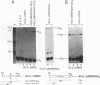
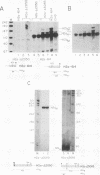
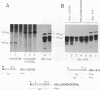
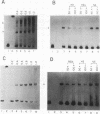
Abstract
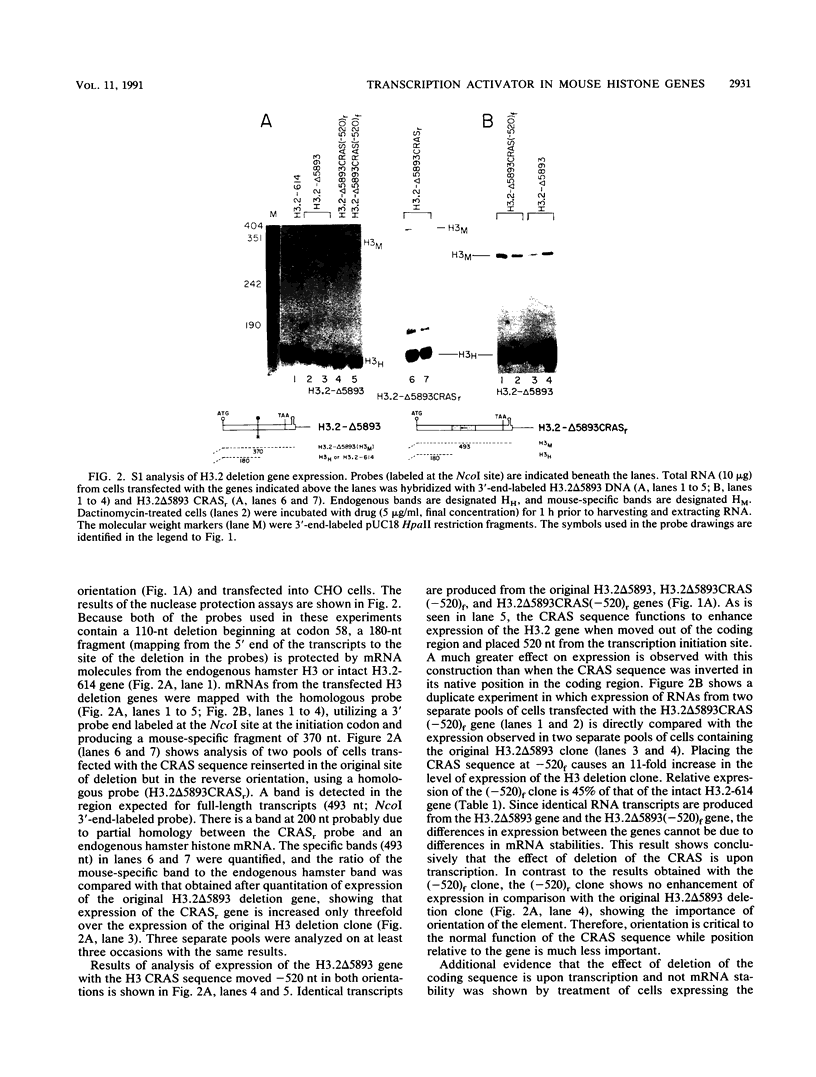
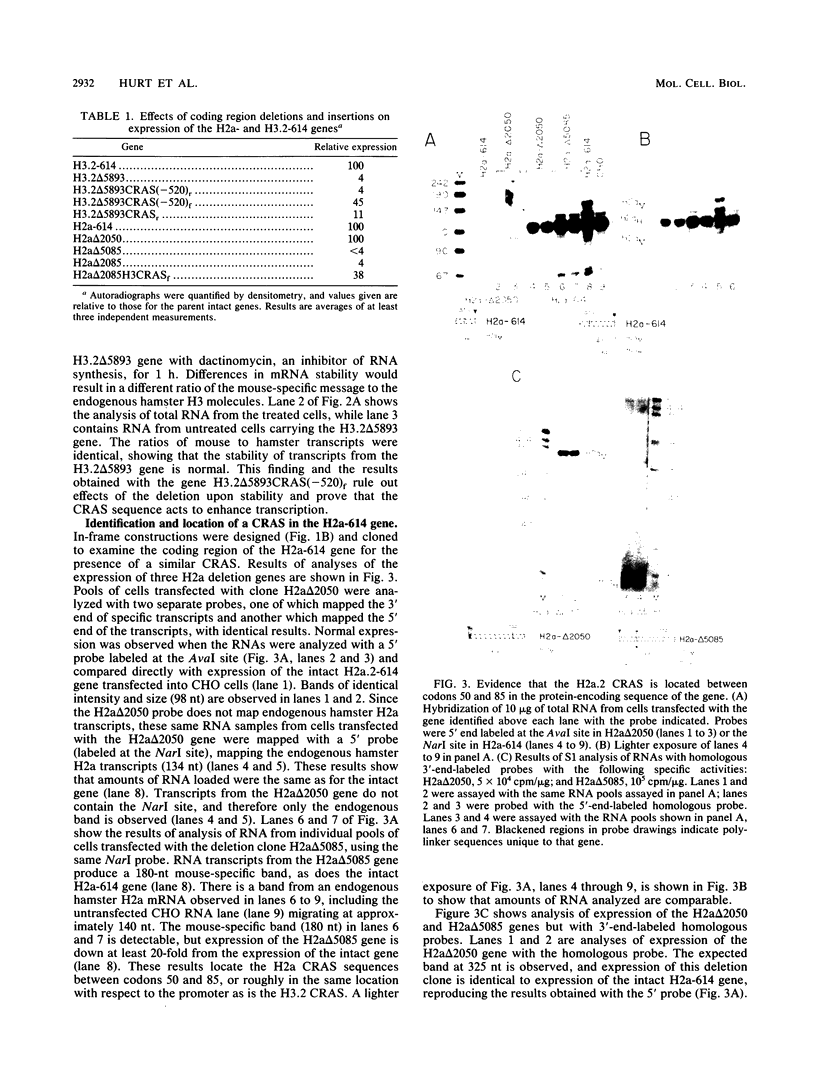
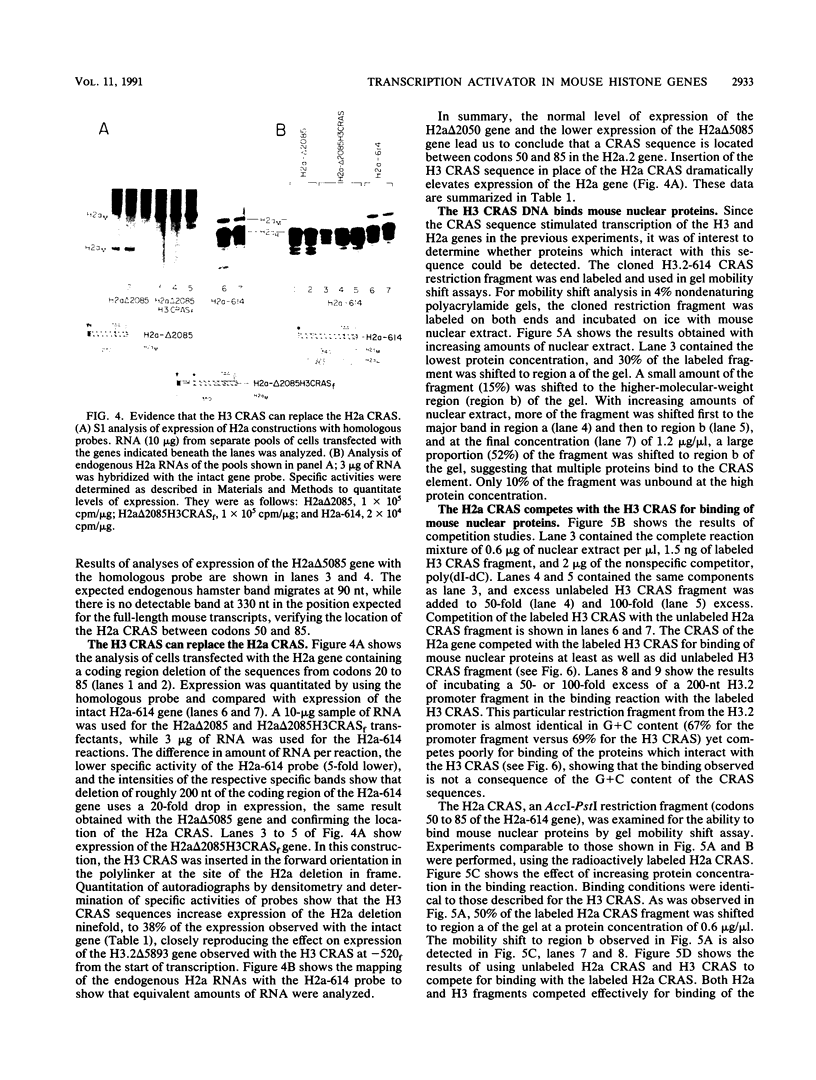
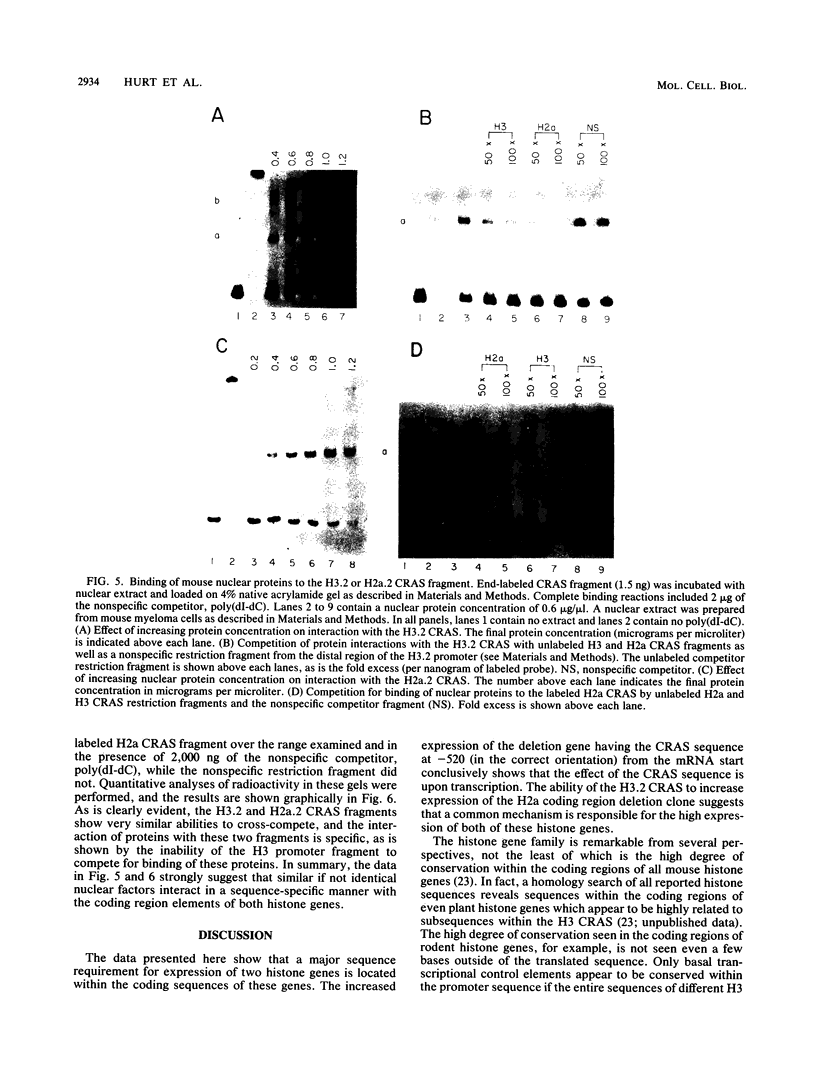
There is a region in the mouse histone H3 gene protein-encoding sequence required for high expression. The 110-nucleotide coding region activating sequence (CRAS) from codons 58 to 93 of the H3.2 gene restored expression when placed 520 nucleotides 5' of the start of transcription in the correct orientation. Since identical mRNA molecules are produced by transcription of the original deletion gene and the deletion gene with the CRAS at -520, effects of the deletions on mRNA stability or other posttranscriptional events are completely ruled out. Inversion of the CRAS sequence in its proper position in the H3 gene resulted in only a threefold increase in expression, and placing the CRAS sequence 5' of the deleted gene in the wrong orientation had no effect on expression. In-frame deletions in the coding region of an H2a.2 gene led to identification of a 105-nucleotide sequence in the coding region between amino acids 50 and 85 necessary for high expression of the gene. Additionally, insertion of the H3 CRAS into the deleted region of the H2a.2 gene restored expression of the H2a gene. Thus, the CRAS element has an orientation-dependent, position-independent effect. Gel mobility shift competition studies indicate that the same proteins interact with both the H3 and H2a CRAS elements, suggesting that a common factor is involved in expression of histone genes.
Full text
PDF

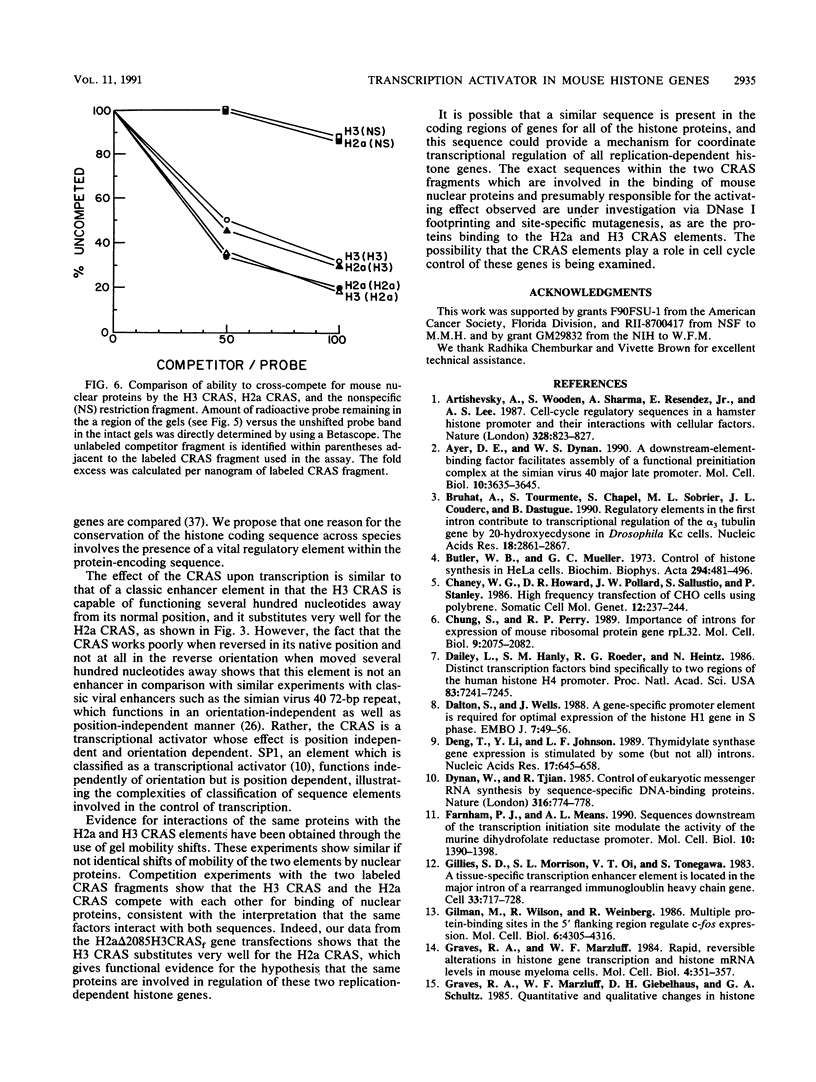

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Artishevsky A., Wooden S., Sharma A., Resendez E., Jr, Lee A. S. Cell-cycle regulatory sequences in a hamster histone promoter and their interactions with cellular factors. 1987 Aug 27-Sep 2Nature. 