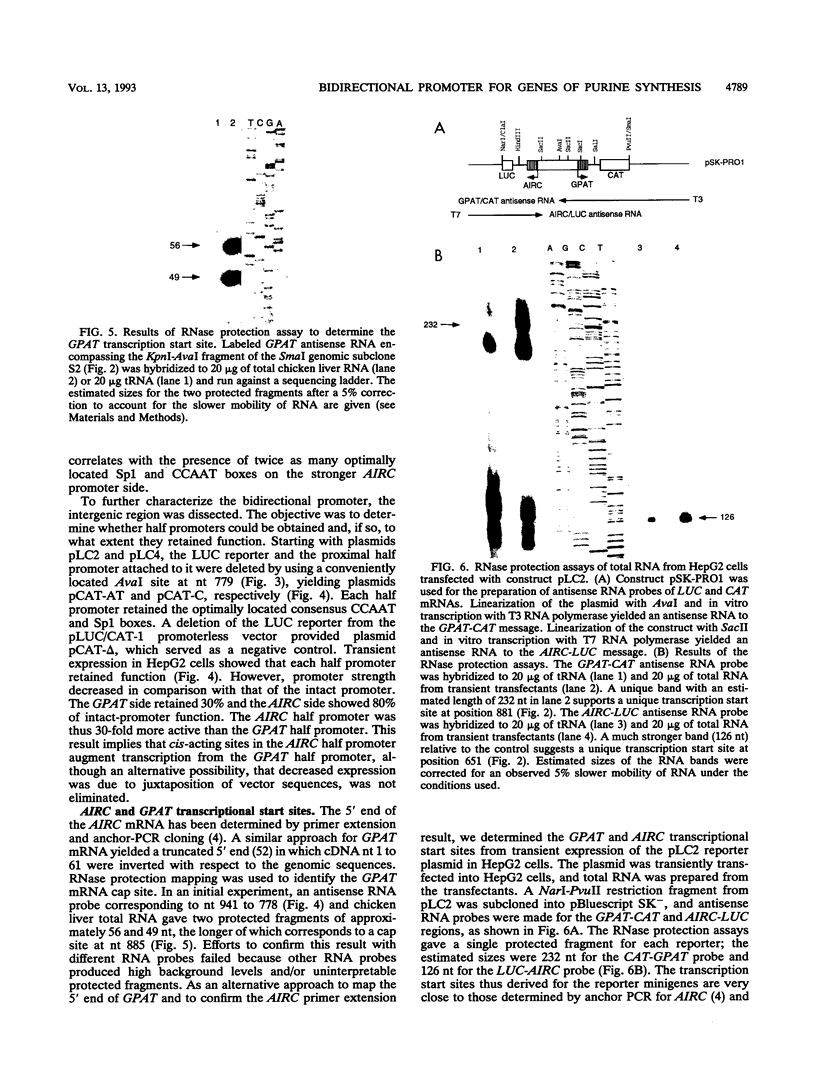
Two avian genes encoding essential steps in the purine nucleotide biosynthetic pathway are transcribed divergently from a bidirectional promoter element. The bidirectional promoter, embedded in a CpG island, directs coexpression of GPAT and AIRC genes from distinct transcriptional start sites 229 bp apart. The bidirectional promoter can be divided in half, with each half retaining partial activity towards the cognate gene. GPAT and AIRC genes encode the enzymes that catalyze step 1 and steps 6 plus 7, respectively, in the de novo purine biosynthetic pathway. This is the first report of genes coding for structurally unrelated enzymes of the same pathway that are tightly linked and transcribed divergently from a bidirectional promoter. This arrangement has the potential to provide for regulated coexpression comparable to that in a prokaryotic operon.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barton J. W., Hart I. M., Patterson D. Mapping of a locus correcting lack of phosphoribosylaminoimidazole carboxylase activity in Chinese hamster ovary cell Ade-D mutants to human chromosome 4. Genomics. 1991 Feb;9(2):314–321. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90259-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. P. CpG-rich islands and the function of DNA methylation. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):209–213. doi: 10.1038/321209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z. D., Dixon J. E., Zalkin H. Cloning of a chicken liver cDNA encoding 5-aminoimidazole ribonucleotide carboxylase and 5-aminoimidazole-4-N-succinocarboxamide ribonucleotide synthetase by functional complementation of Escherichia coli pur mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):3097–3101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.3097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colombo P., Yon J., Garson K., Fried M. Conservation of the organization of five tightly clustered genes over 600 million years of divergent evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6358–6362. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culotta V. C., Hamer D. H. Fine mapping of a mouse metallothionein gene metal response element. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):1376–1380. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.1376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dandekar T., Stripecke R., Gray N. K., Goossen B., Constable A., Johansson H. E., Hentze M. W. Identification of a novel iron-responsive element in murine and human erythroid delta-aminolevulinic acid synthase mRNA. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1903–1909. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07716.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn A., Bollekens J., Staub A., Benoist C., Mathis D. A multiplicity of CCAAT box-binding proteins. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):863–872. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90513-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Control of eukaryotic messenger RNA synthesis by sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):774–778. doi: 10.1038/316774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edlund T., Walker M. D., Barr P. J., Rutter W. J. Cell-specific expression of the rat insulin gene: evidence for role of two distinct 5' flanking elements. Science. 1985 Nov 22;230(4728):912–916. doi: 10.1126/science.3904002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faure M., Camonis J. H., Jacquet M. Molecular characterization of a Dictyostelium discoideum gene encoding a multifunctional enzyme of the pyrimidine pathway. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Feb 1;179(2):345–358. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14560.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felgner P. L., Gadek T. R., Holm M., Roman R., Chan H. W., Wenz M., Northrop J. P., Ringold G. M., Danielsen M. Lipofection: a highly efficient, lipid-mediated DNA-transfection procedure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7413–7417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner-Garden M., Frommer M. CpG islands in vertebrate genomes. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jul 20;196(2):261–282. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90689-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidoni D., Kadonaga J. T., Barrera-Saldaña H., Takahashi K., Chambon P., Tjian R. Bidirectional SV40 transcription mediated by tandem Sp1 binding interactions. Science. 