Abstract
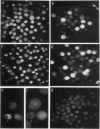
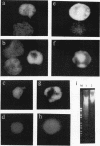
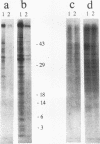
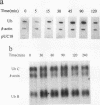
Apoptosis (the classical type of programmed cell death) can be triggered in many cell types by widely diverse stimuli. gamma rays, at low doses, can induce apoptosis in vitro in interphase human lymphocytes. In this type of apoptosis induction, activated gene expression is necessary for the fulfillment of the death program. In this report, we present evidence for a relationship between ubiquitin gene expression or ubiquitination and gamma-irradiation-mediated apoptosis in normal circulating human lymphocytes. Using in vitro nuclear transcription assays (run-on), Northern (RNA) blot analysis, immunolocalization studies, and sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis analysis after immunoprecipitation, we demonstrate that (i) the ubiquitin mRNA level is increased as a consequence of the activation of ubiquitin gene transcription 15 to 90 min after initiation of apoptosis; (ii) specifically in apoptotic cells, and not in all irradiated cells, nuclear proteins are highly ubiquitinated; and (iii) ubiquitin sequence-specific antisense oligonucleotide inhibition results in a decreased level of ubiquitinated nuclear proteins and considerably diminishes the proportion of cells exhibiting the apoptotic death pattern. Each of these results might be explained by different modifications occurring in irradiated cells. Their convergence strongly suggests that the ubiquitin gene is one of the genes with induced activity in the apoptotic death program and that ubiquitination of nuclear proteins might be involved in chromatin disorganization and oligonucleosomal fragmentation, which are among the key events occurring in apoptosis.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmair A., Varshavsky A. The degradation signal in a short-lived protein. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):1019–1032. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90635-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker R. T., Board P. G. The human ubiquitin gene family: structure of a gene and pseudogenes from the Ub B subfamily. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 26;15(2):443–463. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.2.443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball E., Karlik C. C., Beall C. J., Saville D. L., Sparrow J. C., Bullard B., Fyrberg E. A. Arthrin, a myofibrillar protein of insect flight muscle, is an actin-ubiquitin conjugate. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):221–228. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90149-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuende E., Alés-Martínez J. E., Ding L., Gónzalez-García M., Martínez C., Nunez G. Programmed cell death by bcl-2-dependent and independent mechanisms in B lymphoma cells. EMBO J. 1993 Apr;12(4):1555–1560. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05799.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finley D., Bartel B., Varshavsky A. The tails of ubiquitin precursors are ribosomal proteins whose fusion to ubiquitin facilitates ribosome biogenesis. Nature. 1989 Mar 30;338(6214):394–401. doi: 10.1038/338394a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finley D., Ozkaynak E., Varshavsky A. The yeast polyubiquitin gene is essential for resistance to high temperatures, starvation, and other stresses. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):1035–1046. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90711-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fornace A. J., Jr, Alamo I., Jr, Hollander M. C., Lamoreaux E. Ubiquitin mRNA is a major stress-induced transcript in mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 11;17(3):1215–1230. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.3.1215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glotzer M., Murray A. W., Kirschner M. W. Cyclin is degraded by the ubiquitin pathway. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):132–138. doi: 10.1038/349132a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory C. D., Dive C., Henderson S., Smith C. A., Williams G. T., Gordon J., Rickinson A. B. Activation of Epstein-Barr virus latent genes protects human B cells from death by apoptosis. Nature. 1991 Feb 14;349(6310):612–614. doi: 10.1038/349612a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko A. The ubiquitin pathway for protein degradation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Jul;16(7):265–268. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90101-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochstrasser M., Ellison M. J., Chau V., Varshavsky A. The short-lived MAT alpha 2 transcriptional regulator is ubiquitinated in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4606–4610. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hockenbery D., Nuñez G., Milliman C., Schreiber R. D., Korsmeyer S. J. Bcl-2 is an inner mitochondrial membrane protein that blocks programmed cell death. Nature. 1990 Nov 22;348(6299):334–336. doi: 10.1038/348334a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye M., Tamaru M., Kameyama Y. Effects of cycloheximide and actinomycin D on radiation-induced apoptotic cell death in the developing mouse cerebellum. Int J Radiat Biol. 1992 May;61(5):669–674. doi: 10.1080/09553009214551481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jentsch S., McGrath J. P., Varshavsky A. The yeast DNA repair gene RAD6 encodes a ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme. Nature. 1987 Sep 10;329(6135):131–134. doi: 10.1038/329131a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jentsch S., Seufert W., Hauser H. P. Genetic analysis of the ubiquitin system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jun 13;1089(2):127–139. