Abstract
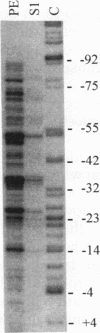
The mouse thymidylate synthase promoter lacks a TATA box and initiates transcription at many sites across a 90-nucleotide initiation window. We showed previously that wild-type promoter activity is maintained with a promoter that extends only 13 nucleotides upstream of the first start site. G/A-rich and G/C-rich promoter elements were identified in the vicinity of the first transcriptional start site. The goals of the present study were to determine whether there are additional promoter elements in the initiation window and to determine why transcription initiates across such a broad region. Minigenes containing a variety of substitution, deletion, and insertion mutations in the promoter region were transfected into cultured cells, and the effects on expression and the pattern of start sites were determined. The results indicate that there are no additional promoter elements downstream of the G/C box. The boundaries of the transcription window are established by elements near the 5' end of the window, whereas the pattern of start sites is determined by sequences within the window. The promoter lacks an initiator element. When an initiator element was inserted, transcription initiated predominantly at the position directed by the initiator when it was inserted within the initiation window but not when it was inserted immediately upstream of the window.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beaupain D., Eléouët J. F., Roméo P. H. Initiation of transcription of the erythroid promoter of the porphobilinogen deaminase gene is regulated by a cis-acting sequence around the cap site. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 25;18(22):6509–6515. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.22.6509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buratowski S., Hahn S., Guarente L., Sharp P. A. Five intermediate complexes in transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):549–561. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90578-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carcamo J., Buckbinder L., Reinberg D. The initiator directs the assembly of a transcription factor IID-dependent transcription complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 15;88(18):8052–8056. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.18.8052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W., Struhl K. Yeast mRNA initiation sites are determined primarily by specific sequences, not by the distance from the TATA element. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3273–3280. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04077.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Concino M. F., Lee R. F., Merryweather J. P., Weinmann R. The adenovirus major late promoter TATA box and initiation site are both necessary for transcription in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Oct 11;12(19):7423–7433. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.19.7423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng T. L., Li D. W., Jenh C. H., Johnson L. F. Structure of the gene for mouse thymidylate synthase. Locations of introns and multiple transcriptional start sites. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 5;261(34):16000–16005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng T. L., Li Y., Johnson L. F. Thymidylate synthase gene expression is stimulated by some (but not all) introns. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 25;17(2):645–658. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.2.645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