1985 Nov 1;230(4725):511–517. doi: 10.1126/science.2996137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gnirke A., Barnes T. S., Patterson D., Schild D., Featherstone T., Olson M. V. Cloning and in vivo expression of the human GART gene using yeast artificial chromosomes. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1629–1634. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07685.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haile D. J., Rouault T. A., Tang C. K., Chin J., Harford J. B., Klausner R. D. Reciprocal control of RNA-binding and aconitase activity in the regulation of the iron-responsive element binding protein: role of the iron-sulfur cluster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7536–7540. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S., Keene M. A., Fechtel K., Fristrom J. W. Gene within a gene: nested Drosophila genes encode unrelated proteins on opposite DNA strands. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):33–42. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90482-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S., Keene M. A., Sloan J. S., Bleskan J., Hards R., Patterson D. Multiple purine pathway enzyme activities are encoded at a single genetic locus in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):720–724. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentschel C. C., Birnstiel M. L. The organization and expression of histone gene families. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):301–313. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90048-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A., Campbell C. E., Bonetta L., McAndrews-Hill M. S., Chilton-MacNeill S., Coppes M. J., Law D. J., Feinberg A. P., Yeger H., Williams B. R. Tissue, developmental, and tumor-specific expression of divergent transcripts in Wilms tumor. Science. 1990 Nov 16;250(4983):991–994. doi: 10.1126/science.2173145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxley C., Fried M. The mouse surfeit locus contains a cluster of six genes associated with four CpG-rich islands in 32 kilobases of genomic DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):605–614. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imagawa M., Chiu R., Karin M. Transcription factor AP-2 mediates induction by two different signal-transduction pathways: protein kinase C and cAMP. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90152-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. C., Rigby P. W., Ziff E. B. Trans-acting protein factors and the regulation of eukaryotic transcription: lessons from studies on DNA tumor viruses. Genes Dev. 1988 Mar;2(3):267–281. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.3.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killen P. D., Burbelo P., Sakurai Y., Yamada Y. Structure of the amino-terminal portion of the murine alpha 1(IV) collagen chain and the corresponding region of the gene. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):8706–8709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koromilas A. E., Lazaris-Karatzas A., Sonenberg N. mRNAs containing extensive secondary structure in their 5' non-coding region translate efficiently in cells overexpressing initiation factor eIF-4E. EMBO J. 1992 Nov;11(11):4153–4158. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05508.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavia P., Macleod D., Bird A. Coincident start sites for divergent transcripts at a randomly selected CpG-rich island of mouse. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2773–2779. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02572.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linton J. P., Yen J. Y., Selby E., Chen Z., Chinsky J. M., Liu K., Kellems R. E., Crouse G. F. Dual bidirectional promoters at the mouse dhfr locus: cloning and characterization of two mRNA classes of the divergently transcribed Rep-1 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):3058–3072. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.3058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Means A. L., Farnham P. J. Transcription initiation from the dihydrofolate reductase promoter is positioned by HIP1 binding at the initiation site. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):653–661. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Wang C., Tjian R. Positive and negative regulation of transcription in vitro: enhancer-binding protein AP-2 is inhibited by SV40 T antigen. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):847–861. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90512-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller P. R., Salser S. J., Wold B. Constitutive and metal-inducible protein:DNA interactions at the mouse metallothionein I promoter examined by in vivo and in vitro footprinting. Genes Dev. 1988 Apr;2(4):412–427. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.4.412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pothier F., Ouellet M., Julien J. P., Guérin S. L. An improved CAT assay for promoter analysis in either transgenic mice or tissue culture cells. DNA Cell Biol. 1992 Jan-Feb;11(1):83–90. doi: 10.1089/dna.1992.11.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizzo M. G., Ottavio L., Travali S., Chang C. D., Kaminska B., Baserga R. The promoter of the human proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) gene is bidirectional. Exp Cell Res. 1990 Jun;188(2):286–293. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(90)90172-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal N. Identification of regulatory elements of cloned genes with functional assays. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:704–720. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52075-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saffer J. D., Singer M. F. Transcription from SV 40-like monkey DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 11;12(11):4769–4788. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.11.4769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schilling L. J., Farnham P. J. Identification of a new promoter upstream of the murine dihydrofolate reductase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4568–4570. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B., Sheen J. Y. A simple phase-extraction assay for chloramphenicol acyltransferase activity. Gene. 1988 Jul 30;67(2):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90403-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada T., Fujii H., Lin H. A 165-base pair sequence between the dihydrofolate reductase gene and the divergently transcribed upstream gene is sufficient for bidirectional transcriptional activity. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20171–20174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Baltimore D. The "initiator" as a transcription control element. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90176-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soininen R., Huotari M., Hostikka S. L., Prockop D. J., Tryggvason K. The structural genes for alpha 1 and alpha 2 chains of human type IV collagen are divergently encoded on opposite DNA strands and have an overlapping promoter region. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 25;263(33):17217–17220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogeli G., Kaytes P. S. Amplification, storage, and replication of libraries. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:407–415. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52047-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T., Admon A., Lüscher B., Tjian R. Cloning and expression of AP-2, a cell-type-specific transcription factor that activates inducible enhancer elements. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1557–1569. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingender E. Transcription regulating proteins and their recognition sequences. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 1990;1(1):11–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. M., Kao M. Y., Gordon D. F., Ridgway E. C. Thyroid hormone regulates the mouse thyrotropin beta-subunit gene promoter in transfected primary thyrotropes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):14840–14847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalkin H., Dixon J. E. De novo purine nucleotide biosynthesis. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1992;42:259–287. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60578-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou G. C., Dixon J. E., Zalkin H. Cloning and expression of avian glutamine phosphoribosylpyrophosphate amidotransferase. Conservation of a bacterial propeptide sequence supports a role for posttranslational processing. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 5;265(34):21152–21159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]