Abstract
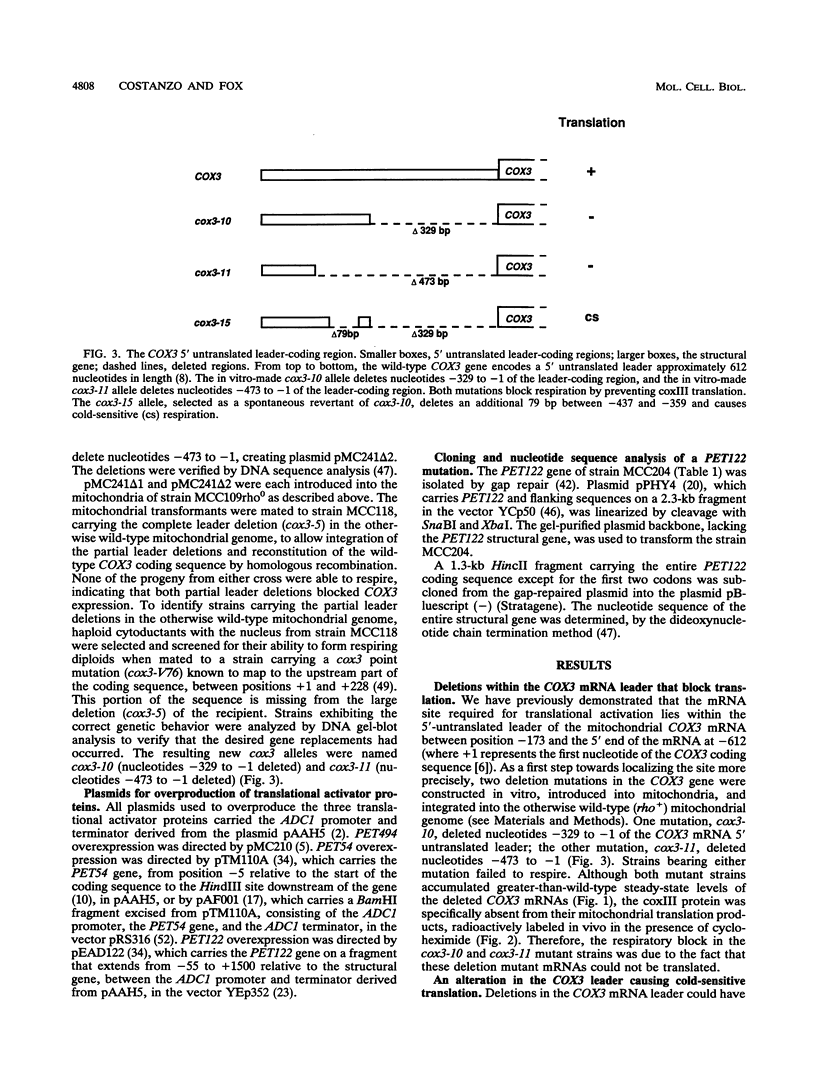
Translation of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae mitochondrial COX3 mRNA, encoding subunit III of cytochrome c oxidase, specifically requires the action of the nuclear gene products PET54, PET122, and PET494 at a site encoded in the 612-base 5' untranslated leader. To identify more precisely the site of action of the translational activators, we constructed two large deletions of the COX3 mRNA 5' untranslated leader. Both deletions blocked translation without affecting mRNA stability. However, one of the large deletions was able to revert to partial function by a small secondary deletion within the remaining 5' leader sequences. Translation of the resulting mutant (cox3-15) mRNA was still dependent on the nuclear-encoded specific activators but was cold sensitive. We selected revertants of this mitochondrial mutant at low temperature to identify genes encoding proteins that might interact with the COX3 mRNA 5' leader. One such revertant carried a missense mutation in the PET122 gene that was a strong and dominant suppressor of the cold-sensitive defect in the mRNA, indicating that the PET122 protein interacts functionally (possibly directly) with the COX3 mRNA 5' leader. The cox3-15 mutation was not suppressed by overproduction of the wild-type PET122 protein but was very weakly suppressed by overproduction of PET494 and slightly better suppressed by co-overproduction of PET494 and PET122.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackerman S. H., Gatti D. L., Gellefors P., Douglas M. G., Tzagoloff A. ATP13, a nuclear gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae essential for the expression of subunit 9 of the mitochondrial ATPase. FEBS Lett. 1991 Jan 28;278(2):234–238. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80124-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ammerer G. Expression of genes in yeast using the ADCI promoter. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:192–201. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabral F., Schatz G. Identification of cytochrome c oxidase subunits in nuclear yeast mutants lacking the functional enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 25;253(12):4396–4401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conde J., Fink G. R. A mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae defective for nuclear fusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3651–3655. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costanzo M. C., Fox T. D. Control of mitochondrial gene expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Annu Rev Genet. 1990;24:91–113. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.24.120190.000515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costanzo M. C., Fox T. D. Product of Saccharomyces cerevisiae nuclear gene PET494 activates translation of a specific mitochondrial mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3694–3703. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costanzo M. C., Fox T. D. Specific translational activation by nuclear gene products occurs in the 5' untranslated leader of a yeast mitochondrial mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2677–2681. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costanzo M. C., Seaver E. C., Fox T. D. At least two nuclear gene products are specifically required for translation of a single yeast mitochondrial mRNA. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3637–3641. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04693.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costanzo M. C., Seaver E. C., Fox T. D. The PET54 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: characterization of a nuclear gene encoding a mitochondrial translational activator and subcellular localization of its product. Genetics. 1989 Jun;122(2):297–305. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.2.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels D., Zuber P., Losick R. Two amino acids in an RNA polymerase sigma factor involved in the recognition of adjacent base pairs in the -10 region of a cognate promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):8075–8079. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.8075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decoster E., Simon M., Hatat D., Faye G. The MSS51 gene product is required for the translation of the COX1 mRNA in yeast mitochondria. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Oct;224(1):111–118. doi: 10.1007/BF00259457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas M. G., Butow R. A. Variant forms of mitochondrial translation products in yeast: evidence for location of determinants on mitochondrial DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1083–1086. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folley L. S., Fox T. D. Site-directed mutagenesis of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae mitochondrial translation initiation codon. Genetics. 1991 Nov;129(3):659–668. doi: 10.1093/genetics/129.3.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox T. D., Folley L. S., Mulero J. J., McMullin T. W., Thorsness P. E., Hedin L. O., Costanzo M. C. Analysis and manipulation of yeast mitochondrial genes. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:149–165. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94013-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox T. D., Sanford J. C., McMullin T. W. Plasmids can stably transform yeast mitochondria lacking endogenous mtDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7288–7292. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardella T., Moyle H., Susskind M. M. A mutant Escherichia coli sigma 70 subunit of RNA polymerase with altered promoter specificity. J Mol Biol. 1989 Apr 20;206(4):579–590. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90567-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haffter P., Fox T. D. Suppression of carboxy-terminal truncations of the yeast mitochondrial mRNA-specific translational activator PET122 by mutations in two new genes, MRP17 and PET127. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Oct;235(1):64–73. doi: 10.1007/BF00286182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haffter P., McMullin T. W., Fox T. D. A genetic link between an mRNA-specific translational activator and the translation system in yeast mitochondria. Genetics. 1990 Jul;125(3):495–503. doi: 10.1093/genetics/125.3.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haffter P., McMullin T. W., Fox T. D. Functional interactions among two yeast mitochondrial ribosomal proteins and an mRNA-specific translational activator. Genetics. 1991 Feb;127(2):319–326. doi: 10.1093/genetics/127.2.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill J. E., Myers A. M., Koerner T. J., Tzagoloff A. Yeast/E. coli shuttle vectors with multiple unique restriction sites. Yeast. 1986 Sep;2(3):163–167. doi: 10.1002/yea.320020304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochschild A., Douhan J., 3rd, Ptashne M. How lambda repressor and lambda Cro distinguish between OR1 and OR3. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):807–816. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90523-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huffaker T. C., Hoyt M. A., Botstein D. Genetic analysis of the yeast cytoskeleton. Annu Rev Genet. 1987;21:259–284. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.21.120187.001355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvik J., Botstein D. Conditional-lethal mutations that suppress genetic defects in morphogenesis by altering structural proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2738–2742. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston S. A., Anziano P. Q., Shark K., Sanford J. C., Butow R. A. Mitochondrial transformation in yeast by bombardment with microprojectiles. Science. 1988 Jun 10;240(4858):1538–1541. doi: 10.1126/science.2836954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenney T. J., Moran C. P., Jr Genetic evidence for interaction of sigma A with two promoters in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(11):3282–3290. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.11.3282-3290.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloeckener-Gruissem B., McEwen J. E., Poyton R. O. Identification of a third nuclear protein-coding gene required specifically for posttranscriptional expression of the mitochondrial COX3 gene is Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1399–1402. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1399-1402.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight K. L., Sauer R. T. Biochemical and genetic analysis of operator contacts made by residues within the beta-sheet DNA binding motif of Mnt repressor. EMBO J. 1992 Jan;11(1):215–223. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05044.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marykwas D. L., Fox T. D. Control of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae regulatory gene PET494: transcriptional repression by glucose and translational induction by oxygen. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):484–491. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMullin T. W., Fox T. D. COX3 mRNA-specific translational activator proteins are associated with the inner mitochondrial membrane in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 5;268(16):11737–11741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMullin T. W., Haffter P., Fox T. D. A novel small-subunit ribosomal protein of yeast mitochondria that interacts functionally with an mRNA-specific translational activator. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4590–4595. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller P. P., Fox T. D. Molecular cloning and genetic mapping of the PET494 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;195(1-2):275–280. doi: 10.1007/BF00332759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller P. P., Reif M. K., Zonghou S., Sengstag C., Mason T. L., Fox T. D. A nuclear mutation that post-transcriptionally blocks accumulation of a yeast mitochondrial gene product can be suppressed by a mitochondrial gene rearrangement. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jun 5;175(4):431–452. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90178-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neff N. F., Thomas J. H., Grisafi P., Botstein D. Isolation of the beta-tubulin gene from yeast and demonstration of its essential function in vivo. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):211–219. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90350-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson H. C., Sauer R. T. Lambda repressor mutations that increase the affinity and specificity of operator binding. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):549–558. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90112-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohmen J. D., Burke K. A., McEwen J. E. Divergent overlapping transcripts at the PET122 locus in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):3027–3035. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.3027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohmen J. D., Kloeckener-Gruissem B., McEwen J. E. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of the nuclear PET122 gene required for expression of the mitochondrial COX3 gene in S. cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 25;16(22):10783–10802. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.22.10783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr-Weaver T. L., Szostak J. W. Yeast recombination: the association between double-strand gap repair and crossing-over. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4417–4421. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne M. J., Schweizer E., Lukins H. B. Properties of two nuclear pet mutants affecting expression of the mitochondrial oli1 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Curr Genet. 1991 May;19(5):343–351. doi: 10.1007/BF00309594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rine J. Gene overexpression in studies of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:239–251. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. D., Novick P., Thomas J. H., Botstein D., Fink G. R. A Saccharomyces cerevisiae genomic plasmid bank based on a centromere-containing shuttle vector. Gene. 1987;60(2-3):237–243. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90232-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer S., Davis R. W. Replacement of chromosome segments with altered DNA sequences constructed in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4951–4955. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegele D. A., Hu J. C., Walter W. A., Gross C. A. Altered promoter recognition by mutant forms of the sigma 70 subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1989 Apr 20;206(4):591–603. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90568-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprague G. F., Jr, Jensen R., Herskowitz I. Control of yeast cell type by the mating type locus: positive regulation of the alpha-specific STE3 gene by the MAT alpha 1 product. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):409–415. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90460-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatti K. M., Jones C. H., Moran C. P., Jr Genetic evidence for interaction of sigma E with the spoIIID promoter in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(24):7828–7833. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.24.7828-7833.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldburger C., Gardella T., Wong R., Susskind M. M. Changes in conserved region 2 of Escherichia coli sigma 70 affecting promoter recognition. J Mol Biol. 1990 Sep 20;215(2):267–276. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(05)80345-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton R. P., Ptashne M. A new-specificity mutant of 434 repressor that defines an amino acid-base pair contact. 1987 Apr 30-May 6Nature. 326(6116):888–891. doi: 10.1038/326888a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuber P., Healy J., Carter H. L., 3rd, Cutting S., Moran C. P., Jr, Losick R. Mutation changing the specificity of an RNA polymerase sigma factor. J Mol Biol. 1989 Apr 20;206(4):605–614. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90569-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]