Abstract
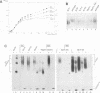
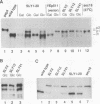
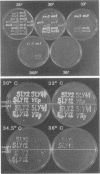
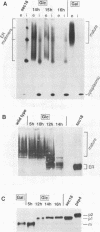
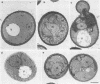
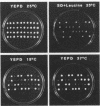
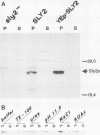
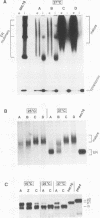
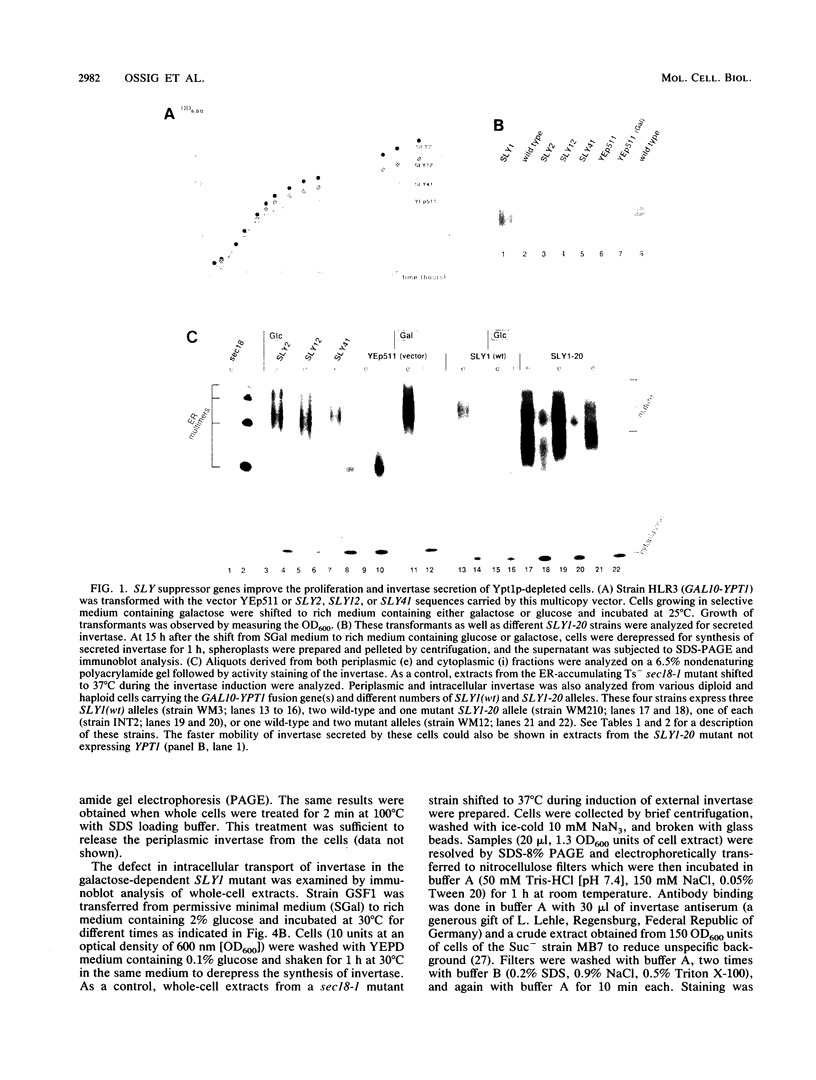
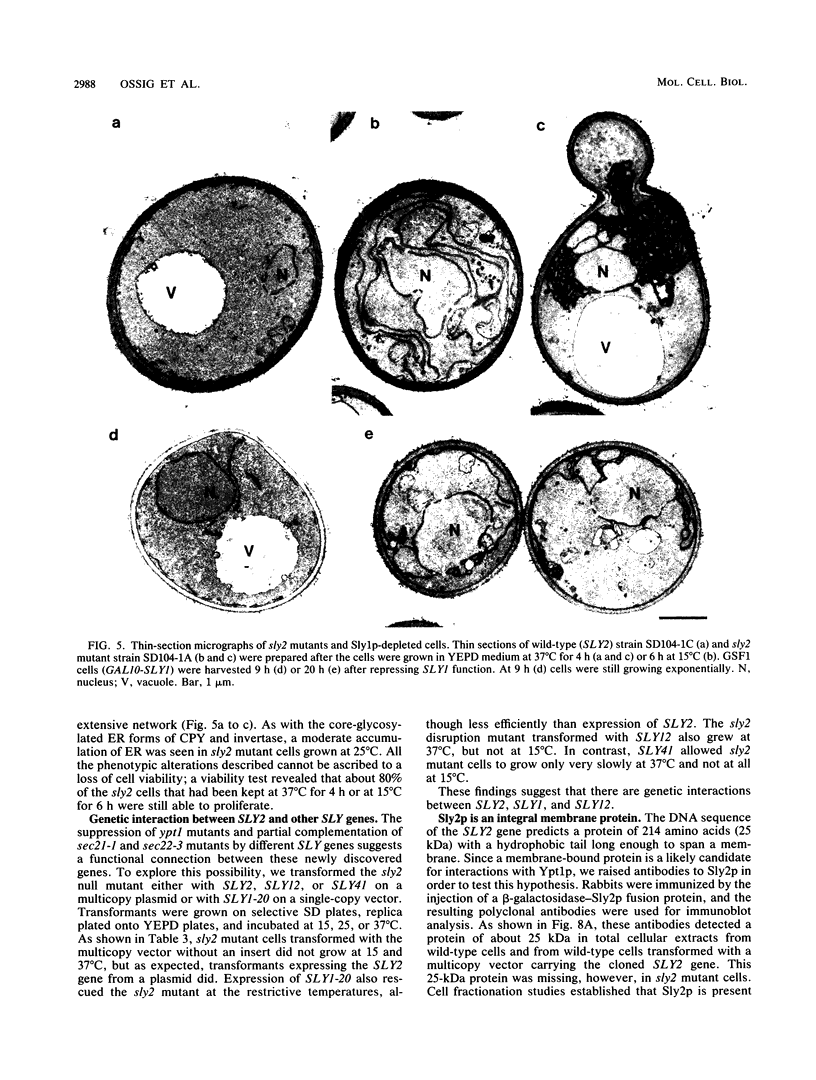
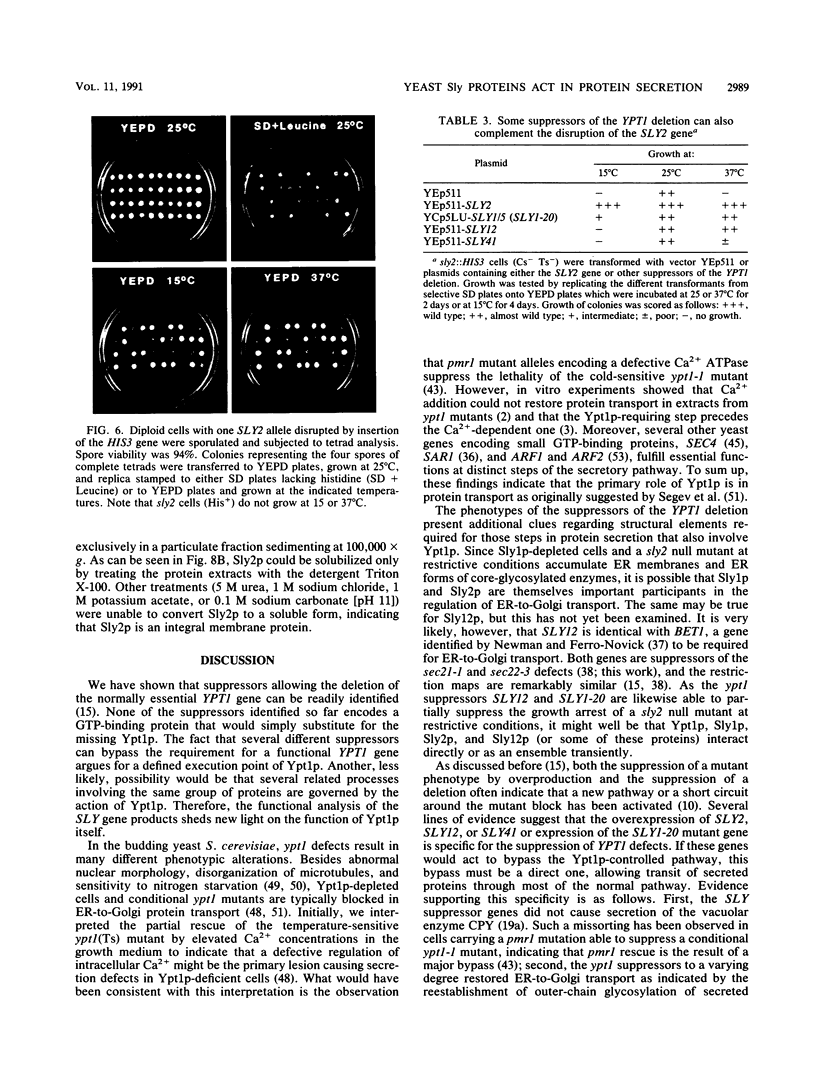
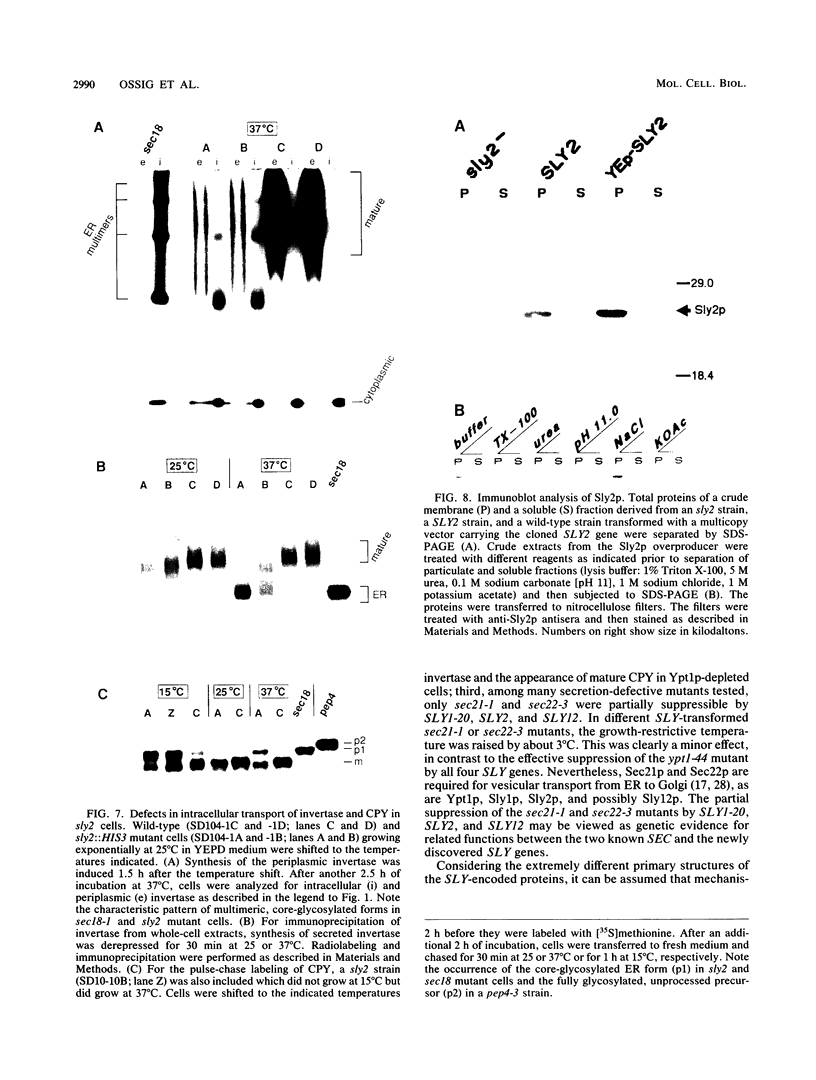
It has been shown previously that defects in the essential GTP-binding protein, Ypt1p, lead to a block in protein transport from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) to the Golgi apparatus in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Here we report that four newly discovered suppressors of YPT1 deletion (SLY1-20, SLY2, SLY12, and SLY41) to a varying degree restore ER-to-Golgi transport defects in cells lacking Ypt1p. These suppressors also partially complement the sec21-1 and sec22-3 mutants which lead to a defect early in the secretory pathway. Sly1p-depleted cells, as well as a conditional lethal sly2 null mutant at nonpermissive temperatures, accumulate ER membranes and core-glycosylated invertase and carboxypeptidase Y. The sly2 null mutant under restrictive conditions (37 degrees C) can be rescued by the multicopy suppressor SLY12 and the single-copy suppressor SLY1-20, indicating that these three SLY genes functionally interact. Sly2p is shown to be an integral membrane protein.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achstetter T., Franzusoff A., Field C., Schekman R. SEC7 encodes an unusual, high molecular weight protein required for membrane traffic from the yeast Golgi apparatus. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 25;263(24):11711–11717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacon R. A., Salminen A., Ruohola H., Novick P., Ferro-Novick S. The GTP-binding protein Ypt1 is required for transport in vitro: the Golgi apparatus is defective in ypt1 mutants. J Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;109(3):1015–1022. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.3.1015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker D., Wuestehube L., Schekman R., Botstein D., Segev N. GTP-binding Ypt1 protein and Ca2+ function independently in a cell-free protein transport reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):355–359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballou L., Gopal P., Krummel B., Tammi M., Ballou C. E. A mutation that prevents glucosylation of the lipid-linked oligosaccharide precursor leads to underglycosylation of secreted yeast invertase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3081–3085. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bankaitis V. A., Malehorn D. E., Emr S. D., Greene R. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae SEC14 gene encodes a cytosolic factor that is required for transport of secretory proteins from the yeast Golgi complex. J Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;108(4):1271–1281. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.4.1271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein M., Hoffmann W., Ammerer G., Schekman R. Characterization of a gene product (Sec53p) required for protein assembly in the yeast endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;101(6):2374–2382. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.6.2374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein M., Kepes F., Schekman R. Sec59 encodes a membrane protein required for core glycosylation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):1191–1199. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.1191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botstein D., Maurer R. Genetic approaches to the analysis of microbial development. Annu Rev Genet. 1982;16:61–83. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.16.120182.000425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R. Do GTPases direct membrane traffic in secretion? Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):669–671. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90081-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhni P. C., Deshaies R. J., Schekman R. W. SEC11 is required for signal peptide processing and yeast cell growth. J Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;106(4):1035–1042. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.4.1035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson M., Botstein D. Two differentially regulated mRNAs with different 5' ends encode secreted with intracellular forms of yeast invertase. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):145–154. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90384-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavrier P., Parton R. G., Hauri H. P., Simons K., Zerial M. Localization of low molecular weight GTP binding proteins to exocytic and endocytic compartments. Cell. 1990 Jul 27;62(2):317–329. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90369-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clary D. O., Griff I. C., Rothman J. E. SNAPs, a family of NSF attachment proteins involved in intracellular membrane fusion in animals and yeast. Cell. 1990 May 18;61(4):709–721. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90482-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eakle K. A., Bernstein M., Emr S. D. Characterization of a component of the yeast secretion machinery: identification of the SEC18 gene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4098–4109. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon B., Novick P., Schekman R. Compartmentalized assembly of oligosaccharides on exported glycoproteins in yeast. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):451–460. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90063-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer von Mollard G., Mignery G. A., Baumert M., Perin M. S., Hanson T. J., Burger P. M., Jahn R., Südhof T. C. rab3 is a small GTP-binding protein exclusively localized to synaptic vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1988–1992. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flügge U. I., Fischer K., Gross A., Sebald W., Lottspeich F., Eckerskorn C. The triose phosphate-3-phosphoglycerate-phosphate translocator from spinach chloroplasts: nucleotide sequence of a full-length cDNA clone and import of the in vitro synthesized precursor protein into chloroplasts. EMBO J. 1989 Jan;8(1):39–46. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03346.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzusoff A., Schekman R. Functional compartments of the yeast Golgi apparatus are defined by the sec7 mutation. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2695–2702. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08410.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallwitz D., Donath C., Sander C. A yeast gene encoding a protein homologous to the human c-has/bas proto-oncogene product. Nature. 1983 Dec 15;306(5944):704–707. doi: 10.1038/306704a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goud B., Salminen A., Walworth N. C., Novick P. J. A GTP-binding protein required for secretion rapidly associates with secretory vesicles and the plasma membrane in yeast. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):753–768. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90093-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goud B., Zahraoui A., Tavitian A., Saraste J. Small GTP-binding protein associated with Golgi cisternae. Nature. 1990 Jun 7;345(6275):553–556. doi: 10.1038/345553a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haubruck H., Prange R., Vorgias C., Gallwitz D. The ras-related mouse ypt1 protein can functionally replace the YPT1 gene product in yeast. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1427–1432. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03524.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hicke L., Schekman R. Yeast Sec23p acts in the cytoplasm to promote protein transport from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi complex in vivo and in vitro. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1677–1684. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03559.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser C. A., Botstein D. Secretion-defective mutations in the signal sequence for Saccharomyces cerevisiae invertase. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2382–2391. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser C. A., Schekman R. Distinct sets of SEC genes govern transport vesicle formation and fusion early in the secretory pathway. Cell. 1990 May 18;61(4):723–733. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90483-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klionsky D. J., Herman P. K., Emr S. D. The fungal vacuole: composition, function, and biogenesis. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Sep;54(3):266–292. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.3.266-292.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malhotra V., Orci L., Glick B. S., Block M. R., Rothman J. E. Role of an N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive transport component in promoting fusion of transport vesicles with cisternae of the Golgi stack. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):221–227. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90554-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melançon P., Glick B. S., Malhotra V., Weidman P. J., Serafini T., Gleason M. L., Orci L., Rothman J. E. Involvement of GTP-binding "G" proteins in transport through the Golgi stack. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1053–1062. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90591-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizoguchi A., Kim S., Ueda T., Kikuchi A., Yorifuji H., Hirokawa N., Takai Y. Localization and subcellular distribution of smg p25A, a ras p21-like GTP-binding protein, in rat brain. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 15;265(20):11872–11879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nair J., Müller H., Peterson M., Novick P. Sec2 protein contains a coiled-coil domain essential for vesicular transport and a dispensable carboxy terminal domain. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;110(6):1897–1909. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.6.1897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamaye K. L., Eckstein F. Inhibition of restriction endonuclease Nci I cleavage by phosphorothioate groups and its application to oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Dec 22;14(24):9679–9698. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.24.9679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano A., Brada D., Schekman R. A membrane glycoprotein, Sec12p, required for protein transport from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi apparatus in yeast. J Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;107(3):851–863. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.3.851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakańo A., Muramatsu M. A novel GTP-binding protein, Sar1p, is involved in transport from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi apparatus. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):2677–2691. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.2677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman A. P., Ferro-Novick S. Characterization of new mutants in the early part of the yeast secretory pathway isolated by a [3H]mannose suicide selection. J Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;105(4):1587–1594. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.4.1587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman A. P., Shim J., Ferro-Novick S. BET1, BOS1, and SEC22 are members of a group of interacting yeast genes required for transport from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3405–3414. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick P., Field C., Schekman R. Identification of 23 complementation groups required for post-translational events in the yeast secretory pathway. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):205–215. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90128-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymond C. K., O'Hara P. J., Eichinger G., Rothman J. H., Stevens T. H. Molecular analysis of the yeast VPS3 gene and the role of its product in vacuolar protein sorting and vacuolar segregation during the cell cycle. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):877–892. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid G. A. Pulse labeling of yeast cells and spheroplasts. Methods Enzymol. 1983;97:324–329. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)97144-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothblatt J., Schekman R. A hitchhiker's guide to analysis of the secretory pathway in yeast. Methods Cell Biol. 1989;32:3–36. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61165-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudolph H. K., Antebi A., Fink G. R., Buckley C. M., Dorman T. E., LeVitre J., Davidow L. S., Mao J. I., Moir D. T. The yeast secretory pathway is perturbed by mutations in PMR1, a member of a Ca2+ ATPase family. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):133–145. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90410-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüther U., Müller-Hill B. Easy identification of cDNA clones. EMBO J. 1983;2(10):1791–1794. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01659.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salminen A., Novick P. J. A ras-like protein is required for a post-Golgi event in yeast secretion. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):527–538. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90455-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salminen A., Novick P. J. The Sec15 protein responds to the function of the GTP binding protein, Sec4, to control vesicular traffic in yeast. J Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;109(3):1023–1036. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.3.1023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauer I., Emr S., Gross C., Schekman R. Invertase signal and mature sequence substitutions that delay intercompartmental transport of active enzyme. J Cell Biol. 1985 May;100(5):1664–1675. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.5.1664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt H. D., Puzicha M., Gallwitz D. Study of a temperature-sensitive mutant of the ras-related YPT1 gene product in yeast suggests a role in the regulation of intracellular calcium. Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):635–647. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90579-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt H. D., Wagner P., Pfaff E., Gallwitz D. The ras-related YPT1 gene product in yeast: a GTP-binding protein that might be involved in microtubule organization. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):401–412. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90597-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segev N., Botstein D. The ras-like yeast YPT1 gene is itself essential for growth, sporulation, and starvation response. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2367–2377. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segev N., Mulholland J., Botstein D. The yeast GTP-binding YPT1 protein and a mammalian counterpart are associated with the secretion machinery. Cell. 1988 Mar 25;52(6):915–924. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90433-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stearns T., Willingham M. C., Botstein D., Kahn R. A. ADP-ribosylation factor is functionally and physically associated with the Golgi complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1238–1242. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens B. J., White J. G. Computer reconstruction of mitochondria from yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1979;56:718–728. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)56064-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens T., Esmon B., Schekman R. Early stages in the yeast secretory pathway are required for transport of carboxypeptidase Y to the vacuole. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):439–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90241-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., Baumert M., Perin M. S., Jahn R. A synaptic vesicle membrane protein is conserved from mammals to Drosophila. Neuron. 1989 May;2(5):1475–1481. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90193-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trimble W. S., Cowan D. M., Scheller R. H. VAMP-1: a synaptic vesicle-associated integral membrane protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4538–4542. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walworth N. C., Goud B., Kabcenell A. K., Novick P. J. Mutational analysis of SEC4 suggests a cyclical mechanism for the regulation of vesicular traffic. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1685–1693. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03560.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. W., Wilcox C. A., Flynn G. C., Chen E., Kuang W. J., Henzel W. J., Block M. R., Ullrich A., Rothman J. E. A fusion protein required for vesicle-mediated transport in both mammalian cells and yeast. Nature. 1989 Jun 1;339(6223):355–359. doi: 10.1038/339355a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]