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(91)90001-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung D. W., Spencer S. A., Cachianes G., Hammonds R. G., Collins C., Henzel W. J., Barnard R., Waters M. J., Wood W. I. Growth hormone receptor and serum binding protein: purification, cloning and expression. Nature. 1987 Dec 10;330(6148):537–543. doi: 10.1038/330537a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui S. I., Seon B. K., Sandberg A. A. Disappearance of a structural chromatin protein A24 in mitosis: implications for molecular basis of chromatin condensation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6386–6390. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer R. J., Arnold J., László L., Landon M., Lowe J. Ubiquitin in health and disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jun 13;1089(2):141–157. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(91)90002-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mezger V., Bensaude O., Morange M. Deficient activation of heat shock gene transcription in embryonal carcinoma cells. Dev Biol. 1987 Dec;124(2):544–550. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90507-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens G. P., Hahn W. E., Cohen J. J. Identification of mRNAs associated with programmed cell death in immature thymocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;11(8):4177–4188. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.8.4177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paolini R., Kinet J. P. Cell surface control of the multiubiquitination and deubiquitination of high-affinity immunoglobulin E receptors. EMBO J. 1993 Feb;12(2):779–786. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05712.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redman K. L., Rechsteiner M. Identification of the long ubiquitin extension as ribosomal protein S27a. Nature. 1989 Mar 30;338(6214):438–440. doi: 10.1038/338438a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffner M., Werness B. A., Huibregtse J. M., Levine A. J., Howley P. M. The E6 oncoprotein encoded by human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 promotes the degradation of p53. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1129–1136. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90409-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. M., Myer A., Kosz L., Engelstein M., Maier C. Activation of polyubiquitin gene expression during developmentally programmed cell death. Neuron. 1990 Oct;5(4):411–419. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90080-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. M., Smith S. W., Jones M. E., Osborne B. A. Do all programmed cell deaths occur via apoptosis? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 1;90(3):980–984. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.3.980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellins K. S., Cohen J. J. Gene induction by gamma-irradiation leads to DNA fragmentation in lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 15;139(10):3199–3206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sentman C. L., Shutter J. R., Hockenbery D., Kanagawa O., Korsmeyer S. J. bcl-2 inhibits multiple forms of apoptosis but not negative selection in thymocytes. Cell. 1991 Nov 29;67(5):879–888. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90361-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegelman M., Bond M. W., Gallatin W. M., St John T., Smith H. T., Fried V. A., Weissman I. L. Cell surface molecule associated with lymphocyte homing is a ubiquitinated branched-chain glycoprotein. Science. 1986 Feb 21;231(4740):823–829. doi: 10.1126/science.3003913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strasser A., Harris A. W., Cory S. bcl-2 transgene inhibits T cell death and perturbs thymic self-censorship. Cell. 1991 Nov 29;67(5):889–899. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90362-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trauth B. C., Klas C., Peters A. M., Matzku S., Möller P., Falk W., Debatin K. M., Krammer P. H. Monoclonal antibody-mediated tumor regression by induction of apoptosis. Science. 1989 Jul 21;245(4915):301–305. doi: 10.1126/science.2787530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viegas-Pequignot E., Dutrillaux B., Magdelenat H., Coppey-Moisan M. Mapping of single-copy DNA sequences on human chromosomes by in situ hybridization with biotinylated probes: enhancement of detection sensitivity by intensified-fluorescence digital-imaging microscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):582–586. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiborg O., Pedersen M. S., Wind A., Berglund L. E., Marcker K. A., Vuust J. The human ubiquitin multigene family: some genes contain multiple directly repeated ubiquitin coding sequences. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):755–759. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03693.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu R. S., Kohn K. W., Bonner W. M. Metabolism of ubiquitinated histones. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5916–5920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Escobedo J. A., Kuang W. J., Yang-Feng T. L., Daniel T. O., Tremble P. M., Chen E. Y., Ando M. E., Harkins R. N., Francke U. Structure of the receptor for platelet-derived growth factor helps define a family of closely related growth factor receptors. Nature. 1986 Sep 18;323(6085):226–232. doi: 10.1038/323226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonish-Rouach E., Resnitzky D., Lotem J., Sachs L., Kimchi A., Oren M. Wild-type p53 induces apoptosis of myeloid leukaemic cells that is inhibited by interleukin-6. Nature. 1991 Jul 25;352(6333):345–347. doi: 10.1038/352345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]