328(6133):823–827. doi: 10.1038/328823a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayer D. E., Dynan W. S. A downstream-element-binding factor facilitates assembly of a functional preinitiation complex at the simian virus 40 major late promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3635–3645. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruhat A., Tourmente S., Chapel S., Sobrier M. L., Couderc J. L., Dastugue B. Regulatory elements in the first intron contribute to transcriptional regulation of the beta 3 tubulin gene by 20-hydroxyecdysone in Drosophila Kc cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 25;18(10):2861–2867. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.10.2861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler W. B., Mueller G. C. Control of histone synthesis in HeLa cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 4;294(1):481–496. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90104-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaney W. G., Howard D. R., Pollard J. W., Sallustio S., Stanley P. High-frequency transfection of CHO cells using polybrene. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1986 May;12(3):237–244. doi: 10.1007/BF01570782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung S., Perry R. P. Importance of introns for expression of mouse ribosomal protein gene rpL32. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2075–2082. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dailey L., Hanly S. M., Roeder R. G., Heintz N. Distinct transcription factors bind specifically to two regions of the human histone H4 promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7241–7245. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalton S., Wells J. R. A gene-specific promoter element is required for optimal expression of the histone H1 gene in S-phase. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):49–56. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02782.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng T. L., Li Y., Johnson L. F. Thymidylate synthase gene expression is stimulated by some (but not all) introns. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 25;17(2):645–658. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.2.645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Control of eukaryotic messenger RNA synthesis by sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):774–778. doi: 10.1038/316774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farnham P. J., Means A. L. Sequences downstream of the transcription initiation site modulate the activity of the murine dihydrofolate reductase promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1390–1398. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies S. D., Morrison S. L., Oi V. T., Tonegawa S. A tissue-specific transcription enhancer element is located in the major intron of a rearranged immunoglobulin heavy chain gene. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman M. Z., Wilson R. N., Weinberg R. A. Multiple protein-binding sites in the 5'-flanking region regulate c-fos expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4305–4316. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves R. A., Marzluff W. F. Rapid reversible changes in the rate of histone gene transcription and histone mRNA levels in mouse myeloma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;4(2):351–357. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.2.351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves R. A., Pandey N. B., Chodchoy N., Marzluff W. F. Translation is required for regulation of histone mRNA degradation. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):615–626. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90240-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves R. A., Wellman S. E., Chiu I. M., Marzluff W. F. Differential expression of two clusters of mouse histone genes. J Mol Biol. 1985 May 25;183(2):179–194. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90211-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurt M. M., Chodchoy N., Marzluff W. F. The mouse histone H2a.2 gene from chromosome 3. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 11;17(21):8876–8876. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.21.8876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurt M. M., Pandey N. B., Marzluff W. F. A region in the coding sequence is required for high-level expression of murine histone H3 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4450–4454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaBella F., Sive H. L., Roeder R. G., Heintz N. Cell-cycle regulation of a human histone H2b gene is mediated by the H2b subtype-specific consensus element. Genes Dev. 1988 Jan;2(1):32–39. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.1.32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb N. J., Fernandez A., Tourkine N., Jeanteur P., Blanchard J. M. Demonstration in living cells of an intragenic negative regulatory element within the rodent c-fos gene. Cell. 1990 May 4;61(3):485–496. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90530-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine B. J., Liu T. J., Marzluff W. F., Skoultchi A. I. Differential expression of individual members of the histone multigene family due to sequences in the 5' and 3' regions of the genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):1887–1895. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.1887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill G. F., Hauschka S. D., McKnight S. L. tk Enzyme expression in differentiating muscle cells is regulated through an internal segment of the cellular tk gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1777–1784. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreau P., Hen R., Wasylyk B., Everett R., Gaub M. P., Chambon P. The SV40 72 base repair repeat has a striking effect on gene expression both in SV40 and other chimeric recombinants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):6047–6068. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.6047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moura-Neto R., Dudov K. P., Perry R. P. An element downstream of the cap site is required for transcription of the gene encoding mouse ribosomal protein L32. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):3997–4001. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.3997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mous J., Stunnenberg H., Georgiev O., Birnstiel M. L. Stimulation of sea urchin H2B histone gene transcription by a chromatin-associated protein fraction depends on gene sequences downstream of the transcription start site. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2764–2769. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakatani Y., Brenner M., Freese E. An RNA polymerase II promoter containing sequences upstream and downstream from the RNA startpoint that direct initiation of transcription from the same site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4289–4293. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oshima R. G., Abrams L., Kulesh D. Activation of an intron enhancer within the keratin 18 gene by expression of c-fos and c-jun in undifferentiated F9 embryonal carcinoma cells. Genes Dev. 1990 May;4(5):835–848. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.5.835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plumb M., Stein J., Stein G. Coordinate regulation of multiple histone mRNAs during the cell cycle in HeLa cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2391–2410. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid L. H., Gregg R. G., Smithies O., Koller B. H. Regulatory elements in the introns of the human HPRT gene are necessary for its expression in embryonic stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4299–4303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid L. H., Gregg R. G., Smithies O., Koller B. H. Regulatory elements in the introns of the human HPRT gene are necessary for its expression in embryonic stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4299–4303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scotto L., Vaduva P. I., Wager R. E., Assoian R. K. Type beta 1 transforming growth factor gene expression. A corrected mRNA structure reveals a downstream phorbol ester responsive element in human cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 5;265(4):2203–2208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro D. J., Sharp P. A., Wahli W. W., Keller M. J. A high-efficiency HeLa cell nuclear transcription extract. DNA. 1988 Jan-Feb;7(1):47–55. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sive H. L., Heintz N., Roeder R. G. Multiple sequence elements are required for maximal in vitro transcription of a human histone H2B gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3329–3340. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater E. P., Rabenau O., Karin M., Baxter J. D., Beato M. Glucocorticoid receptor binding and activation of a heterologous promoter by dexamethasone by the first intron of the human growth hormone gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):2984–2992. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.2984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. D., Wellman S. E., Marzluff W. F. Sequences of four mouse histone H3 genes: implications for evolution of mouse histone genes. J Mol Evol. 1986;23(3):242–249. doi: 10.1007/BF02115580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S., Rosenthal A., Flavell R., Grosveld F. DNA sequences required for regulated expression of beta-globin genes in murine erythroleukemia cells. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):265–273. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90548-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu R. S., Bonner W. M. Separation of basal histone synthesis from S-phase histone synthesis in dividing cells. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):321–330. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90415-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Wijnen A. J., Wright K. L., Massung R. F., Gerretsen M., Stein J. L., Stein G. S. Two target sites for protein binding in the promoter region of a cell cycle regulated human H1 histone gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 25;16(2):571–592. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.2.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]