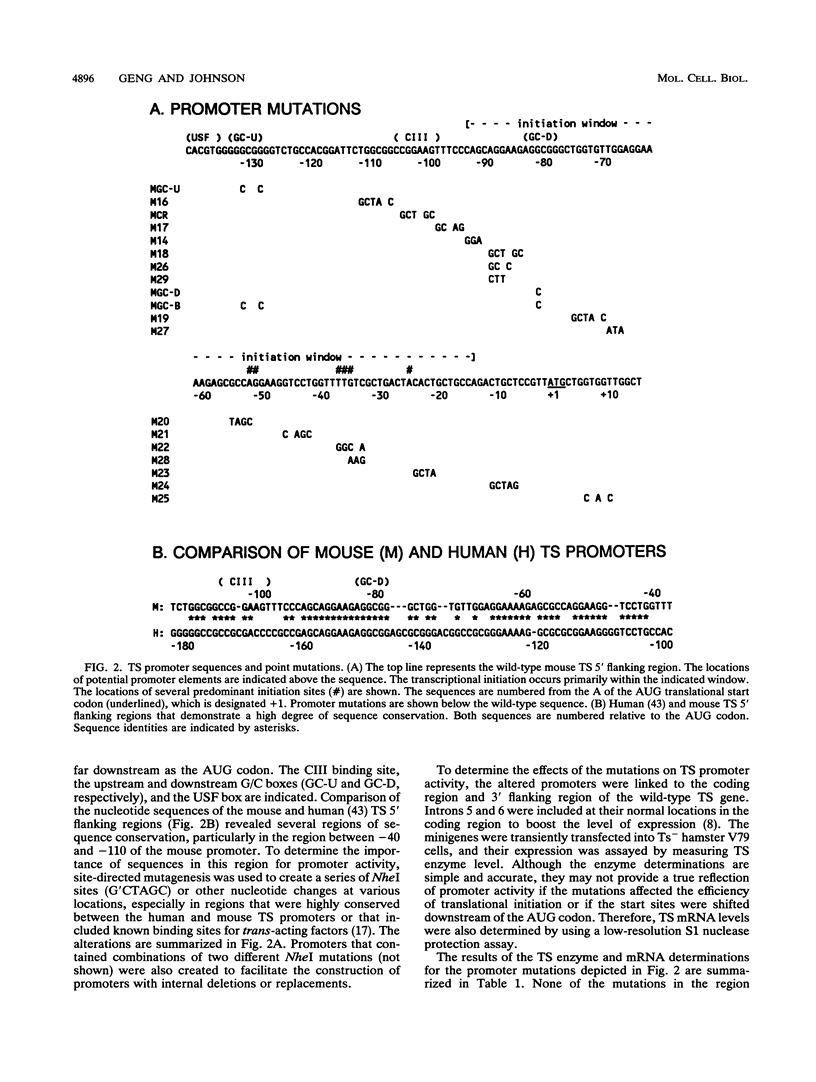
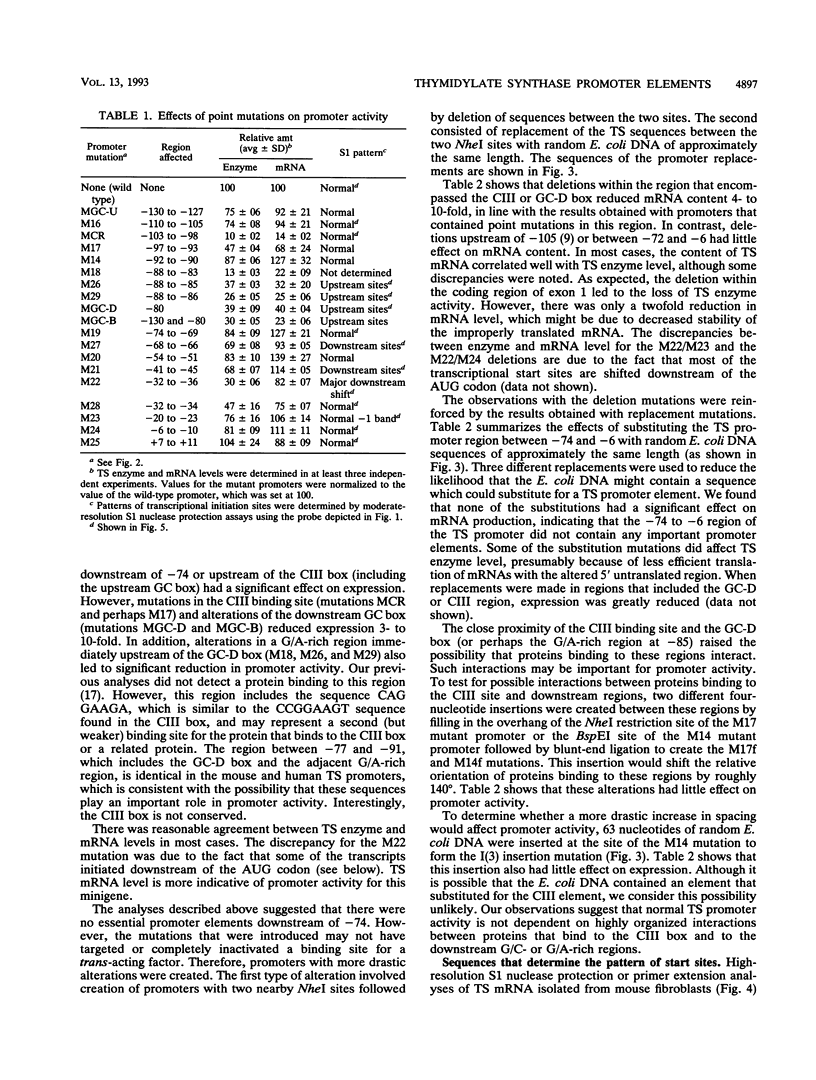
- Deng T., Li Y., Jolliff K., Johnson L. F. The mouse thymidylate synthase promoter: essential elements are in close proximity to the transcriptional initiation sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):4079–4082. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.4079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favaloro J., Treisman R., Kamen R. Transcription maps of polyoma virus-specific RNA: analysis by two-dimensional nuclease S1 gel mapping. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):718–749. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn S., Hoar E. T., Guarente L. Each of three "TATA elements" specifies a subset of the transcription initiation sites at the CYC-1 promoter of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8562–8566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hariharan N., Perry R. P. Functional dissection of a mouse ribosomal protein promoter: significance of the polypyrimidine initiator and an element in the TATA-box region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1526–1530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii S., Merlino G. T., Pastan I. Promoter region of the human Harvey ras proto-oncogene: similarity to the EGF receptor proto-oncogene promoter. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1378–1381. doi: 10.1126/science.2999983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii S., Xu Y. H., Stratton R. H., Roe B. A., Merlino G. T., Pastan I. Characterization and sequence of the promoter region of the human epidermal growth factor receptor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4920–4924. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobovits E. B., Schlokat U., Vannice J. L., Derynck R., Levinson A. D. The human transforming growth factor alpha promoter directs transcription initiation from a single site in the absence of a TATA sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5549–5554. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
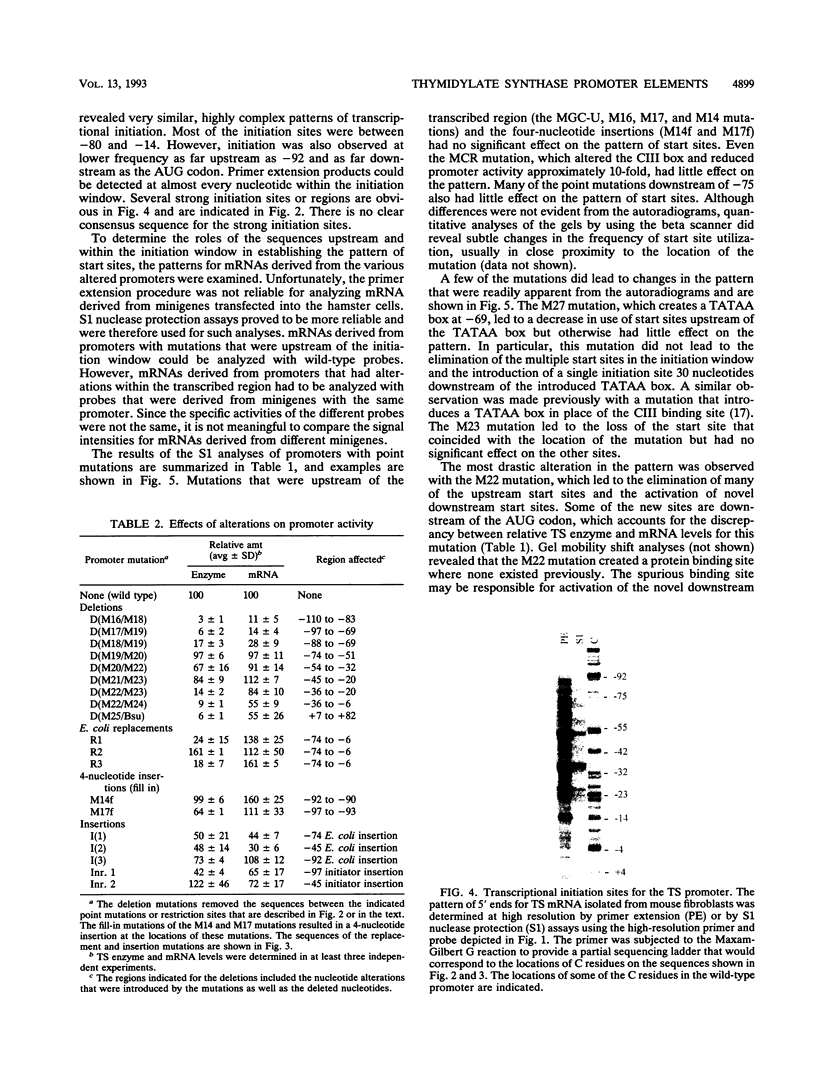
- Jolliff K., Li Y., Johnson L. F. Multiple protein-DNA interactions in the TATAA-less mouse thymidylate synthase promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 11;19(9):2267–2274. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.9.2267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawn R. M., Efstratiadis A., O'Connell C., Maniatis T. The nucleotide sequence of the human beta-globin gene. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):647–651. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90428-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Li D., Osborn K., Johnson L. F. The 5'-flanking region of the mouse thymidylate synthase gene is necessary but not sufficient for normal regulation in growth-stimulated cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):1023–1029. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.1023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockshin A., Moran R. G., Danenberg P. V. Thymidylate synthetase purified to homogeneity from human leukemic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):750–754. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin M. E., Piette J., Yaniv M., Tang W. J., Folk W. R. Activation of the polyomavirus enhancer by a murine activator protein 1 (AP1) homolog and two contiguous proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5839–5843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathis D. J., Chambon P. The SV40 early region TATA box is required for accurate in vitro initiation of transcription. Nature. 1981 Mar 26;290(5804):310–315. doi: 10.1038/290310a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Means A. L., Farnham P. J. Transcription initiation from the dihydrofolate reductase promoter is positioned by HIP1 binding at the initiation site. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):653–661. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. W., McEwan C., McKie A. B., Reid A. M. Expression of the mouse HPRT gene: deletional analysis of the promoter region of an X-chromosome linked housekeeping gene. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):319–328. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90766-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagawa F., Fink G. R. The relationship between the "TATA" sequence and transcription initiation sites at the HIS4 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8557–8561. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima N., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II: purification, genetic specificity, and TATA box-promoter interactions of TFIID. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4028–4040. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakatani Y., Horikoshi M., Brenner M., Yamamoto T., Besnard F., Roeder R. G., Freese E. A downstream initiation element required for efficient TATA box binding and in vitro function of TFIID. Nature. 1990 Nov 1;348(6296):86–88. doi: 10.1038/348086a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussbaum R. L., Walmsley R. M., Lesko J. G., Airhart S. D., Ledbetter D. H. Thymidylate synthase-deficient Chinese hamster cells: a selection system for human chromosome 18 and experimental system for the study of thymidylate synthase regulation and fragile X expression. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 Nov;37(6):1192–1205. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Shea-Greenfield A., Smale S. T. Roles of TATA and initiator elements in determining the start site location and direction of RNA polymerase II transcription. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):1391–1402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Diverse transcriptional functions of the multisubunit eukaryotic TFIID complex. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):679–682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Transcription from a TATA-less promoter requires a multisubunit TFIID complex. Genes Dev. 1991 Nov;5(11):1935–1945. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.11.1935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds G. A., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Multiple mRNAs for 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase determined by multiple transcription initiation sites and intron splicing sites in the 5'-untranslated region. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 25;260(18):10369–10377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy A. L., Meisterernst M., Pognonec P., Roeder R. G. Cooperative interaction of an initiator-binding transcription initiation factor and the helix-loop-helix activator USF. Nature. 1991 Nov 21;354(6350):245–248. doi: 10.1038/354245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Interaction of a gene-specific transcription factor with the adenovirus major late promoter upstream of the TATA box region. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):165–175. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Sentenac A. RNA polymerase B (II) and general transcription factors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:711–754. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.003431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto E., Shi Y., Shenk T. YY1 is an initiator sequence-binding protein that directs and activates transcription in vitro. Nature. 1991 Nov 21;354(6350):241–245. doi: 10.1038/354241a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Baltimore D. The "initiator" as a transcription control element. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90176-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Schmidt M. C., Berk A. J., Baltimore D. Transcriptional activation by Sp1 as directed through TATA or initiator: specific requirement for mammalian transcription factor IID. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4509–4513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeishi K., Kaneda S., Ayusawa D., Shimizu K., Gotoh O., Seno T. Human thymidylate synthase gene: isolation of phage clones which cover a functionally active gene and structural analysis of the region upstream from the translation initiation codon. J Biochem. 1989 Oct;106(4):575–583. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis A., Hagman J., Grosschedl R. Heterogeneously initiated transcription from the pre-B- and B-cell-specific mb-1 promoter: analysis of the requirement for upstream factor-binding sites and initiation site sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;11(11):5756–5766. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.11.5756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Wasylyk C., Flores P., Begue A., Leprince D., Stehelin D. The c-ets proto-oncogenes encode transcription factors that cooperate with c-Fos and c-Jun for transcriptional activation. Nature. 1990 Jul 12;346(6280):191–193. doi: 10.1038/346191a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xin J. H., Cowie A., Lachance P., Hassell J. A. Molecular cloning and characterization of PEA3, a new member of the Ets oncogene family that is differentially expressed in mouse embryonic cells. Genes Dev. 1992 Mar;6(3):481–496. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.3.481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenzie-Gregory B., O'Shea-Greenfield A., Smale S. T. Similar mechanisms for transcription initiation mediated through a TATA box or an initiator element. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 5;267(4):2823–2830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]